Abstract
Bordetella bronchiseptica can establish prolonged airway infection consistent with a highly developed ability to evade mammalian host immune responses. Upon initial interaction with the host upper respiratory tract mucosa, B. bronchiseptica are subjected to antimicrobial reactive nitrogen species (RNS) and reactive oxygen species (ROS), effector molecules of the innate immune system. However, the responses of B. bronchiseptica to redox species at physiologically relevant concentrations (nM-µM) have not been investigated. Using predicted physiological concentrations of nitric oxide (NO), superoxide (O2.−) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) on low numbers of colony forming units (CFU) of B. bronchiseptica, all redox active species displayed dose-dependent antimicrobial activity. Susceptibility to individual redox active species was significantly increased upon introduction of a second species at sub-antimicrobial concentrations. An increased bacteriostatic activity of NO was observed relative to H2O2. The understanding of Bordetella responses to physiologically relevant levels of exogenous RNS and ROS will aid in defining the role of endogenous production of these molecules in host innate immunity against Bordetella and other respiratory pathogens.
Keywords: bacterial stress, nitric oxide, hydrogen peroxide, superoxide, reactive nitrogen species (RNS), reactive oxygen species (ROS)
INTRODUCTION
The Bordetella genus includes the closely related bacterial species B. pertussis, B. parapertussis and B. bronchiseptica. The human pathogens B. pertussis and B. parapertussis are etiological agents of whooping cough, a potentially lethal respiratory syndrome primarily affecting young children (Bjornstad & Harvill, 2005, Greenberg, et al., 2005). B. bronchiseptica infects a variety of mammals and can result in asymptomatic infection or symptomatic disease (Goodnow, 1980). B. bronchiseptica expresses most of the virulence factors identified in B. pertussis, with the notable exception of pertussis toxin. In both species, virulence factor expression is regulated by a two-component sensory system, Bordetella virulence gene activator-sensor (BvgAS) (Martinez de Tejada, et al., 1996, Cotter & Jones, 2003). Comparative analysis of the B. pertussis and B. bronchiseptica genomes underscores the conservation of their pathogenic machineries and supports the use of B. bronchiseptica as a model for Bordetella physiology and pathogenesis (Parkhill, et al., 2003).
Respiratory pathogens must overcome innate airway defenses including antimicrobial molecules secreted into the airway surface liquid (ASL) (Wilson, et al., 1996). Both reactive nitrogen species (RNS) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) can provide antimicrobial activity by inactivating bacterial cell enzymes through reaction with metal prosthetic groups, modification of specific amino acids, or by induction of DNA mutations (Imlay, 2003, Borisov, et al., 2004, Weber, et al., 2004). Bacterial responses to redox species are dependent on concentration, duration of exposure and the ability of the pathogen to detoxify specific RNS and ROS (Khelef, et al., 1996, Gardner, et al., 1998, Bryk, et al., 2000).
Nitric oxide (NO) is produced by NO synthases (NOS) in many cell types including respiratory epithelial cells (Donnelly & Barnes, 2002), where it may have antibacterial activity (Morris, et al., 1984, Schmidt & Walter, 1994, Fang, 1997, Nathan & Shiloh, 2000). Because NO can be oxidized to RNS such as nitrogen dioxide (NO2), dinitrogen trioxide (N2O3), and peroxynitrite (ONOO−) (Ischiropoulos, et al., 1992), its antimicrobial effects may be due to alternate RNS species. Superoxide (O2.−) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) are ROS produced by resident epithelial cells and/or migratory immune cells in the airway (Hampton, et al., 1996, Geiszt, et al., 2003, Forteza, et al., 2005, Pantano, et al., 2007). Bordetellae produce superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase to detoxify these compounds, and increased bacterial susceptibility to ROS has been observed in B. pertussis strains with mutations in SOD (Khelef, et al., 1996) or catalase (DeShazer, et al., 1994). In this study, we assessed antimicrobial effects of physiologically relevant concentrations of individual or combined RNS and ROS on low CFU of B. bronchiseptica to model the redox stress level in the airway during infection.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Bordet Gengou (BG) agar plates, Bacto Agar, and Bacto Yeast Extract were purchased from Becton Dickinson (Sparks, Maryland). Stock H2O2 was from Acros Organics (Morris Plaines, New Jersey). Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA), hypoxanthine (HX), SOD, and catalase were from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, Missouri). Cytochrome c was from Calbiochem (San Diego, California). S-Nitroso-N-acetyl-D,L-penicillamine (SNAP) was from Cayman Chemical (Ann Arbor, Michigan). Spermine NONOate (SPER/NO) was synthesized according to published procedures (Hrabie, et al., 1993). All other chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, Missouri), VWR (West Chester, Pennsylvania) or Fisher Scientific (Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania).
