Abstract
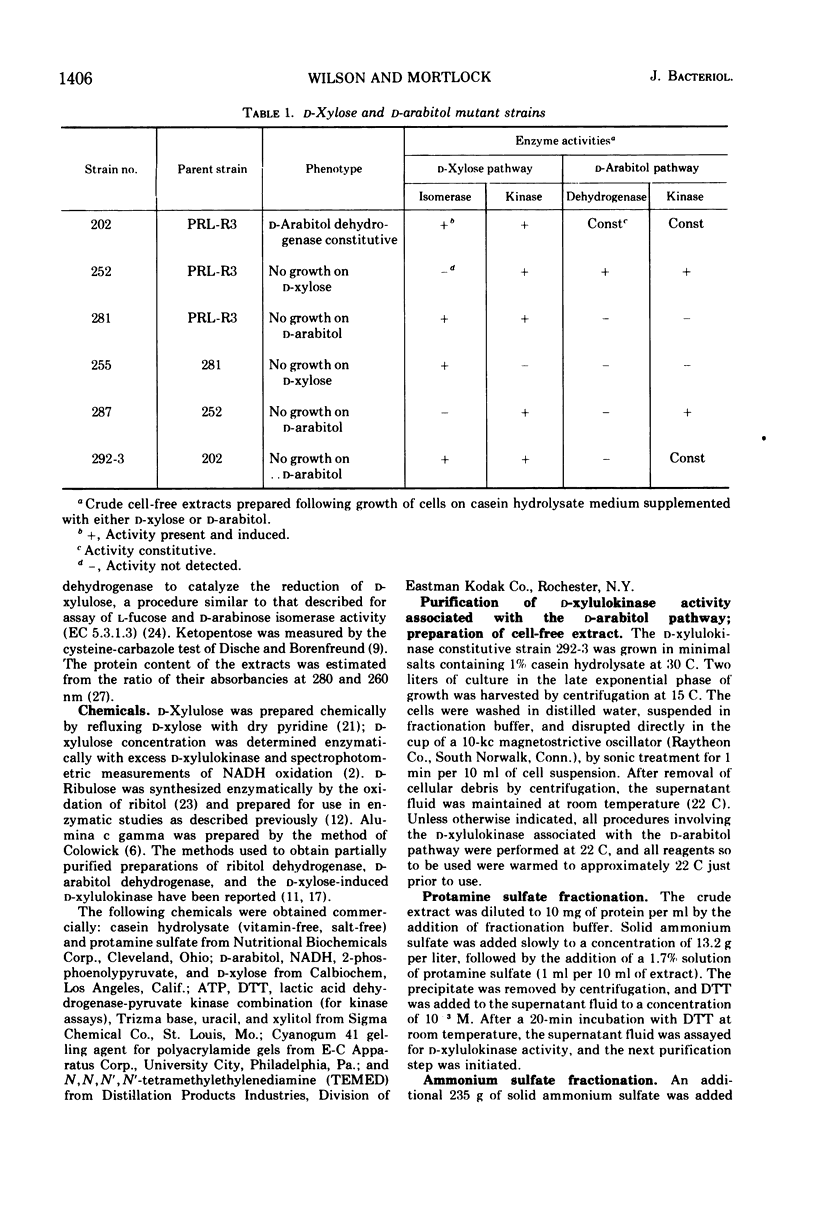
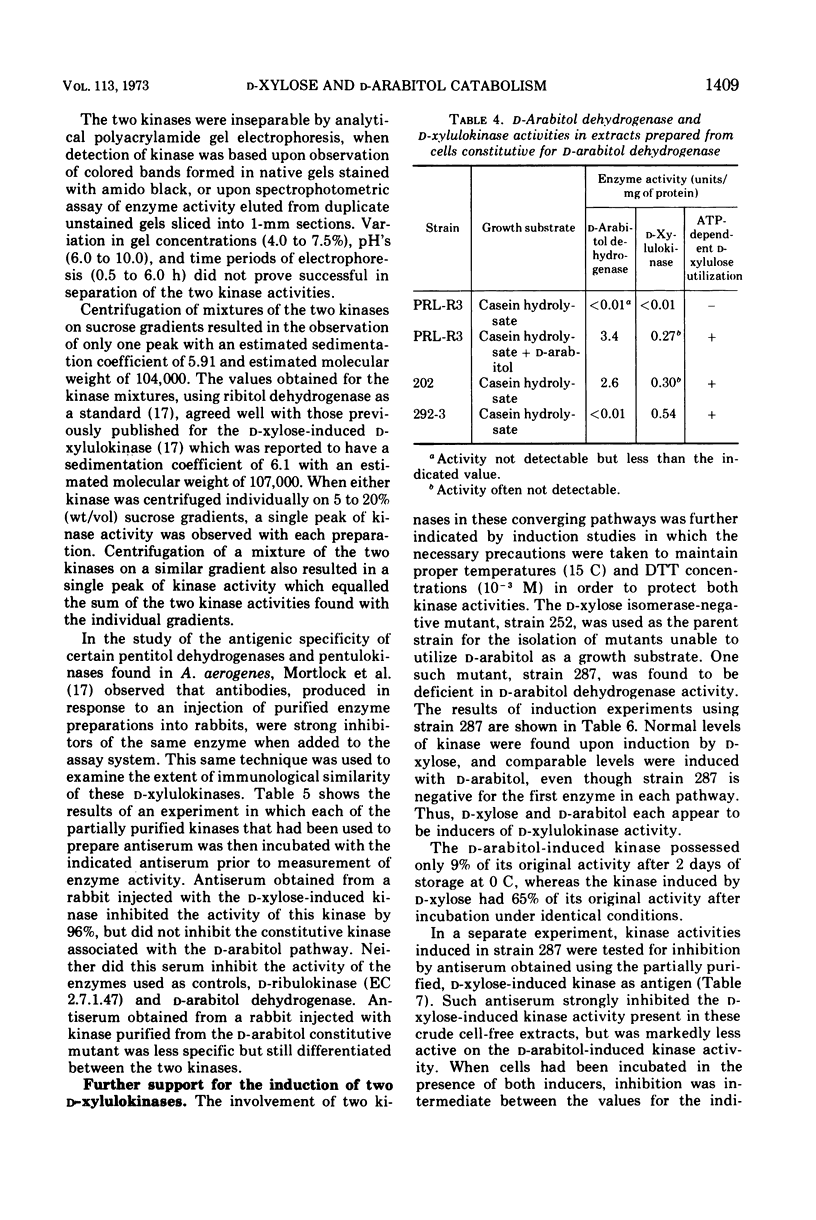
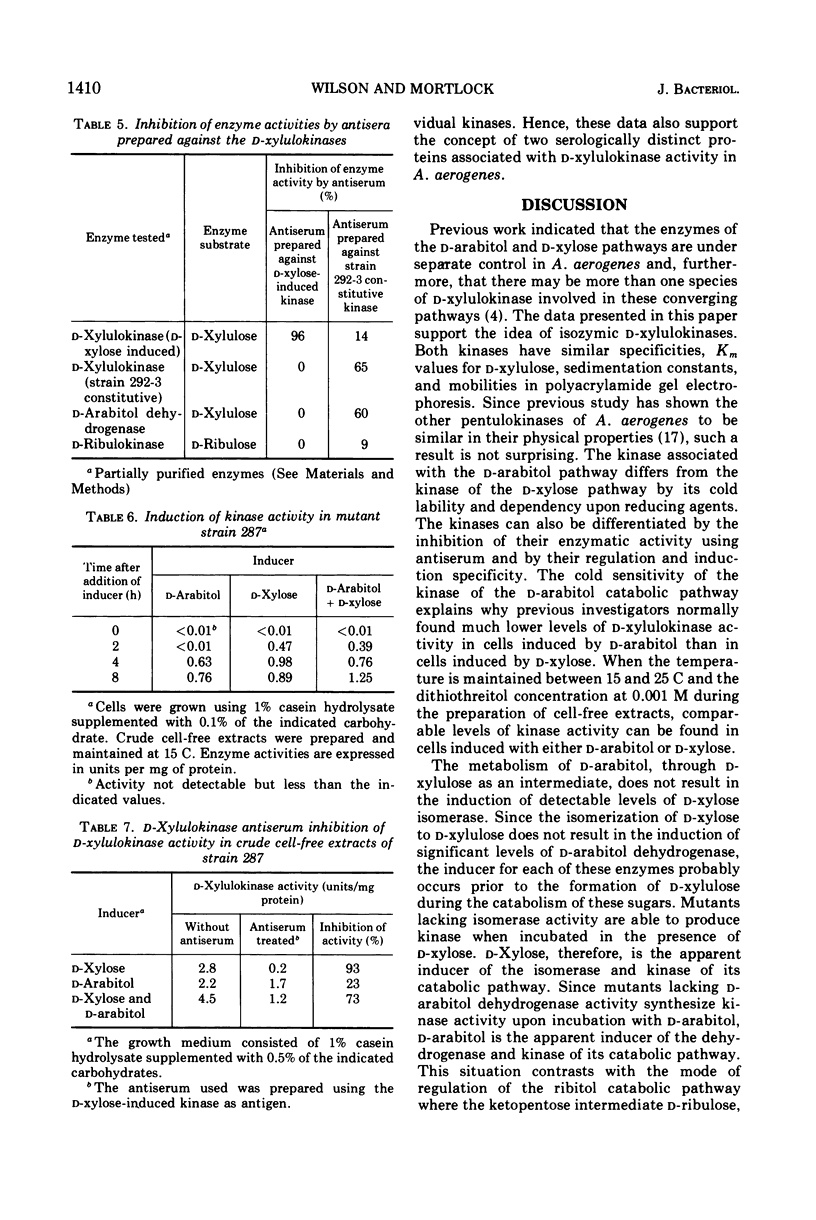
Aerobacter aerogenes strain PRL-R3 possesses inducible enzyme pathways for the catabolism of d-xylose and d-arabitol. d-Xylose is the apparent inducer for d-xylose isomerase and d-xylulokinase. d-Arabitol is the apparent inducer for d-arabitol dehydrogenase and a separate d-xylulokinase. Both kinases had similar Km values and substrate specificities, and could not be separated by sucrose gradient centrifugation or polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. They could be differentiated, however, by their separate regulation, their inhibition by antisera, and by the cold sensitivity of the kinase of the d-arabitol catabolic pathway.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON R. L., WOOD W. A. Pathway of L-xylose and L-lyxose degradation in Aerobacter aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:296–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisson T. M., Mortlock R. P. Regulation of pentitol metabolism by Aerobacter aerogenes. I. Coordinate control of ribitol dehydrogenase and D-ribulokinase activities. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):925–931. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.925-931.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisson T. M., Oliver E. J., Mortlock R. P. Regulation of pentitol metabolism by aerobacter aerogenes. II. Induction of the ribitol pathway. