Abstract
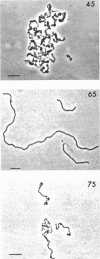
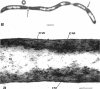
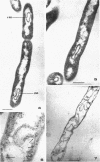
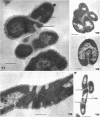
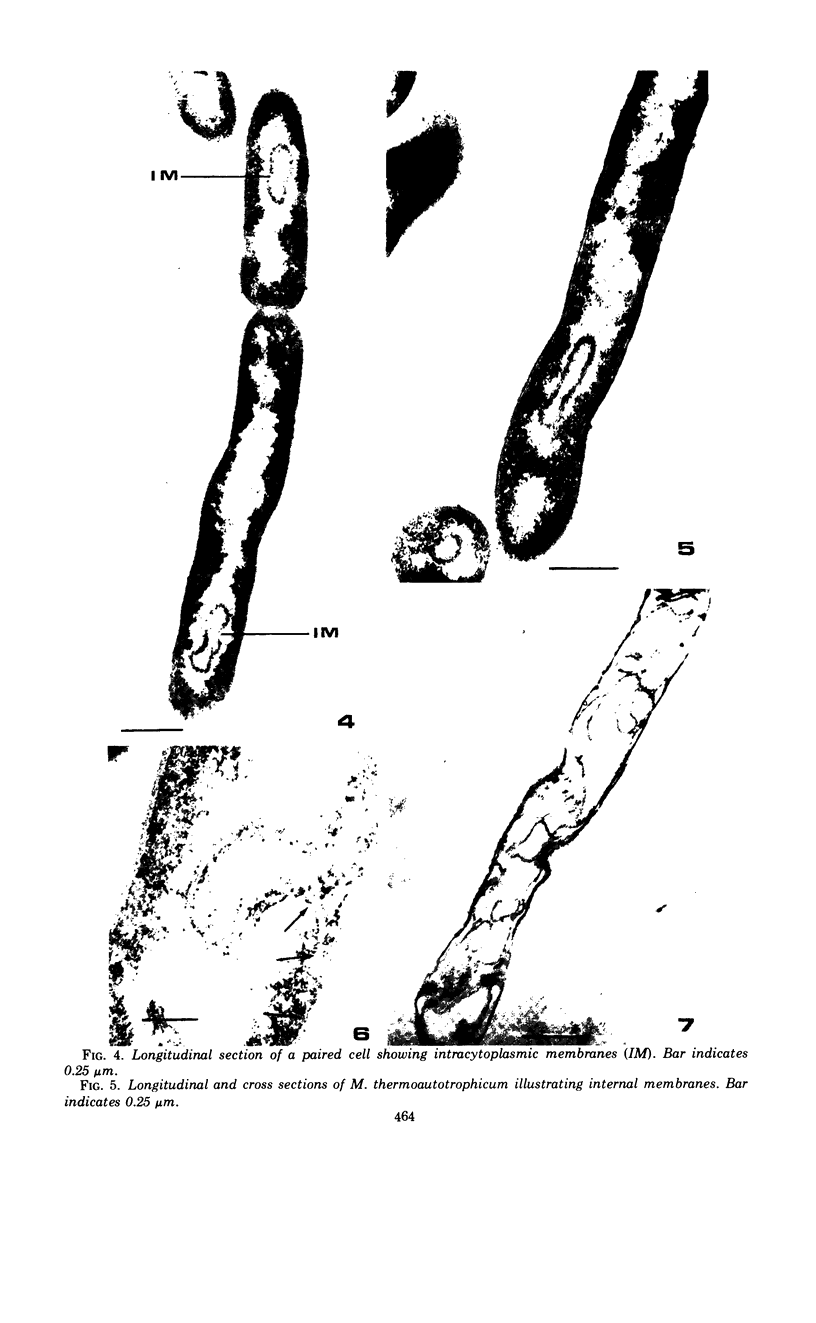
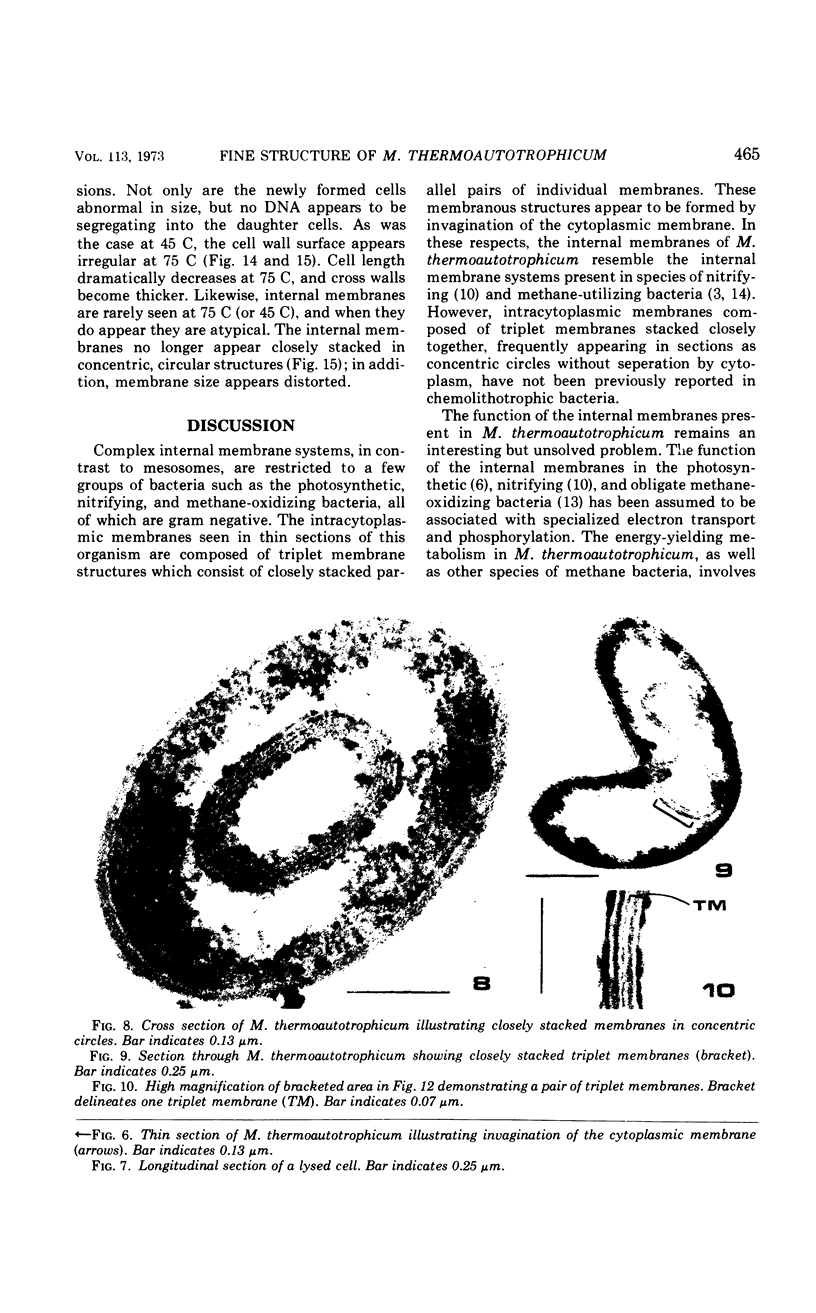
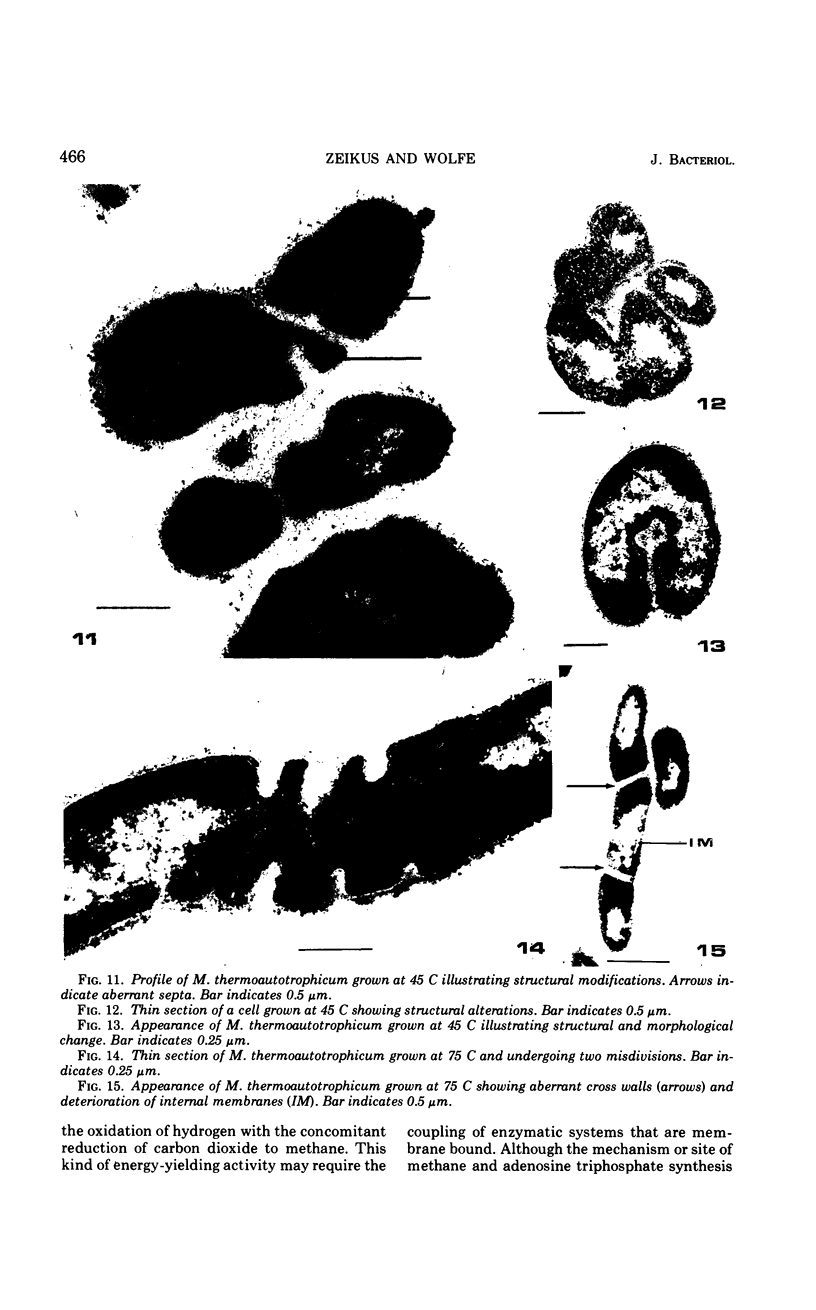
The fine structure of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum which was grown at the optimal temperature, 65 C, as well as at the temperature extremes for growth is described. The most distinguishing feature of this organism is the presence of intracytoplasmic membranes. The internal membrane system consists of triplet membranes which are stacked closely together, frequently appearing as concentric circles without separation by cytoplasm. Aside from this feature, M. thermoautotrophicum proliferates as irregularly curved rods at 65 C and has a fine structure similar to most other gram-positive bacteria. Both low (45 C) and high (75 C) growth temperatures induce structural modifications. These structural changes include rod to spheroidal morphological changes, cell wall abberations, distortion of division septa, misdivisions, and internal membrane deterioration.