B. bronchiseptica cultures
Stocks of B. bronchiseptica strain RB50 (Cotter & Miller, 1994) were cultured on BG agar plates or in Stainer-Scholte medium (63 mM L-glutamic acid, 2 mM L-proline, 43 mM NaCl, 3.7 mM KH2PO4, 2.7 mM KCl, 1.0 mM MgCl2, 0.14 mM CaCl2·2H2O, 10g/L casamino acids and 39 mM Tris, pH 7.6) at 37°C with supplements (0.33 mM L-cysteine, 36 µM FeSO4·7H2O, 32 µM nicotinic acid, 0.49 mM glutathione, and 2.3 mM ascorbic acid) added at the time of preparation of broth cultures (Stainer & Scholte, 1970). Airway surface liquid (ASL) mimic medium was prepared in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) with specific components derived from published chemical analysis of ASL (Robinson, et al., 1989, Joris, et al., 1993, Cowley, et al., 1997, Donaldson, et al., 2000, Kozlova, et al., 2005): 90.4 mM Na+, 106.0 mM Cl−, 10.0 mM Mg2+, 1.0 mM Ca2+, 0.1 mM NO2−, 0.1 mM NO3−, 20.0 mM K+, 11.9 mM PO4−, 2.0 mM SO42−, 4.0 g/L casamino acids and 550 nM ATP, pH 7.2.
In vitro generation of RNS and ROS
NO was produced by decomposition of the NO donor SPER/NO diluted in PBS (Keefer, et al., 1996). Peak absorption (250 nm) for SPER/NO stock in 10 mM NaOH was evaluated spectrophotometrically before each experiment to verify activity and effective concentration (ε of 8,000 M−1cm−1 (Maragos, et al., 1991)). Expired SPER/NO for control experiments was produced by incubation of stock solution at 37°C until complete loss of absorption at 250 nm. Steady state concentrations of NO (300–400 nM and 3–4 µM) in solution were measured directly for 6 µM and 62.5 µM SPER/NO respectively, using an ISO-NO Mark II isolated NO meter and SNAP as a NO standard (WPI, Sarasota, Florida). Due to the non-linear response of the ISO-NOPMC NO microchip sensor, NO concentrations at higher SPER/NO levels were estimated from a standard curve (12–15 µM steady state NO at 250 µM SPER/NO; 50–60 µM NO at 1,000 µM SPER/NO). The level of NO released from 1,000 µM SPER/NO likely represents a hyperphysiological concentration of NO.
H2O2 was diluted to the desired concentrations from a commercial stock solution. Because of its high reactivity (Riley, et al., 1991), O2.− gradients were established by continuous enzymatic production during oxidation of HX by xanthine oxidase (XO) in HX-buffer (500 µM HX, 50 µM DTPA in PBS, pH 7.2) containing 200 U/ml catalase and a concentration gradient of XO. The steady rate of synthesis for O2.− at 3.75 × 10−4 U/ml (0.1 µM/min) and 3.75 × 10−3 U/ml (1.0 µM/min) were determined by spectrophotometric monitoring of the reduction of cytochrome c at 550 nm (McCord & Fridovich, 1969). Higher steady state productions were estimated from standard curves. SOD or catalase (200 U/ml) were used to consume O2.−, and H2O2, respectively. When both O2.− and H2O2 were required in bacterial challenge experiments, catalase was removed from the reaction mixture. HX-buffer was used as a control.
Exposure of B. bronchiseptica to RNS and ROS
Because growth phase can influence bacterial responses to redox stress (Gonzalez-Flecha & Demple, 1997, Michan, et al., 1999), all experiments were conducted with bacteria cultured at early to mid log phase from a standardized inoculum. Inocula were standardized by suspending 5 – 10 colonies from BG agar in PBS to achieve a working suspension with an OD600 of 0.3. A 50 µl aliquot of working suspension (~ 5.0 × 107 colony forming units (CFU)) was placed in 4.0 ml Stainer-Scholte medium and incubated at 37°C with shaking (250 rpm) for 19 – 20 h. Bacteria were pelleted, re-suspended in PBS to an OD600 of 0.3, and diluted 1,000-fold. Bacterial suspension (5 µl, or ~5,000 CFU) was added to redox challenge reactions in 96-well plates (100 µl reaction volume) or to control buffer for 5 h at 37°C with agitation (150 rpm). Sample aliquots were then plated in duplicate onto Luria-Bertani (LB) agar for analysis of bactericidal activity. Bacterial survival following challenge with RNS and/or ROS were determined by dividing the average number of CFU surviving the challenge by the number of CFU surviving incubation in buffer alone (100%).
Analysis of colony morphology after 50% Lethal Dose (LD50) challenge of B. bronchiseptica by NO or H2O2
B. bronchiseptica were exposed to 250 µM active or expired SPER/NO, 5 µM H2O2 or PBS. Aliquots were plated onto BG agar and incubated at 37°C for 48 h. Plates were imaged using a Chemi-Doc imaging system controlled by Quantity One Software (BioRad, Hercules, California). To quantify colony size after exposure of bacteria to RNS or ROS, individual colonies were excised with a sterile scalpel and immediately suspended into 1.0 ml PBS, vortexed and subjected to serial dilution. The determined number of CFU/colony represents the average of a total of 40 randomly selected colonies from at least two independent experiments for each treatment.
