Abstract
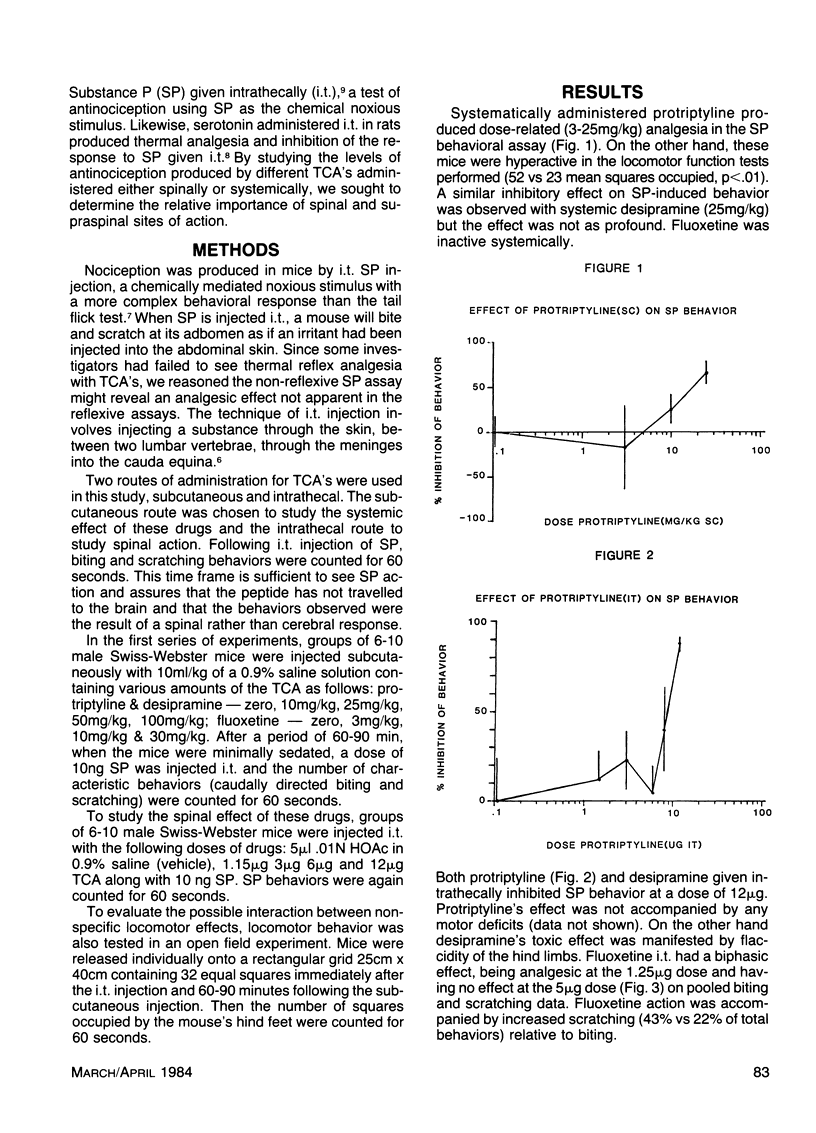
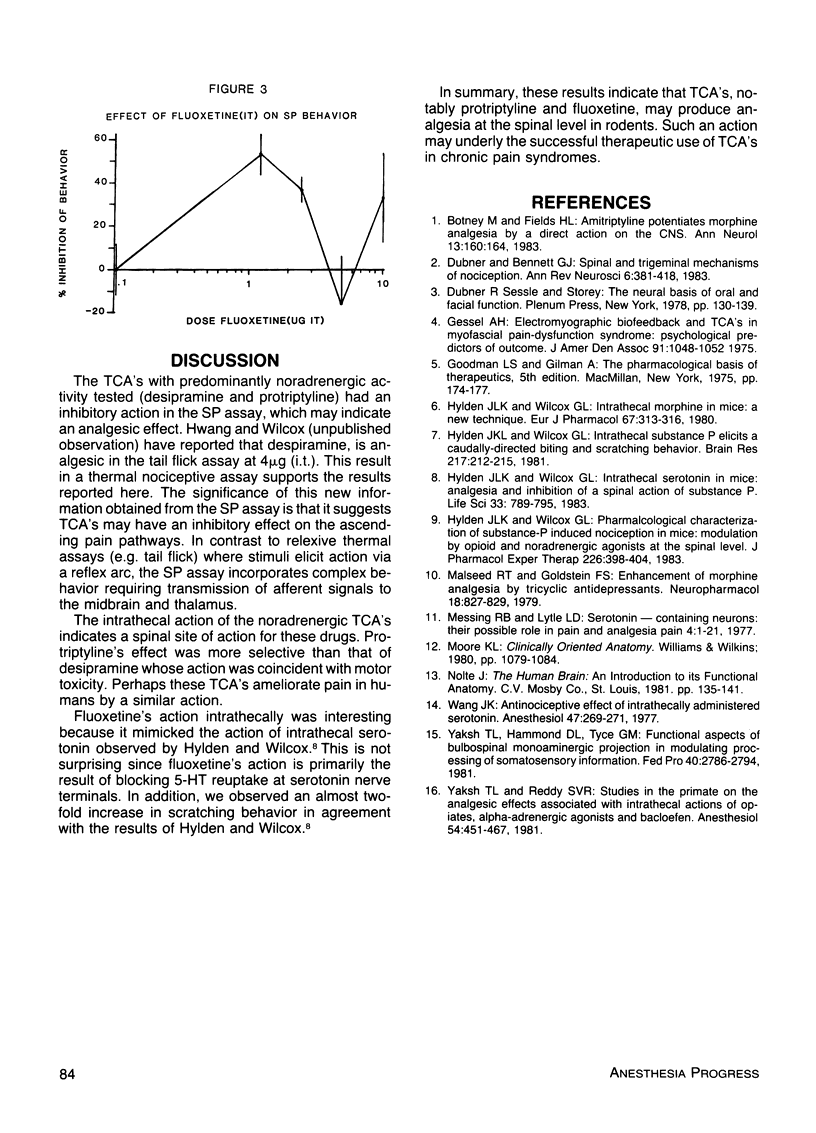
The anti-nociceptive effects of three tricyclic anti-depressants (desipramine, protriptyline, fluoxetine) were evaluated in mice following intrathecal administration. Nociceptive behavior was produced by intrathecal administration of Substance P and measured for 60 seconds following subcutaneous and intrathecal administration of vehicle and increasing doses of the drugs being tested. Systemically administered protriptyline produced dose related antinociception in this paradigm. A similar effect was seen following systemic desipramine; while fluoxetine was inactive systemically. Both protriptyline and desipramine given intrathecally were antinociceptive while fluoxetine had a biphasic effect, being analgesic only at low doses. These results indicate that tricyclic antidepressants may produce analgesia at the spinal level in rodents. This action may be related to the therapeutic success of tricyclic antidepressants in chronic pain syndromes.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botney M., Fields H. L. Amitriptyline potentiates morphine analgesia by a direct action on the central nervous system. Ann Neurol. 1983 Feb;13(2):160–164. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubner R., Bennett G. J. Spinal and trigeminal mechanisms of nociception. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1983;6:381–418. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.06.030183.002121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessel A. H. Electromygraphic biofeedback and tricyclic antidepressants in myofascial pain-dysfunction syndrome: psychological predictors of outcome. J Am Dent Assoc. 1975 Nov;91(5):1048–1052. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1975.0512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylden J. L., Wilcox G. L. Intrathecal morphine in mice: a new technique. