Abstract
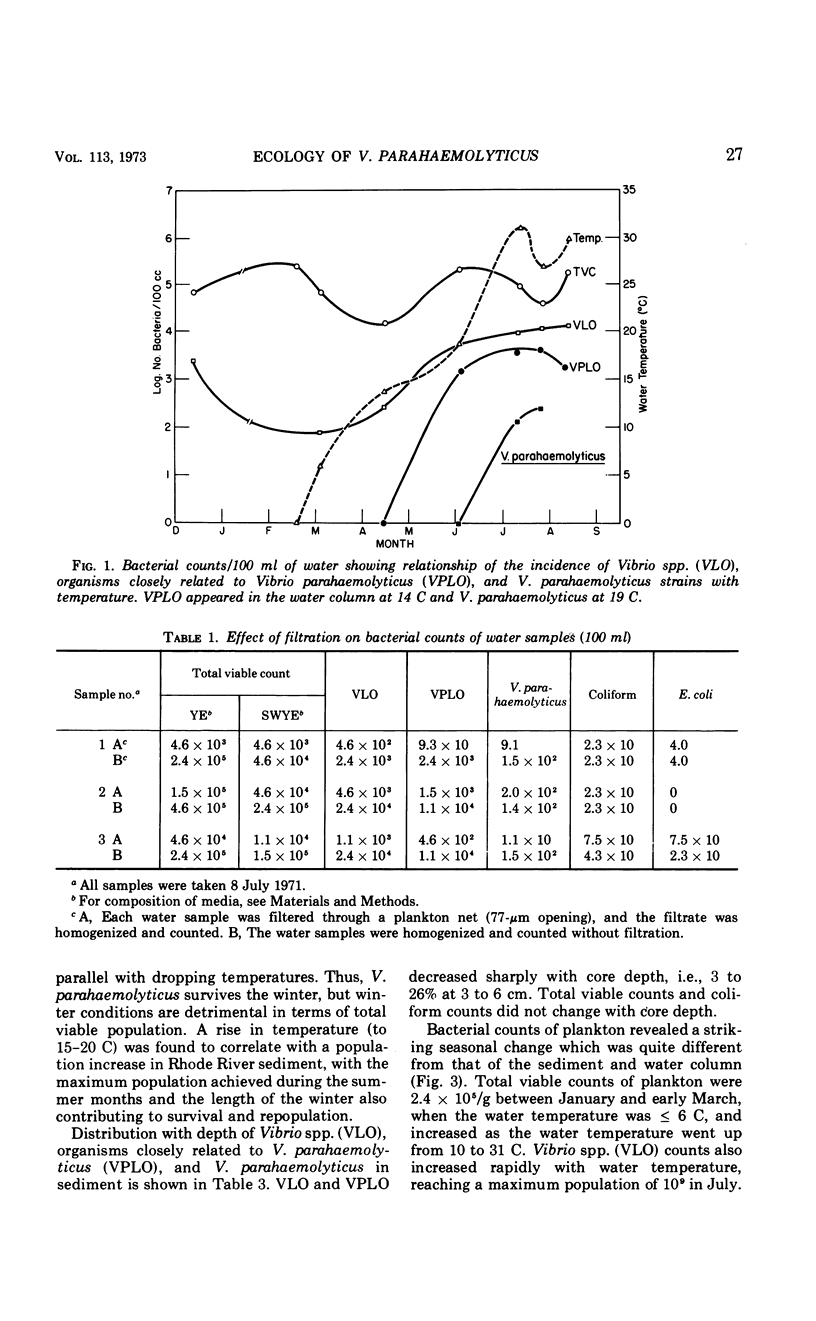
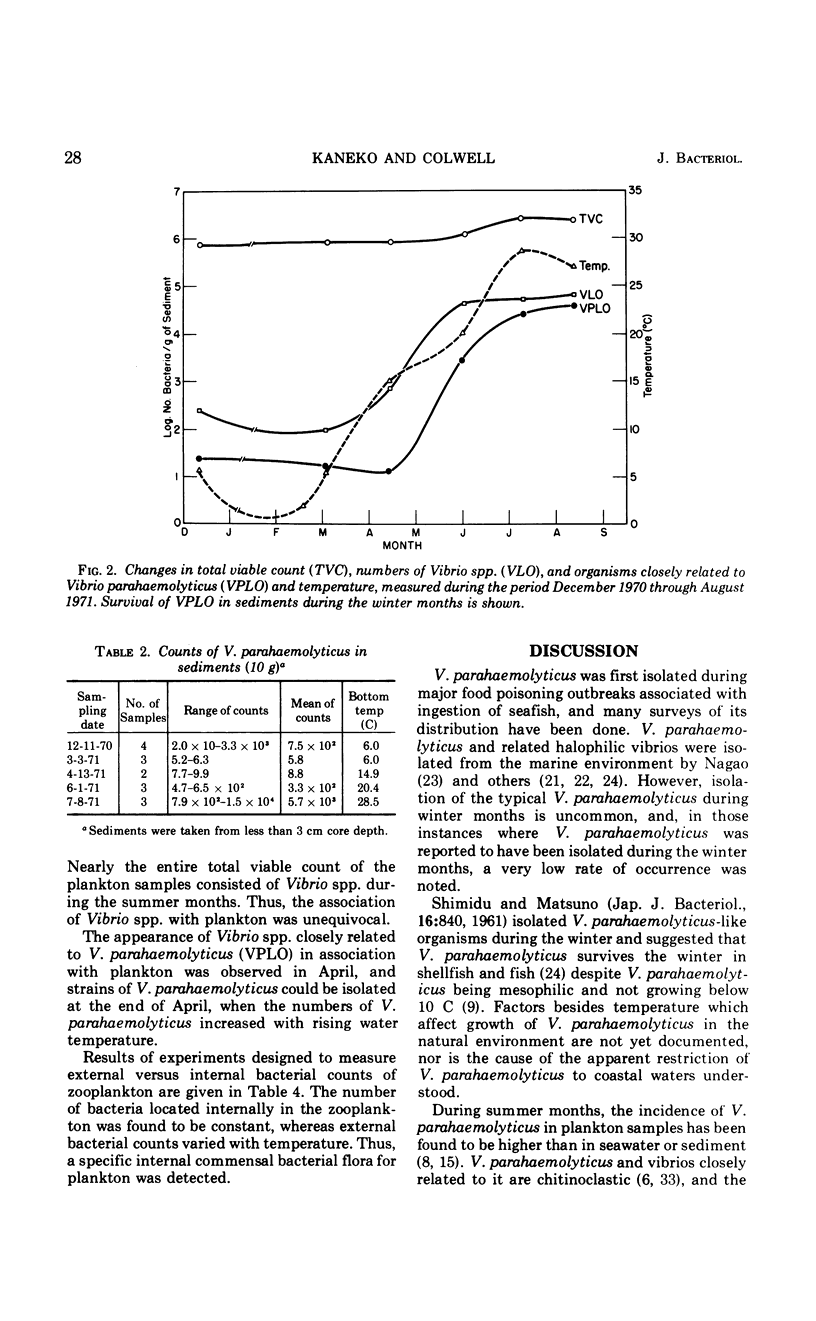
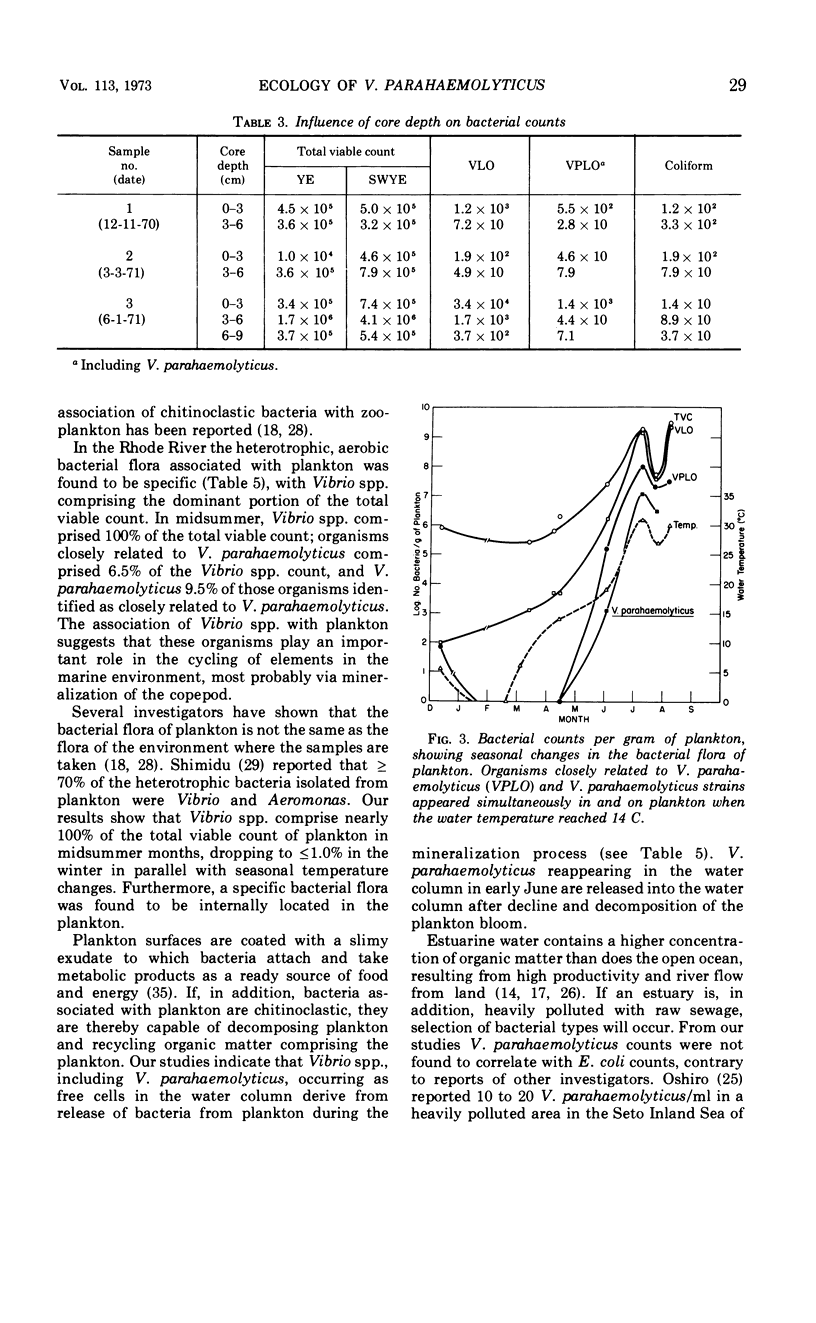
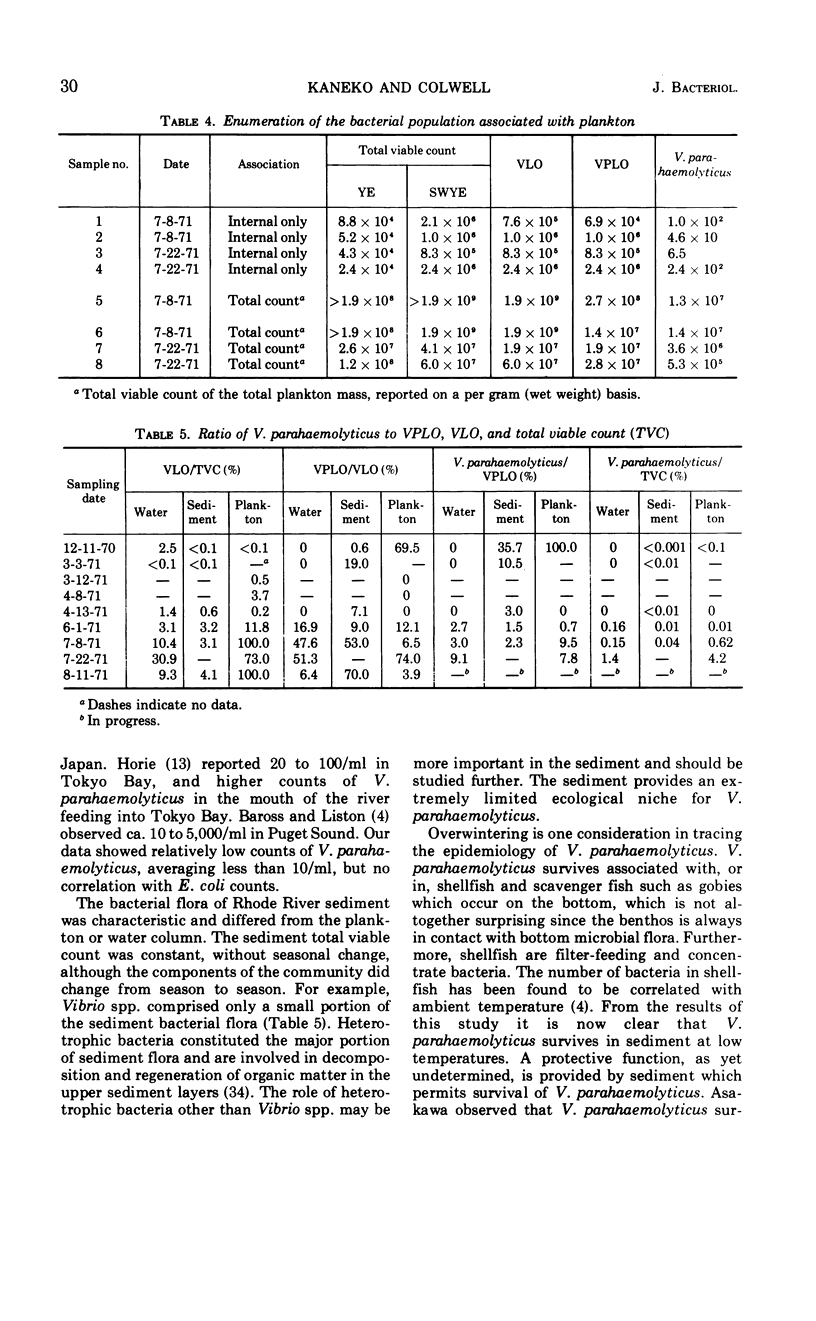
A study of the ecology of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and related vibrios in the Rhode River area of Chesapeake Bay was carried out over the period December 1970 through August 1971. The incidence of V. parahaemolyticus and related vibrios was found to be correlated with water temperature. The vibrios could not be detected in the water column during the winter months, although they were present in sediment. From late spring to early summer, when water temperatures were 14 ± 1 C, vibrios over-wintering in sediment were released from the bottom communities and attached to zooplankton, proliferating as the temperature rose. The number of vibrios in and on plankton was reflected in the water column bacterial population densities at water temperatures of ca. 19 C. Thus, temperature of