Abstract
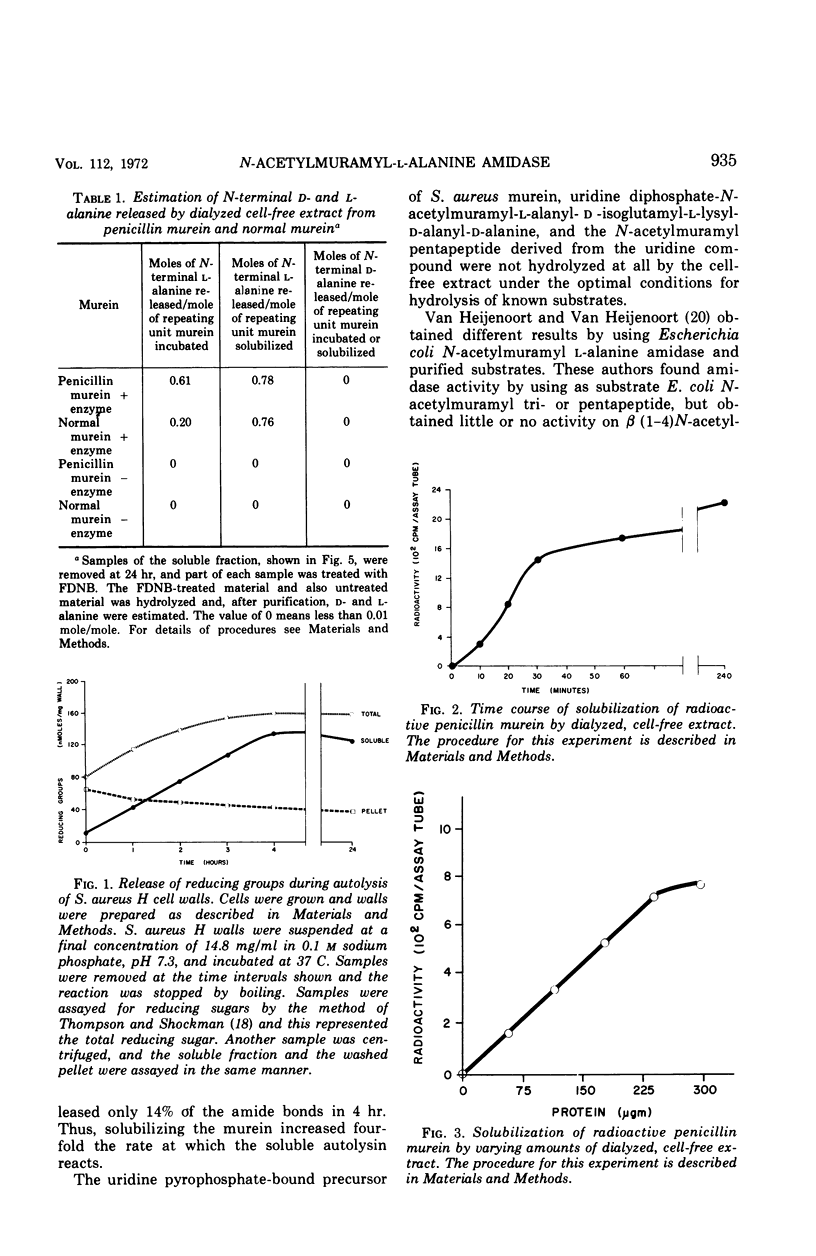
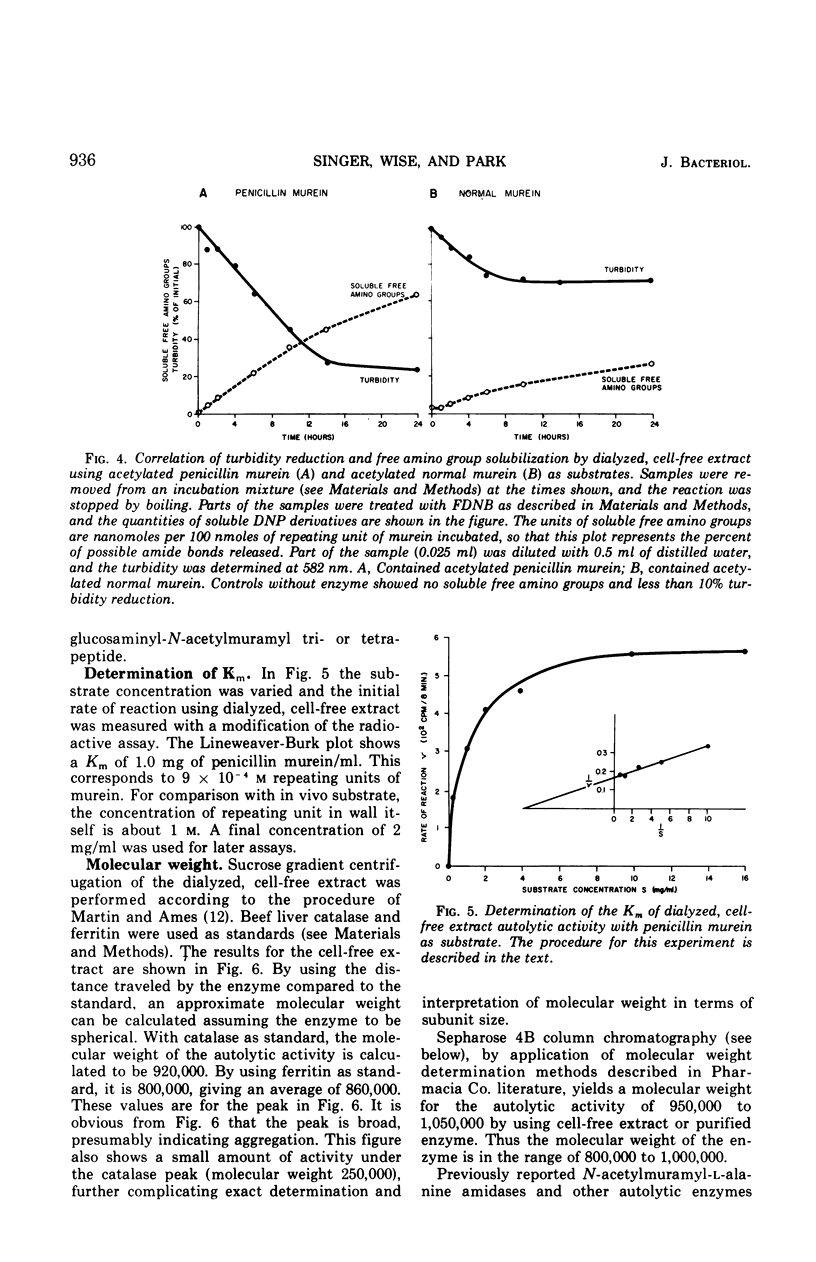
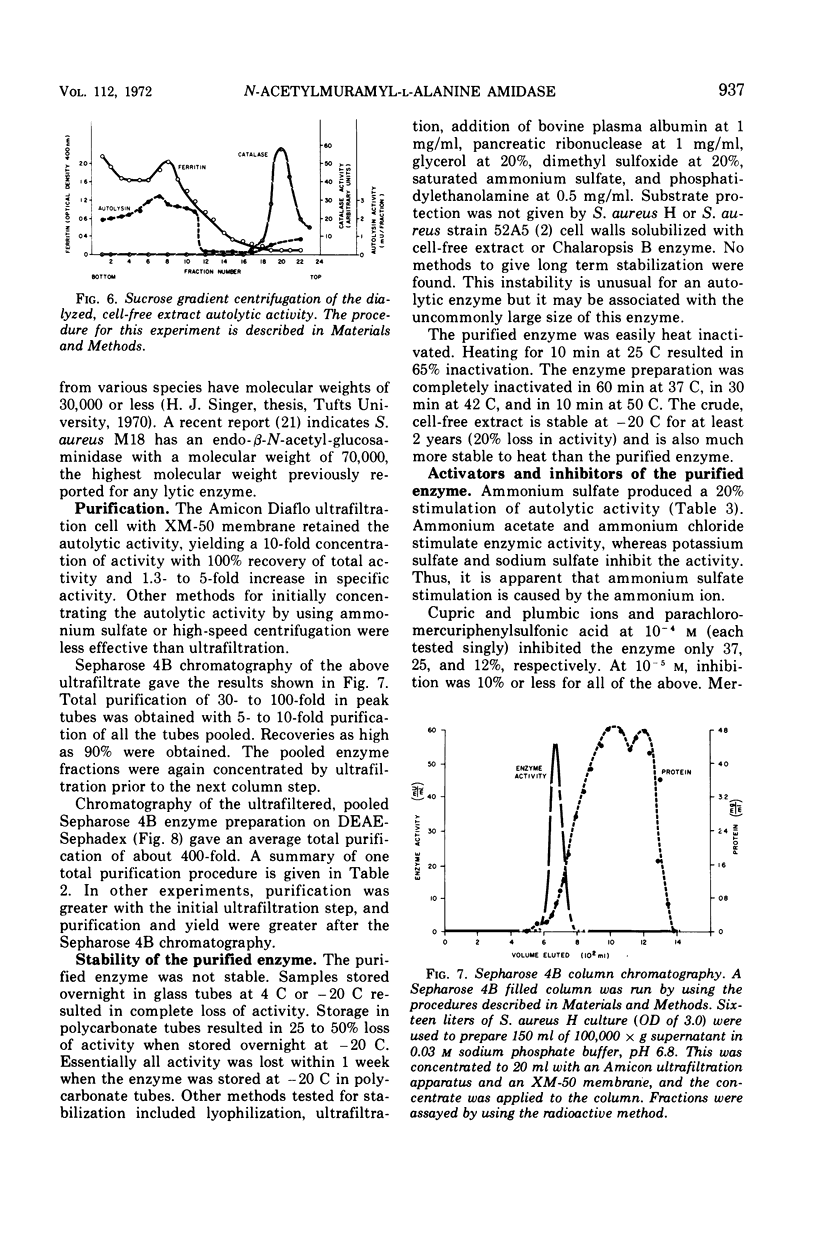
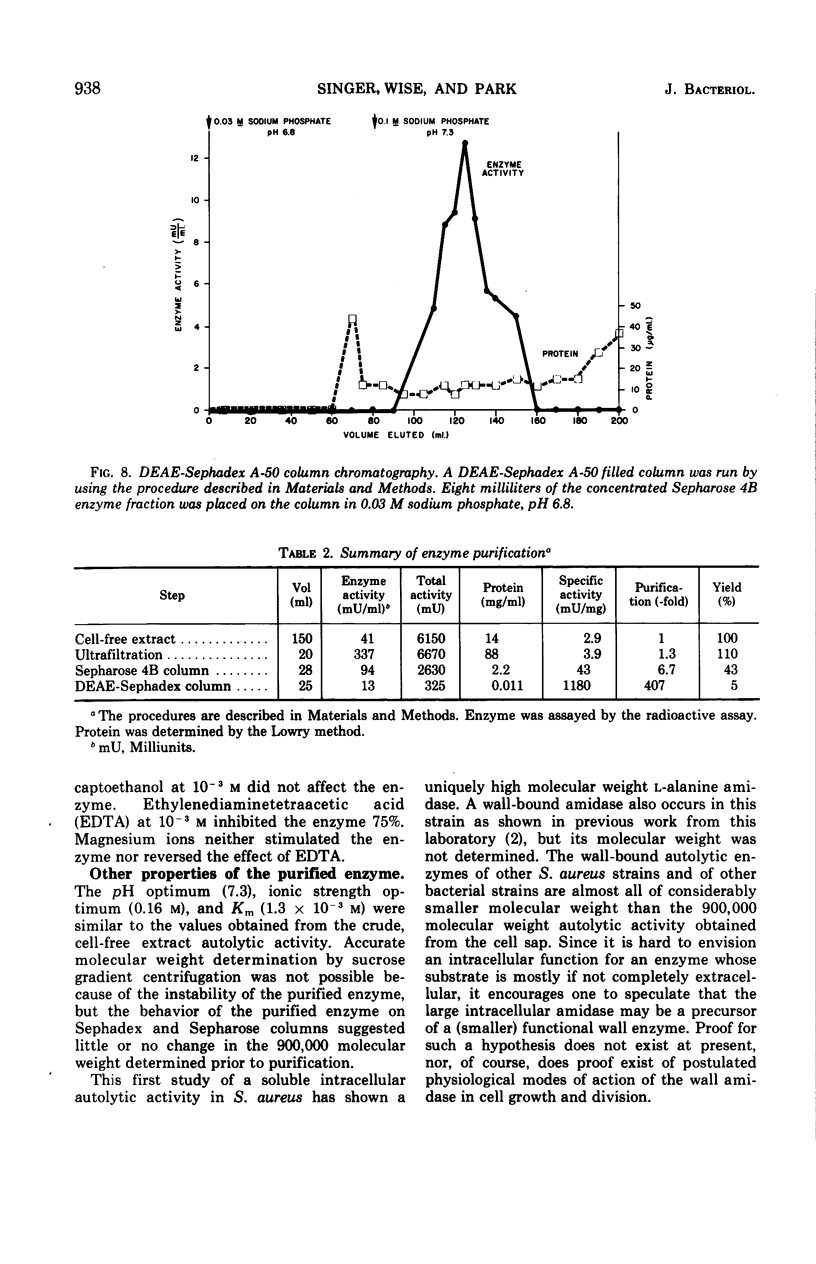
The principal autolytic enzyme activity of the cell sap of Staphylococcus aureus H has been purified 400-fold. It is an N-acetylmuramyl-l-alanine amidase. This enzyme has a molecular weight of 8 to 10 × 105, a pH optimum of 7.3, an ionic strength optimum of 0.16 m and a Km of 10−3m murein repeating units.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWDER H. P., ZYGMUNT W. A., YOUNG J. R., TAVORMINA P. A. LYSOSTAPHIN: ENZYMATIC MODE OF ACTION. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Apr 23;19:383–389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90473-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee A. N., Mirelman D., Singer H. J., Park J. T. Properties of a novel pleiotropic bacteriophage-resistant mutant of Staphylococcus aureus H. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):846–853. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.846-853.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensign J. C., Wolfe R. S. Characterization of a small proteolytic enzyme which lyses bacterial cell walls. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):524–534. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.524-534.