Abstract
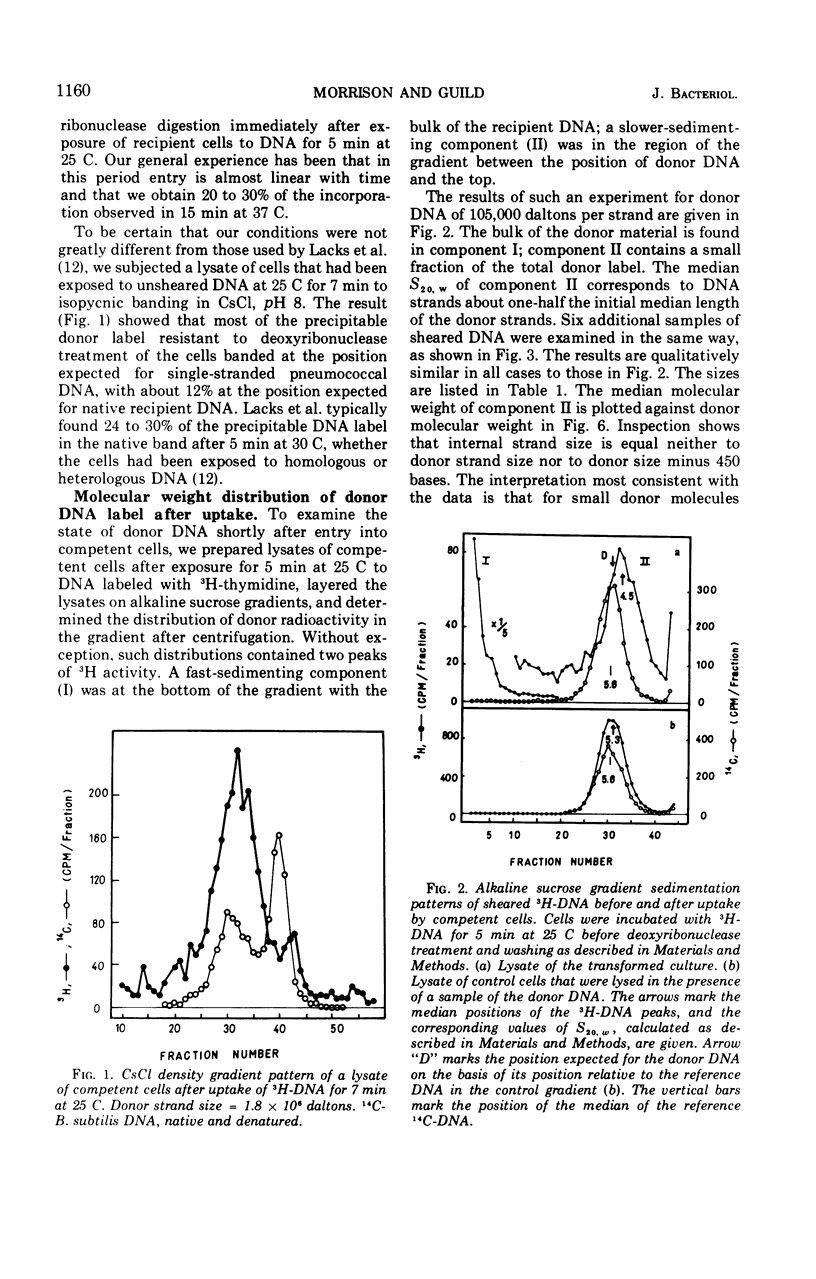
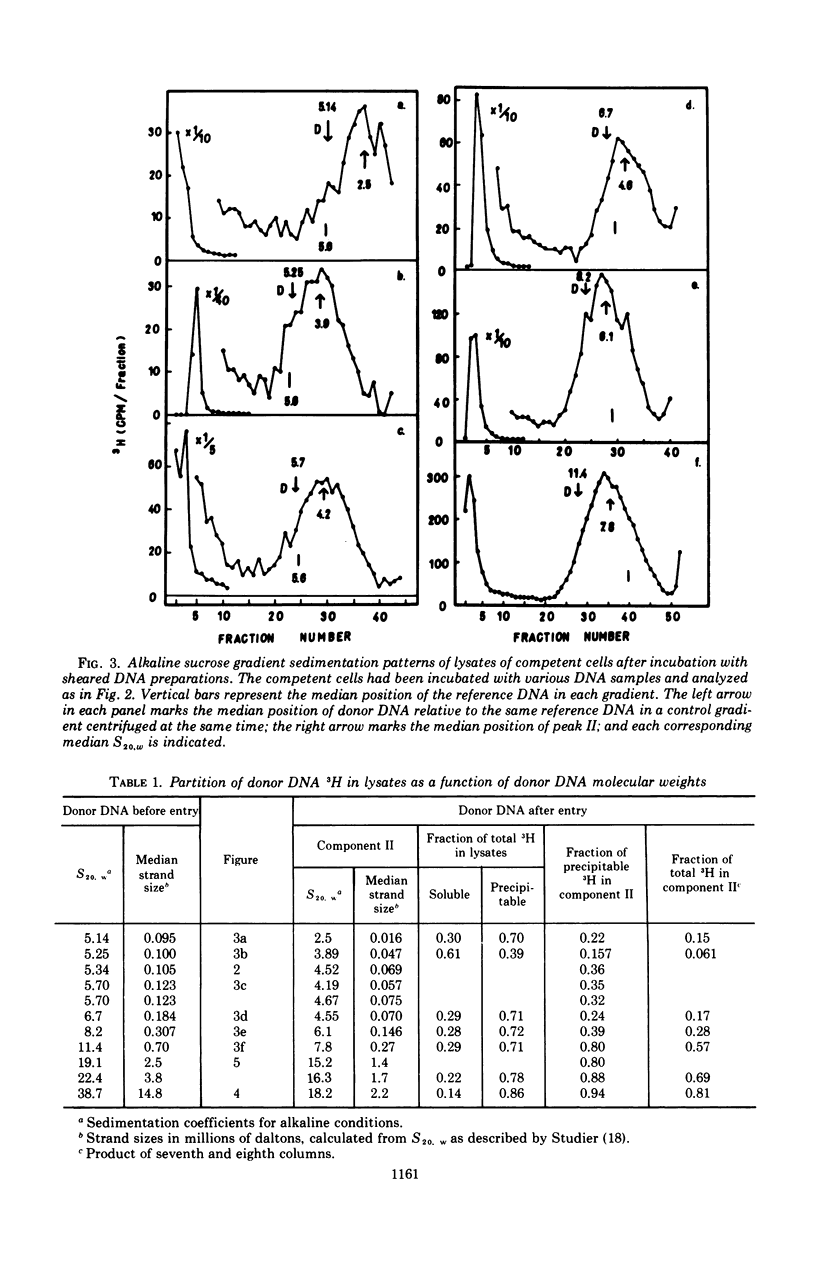
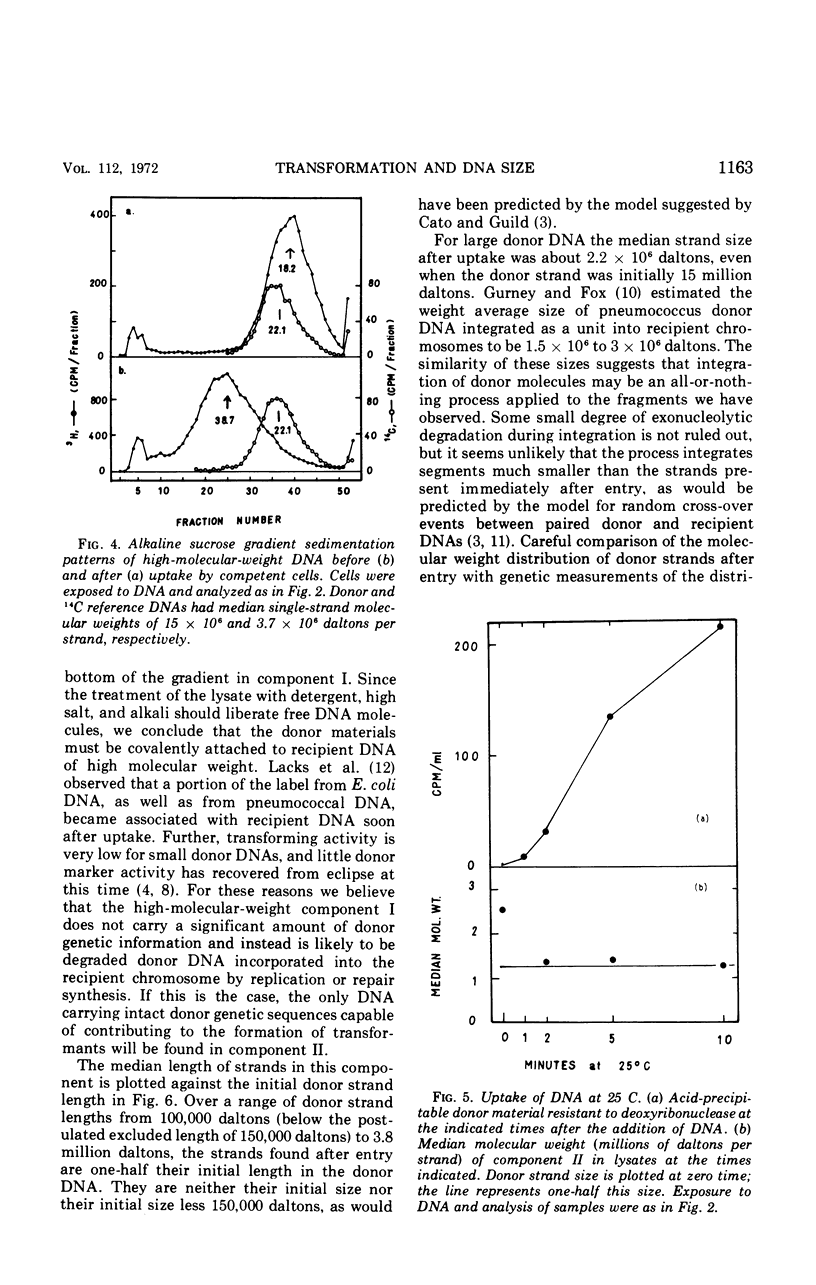
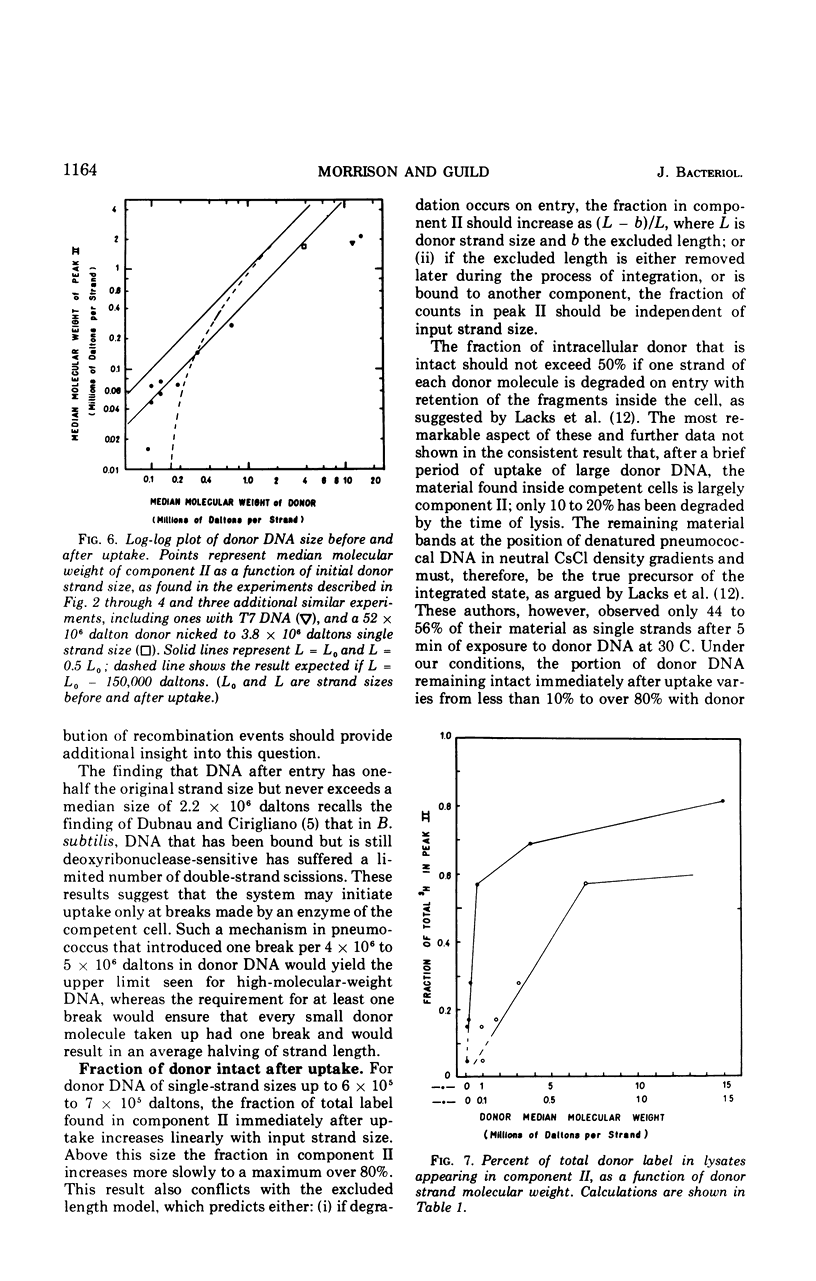
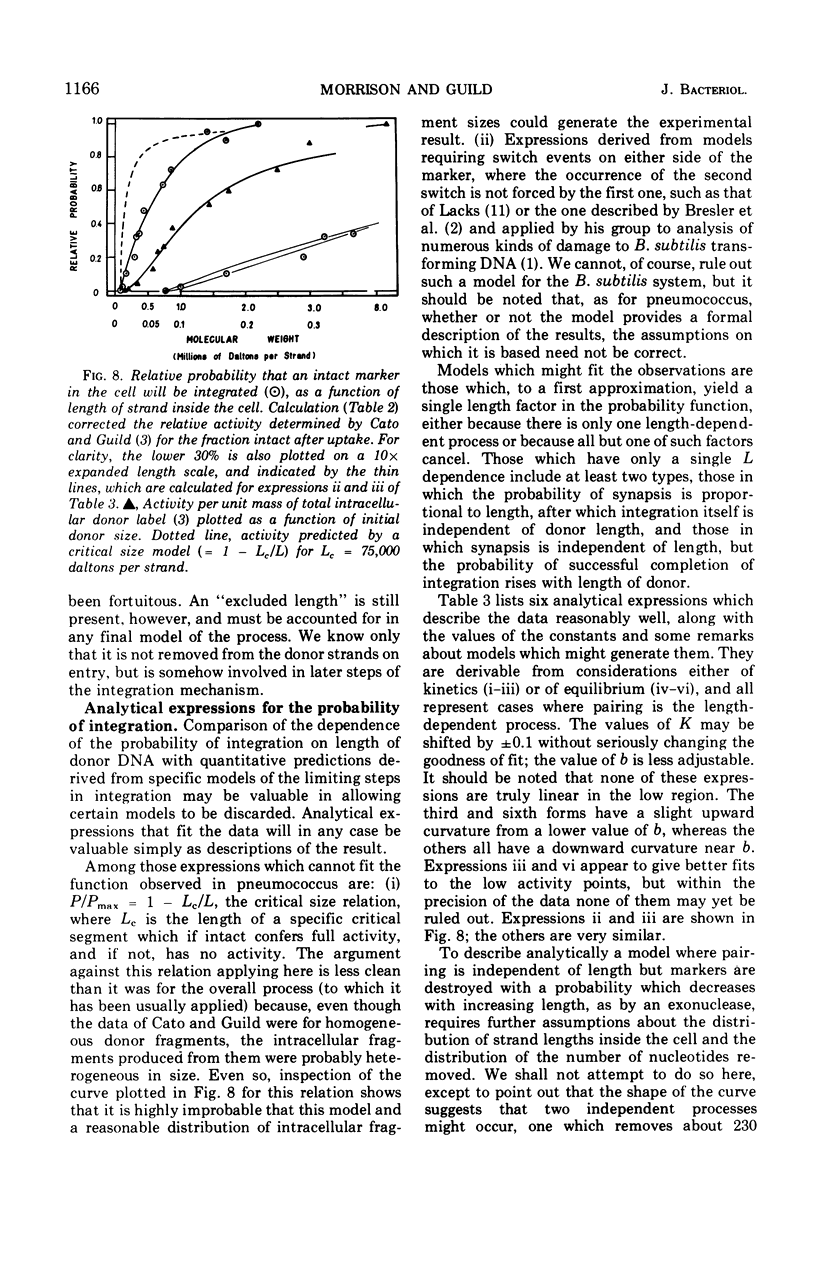
The fate of label introduced as donor deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) into competent cells of Diplococcus pneumoniae was determined immediately after entry at 25 C, as a function of the size of the donor DNA. Part of the label is found to be acid soluble, part has been incorporated into chromosomal DNA, apparently through reincorporation of degraded donor DNA, and part is found in single strands of length smaller than that of the input donor DNA strands. The last fraction apparently constitutes the precursor for integration of intact donor genetic markers and is referred to as the intact fraction. For large donor DNA the intact fraction contains over 80% of the total intracellular label, but the median strand length has been reduced to 2.2 × 106 daltons. For