Abstract
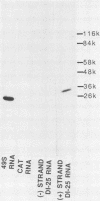
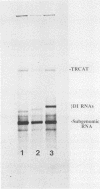
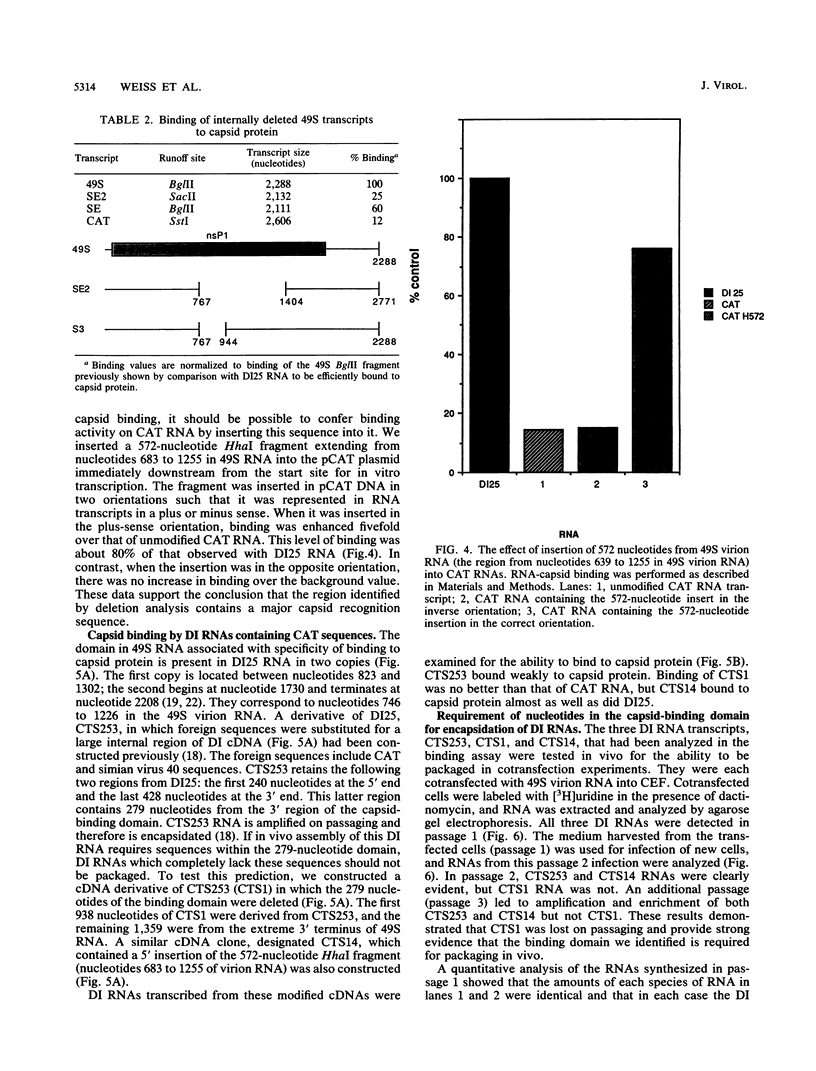
We investigated the interaction of the capsid protein of Sindbis virus with Sindbis viral RNAs and defined a region of the genome that is required for binding in vitro and for packaging in vivo. The binding studies were performed with purified capsid protein immobilized on nitrocellulose and 32P-labeled RNAs transcribed in vitro from viral and nonspecific cDNAs. Genomic and defective interfering (DI) RNAs bound capsid protein significantly better than either the subgenomic (26S) RNA or nonspecific RNAs. Transcripts prepared from either truncated or deleted cDNAs were used to define the segment required for binding. This segment, which is represented twice in DI RNA, lies between nucleotides 746 and 1226 of the genomic RNA and is within the coding region of the nonstructural protein nsP1. Insertion of a domain covering these sequences into a nonviral RNA was able to convert it from a background level of binding to an activity that was 80% that of the Sindbis virus DI RNA. We analyzed DI RNA transcripts in detail because they could be studied not only for the ability to bind capsid protein in vitro but also for the ability to be replicated and packaged in vivo in the presence of helper virion RNA. The results obtained with three DI RNAs are reported. One (CTS14), which has one copy of the binding domain, bound efficiently to capsid protein in vitro and was packaged in vivo as measured by amplification on passaging. In contrast, a DI RNA (CTS1) which lacked this region did not bind to capsid protein and was not detected on passaging. By using lipofectin (P. L. Felgner, T. R. Gadek, M. Holm, R. Roman, H. W. Chan, M. Wenz, J.P. Northrop, G. M. Ringold, and M. Danielson, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:7413-7417, 1987) to enhance RNA uptake, we were able to demonstrate that CTS1 RNA was replicated in the transfected cells. It was replicated to the same level as another DI RNA (CTS253) which has only the 3' 279 nucleotides of the binding domain and these are located near the 3' terminus of the RNA. CTS253 bound capsid protein to an intermediate level but was amplified on passaging. The binding studies and the in vivo packaging data, taken together, provide strong support for the conclusion that there is a specific capsid recognition domain in Sindbis virus RNA that plays a role in nucleocapsid assembly.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam M. A., Miller A. D. Identification of a signal in a murine retrovirus that is sufficient for packaging of nonretroviral RNA into virions. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3802–3806. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3802-3806.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahlquist P., Strauss E. G., Rice C. M., Strauss J. H., Haseloff J., Zimmern D. Sindbis virus proteins nsP1 and nsP2 contain homology to nonstructural proteins from several RNA plant viruses. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):536–542. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.536-542.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen B., Steinberg J., Laemmli U. K., Weintraub H. The detection of DNA-binding proteins by protein blotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):1–20. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael G. G., McMaster G. K. The analysis of nucleic acids in gels using glyoxal and acridine orange. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):380–391. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. D. The T=4 envelope of Sindbis virus is organized by interactions with a complementary T=3 capsid. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):923–934. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90701-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R., Sleat D. E., Watts J. W., Turner P. C., Wilson T. M. In vivo uncoating and efficient expression of foreign mRNAs packaged in TMV-like particles. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1122–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.3472350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseloff J., Goelet P., Zimmern D., Ahlquist P., Dasgupta R., Kaesberg P. Striking similarities in amino acid sequence among nonstructural proteins encoded by RNA viruses that have dissimilar genomic organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4358–4362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houwing C. J., Jaspars E. M. Protein binding sites in nucleation complexes of alfalfa mosaic virus RNA 4. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 6;21(14):3408–3414. doi: 10.1021/bi00257a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalanko A., Söderlund H. The repeated regions of Semliki Forest virus defective-inferfering RNA interferes with the encapsidation process of the standard virus. Virology. 1985 Mar;141(2):257–266. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Pettersson R. F., Keränen S., Lehtovaara P., Söderlund H., Ukkonen P. Multiple structurally related defective-interfering RNAs formed during undiluted passages of Semliki forest virus. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):686–697. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90197-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtovaara P., Söderlund H., Keränen S., Pettersson R. F., Käriäinen L. 18S defective interfering RNA of Semliki Forest virus contains a triplicated linear repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5353–5357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtovaara P., Söderlund H., Keränen S., Pettersson R. F., Käriäinen L. Extreme ends of the genome are conserved and rearranged in the defective interfering RNAs of Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 25;156(4):731–748. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90139-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Huang H., Schlesinger S. Engineered defective interfering RNAs of Sindbis virus express bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in avian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4811–4815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Weiss B. G., Tsiang M., Huang H., Schlesinger S. Deletion mapping of Sindbis virus DI RNAs derived from cDNAs defines the sequences essential for replication and packaging. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):137–145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90492-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe S. S., Schlesinger S. Common and distinct regions of defective-interfering RNAs of Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):865–872. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.865-872.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe S. S., Schlesinger S. RNAs from two independently isolated defective interfering particles of Sindbis virus contain a cellular tRNA sequence at their 5' ends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3279–3283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. H., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. The 5'-terminal sequences of the genomic RNAs of several alphaviruses. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 25;168(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80319-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Levis R., Strauss J. H., Huang H. V. Production of infectious RNA transcripts from Sindbis virus cDNA clones: mapping of lethal mutations, rescue of a temperature-sensitive marker, and in vitro mutagenesis to generate defined mutants. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3809–3819. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3809-3819.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacher R., French R., Ahlquist P. Hybrid brome mosaic virus RNAs express and are packaged in tobacco mosaic virus coat protein in vivo. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):15–24. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Stockley P. G., Harrison S. C. Structure and assembly of turnip crinkle virus. II. Mechanism of reassembly in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 20;191(4):639–658. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90451-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohlman S. A., Baric R. S., Nelson G. N., Soe L. H., Welter L. M., Deans R. J. Specific interaction between coronavirus leader RNA and nucleocapsid protein. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4288–4295. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4288-4295.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. G., Rice C. M., Strauss J. H. Complete nucleotide sequence of the genomic RNA of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):92–110. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90428-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiang M., Weiss B. G., Schlesinger S. Effects of 5'-terminal modifications on the biological activity of defective interfering RNAs of Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):47–53. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.47-53.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. R., Joyce L. E., Butler P. J. The tobacco mosaic virus assembly origin RNA. Functional characteristics defined by directed mutagenesis. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):531–547. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90190-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmanen I., Söderlund H., Käriäinen L. Semliki Forest virus capsid protein associates with the 60S ribosomal subunit in infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):203–210. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.203-210.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. J., Helenius A., Mellman I. Spike--nucleocapsid interaction in Semliki Forest virus reconstructed using network antibodies. Nature. 1988 Nov 3;336(6194):36–42. doi: 10.1038/336036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Boege U., Wengler G., Bischoff H., Wahn K. The core protein of the alphavirus Sindbis virus assembles into core-like nucleoproteins with the viral genome RNA and with other single-stranded nucleic acids in vitro. Virology. 1982 Apr 30;118(2):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G. The mode of assembly of alphavirus cores implies a mechanism for the disassembly of the cores in the early stages of infection. Brief review. Arch Virol. 1987;94(1-2):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01313721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G., Boege U., Wahn K. Establishment and analysis of a system which allows assembly and disassembly of alphavirus core-like particles under physiological conditions in vitro. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Specific RNA binding by Q beta coat protein. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):71–76. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong C., Levis R., Shen P., Schlesinger S., Rice C. M., Huang H. V. Sindbis virus: an efficient, broad host range vector for gene expression in animal cells. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1188–1191. doi: 10.1126/science.2922607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuidema D., Bierhuizen M. F., Cornelissen B. J., Bol J. F., Jaspars E. M. Coat protein binding sites on RNA 1 of alfalfa mosaic virus. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]