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brock T. D. Life at high temperatures. Evolutionary, ecological, and biochemical significance of organisms living in hot springs is discussed. Science. 1967 Nov;158(3804):1012–1019. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3804.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. M., Popkin T. J., Boylan R. J., Mendelson N. H. Ultrastructure of a temperature-sensitive rod- mutant of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):793–810. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.793-810.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies S. L., Whittenbury R. Fine structure of methane and other hydrocarbon-utilizing bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 May;61(2):227–232. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-2-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIESBRECHT P., DREWS G. [Electron microscope studies on the development of "chromatophores" by Rhodospirillum molischianum Giesberger]. Arch Mikrobiol. 1962;43:152–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLAUERT A. M., BRIEGER E. M., ALLEN J. M. The fine structure of vegetative cells of Bacillus subtilis. Exp Cell Res. 1961 Jan;22:73–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLT S. C., MARR A. G. LOCATION OF CHLOROPHYLL IN RHODOSPIRILLUM RUBRUM. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1402–1412. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1402-1412.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langenberg K. F., Bryant M. P., Wolfe R. S. Hydrogen-oxidizing methane bacteria. II. Electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1124–1129. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1124-1129.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. G., WATSON S. W. STRUCTURE OF NITROSOCYSTIS OCEANUS AND COMPARISON WITH NITROSOMONAS AND NITROBACTER. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1594–1609. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1594-1609.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Wolfe R. S. Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicus sp. n., an anaerobic, autotrophic, extreme thermophile. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):707–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.707-713.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhilina T. N. Tonkoe stroenie metanosartsiny. Mikrobiologiia. 1971 Jul-Aug;40(4):674–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]