Abstract
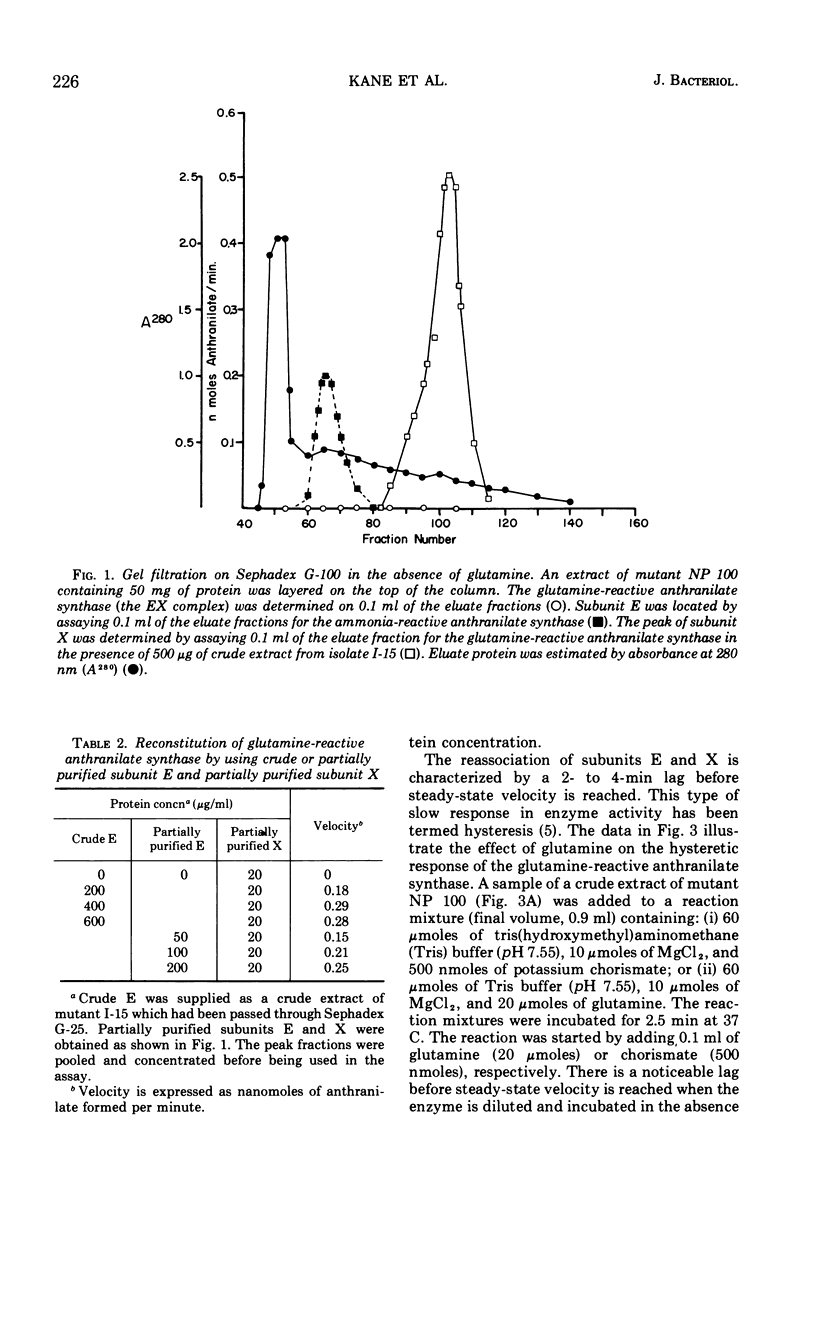
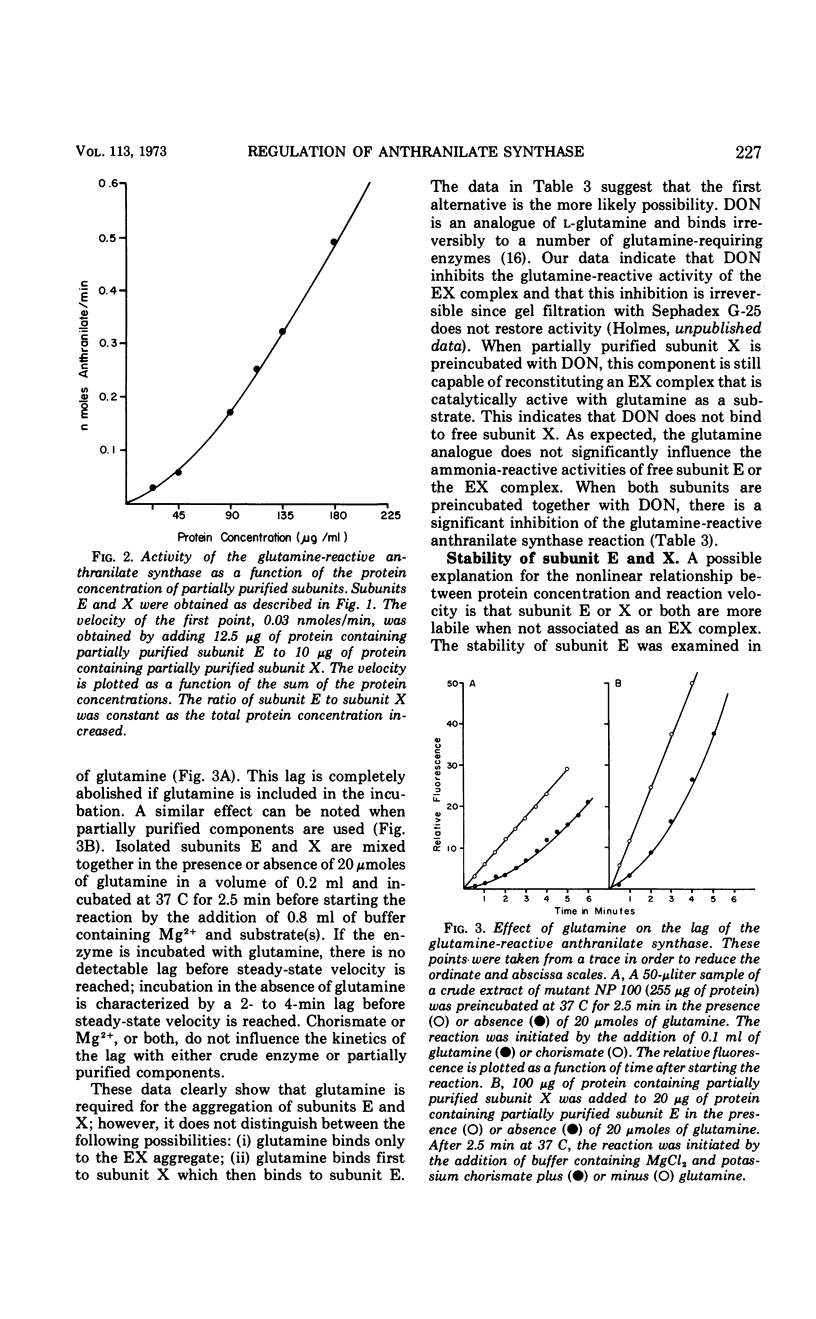
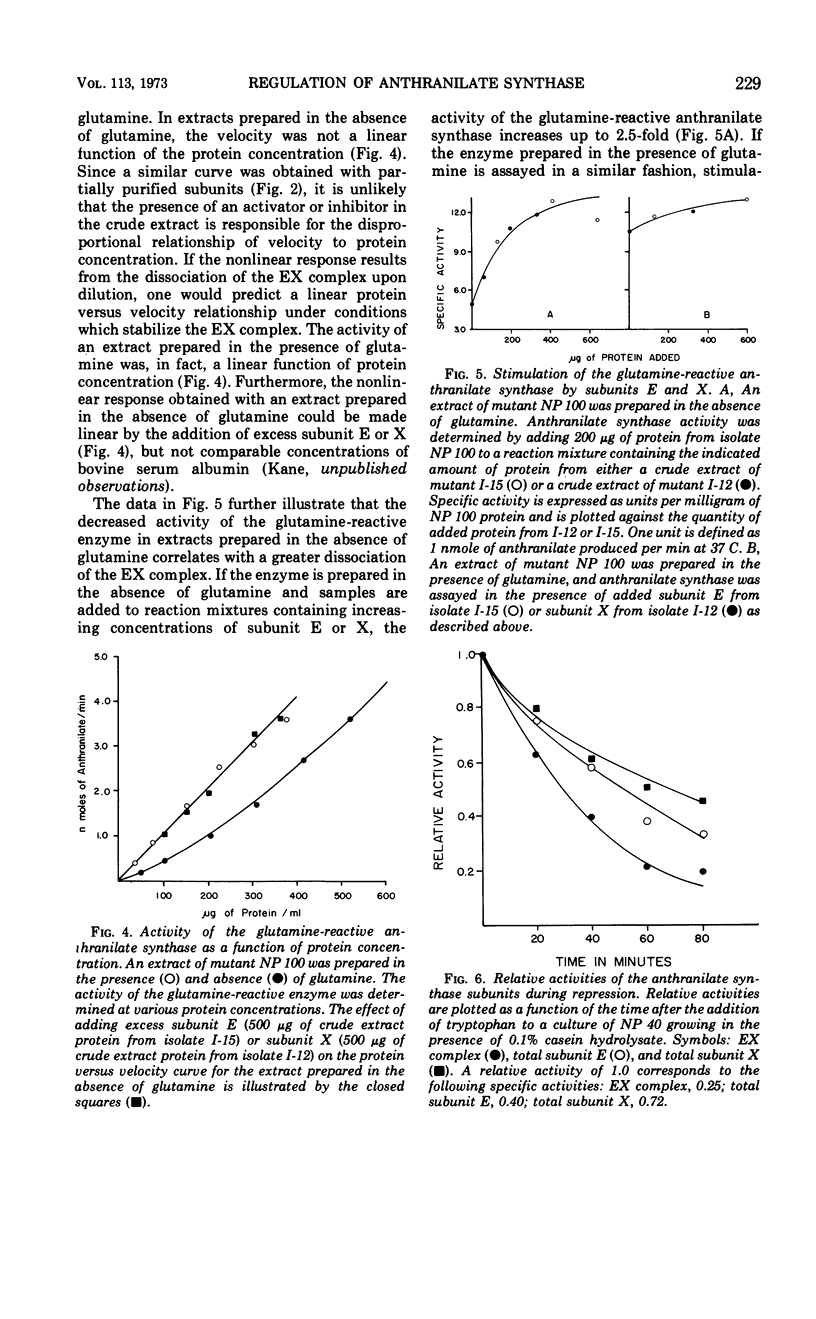
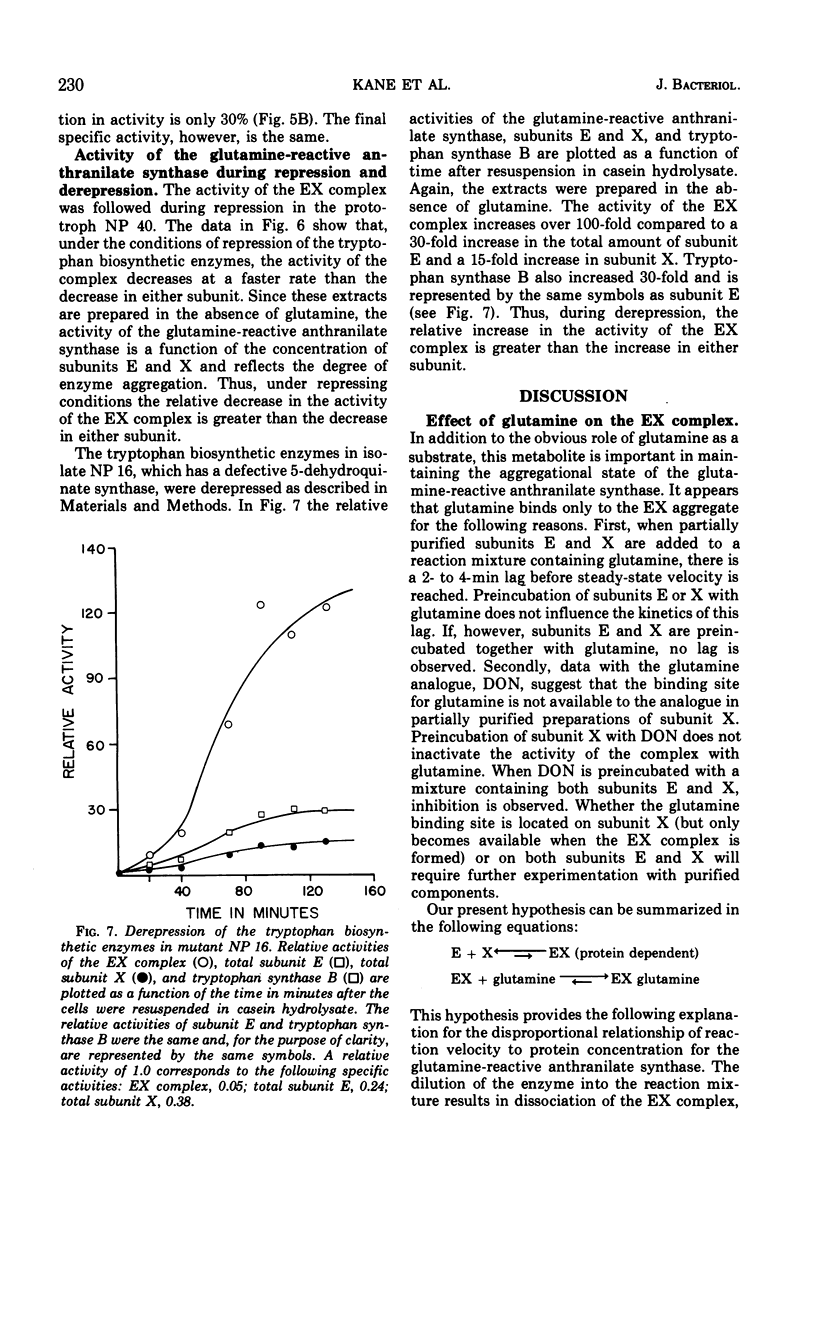
The anthranilate synthase aggregate from Bacillus subtilis is composed of two nonidentical subunits, denoted E and X, which are readily associated or dissociated. A complex of subunit E and X can utilize glutamine or ammonia as substrates in the formation of anthranilate. Partially purified subunit E is capable of using only ammonia as the amide donor in the anthranilate synthase reaction. The stability of the EX complex is strongly influenced by glutamine and by the concentrations of the subunits. Glutamine stabilizes the aggregate as a molecular species in which the velocity of the glutamine-reactive anthranilate synthase is a linear function of protein concentration. In the absence of glutamine the aggregate is readily dissociated following dilution of the extract; that is, velocity concaves upward as a function of increasing protein concentration. Reassociation of the EX complex is characterized by a velocity lag (or hysteretic response) before steady-state velocity for the glutamine-reactive anthranilate synthase is reached. We propose that association and dissociation of the anthranilate synthase aggregate may be