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):932–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.932-936.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z., BORENFREUND E. A new spectrophotometric method for the detection and determination of keto sugars and trioses. J Biol Chem. 1951 Oct;192(2):583–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIN E. C., LERNER S. A., JORGENSEN S. E. A method for isolating constitutive mutants for carbohydrate-catabolizing enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 2;60:422–424. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90423-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc D. J., Mortlock R. P. Metabolism of D-arabinose: origin of a D-ribulokinase activity in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):82–89. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.82-89.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim R., Cohen S. S. D-phosphoarabinoisomerase and D-ribulokinase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 10;241(19):4304–4315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTLOCK R. P., FOSSITT D. D., PETERING D. H., WOOD W. A. METABOLISM OF PENTOSES AND PENTITOLS BY AEROBACTER AEROGENES. 3. PHYSICAL AND IMMUNOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF PENITOL DEHYDROGENASES AND PENTULOKINASES. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:129–135. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.129-135.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTLOCK R. P., WOOD W. A. METABOLISM OF PENTOSES AND PENTITOLS BY AEROBACTER AEROGENES. I. DEMONSTRATION OF PENTOSE ISOMERASE, PENTULOKINASE, AND PENTITOL DEHYDROGENASE ENZYME FAMILIES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:838–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.838-844.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTLOCK R. P., WOOD W. A. METABOLISM OF PENTOSES AND PENTITOLS BY AEROBACTER AEROGENES. II. MECHANISM OF ACQUISITION OF KINASE, ISOMERASE, AND DEHYDROGENASE ACTIVITY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:845–849. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.845-849.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortlock R. P., Fossitt D. D., Wood W. A. A basis for utlization of unnatural pentoses and pentitols by Aerobacter aerogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):572–579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver E. J., Bisson T. M., LeBlanc D. J., Mortlock R. P. D-Ribulose production by a mutant of Aerobacter aerogens. Anal Biochem. 1969 Feb;27(2):300–305. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver E. J., Mortlock R. P. Growth of Aerobacter aerogenes on D-arabinose: origin of the enzyme activities. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):287–292. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.287-292.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


