Abstract
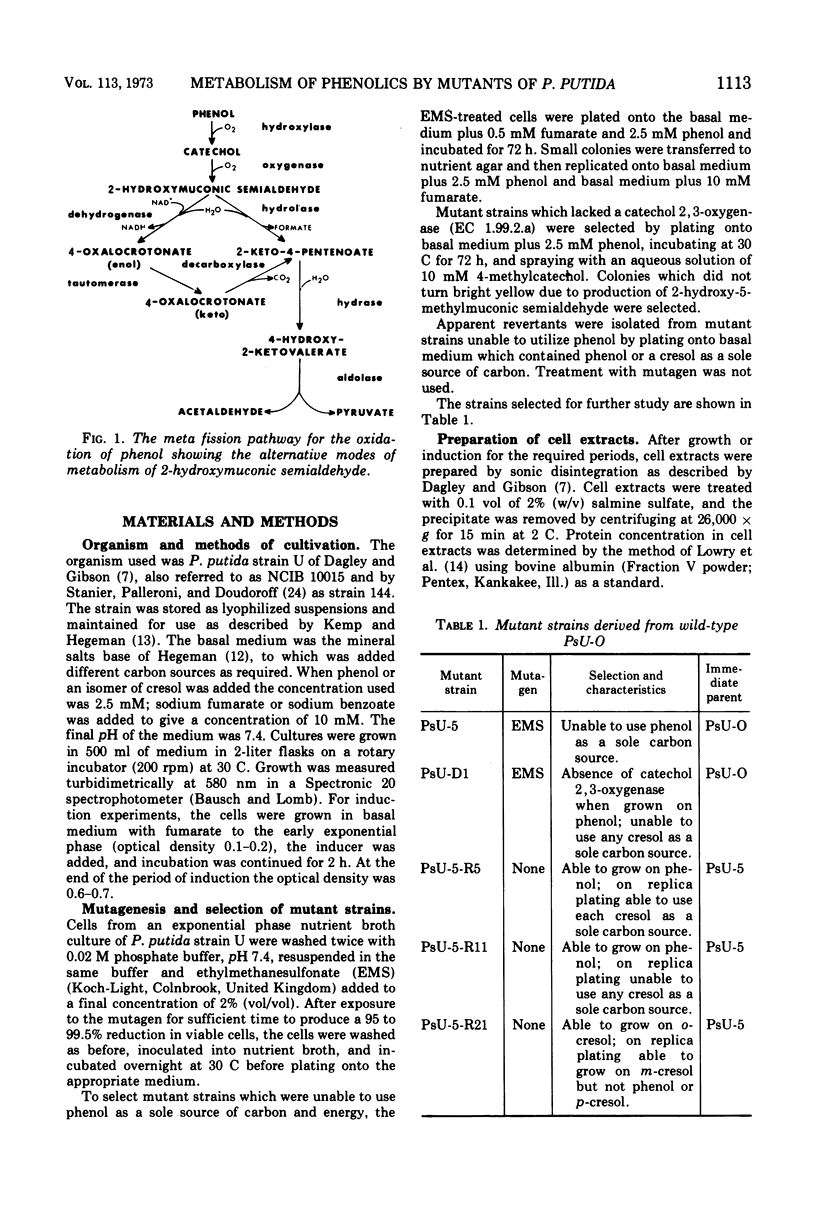
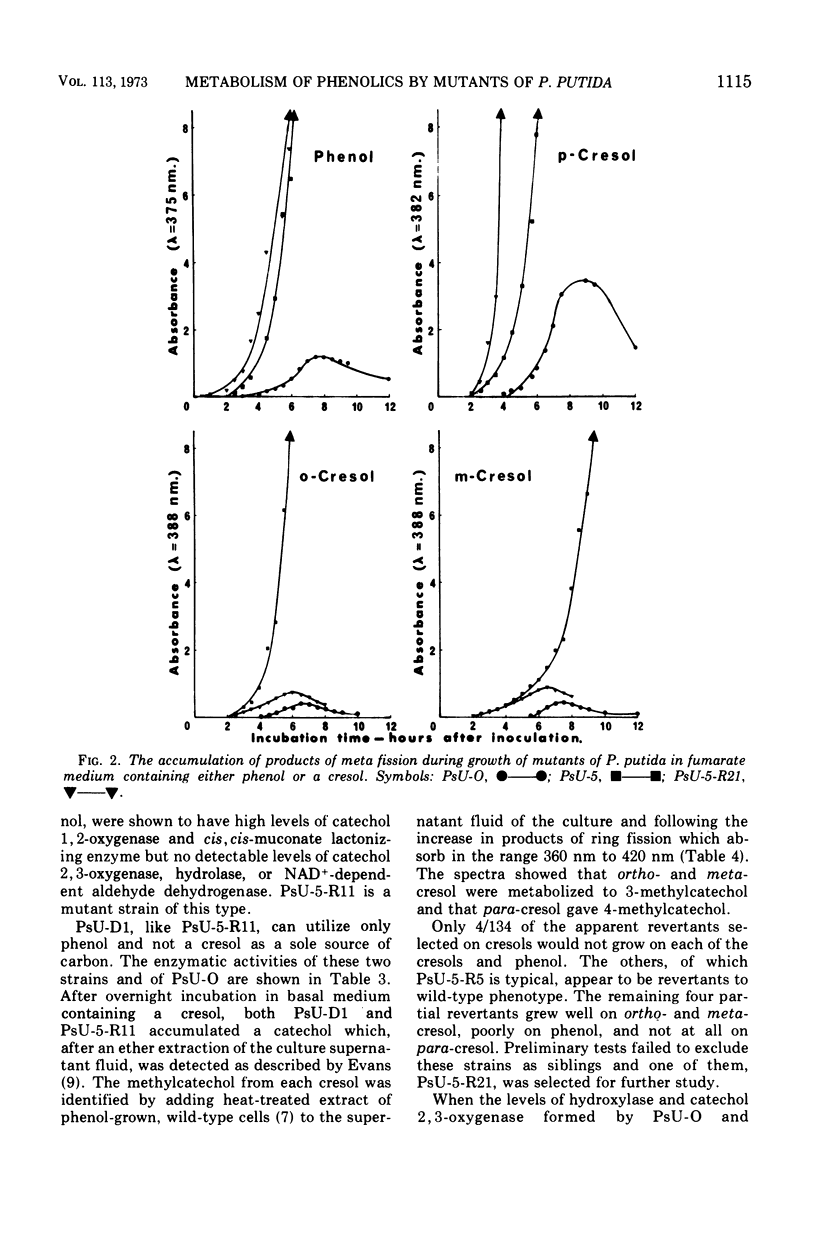
Mutant strains of Pseudomonas putida strain U have been obtained which are deficient in enzymes of the degradative pathways of phenol and cresols. Mutant strains deficient in catechol 2, 3-oxygenase accumulated the appropriate catechol derivative from cresols. A mutant strain which would not grow on either phenol or a cresol was shown to be deficient in both 2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde hydrolase and a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, oxidized form, (NAD+)-dependent aldehyde dehydrogenase. When this strain was grown in the presence of phenol or a cresol, the appropriate product of meta fission of these compounds accumulated in the growth medium. A partial revertant of this mutant strain, which was able to grow on ortho- and meta-cresol but not para-cresol, was shown to have regained only the hydrolase activity. This strain was used to show that the products of meta ring fission of the cresols and phenol are metabolized as follows: (i) ortho- and meta-cresol exclusively by a hydrolase; (ii) para-cresol exclusively by a NAD+-dependent aldehyde dehydrogenase; (iii) phenol by both a NAD+-dependent dehydrogenase and a hydrolase in the approximate ratio of 5 to 1. This conclusion is supported by the substrate specificity and enzymatic activity of the hydrolase and NAD+-dependent aldehyde dehydrogenase enzymes of the wild-type strain. The results are discussed in terms of the physiological significance of the pathway. Properties of some of the mutant strains isolated are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayly R. C., Dagley S., Gibson D. T. The metabolism of cresols by species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):293–301. doi: 10.1042/bj1010293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayly R. C., Dagley S. Oxoenoic acids as metabolites in the bacterial degradation of catechols. Biochem J. 1969 Feb;111(3):303–307. doi: 10.1042/bj1110303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain R. B., Farr D. R. Metabolism of arylsulphonates by micro-organisms. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(4):859–877. doi: 10.1042/bj1060859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catelani D., Fiecchi A., Galli E. Formation of 2-hydroxy-6-oxo-2, trans-4, trans-heptad-ienoic acid from 3-methylcatechol by a Pseudomonas. Experientia. 1968 Feb 15;24(2):113–113. doi: 10.1007/BF02146927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall F. A., Sala-Trepat J. M., Williams P. A. The coexistence of two pathways for the metabolism of 2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde in a naphthalene-grown pseudomonad. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 7;43(3):463–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90636-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., EVANS W. C., RIBBONS D. W. New pathways in the oxidative metabolism of aromatic compounds by microorganisms. Nature. 