Abstract
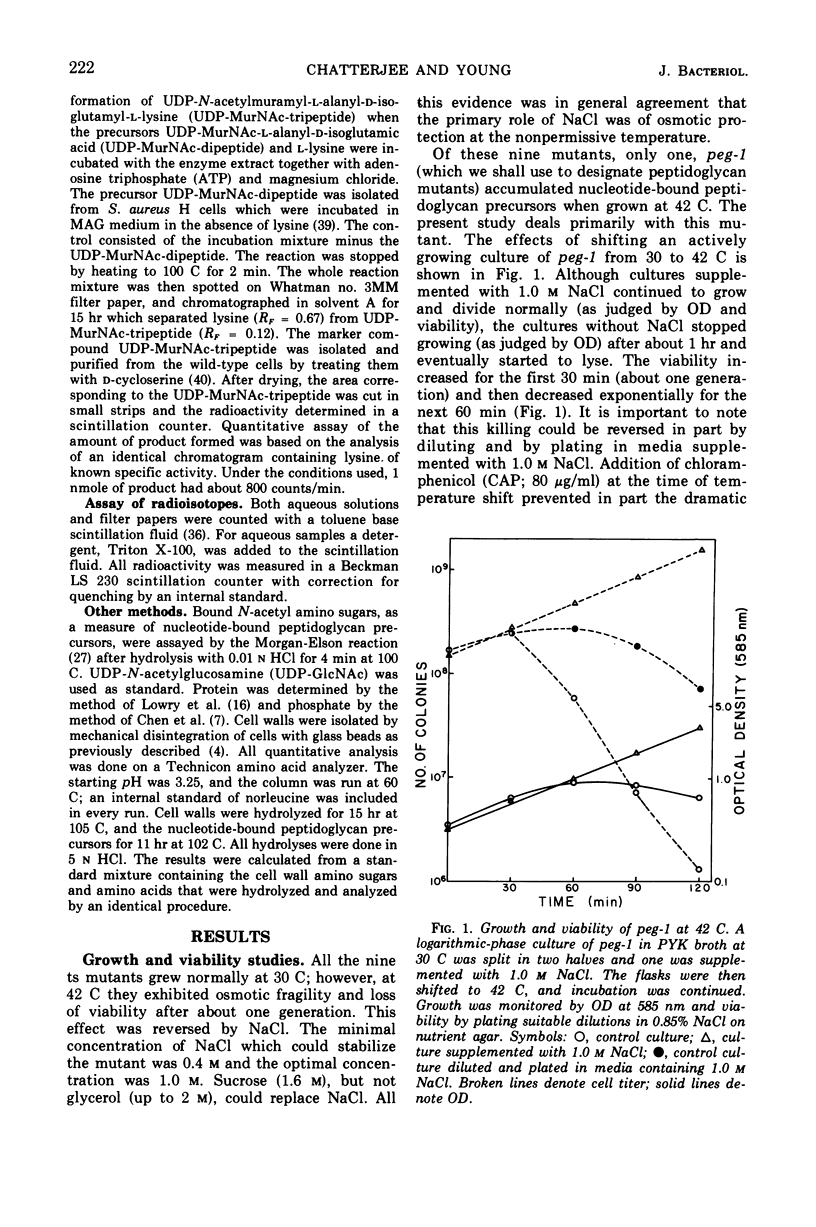
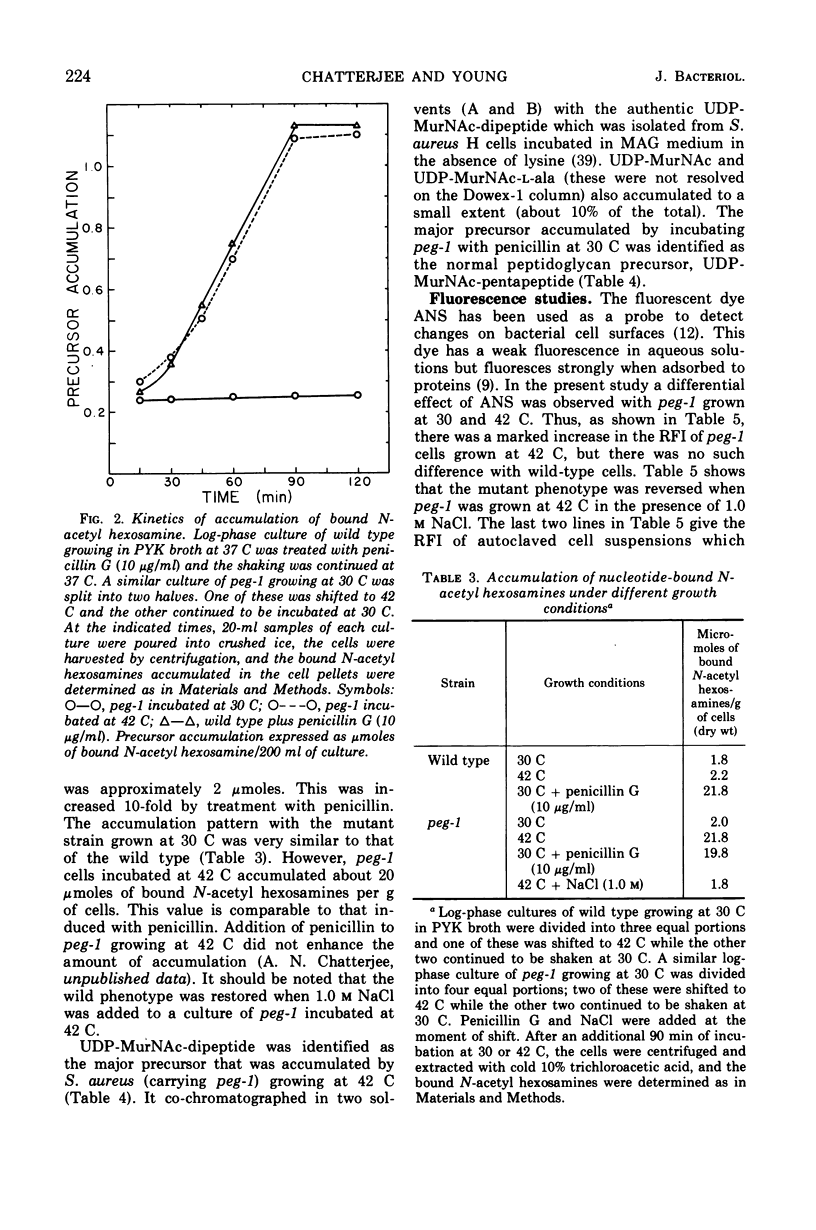
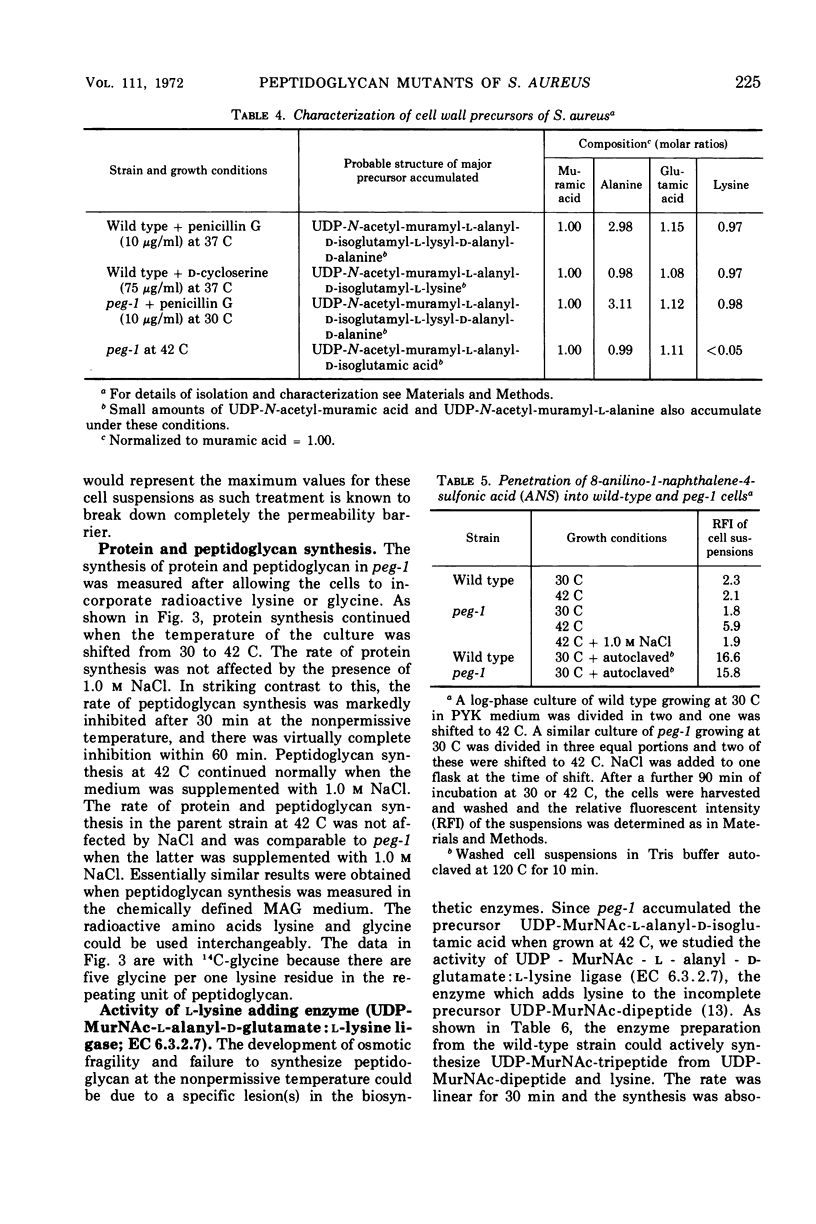
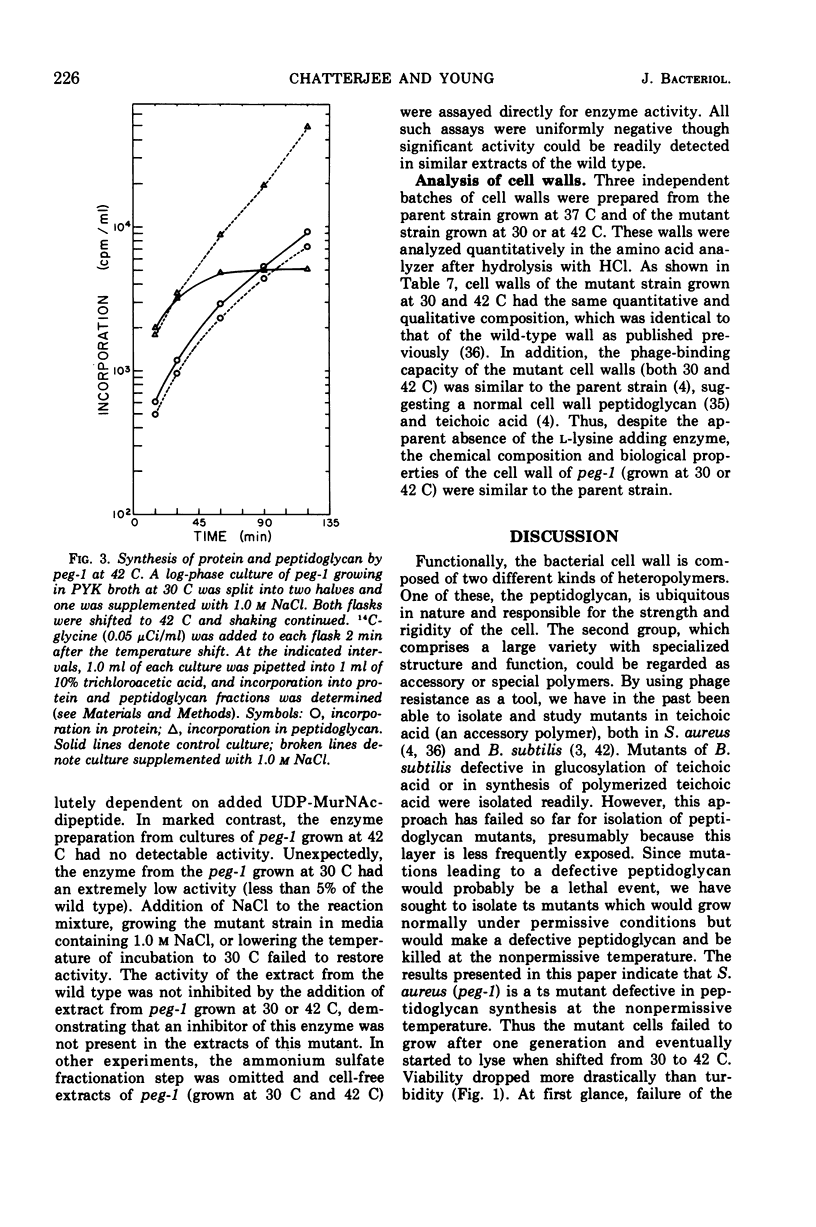
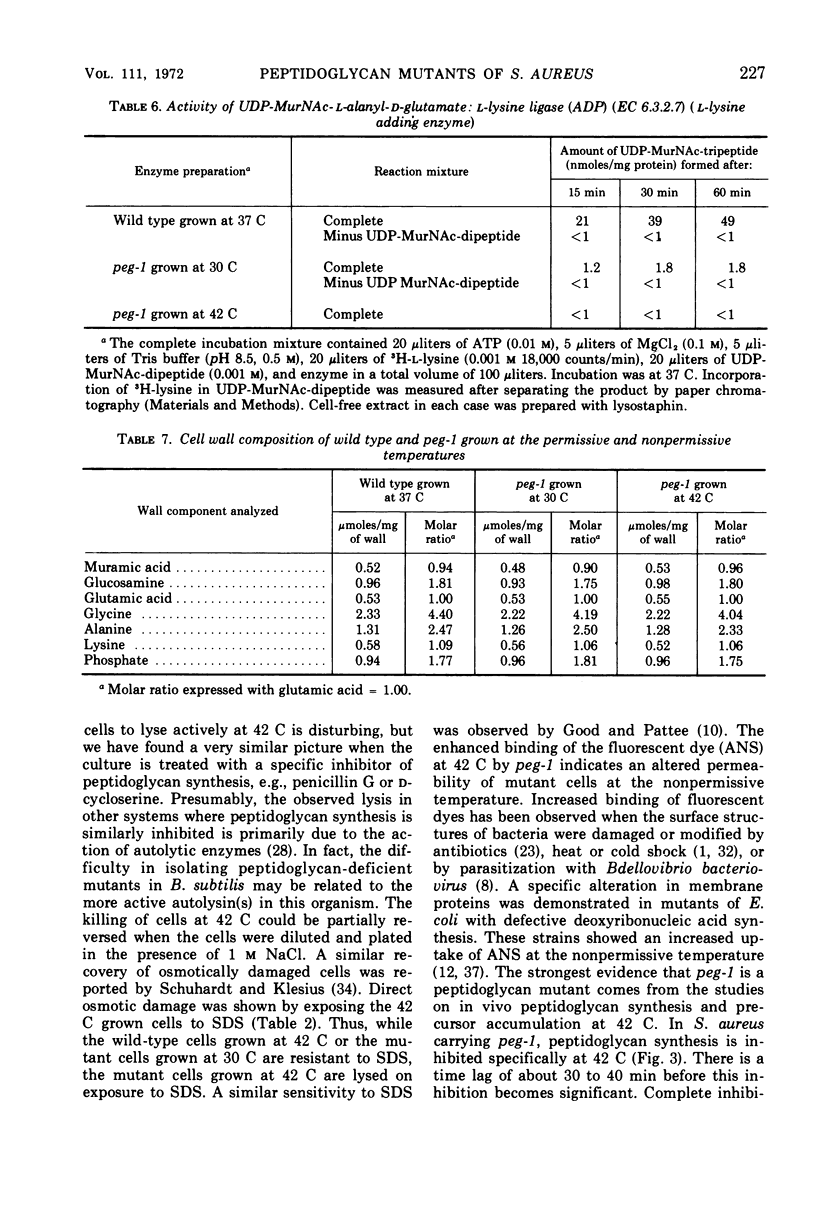
Temperature-sensitive mutants of Staphylococcus aureus H which require 1.0 m NaCl for growth at 42 C can be divided into two major classes. Most of the mutants (class A) do not accumulate nucleotide precursors of cell wall biosynthesis in the absence of salt at the nonpermissive temperatures, whereas the class B mutants accumulate these precursors. The most extensively studied mutant RUS 1 (carrying peg-1) is defective in biosynthesis of peptidoglycan at the nonpermissive conditions as evidenced by: (i) reduced incorporation of cell wall precursors into peptidoglycan; (ii) accumulation of the nucleotide, uridine diphosphate (UDP) muramyl-l-alanyl-d-glutamic acid; (iii) reduced specific activity of UDP N-acetylmuramyl (MurNAc)-l-alanyl-d-glutamate: l-lysine ligase (EC 6.3.2.7); and (iv) an increased susceptibility to lysis with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Addition of 1.0 m NaCl reverses these defects with the exception of the specific activity of UDP-MurNAc-l-alanyl-d-glutamate: l-lysine ligase. Nevertheless, the structure of the cell wall is normal at the nonpermissive conditions if 1.0 m NaCl is present. An alteration in the binding of a fluorescent dye, 8-anilino-1-napthalene-4-sulfonic acid at the nonpermissive conditions in the absence of 1.0 m NaCl suggests that there may also be defects in the membrane in this strain.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allwood M. C., Russell A. D. Mechanism of Thermal Injury in Staphylococcus aureus: I. Relationship Between Viability and Leakage. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Nov;15(6):1266–1269. doi: 10.1128/am.15.6.1266-1269.