Abstract
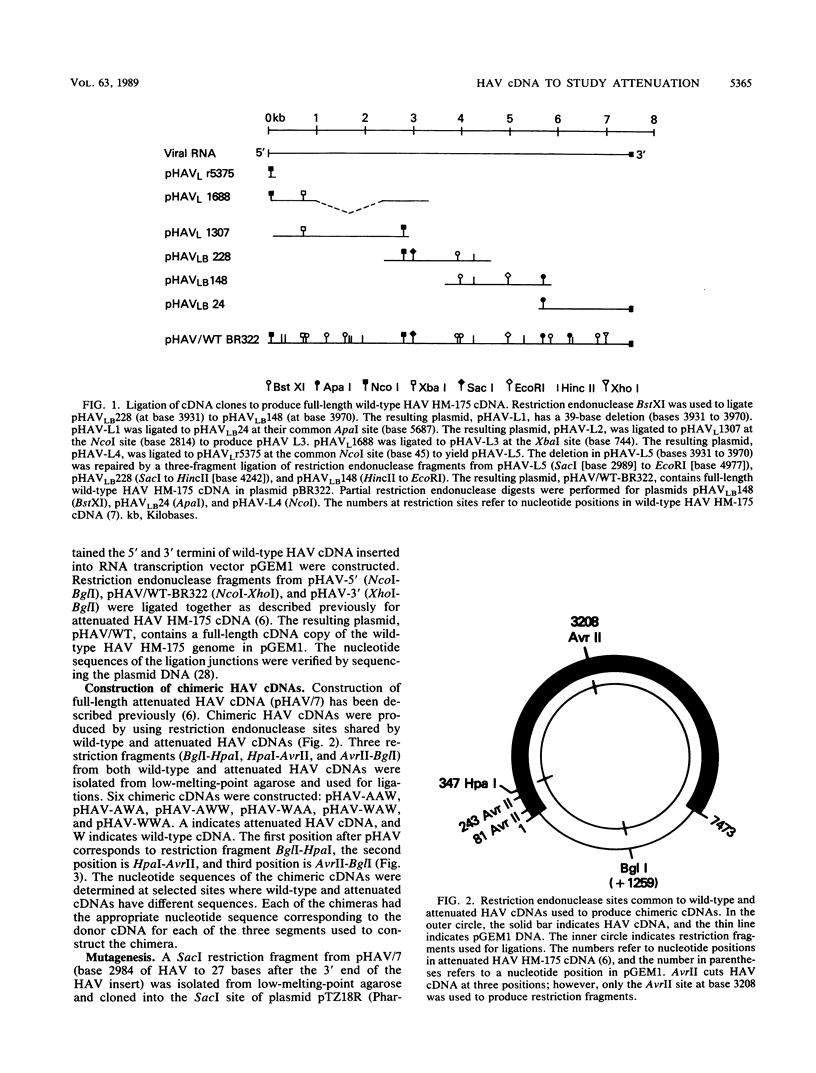
RNA transcripts of hepatitis A virus (HAV) HM-175 cDNA from attenuated, cell culture-adapted HAV were infectious in cell culture. A full-length HAV cDNA from wild-type HAV (propagated in marmosets in vivo) was constructed. Chimeric cDNAs that contained portions of both wild-type and attenuated genomes were produced. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis was used to engineer a point mutation into the VP1 gene of attenuated HAV cDNA, so that the sequence of this capsid protein would be identical to that of the wild-type virus. Transfection of monkey kidney cells with RNA transcripts from several of the chimeric cDNAs and from the mutagenized cDNA induced production of HAV. Comparison of the growth of attenuated, wild-type, chimeric, and mutant viruses in vitro indicated that the P2-P3 (nonstructural protein) region is important for cell culture adaptation of the virus; the 5' noncoding region may also contribute to adaptation, but to a lesser extent. Inoculation of marmosets with transfection-derived virus also suggested that the P2-P3 region plays an important role in attenuation of HAV HM-175.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almond J. W., Westrop G. D., Evans D. M., Dunn G., Minor P. D., Magrath D., Schild G. C. Studies on the attenuation of the Sabin type 3 oral polio vaccine. J Virol Methods. 1987 Aug;17(1-2):183–189. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(87)90081-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. W., Schable C. A., McCaustland K. A., Cook E. H., Murphy B. L., Fields H. A., Ebert J. W., Wheeler C., Maynard J. E. Hepatitis A virus: growth characteristics of in vivo and in vitro propagated wild and attenuated virus strains. J Med Virol. 1984;14(4):373–386. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890140410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Rosenblum B., Ticehurst J. R., Daemer R. J., Feinstone S. M., Purcell R. H. Complete nucleotide sequence of an attenuated hepatitis A virus: comparison with wild-type virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2497–2501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Ticehurst J. R., Feinstone S. M., Rosenblum B., Purcell R. H. Hepatitis A virus cDNA and its RNA transcripts are infectious in cell culture. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3035–3039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3035-3039.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Ticehurst J. R., Purcell R. H., Buckler-White A., Baroudy B. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of wild-type hepatitis A virus: comparison with different strains of hepatitis A virus and other picornaviruses. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):50–59. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.50-59.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daemer R. J., Feinstone S. M., Gust I. D., Purcell R. H. Propagation of human hepatitis A virus in African green monkey kidney cell culture: primary isolation and serial passage. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):388–393. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.388-393.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. M., Dunn G., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Cann A. J., Stanway G., Almond J. W., Currey K., Maizel J. V., Jr Increased neurovirulence associated with a single nucleotide change in a noncoding region of the Sabin type 3 poliovaccine genome. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):548–550. doi: 10.1038/314548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstone S. M., Daemer R. J., Gust I. D., Purcell R. H. Live attenuated vaccine for hepatitis A. Dev Biol Stand. 