Abstract
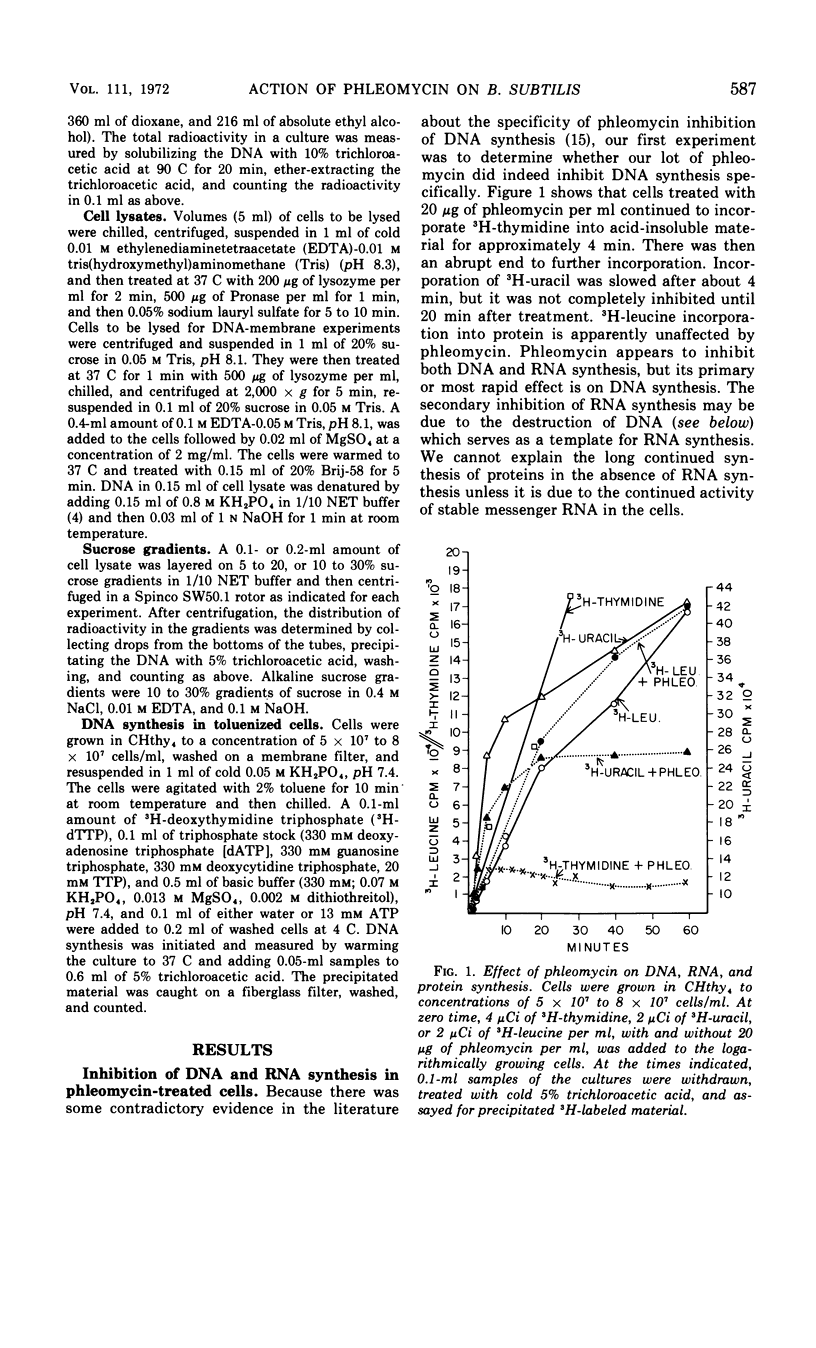
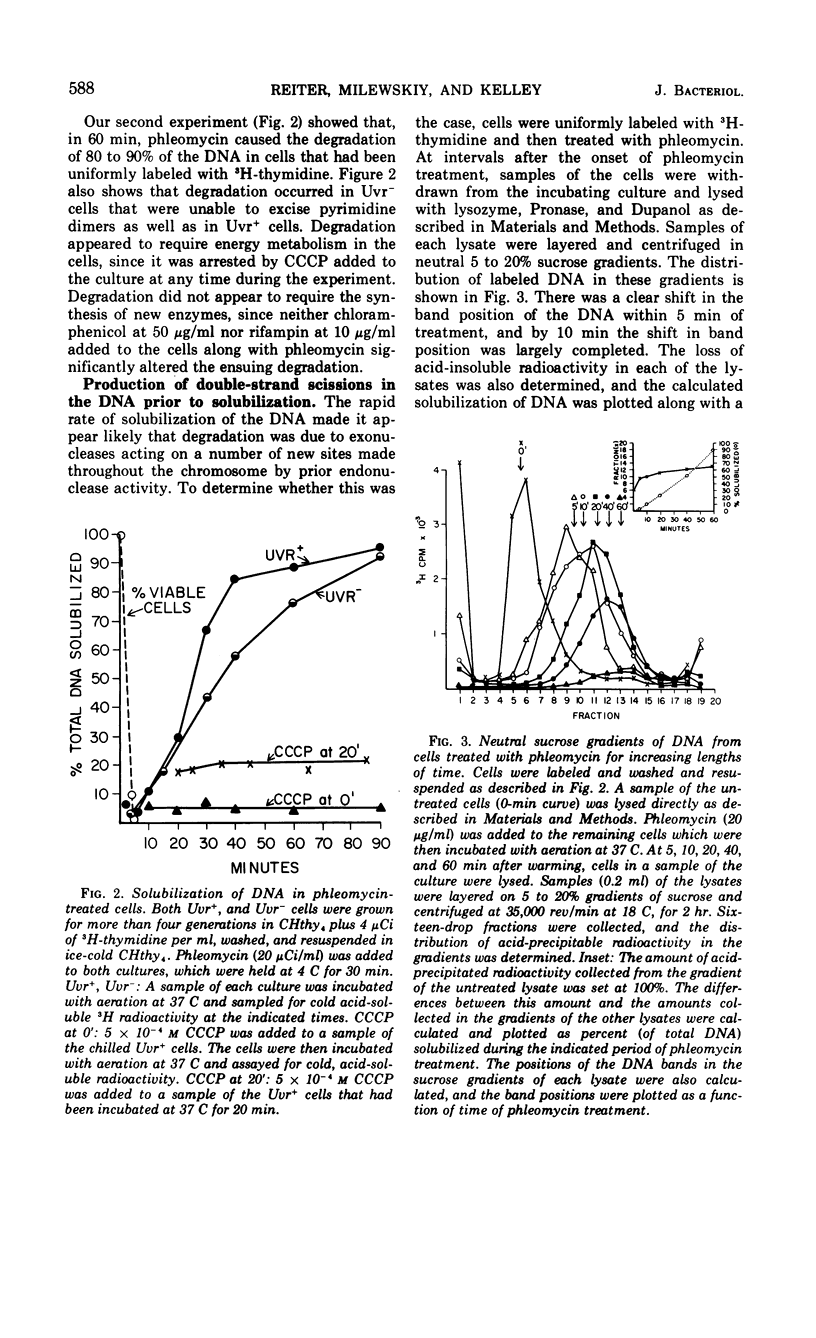
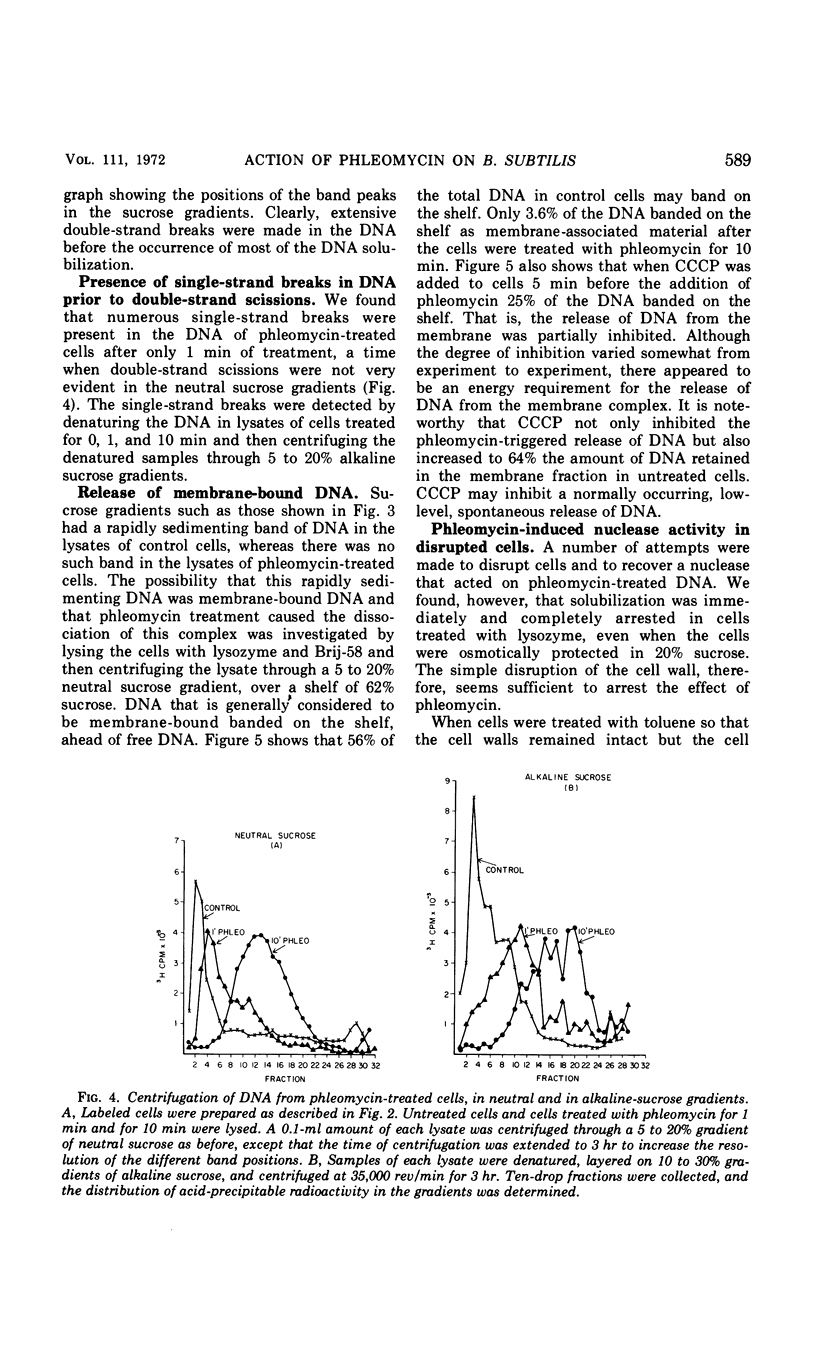
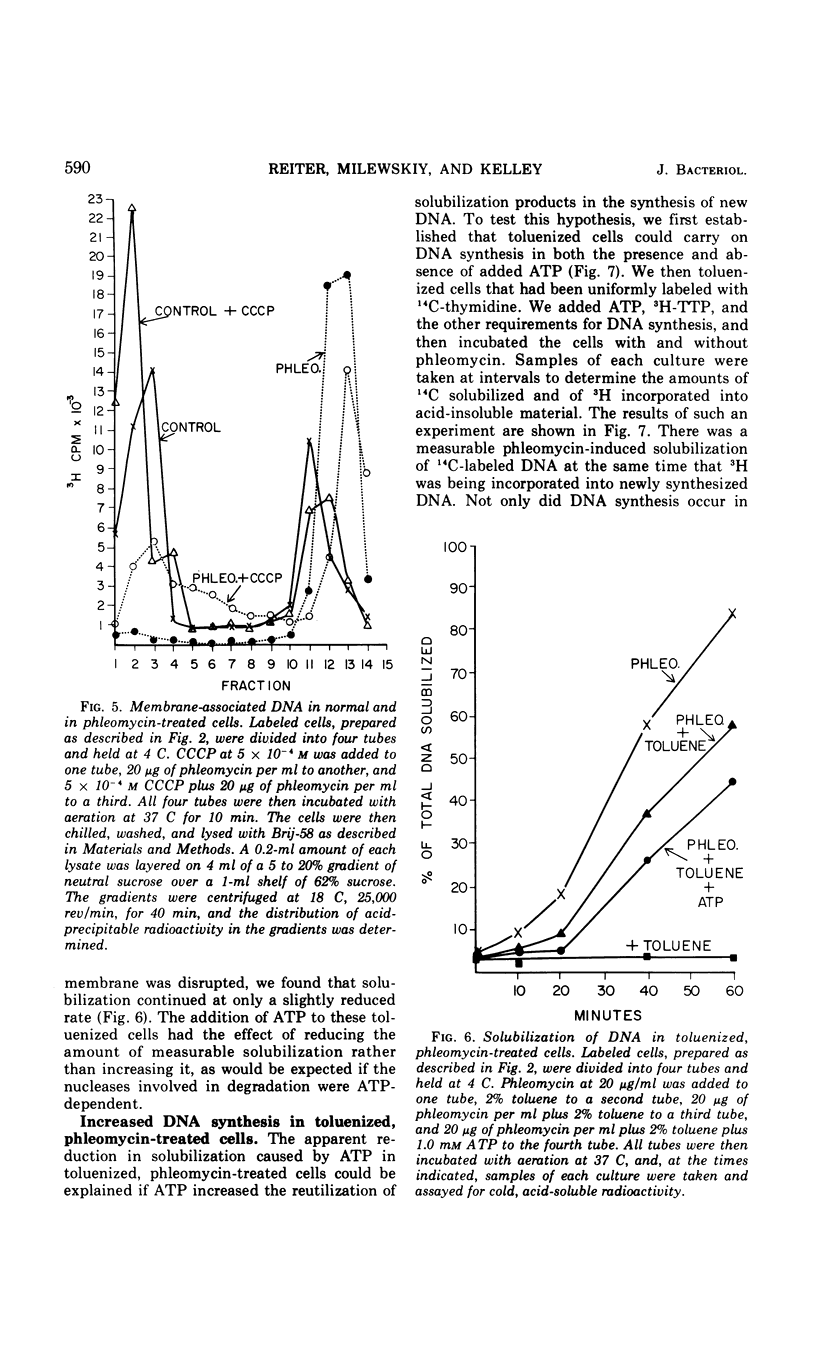
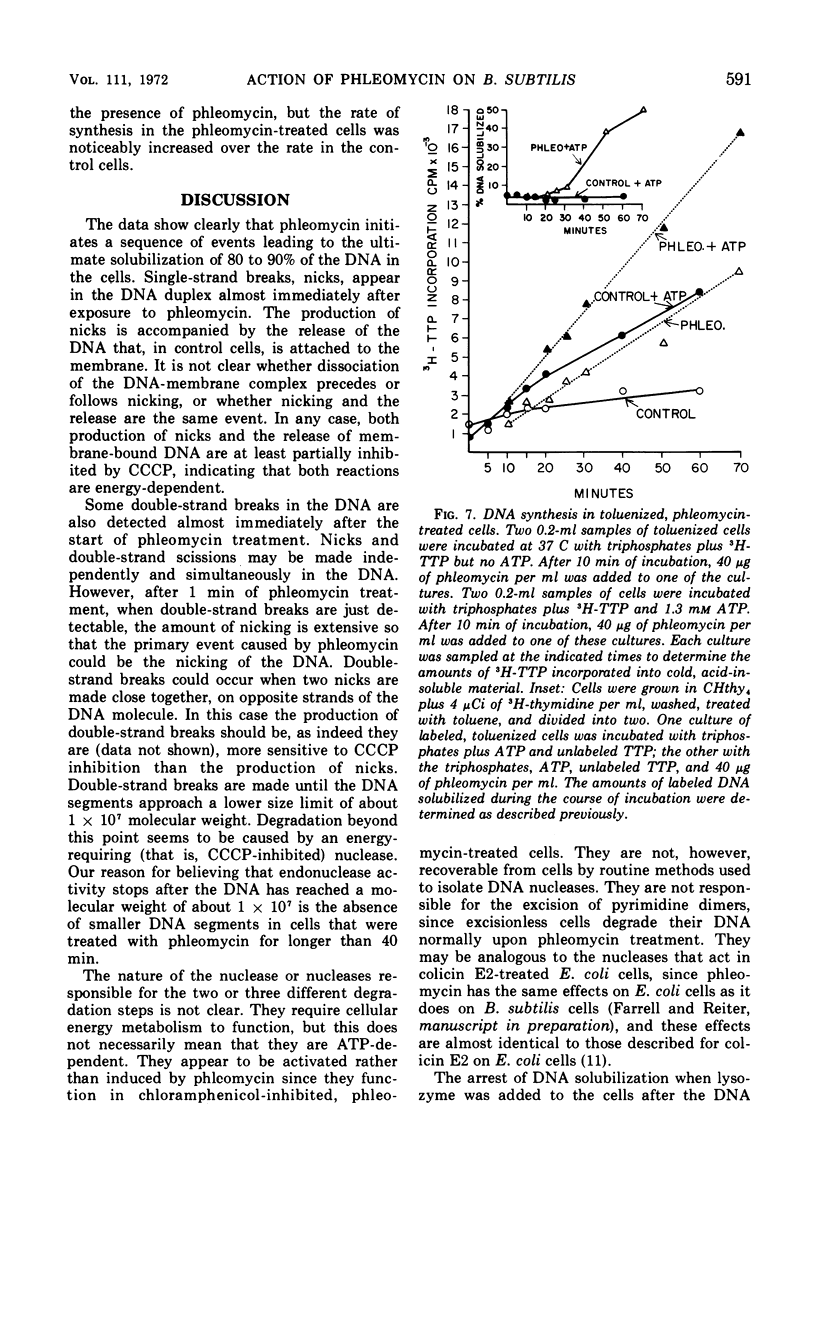
Phleomycin appears to act on the cell wall and membrane to induce the release of membrane-associated deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and the degradation of the DNA. Degradation occurs in a series of energy-requiring endonuclease and exonuclease reactions. These produce, first, single-strand breaks, then double-strand breaks, and finally almost complete solubilization of the cellular DNA. The in vivo inhibition of DNA synthesis by phleomycin is probably a secondary effect caused by the destruction of template DNA.