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassel J., Douglas H. C. Osmotic remedial response in a galactose-negative mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1103–1110. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1103-1110.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan R. J., Mendelson N. H., Brooks D., Young F. E. Regulation of the bacterial cell wall: analysis of a mutant of Bacillus subtilis defective in biosynthesis of teichoic acid. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):281–290. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.281-290.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHATTERJEE A. N., PARK J. T. BIOSYNTHESIS OF CELL WALL MUCOPEPTIDE BY A PARTICULATE FRACTION FROM STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jan;51:9–16. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee A. N., Mirelman D., Singer H. J., Park J. T. Properties of a novel pleiotropic bacteriophage-resistant mutant of Staphylococcus aureus H. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):846–853. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.846-853.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee A. N. Use of bacteriophage-resistant mutants to study the nature of the bacteriophage receptor site of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):519–527. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.519-527.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers S. F., Robinson J. Changes in the permeability of Escherichia coli during parasitization by Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. Can J Microbiol. 1971 May;17(5):689–697. doi: 10.1139/m71-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good C. M., Pattee P. A. Temperature-Sensitive Osmotically Fragile Mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1401–1403. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1401-1403.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAWTHORNE D. C., FRIIS J. OSMOTIC-REMEDIAL MUTANTS. A NEW CLASSIFICATION FOR NUTRITIONAL MUTANTS IN YEAST. Genetics. 1964 Nov;50:829–839. doi: 10.1093/genetics/50.5.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota Y., Mordoh J., Jacob F. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli. 3. Thermosensitive mutants of Escherichia coli altered in the process of DNA initiation. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 14;53(3):369–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITO E., STROMINGER J. L. ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF THE PEPTIDE IN BACTERIAL URIDINE NUCLEOTIDES. III. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF L-LYSIN-ADDING ENZYME. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:210–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaki K., Matsuhashi M., Strominger J. L. Glycopeptide transpeptidase and D-alanine carboxypeptidase: penicillin-sensitive enzymatic reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Mar;55(3):656–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.3.656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P., MOYLE J. Autolytic release and osmotic properties of protoplasts from Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Feb;16(1):184–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-1-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P., MOYLE J. Permeability of the envelopes of Staphylococcus aureus to some salts, amino acids, and non-electrolytes. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Apr;20(2):434–441. doi: 10.1099/00221287-20-2-434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiarotti G., Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Selection of sucrose-dependent Escherichia coli to obtain envelope mutants and fragile cultures. Science. 1966 Aug 19;153(3738):892–894. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3738.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzawa H., Matsuhashi M., Oka A., Sugino Y. Genetic and biochemical studies on cell wall peptidoglycan synthesis in Escherichia coli K-12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Aug 15;36(4):682–689. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90360-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf R. H., Deibel R. H. Differential lytic response of enterococci associated with addition order of lysozyme and anions. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):674–680. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.674-680.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzenberg R. L. Repair of multiple defects of a regulatory mutant of Neurospora by high osmotic pressure and by reversion. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 May;125(2):532–541. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90611-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON B. A. Site of action of polymyxin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa: antagonism by cations. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Jun;10(3):491–499. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-3-491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J. Structure and biosynthesis of the bacterial cell wall. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:501–538. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., HANCOCK R. A fractionation procedure for studies of the synthesis of cell-wall mucopeptide and of other polymers in cells of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Feb;22:249–258. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-1-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., STROMINGER J. L. Mode of action of penicillin. Science. 1957 Jan 18;125(3238):99–101. doi: 10.1126/science.125.3238.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISSIG J. L., STORMINGER J. L., LELOIR L. F. A modified colorimetric method for the estimation of N-acetylamino sugars. J Biol Chem. 1955 Dec;217(2):959–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J., McConnell M., Burdett I. D. Cell wall or membrane mutants of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis with grossly deformed morphology. Nature. 1968 Jul 20;219(5151):285–288. doi: 10.1038/219285a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J., McConnell M., Burdett I. D. The isolation and characterization of mutants of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis with disturbed morphology and cell division. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 May;61(2):155–171. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-2-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J., McConnell M. The role of L-glutamine in the phenotypic change of a rod mutant derived from Bacillus subtilis 168. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 May;61(2):173–181. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-2-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHINDLER C. A., SCHUHARDT V. T. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF LYSOSTAPHIN--A LYTIC AGENT FOR STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Feb 15;97:242–250. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L. Biosynthesis of bacterial cell walls. Fed Proc. 1962 Jan-Feb;21:134–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., THRENN R. H. Accumulation of a uridine nucleotide in Staphylococcus aureus as the consequence of lysine deprivation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Nov;36:83–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuhardt V. T., Klesius P. H. Osmotic fragility and viability of lysostaphin-induced staphylococcal spheroplasts. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):734–737. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.734-737.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. R., Chatterjee A. N. O-Acetyl groups as a component of the bacteriophage receptor on Staphylococcus aureus cell walls. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):584–585. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.584-585.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. R., Mirelman D., Chatterjee A. N., Park J. T. Ribitol teichoic acid synthesis in bacteriophage-resistant mutants of Staphylococcus aureus H. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5101–5106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siccardi A. G., Shapiro B. M. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli. IV. Altered protein composition and turnover of the membranes of thermosensitive mutants defective in chromosomal replication. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 28;56(3):475–490. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90395-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise E. M., Jr, Park J. T. Penicillin: its basic site of action as an inhibitor of a peptide cross-linking reaction in cell wall mucopeptide synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):75–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F. E., Haywood P., Pollock M. Isolation of L-forms of Bacillus subtilis which grow in liquid medium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):867–870. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.867-870.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F. E. Requirement of glucosylated teichoic acid for adsorption of phage in Bacillus subtilis 168. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2377–2384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