1960 Nov 12;188:560–566. doi: 10.1038/188560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., GIBSON D. T. THE BACTERIAL DEGRADATION OF CATECHOL. Biochem J. 1965 May;95:466–474. doi: 10.1042/bj0950466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C. Oxidation of phenol and benzoic acid by some soil bacteria. Biochem J. 1947;41(3):373–382. doi: 10.1042/bj0410373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feist C. F., Hegeman G. D. Phenol and benzoate metabolism by Pseudomonas putida: regulation of tangential pathways. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):869–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.869-877.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegeman G. D. Synthesis of the enzymes of the mandelate pathway by Pseudomonas putida. I. Synthesis of enzymes by the wild type. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1140–1154. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1140-1154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp M. B., Hegeman G. D. Genetic control of the beta-ketoadipate pathway in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1488–1499. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1488-1499.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K., Duggleby C. J., Sala-Trepat J. M., Williams P. A. The metabolism of benzoate and methylbenzoates via the meta-cleavage pathway by Pseudomonas arvilla mt-2. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 24;28(3):301–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N. Regulation of catabolic pathways in Pseudomonas. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Jun;35(2):87–116. doi: 10.1128/br.35.2.87-116.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. 3. Enzymes of the catechol pathway. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3795–3799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribbons D. W. Metabolism of omicron-cresol by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain T1. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Aug;44(2):221–231. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Murray K., Williams P. A. The metabolic divergence in the meta cleavage of catechols by Pseudomonas putida NCIB 10015. Physiological significance and evolutionary implications. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 24;28(3):347–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarabhai A., Brenner S. A mutant which reinitiates the polypeptide chain after chain termination. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):145–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90357-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuesthoff G., Bauerle R. H. Mutations creating internal promoter elements in the tryptophan operon of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 14;49(1):171–196. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