small donor molecules (1 × 105 to 6 × 105 daltons per strand) the fraction intact increases with donor size from 10 to 50% of the total intracellular label, and the median strand length of this fraction is half that of the donor strands. By combining these results with earlier data on the size dependence of the yield of transformants per unit of total intracellular donor label, we have calculated the probability that a marker in the intact fraction will be integrated, as a function of the length of the donor strand after entry. This probability has a linear dependence on strand length for activities below 40% of maximum, and extrapolates to zero activity at 77,000 daltons per strand.
Full text
PDF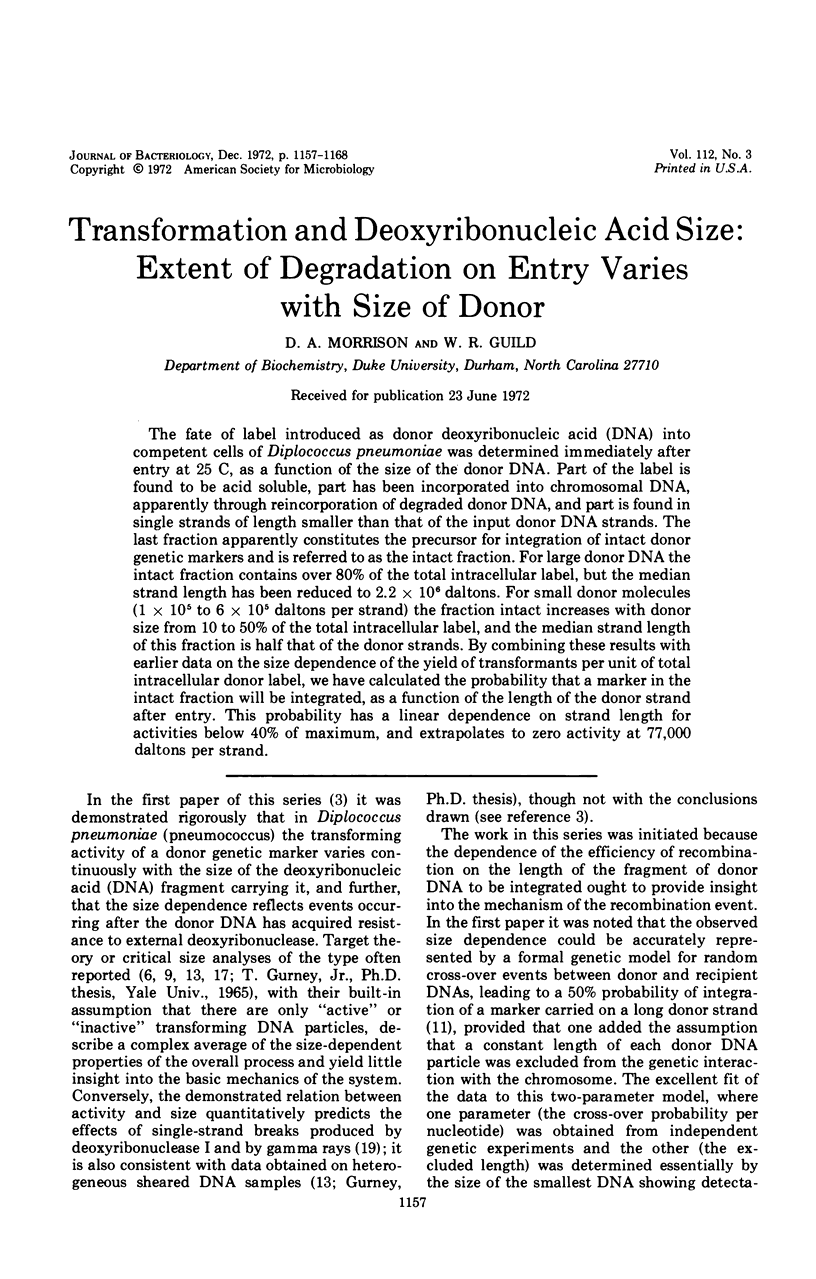






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bresler S. E., Kalinin V. L., Perumov D. A. Inactivation and mutagenesis on isolated DNA. I. Theory of inactivation of transforming DNA. Mutat Res. 1967 