1983;54:429–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen R. W., Newbold J. E., Lemon S. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of a cell culture-adapted variant of hepatitis A virus: comparison with wild-type virus with restricted capacity for in vitro replication. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90270-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karron R. A., Daemer R., Ticehurst J., D'Hondt E., Popper H., Mihalik K., Phillips J., Feinstone S., Purcell R. H. Studies of prototype live hepatitis A virus vaccines in primate models. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):338–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathiesen L. R., Feinstone S. M., Purcell R. H., Wagner J. A. Detection of hepatitis A antigen by immunofluorescence. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):524–530. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.524-530.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Omata T., Toyoda H., Kuge S., Horie H., Kataoka Y., Genba Y., Nakano Y., Imura N. Complete nucleotide sequence of the attenuated poliovirus Sabin 1 strain genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata T., Kohara M., Kuge S., Komatsu T., Abe S., Semler B. L., Kameda A., Itoh H., Arita M., Wimmer E. Genetic analysis of the attenuation phenotype of poliovirus type 1. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):348–358. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.348-358.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost P. J., Bishop R. P., Gerety R. J., Hilleman M. R., McAleer W. J., Scolnick E. M., Stevens C. E. New findings in live, attenuated hepatitis A vaccine development. J Med Virol. 1986 Oct;20(2):165–175. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890200208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Cloned poliovirus complementary DNA is infectious in mammalian cells. Science. 1981 Nov 20;214(4523):916–919. doi: 10.1126/science.6272391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B. C., Anderson B. N., Coulepis A. G., Chenoweth M. P., Gust I. D. Molecular cloning of cDNA from hepatitis A virus strain HM-175 after multiple passages in vivo and in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1986 Aug;67(Pt 8):1741–1744. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-8-1741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G., Hughes P. J., Mountford R. C., Reeve P., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Almond J. W. Comparison of the complete nucleotide sequences of the genomes of the neurovirulent poliovirus P3/Leon/37 and its attenuated Sabin vaccine derivative P3/Leon 12a1b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1539–1543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticehurst J. R., Feinstone S. M., Chestnut T., Tassopoulos N. C., Popper H., Purcell R. H. Detection of hepatitis A virus by extraction of viral RNA and molecular hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1822–1829. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1822-1829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticehurst J. R., Racaniello V. R., Baroudy B. M., Baltimore D., Purcell R. H., Feinstone S. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of hepatitis A virus cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5885–5889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitz M., Baroudy B. M., Maloy W. L., Ticehurst J. R., Purcell R. H. Detection of a genome-linked protein (VPg) of hepatitis A virus and its comparison with other picornaviral VPgs. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):124–130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.124-130.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