physiologically significant and provide a control mechanism whereby repression or derepression causes disproportionate losses or gains in activity by virtue of protein-protein interactions between subunits E and X.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Catena A., DeMoss R. D. Physiological and kinetic studies with anthranilate synthetase of Bacillus alvei. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):476–482. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.476-482.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Ginsburg A., Yeh J., Shelton E., Stadtman E. R. Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase. Purification and physical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 25;245(20):5195–5205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Stadtman E. R. Some kinetic properties of Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 25;245(20):5206–5213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieden C. Kinetic aspects of regulation of metabolic processes. The hysteretic enzyme concept. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5788–5799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieden C. Protein-protein interaction and enzymatic activity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:653–696. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.003253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch S. O., Roth C. W., Crawford I. P., Nester E. W. Control of tryptophan biosynthesis by the methyltryptophan resistance gene in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):38–45. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.38-45.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hütter R., DeMoss J. A. Organization of the tryptophan pathway: a phylogenetic study of the fungi. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1896–1907. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1896-1907.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. A. A biochemical basis for apparent abortive transformation in Bacillus subtilis. Genetics. 1968 Dec;60(4):707–717. doi: 10.1093/genetics/60.4.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. F., Holmes W. M., Jensen R. A. Metabolic interlock. The dual function of a folate pathway gene as an extra-operonic gene of tryptophan biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 10;247(5):1587–1596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. F., Jensen R. A. Metabolic interlock. The influence of histidine on tryptophan biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 10;245(9):2384–2390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. F., Jensen R. A. The molecular aggregation of anthranilate synthase in Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Oct 23;41(2):328–333. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90507-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. F., Stenmark S. L., Calhoun D. H., Jensen R. A. Metabolic interlock. The role of the subordinate type of enzyme in the regulation of a complex pathway. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4308–4316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nester E W, Schafer M, Lederberg J. Gene Linkage in DNA Transfer: A Cluster of Genes Concerned with Aromatic Biosynthesis in Bacillus Subtilis. Genetics. 1963 Apr;48(4):529–551. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.4.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queener S. F., Gunsalus I. C. Anthranilate synthase enzyme system and complementation in Pseudomonas species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1225–1232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebello J. L., Strauss N. Regulation of synthesis of glutamine synthase in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):683–688. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.683-688.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