Jul-Aug;4(4):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(67)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A., Jr, Guild W. R. Transformation and DNA size. I. Activity of fragments of defined size and a fit to a random double cross-over model. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):157–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. J., Guild W. R. Events occurring near the time of synapsis during transformation in Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):266–275. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.266-275.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Cirigliano C. Fate of transforming DNA following uptake by competent Bacillus subtilis. Formation and properties of products isolated from transformed cells which are derived entirely from donor DNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 28;64(1):9–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90318-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX M. S. Biological effects of the decay of incorporated radioactive phosphorus in transforming deoxyribonucleate. J Mol Biol. 1963 Jan;6:85–94. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUILD W. R., DEFILIPPES F. M. Ionizing radiation and ultrasonic evidence for a minimum unit of transforming principle DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Nov;26(2):241–251. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghei O. K., Lacks S. A. Recovery of donor deoxyribonucleic acid marker activity from eclipse in pneumococcal transformation. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):816–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.816-829.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney T., Jr, Fox M. S. Physical and genetic hybrids formed in bacterial transformation. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 28;32(1):83–100. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. Theoretical relationship between probability of marker integration and length of donor DNA in pneumococcal transformation. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):179–180. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90081-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M., Marmur J., Ephrussi-Taylor H., Doty P. THE DEPENDENCE OF PNEUMOCOCCAL TRANSFORMATION ON THE MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF DEOXYRIBOSE NUCLEIC ACID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Feb;44(2):144–152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.2.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Early intermediate state of transforming deoxyribonucleic acid during uptake by Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.38-44.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. D., Guild W. R. Number of transformable units per cell in Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1033–1035. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1033-1035.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON C. C., LEHMAN I. R., KORNBERG A. A DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID PHOSPHATASE-EXONUCLEASE FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI. II. CHARACTERIZATION OF THE EXONUCLEASE ACTIVITY. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal P. N., Fox M. S. Effects of disintegration of incorporated 3H and 32P on the physical and biological properties of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 28;54(3):441–463. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90120-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUDIER F. W. SEDIMENTATION STUDIES OF THE SIZE AND SHAPE OF DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:373–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsett G. O., Hutchinson F. Effects on bacterial transformation of single-strand breaks in DNA produced by deoxyribonuclease I and gamma rays. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 29;238(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


