Abstract
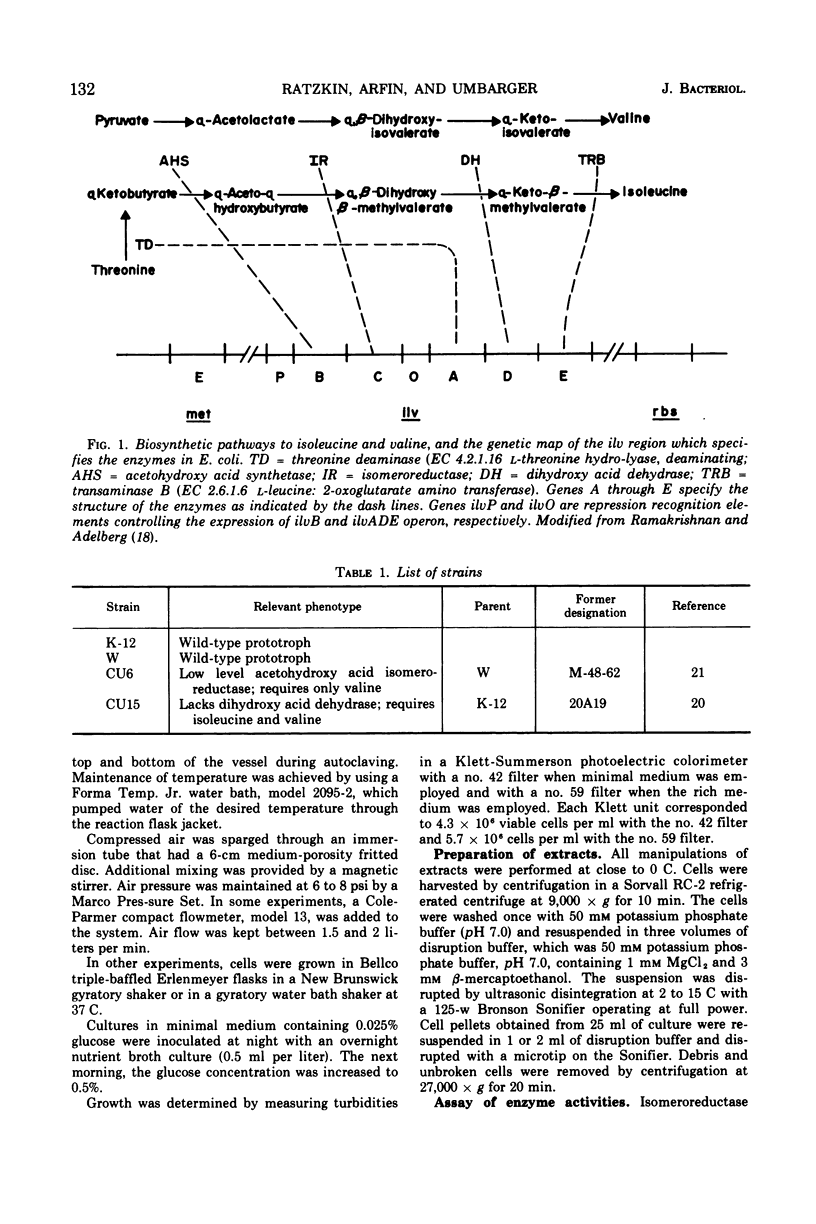
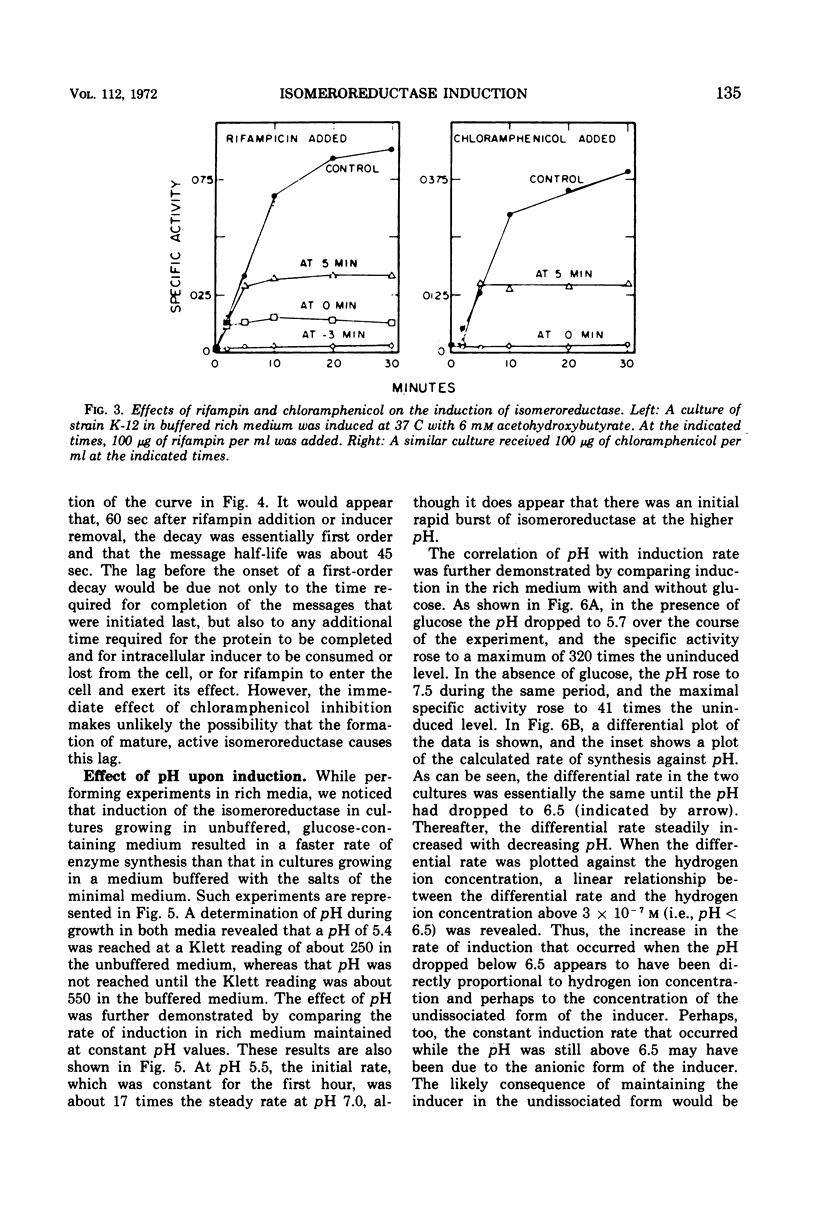
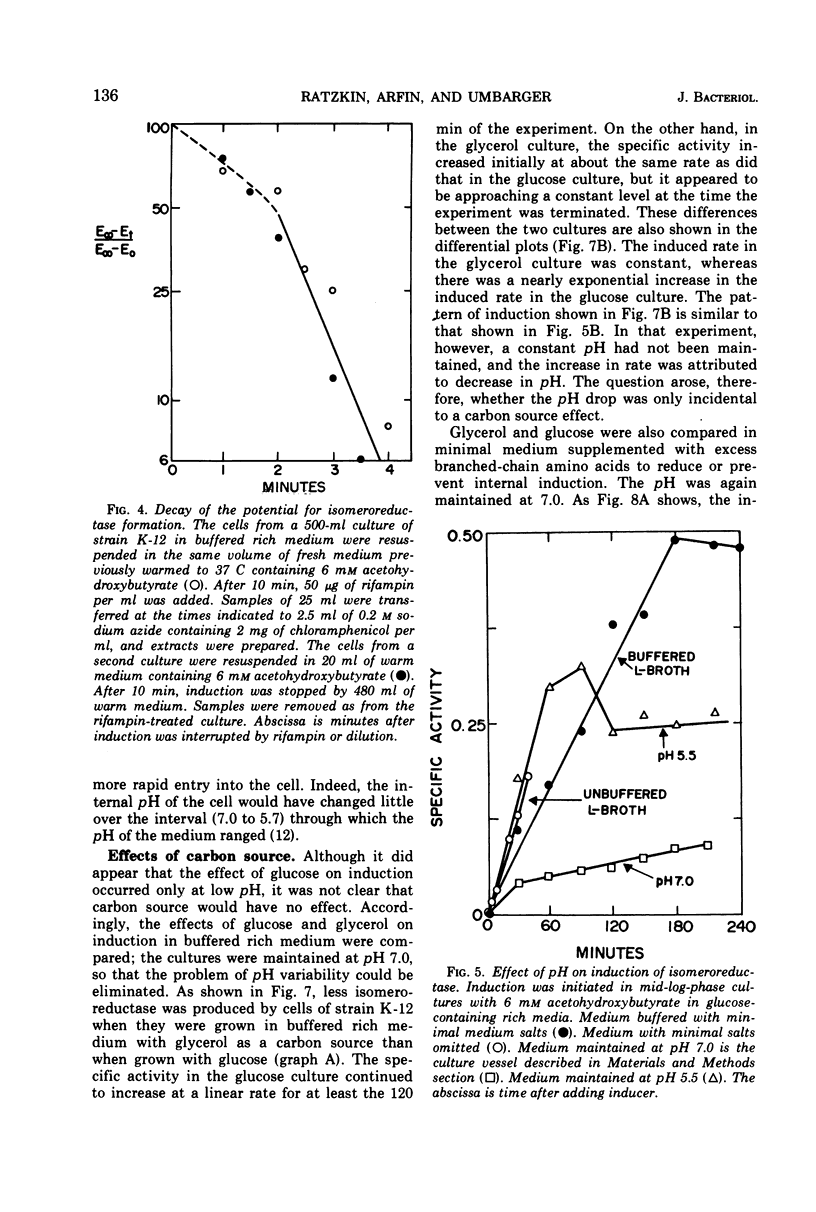
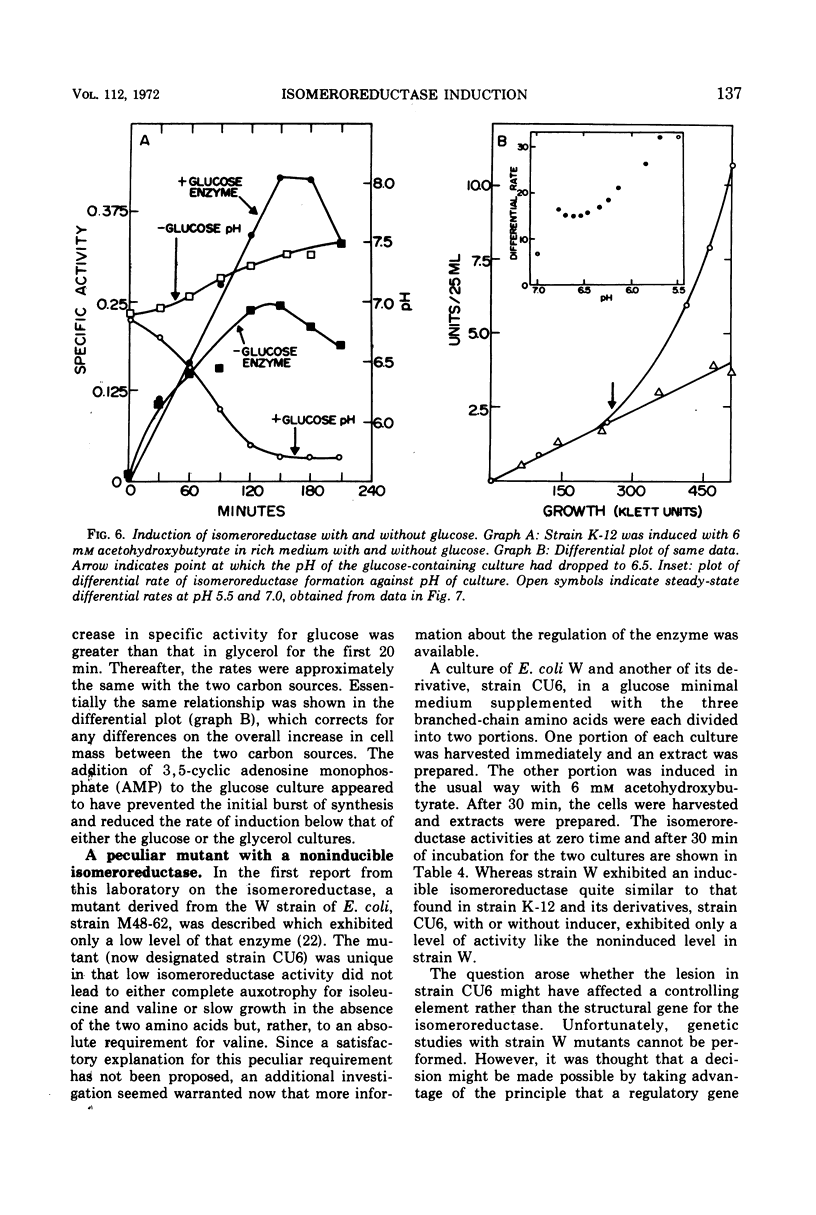
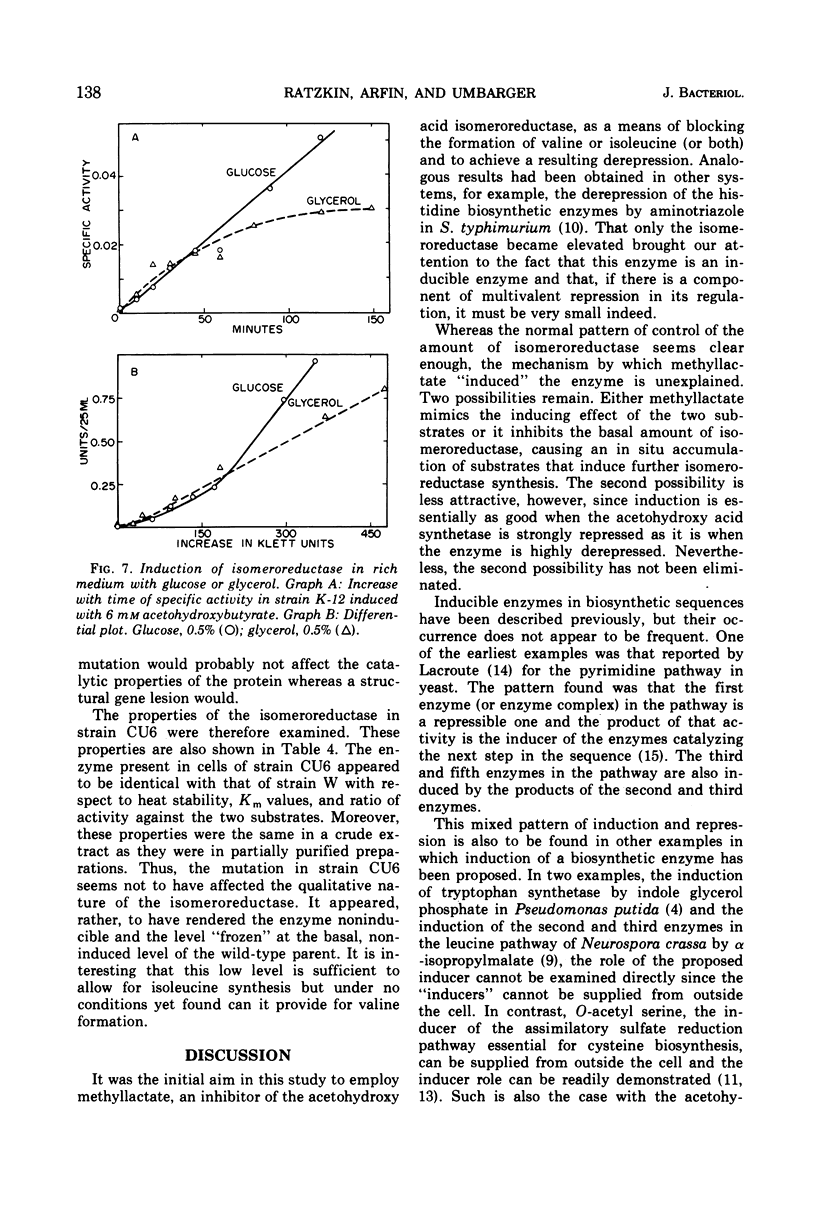
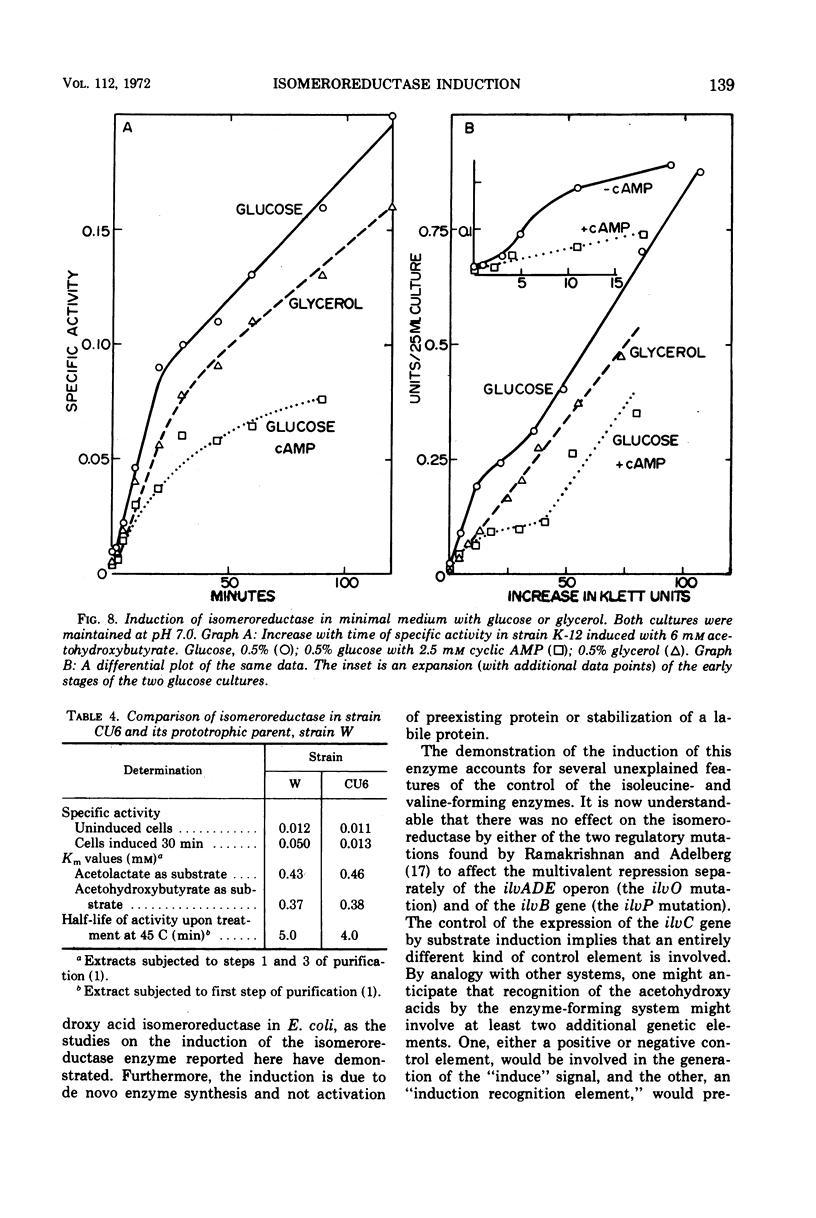
The regulation by substrate induction of the acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase was studied in Escherichia coli. Induction was inhibited by chloramphenicol and rifampin. The addition of rifampin resulted in a decay of the capacity to form isomeroreductase. This was attributed to the breakdown of the isomeroreductase messenger, which had a half-life of about 45 sec at 37 C. Induction of isomeroreductase was enhanced by including glucose in the medium. This effect was shown to be due in part to the lowering of the pH of the medium, which presumably made inducer entry more rapid.