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostopoulos C., Spizizen J. REQUIREMENTS FOR TRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALASCHI A., KORNBERG A. ANTIMETABOLITES AFFECTING PROTEIN OR NUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS. PHLEOMYCIN, AN INHIBITOR OF DNA POLYMERASE. Fed Proc. 1964 Sep-Oct;23:940–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigg G. W. Induction of DNA breakdown and death in Escherichia coli by phleomycin. Its association with dark-repair processes. Mol Gen Genet. 1969;104(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00277357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANAWALT P. C., RAY D. S. ISOLATION OF THE GROWING POINT IN THE BACTERIAL CHROMOSOME. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52:125–132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland E. M., Holland I. B. Induction of DNA breakdown and inhibition of cell division by colicin E2. Nature of some early steps in the process and properties of the E-2-specific nuclease system. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(2):223–239. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-2-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata A., Consigli R. A. Effect of phleomycin on polyoma virus synthesis in mouse embryo cells. J Virol. 1971 Jan;7(1):29–40. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.1.29-40.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAEDA K., KOSAKA H., YAGISHITA K., UMEZAWA H. A new antibiotic, phleomycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1956 Mar;9(2):82–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M. Colicins and related bacteriocins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:257–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitts J. D., Sinsheimer R. L. Effect of phleomycin upon replication of bacteriophage phiX174. J Mol Biol. 1966 Feb;15(2):676–680. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80136-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter H., Strauss B. Repair of damage induced by a monofunctional alkylating agent in a transformable, ultraviolet-sensitive strain of Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1965 Nov;14(1):179–194. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80239-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringrose P. Sedimentation analysis of DNA degradation products resulting from the action of colicin E2 on Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 8;213(2):320–334. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuve S. J., Rauth A. M. The effects of phleomycin on mouse L-cells. Cancer Res. 1971 Oct;31(10):1422–1428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tevethia S. S., Rapp F. The effect of phleomycin on the replication of papovavirus SV40 and other DNA viruses in simian cells. Cancer Res. 1969 Apr;29(4):912–917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., August J. T. Replication of RNA bacteriophage R23. II. Inhibition of phage-specific RNA synthesis by phleomycin. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):21–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90278-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


