Abstract
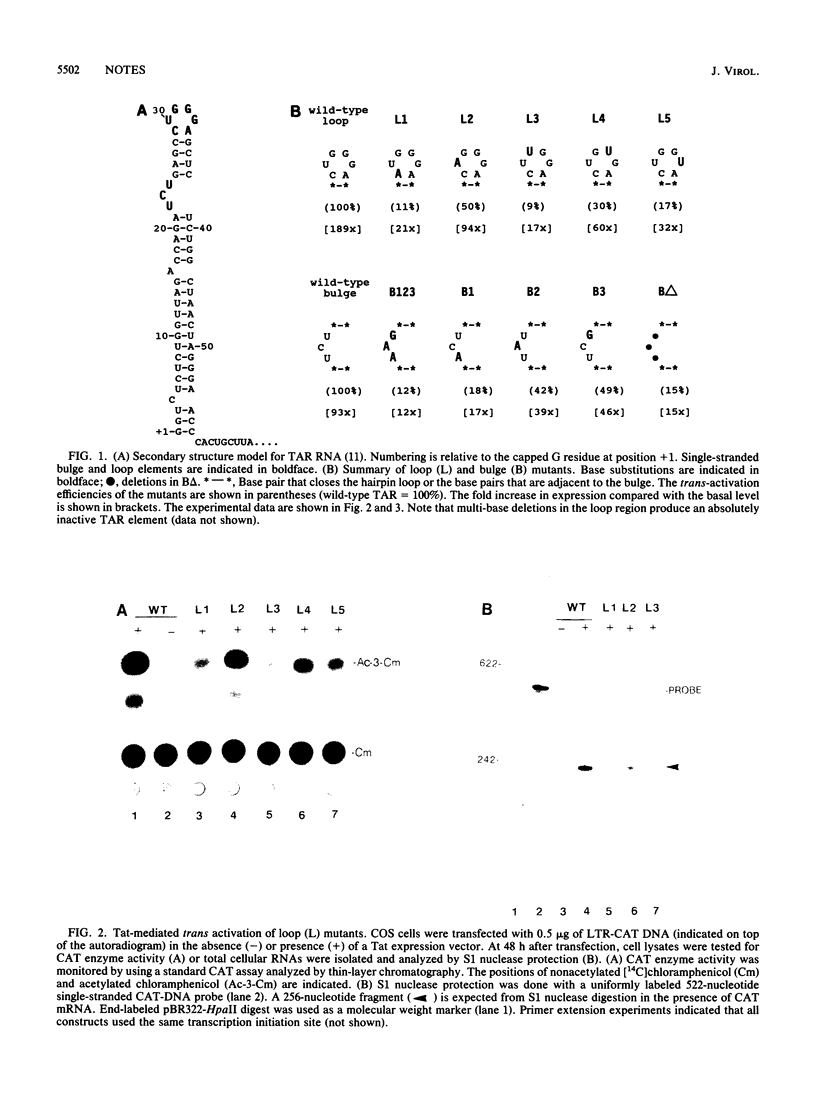
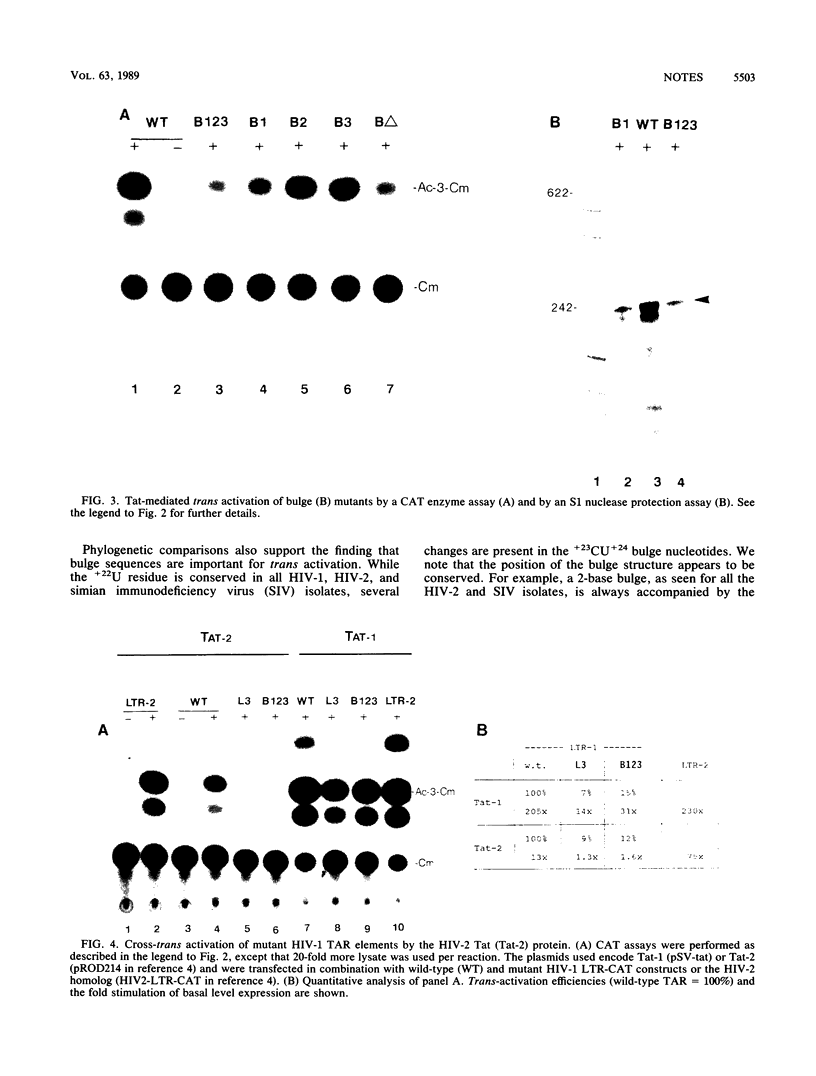
We have used site-directed mutagenesis to delineate sequence specific domains within the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) trans-acting-responsive (TAR) RNA element that are required for trans activation by the viral Tat protein. Our data in part corroborate a recent report [S. Feng and E. C. Holland, Nature (London) 334:165-167, 1988] that five nucleotides within the loop (+29 to +33) of the TAR hairpin are important for trans activation. We, however, found no absolute requirement for the CUGGG loop sequence. Mutants with substitutions within the loop retained between 9 and 50% activity compared with the wild type. A second sequence, important for trans activation, was found in the 3-base bulge loop (+22 to +24) of the TAR hairpin. Cross-trans-activation studies of mutant HIV-1 TAR elements with the HIV-2 Tat protein suggest that a similar recognition event(s) forms the basis for trans activation of HIV-1 and HIV-2.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arya S. K., Beaver B., Jagodzinski L., Ensoli B., Kanki P. J., Albert J., Fenyo E. M., Biberfeld G., Zagury J. F., Laure F. New human and simian HIV-related retroviruses possess functional transactivator (tat) gene. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):548–550. doi: 10.1038/328548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arya S. K., Gallo R. C. Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 long terminal repeat: analysis of regulatory elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9753–9757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton A. I., Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Goh W. C., Haseltine W. A. The trans-activator gene of the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III is required for replication. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):941–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Guyader M., Montagnier L., Baltimore D., Muesing M. A. The specificity of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2 transactivator is different from that of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3755–3760. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02710.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng S., Holland E. C. HIV-1 tat trans-activation requires the loop sequence within tar. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):165–167. doi: 10.1038/334165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. G., Feinberg M. B., Josephs S. F., Harper M. E., Marselle L. M., Reyes G., Gonda M. A., Aldovini A., Debouk C., Gallo R. C. The trans-activator gene of HTLV-III is essential for virus replication. 1986 Mar 27-Apr 2Nature. 320(6060):367–371. doi: 10.1038/320367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. A., Harrich D., Soultanakis E., Wu F., Mitsuyasu R., Gaynor R. B. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 LTR TATA and TAR region sequences required for transcriptional regulation. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):765–778. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyader M., Emerman M., Sonigo P., Clavel F., Montagnier L., Alizon M. Genome organization and transactivation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):662–669. doi: 10.1038/326662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauber J., Malim M. H., Cullen B. R. Mutational analysis of the conserved basic domain of human immunodeficiency virus tat protein. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1181–1187. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1181-1187.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits A., Smith D. H., Jakobovits E. B., Capon D. J. A discrete element 3' of human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) and HIV-2 mRNA initiation sites mediates transcriptional activation by an HIV trans activator. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2555–2561. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Capon D. J. Regulation of mRNA accumulation by a human immunodeficiency virus trans-activator protein. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):691–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J., Lowary P., Wu H. N., Stormo G., Uhlenbeck O. C. RNA binding site of R17 coat protein. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 24;26(6):1563–1568. doi: 10.1021/bi00380a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby M. J., Bain E. S., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Structure, sequence, and position of the stem-loop in tar determine transcriptional elongation by tat through the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):547–558. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viglianti G. A., Mullins J. I. Functional comparison of transactivation by simian immunodeficiency virus from rhesus macaques and human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4523–4532. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4523-4532.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]