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Oct 17;67(2-3):313–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90515-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylden J. L., Wilcox G. L. Intrathecal serotonin in mice: analgesia and inhibition of a spinal action of substance P. Life Sci. 1983 Aug 22;33(8):789–795. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90785-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylden J. L., Wilcox G. L. Intrathecal substance P elicits a caudally-directed biting and scratching behavior in mice. Brain Res. 1981 Jul 27;217(1):212–215. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90203-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylden J. L., Wilcox G. L. Pharmacological characterization of substance P-induced nociception in mice: modulation by opioid and noradrenergic agonists at the spinal level. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Aug;226(2):398–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malseed R. T., Goldstein F. J. Enhancement of morphine analgesia by tricyclic antidepressants. Neuropharmacology. 1979 Oct;18(10):827–829. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(79)90028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing R. B., Lytle L. D. Serotonin-containing neurons: their possible role in pain and analgesia. Pain. 1977 Oct;4(1):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(77)90083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. K. Antinociceptive effect of intrathecally administered serotonin. Anesthesiology. 1977 Sep;47(3):269–271. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197709000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Hammond D. L., Tyce G. M. Functional aspects of bulbospinal monoaminergic projections in modulating processing of somatosensory information. Fed Proc. 1981 Nov;40(13):2786–2794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Reddy S. V. Studies in the primate on the analgetic effects associated with intrathecal actions of opiates, alpha-adrenergic agonists and baclofen. Anesthesiology. 1981 Jun;54(6):451–467. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198106000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


