Abstract
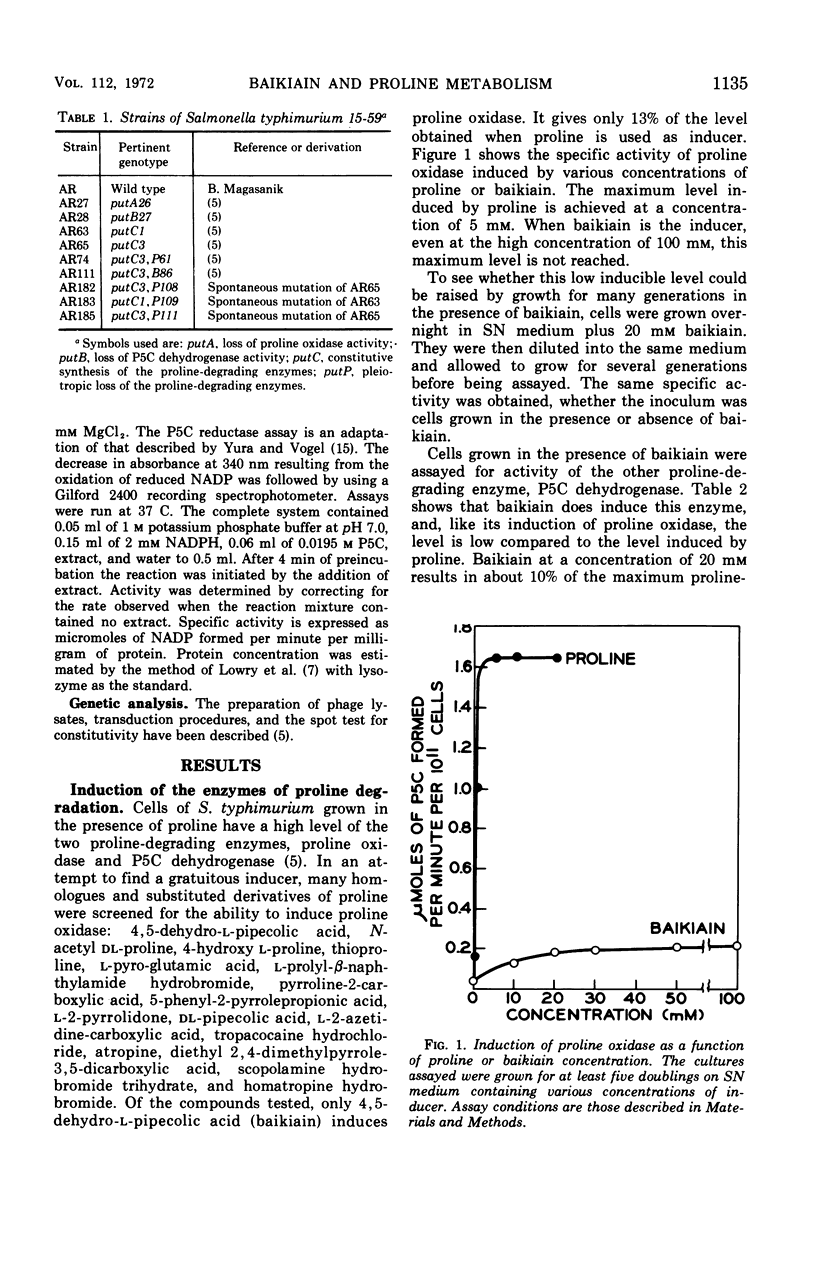
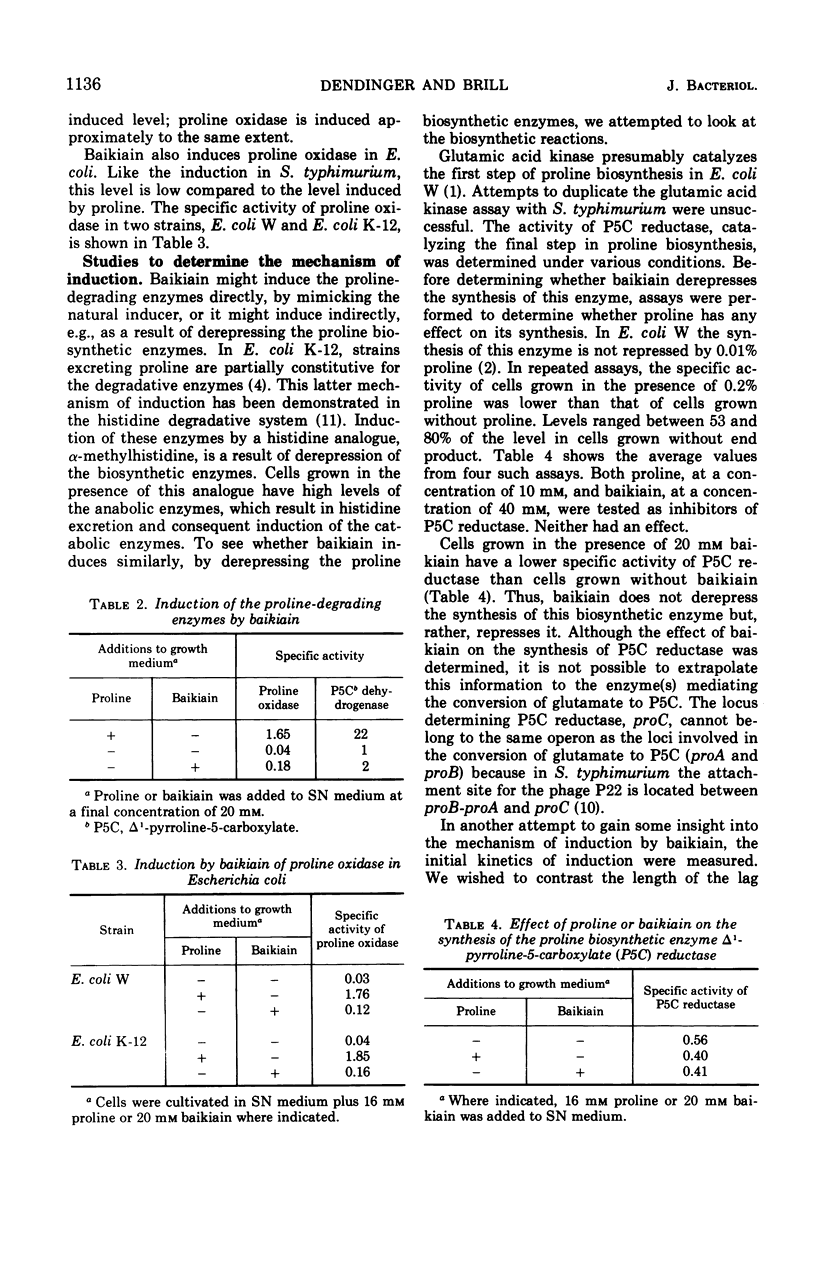
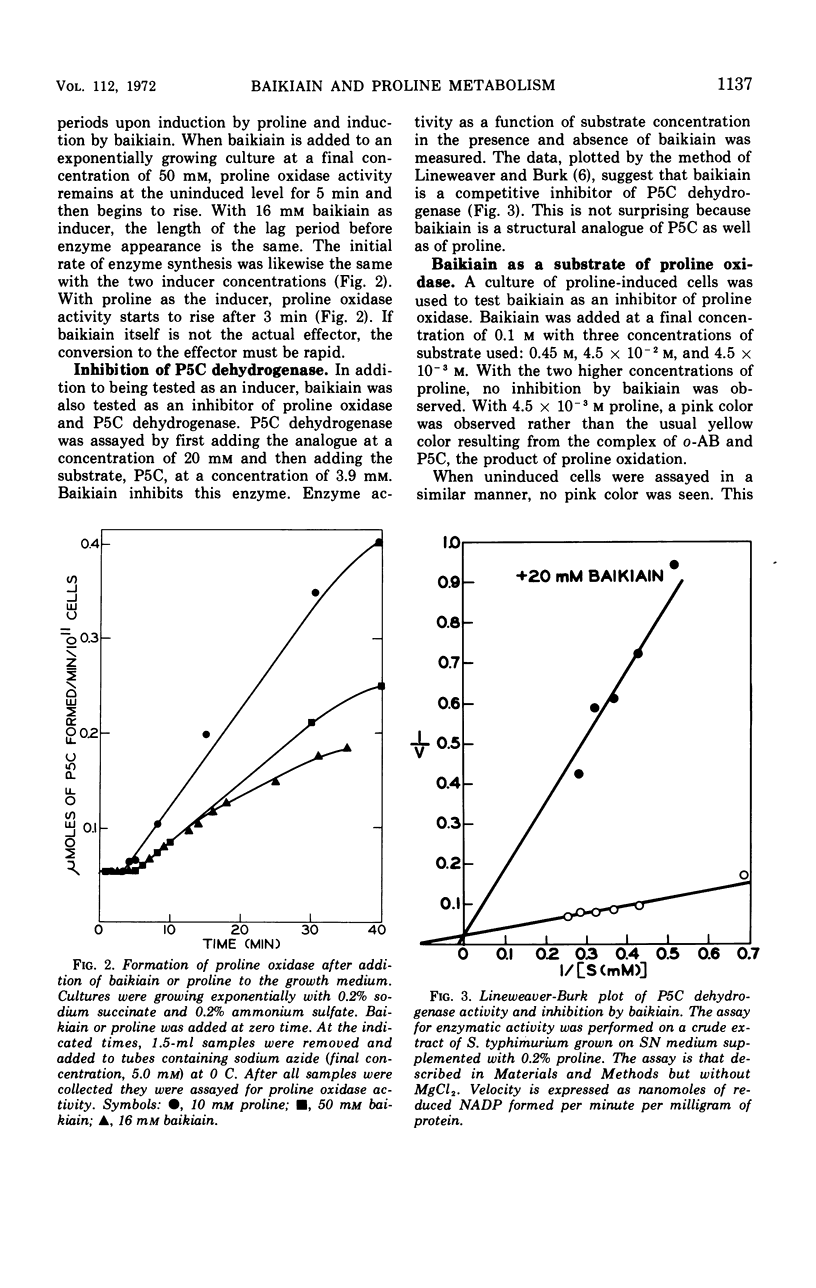
A proline analogue, 4,5-dehydro-l-pipecolic acid (baikiain) induces the formation in Salmonella typhimurium of the two enzymes catalyzing the degradation of proline, proline oxidase and Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid (P5C) dehydrogenase. The level of induction by 20 mm baikiain is about 10% of the maximum level induced by proline. Since the analogue is a substrate of proline oxidase the first enzyme of the proline catabolic pathway, the oxidation derivative rather than baikiain itself might be the actual effector. Baikiain is also an inducer of proline oxidase in Escherichia coli K-12 and E. coli W. An additional effect of this analogue on proline degradation in S. typhimurium is inhibition of P5C dehydrogenase. At a concentration of 5 × 10−4m, baikiain inhibits completely the growth of strains constitutive for proline oxidase. This inhibition, which can be overcome by proline, occurs in the presence or absence of P5C dehydrogenase activity. Three spontaneously occurring mutants resistant to baikiain were isolated from constitutive strains. All are pleiotropic-negative for the proline-degrading enzymes. The sites of these mutations are linked to the put region. Although the mechanism of toxicity has not been determined, baikiain provides a simple and direct selection for obtaining mutants unable to degrade proline. In addition, it allows selection for strains with an inducible rather than constitutive phenotype.