Abstract
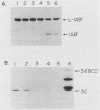
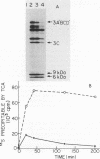
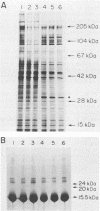
An inducible expression vector system has been developed to facilitate the study of the effects of individual virus gene products on cell function. The vector utilizes the mouse metallothionein promoter carried on the bovine papillomavirus genome. Conditions which optimize the induced expression of open reading frames inserted downstream from the mouse metallothionein promoter have recently been described. In this communication we describe the use of this system to clone and express the encephalomyocarditis virus 3C protease in cultured mouse cells. Stably transformed cell lines could be induced to produce levels of 3C protease activity comparable to those observed during normal virus infection. In spite of this, no effects on cellular protein synthesis rate or membrane permeability were observed. It was also discovered that 3C protease as well as 3C protease-containing polyproteins are turned over. This was true not only in the induced cell clones, but also during the normal course of encephalomyocarditis virus infection, as well as in translation systems in vitro. This phenomenon was highly specific for this family of polypeptides, perhaps explaining their apparent lack of cytotoxic effects.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold E., Luo M., Vriend G., Rossmann M. G., Palmenberg A. C., Parks G. D., Nicklin M. J., Wimmer E. Implications of the picornavirus capsid structure for polyprotein processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Walling M. Regulation in vivo of a cloned mammalian gene: cadmium induces the transcription of a mouse metallothionein gene in SV40 vectors. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):273–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Ariga H., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Expression of a cloned gene segment of poliovirus in E. coli: evidence for autocatalytic production of the viral proteinase. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1063–1073. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90441-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jen G., Birge C. H., Thach R. E. Comparison of initiation rates of encephalomyocarditis virus and host protein synthesis in infected cells. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):640–647. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.640-647.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jore J., De Geus B., Jackson R. J., Pouwels P. H., Enger-Valk B. E. Poliovirus protein 3CD is the active protease for processing of the precursor protein P1 in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1627–1636. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyse S. M., Tyrrell R. M. Heme oxygenase is the major 32-kDa stress protein induced in human skin fibroblasts by UVA radiation, hydrogen peroxide, and sodium arsenite. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):99–103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Lee C. K., Wimmer E. Polyprotein processing in picornavirus replication. Biochimie. 1988 Jan;70(1):119–130. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90166-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence C., Thach R. E. Identification of a viral protein involved in post-translational maturation of the encephalomyocarditis virus capsid precursor. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):918–928. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.918-928.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson T. G., Ray B. K., Dodds J. T., Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Merrick W. C., Betsch D. F., Weith H. L., Thach R. E. Influence of 5' proximal secondary structure on the translational efficiency of eukaryotic mRNAs and on their interaction with initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):13979–13989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Kirby E. M., Janda M. R., Drake N. L., Duke G. M., Potratz K. F., Collett M. S. The nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of the encephalomyocarditis viral polyprotein coding region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2969–2985. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Pallansch M. A., Rueckert R. R. Protease required for processing picornaviral coat protein resides in the viral replicase gene. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):770–778. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.770-778.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C. Picornaviral processing: some new ideas. J Cell Biochem. 1987 Mar;33(3):191–198. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240330306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Rueckert R. R. Evidence for intramolecular self-cleavage of picornaviral replicase precursors. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):244–249. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.244-249.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks G. D., Baker J. C., Palmenberg A. C. Proteolytic cleavage of encephalomyocarditis virus capsid region substrates by precursors to the 3C enzyme. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1054–1058. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1054-1058.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks G. D., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C. Encephalomyocarditis virus 3C protease: efficient cell-free expression from clones which link viral 5' noncoding sequences to the P3 region. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.376-384.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks G. D., Palmenberg A. C. Site-specific mutations at a picornavirus VP3/VP1 cleavage site disrupt in vitro processing and assembly of capsid precursors. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3680–3687. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3680-3687.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakis G. N., Hamer D. H. Regulation of a metallothionein-growth hormone hybrid gene in bovine papilloma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):397–401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S., Rosbash M., Penman M. Messenger and heterogeneous nuclear RNA in HeLa cells: differential inhibition by cordycepin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1878–1885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramabhadran T. V., Reitz B. A., Tiemeier D. C. Synthesis and glycosylation of the common alpha subunit of human glycoprotein hormones in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6701–6705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramabhadran T. V., Thach R. E. Translational elongation rate changes in encephalomyocarditis virus-infected and interferon-treated cells. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):573–583. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.573-583.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Munro H. Translation of ferritin light and heavy subunit mRNAs is regulated by intracellular chelatable iron levels in rat hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2277–2281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Gruss P., Law M. F., Khoury G., Howley P. M. Bovine papilloma virus deoxyribonucleic acid: a novel eucaryotic cloning vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;1(6):486–496. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.6.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walden W. E., Daniels-McQueen S., Smith L. L., Thach R. E. Procedures for enhancing the utility of the metallothionein promoter for the regulated expression of downstream open reading frames. Gene. 1987;61(3):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90195-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypma-Wong M. F., Dewalt P. G., Johnson V. H., Lamb J. G., Semler B. L. Protein 3CD is the major poliovirus proteinase responsible for cleavage of the P1 capsid precursor. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypma-Wong M. F., Semler B. L. In vitro molecular genetics as a tool for determining the differential cleavage specificities of the poliovirus 3C proteinase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2069–2088. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]