the water column in the range of 14 to 19 C was found to be critical in the annual cycle of the vibrios. Interaction between sediment, water, and zooplankton was found to be essential in the natural estuarine ecosystem. Bacterial counts of zooplankton were found to be temperature dependent. The bacterial population associated with zooplankton was found to be predominantly on external surfaces and was specific, differing from that of the sediment. Vibrio spp. and related organisms comprised the total bacterial population associated with zooplankton in summer months. The ecological role of Vibrio spp., including V. parahaemolyticus, was found to be significant, with respect to their property of chitin digestion and in relation to the population dynamics of zooplankton in Chesapeake Bay.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baross J., Liston J. Isolation of vibrio parahaemolyticus from the Northwest Pacific. Nature. 1968 Mar 30;217(5135):1263–1264. doi: 10.1038/2171263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baross J., Liston J. Occurrence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and related hemolytic vibrios in marine environments of Washington State. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Aug;20(2):179–186. doi: 10.1128/am.20.2.179-186.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartley C. H., Slanetz L. W. Occurrence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in estuarine waters and oysters of New Hampshire. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):965–966. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.965-966.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Baumann L., Mandel M. Taxonomy of marine bacteria: the genus Beneckea. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):268–294. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.268-294.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz G. E., Colwell R. R., Lovelace E. Vibrio parahaemolyticus from the blue crab Callinectes sapidus in Chesapeake Bay. Science. 1969 Jun 13;164(3885):1286–1287. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3885.1286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matches J. R., Liston J., Daneault L. P. Survival of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in fish homogenate during storage at low temperatures. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):951–952. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.951-952.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simidu U., Ashino K., Kaneko E. Bacterial flora of phyto- and zoo-plankton in the inshore water of Japan. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Sep;17(9):1157–1160. doi: 10.1139/m71-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zobell C. E. The Effect of Solid Surfaces upon Bacterial Activity. J Bacteriol. 1943 Jul;46(1):39–56. doi: 10.1128/jb.46.1.39-56.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