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BASSO L. V., RAO D. R., RODWELL V. W. Metabolism of pipecolic acid in a Pseudomonas species. II. delta1-Piperideine-6-carboxylic acid and alpha-aminoadipic acid-delta-semial-dehyde. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jul;237:2239–2245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baich A., Pierson D. J. Control of proline synthesis in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 8;104(2):397–404. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90345-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baich A. Proline synthesis in Escherichia coli. A proline-inhibitable glutamic acid kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Dec 30;192(3):462–467. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90395-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condamine H. Sur la régulation de la production de proline chez E. Coli K 12. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1971 Feb;120(2):126–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dendinger S., Brill W. J. Regulation of proline degradation in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):144–152. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.144-152.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiss H. K., Brill W. J., Magasanik B. Genetic control of histidine degradation in Salmonella typhimurium, strain LT-2. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5382–5391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLESINGER S., MAGASANIK B. EFFECT OF ALPHA-METHYLHISTIDINE ON THE CONTROL OF HISTIDINE SYNTHESIS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Sep;9:670–682. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80174-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRECKER H. J. The interconversion of glutamic acid and proline. II. The preparation and properties of delta 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jul;235:2045–2050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E. Current linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Jun;34(2):176–193. doi: 10.1128/br.34.2.176-193.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbarger H. E. Metabolite analogs as genetic and biochemical probes. Adv Genet. 1971;16:119–140. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60356-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YURA T., VOGEL H. J. On the biosynthesis of proline in Neurospora crassa: enzymic reduction of delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Aug;17(4):582–582. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