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN T., HARRISON P. M. The structure of apoferritin: degradation into and molecular weight of subunits. J Mol Biol. 1963 Apr;6:256–267. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hash J. H., Rothlauf M. V. The N,O-diacetylmuramidase of Chalaropsis species. I. Purification and crystallization. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 10;242(23):5586–5590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J. Purification and properties of lysozyme produced by Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.376-384.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisatsune K., DeCourcy S. J., Jr, Mudd S. Studies on the carbohydrate-peptide fraction of the centrifugal supernatants of Staphylococcus aureus cultures. Biochemistry. 1967 Feb;6(2):586–594. doi: 10.1021/bi00854a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisatsune K., DeCourcy S. J., Jr, Mudd S. The immunologically active cell wall peptide polymer of Staphylococcus aureus. Biochemistry. 1967 Feb;6(2):595–603. doi: 10.1021/bi00854a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff E., Silverman C. S., Adams N. J., Awkard W. S. Extracellular cell wall lytic enzyme from Staphylococcus aureus: purification and partial characterization. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):761–769. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.761-769.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff E., Silverman C. S. Lysis of Staphylococcus aureus cell walls by a soluble staphylococcal enzyme. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):99–106. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.99-106.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P., MOYLE J. Autolytic release and osmotic properties of protoplasts from Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Feb;16(1):184–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-1-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon N., Jeanloz R. W. A procedure for the preparation of gram-quantities of bacterial cell walls. Experientia. 1964 May 15;20(5):253–254. doi: 10.1007/BF02151786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H., Kashiba S., Amano T., Kotani S., Imanishi T. Purification and properties of a staphylolytic factor produced by a strain of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Biken J. 1967 Sep;10(3):109–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe I., Singer H. J., Wise E. M., Jr, Park J. T. Staphylococcus aureus H autolytic activity: general properties. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):14–19. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.14-19.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. S., Shockman G. D. A modification of the Park and Johnson reducing sugar determination suitable for the assay of insoluble materials: its application to bacterial cell walls. Anal Biochem. 1968 Feb;22(2):260–268. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90315-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J. Mechanism of autolysis of isolated cell walls of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):837–847. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.837-847.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heijenoort Y., Van Heijenoort J. Study of the N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase activity in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 10;15(2):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELSCH M., SALMON J. Quelques aspects de la staphylolyse. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1950 Nov;79(5):802–813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Hisatsune K. Bacteriolytic enzymes from Staphylococcus aureus. Purification of an endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(4):725–734. doi: 10.1042/bj1200725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