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arfin S. M., Ratzkin B., Umbarger H. E. The metabolism of valine and isoleucine in Escherichia coli. XVII. The role of induction in the derepression of acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Dec 4;37(6):902–908. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arfin S. M., Umbarger H. E. Purification and properties of the acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1118–1127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt J. M., Umbarger H. E. On the role of isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase in multivalent repression. Biochem Genet. 1972 Apr;6(2):99–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00486395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvo J. M., Freundlich M., Umbarger H. E. Regulation of branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium: isolation of regulatory mutants. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1272–1282. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1272-1282.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford I. P., Gunsalus I. C. Inducibility of tryptophan synthetase in Pseudomonas putida. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):717–724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer S. B., Umbarger H. E. Isoleucine and valine metabolism of Escherichia coli. XVI. Pattern of multivalent repression in strain K-12. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1680–1684. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1680-1684.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREUNDLICH M., BURNS R. O., UMBARGER H. E. Control of isoleucine, valine, and leucine biosynthesis. I. Multivalent repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Oct 15;48:1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.10.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. R. The regulation of synthesis of leucine biosynthetic enzymes in Neurospora. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1538–1546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton J. L., Kearney P. C., Ames B. N. Mode of action of the herbicide, 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole(amitrole): inhibition of an enzyme of histidine biosynthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Dec;112(3):544–547. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones-Mortimer M. C., Wheldrake J. F., Pasternak C. A. The control of sulphate reduction in Escherichia coli by O-acetyl-L-serine. Biochem J. 1968 Mar;107(1):51–53. doi: 10.1042/bj1070051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Wong P. T. The intracellular pH of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 14;193(1):212–214. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90074-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kredich N. M. Regulation of L-cysteine biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium. I. Effects of growth of varying sulfur sources and O-acetyl-L-serine on gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3474–3484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroute F. Regulation of pyrimidine biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):824–832. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.824-832.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMAKRISHNAN T., ADELBERG E. A. REGULATORY MECHANISMS IN THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF ISOLEUCINE AND VALINE. 3. MAP ORDER OF THE STRUCTURAL GENES AND OPERATOR GENES. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:661–664. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.661-664.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMAKRISHNAN T., ADELBERG E. A. REGULATORY MECHANISMS IN THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF ISOLEUCINE AND VALINE. II. IDENTIFICATION OF TWO OPERATOR GENES. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:654–660. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.654-660.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szentirmai A., Szentirmai M., Umbarger H. E. Isoleucine and valine metabolism of Escherichia coli. XV. Biochemical properties of mutants resistant to thiaisoleucine. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1672–1679. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1672-1679.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B., Magasanik B. Molecular basis of transient repression of beta-galactosidase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):550–556. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.550-556.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UMBARGER H. E., ADELBERG E. A. The rôle of alpha-keto- beta-ethylbutyric acid in the biosynthesis of isoleucine. J Biol Chem. 1951 Oct;192(2):883–889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UMBARGER H. E., BROWN B., EYRING E. J. Isoleucine and valine metabolism in Escherichia coli. IX. Utilization of acetolactate and acetohydroxybutyrate. J Biol Chem. 1960 May;235:1425–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]