Comparison of B. bronchiseptica growth
Following exposure to 250 µM SPER/NO, 5 µM H2O2 or PBS control, sample aliquots were plated on BG agar and incubated for 48 h. Ten to fifteen individual colonies (normal sized or microcolonies) were recovered from the agar plates and normalized in PBS to achieve an OD600 of 0.3. A 50 µl aliquot of bacterial suspension was used to seed 4.0 ml liquid cultures at 37°C. Growth in Stainer-Scholte medium was monitored spectrophotometrically at 600 nm at 3 h intervals. Growth in ASL mimic medium was assessed by plating samples from developing cultures on LB agar plates using a conventional serial dilution assay.
Statistical methods
Using Prism (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, California), one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test was used to determine statistical significance within each experiment. Two-tailed unpaired student-t tests were used to analyze statistical significance between different experiments. For all comparisons, a value of P < 0.05 conferred statistically significant differences.
RESULTS
B. bronchiseptica is sensitive to prototypical redox species of the airway
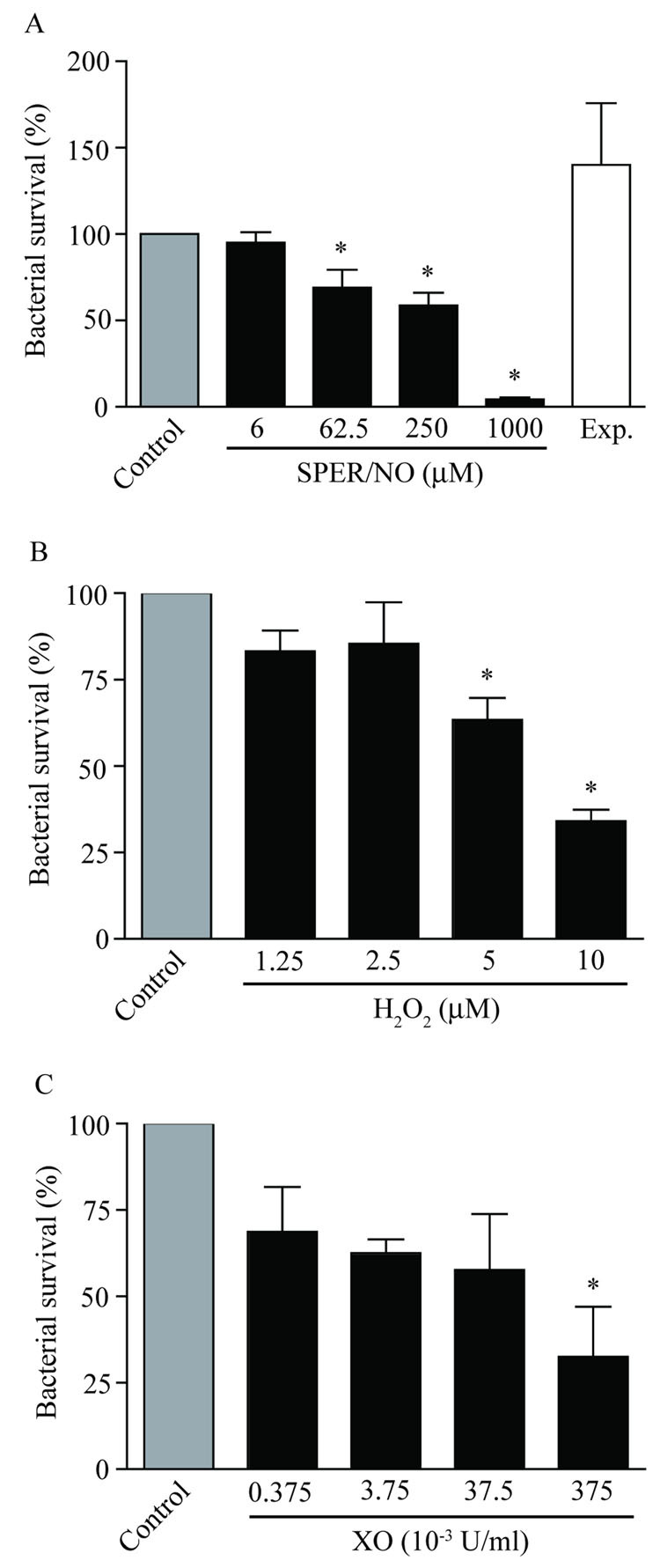
To determine the responses of B. bronchiseptica to RNS and ROS, dose response analyses of antimicrobial activity were performed with NO, H2O2, and O2.− (Figure 1). The use of low CFU in log growth phase to mimic physiological infection allowed for the measurement of subtle yet significant changes in bacterial killing on a sub-logarithmic scale. B. bronchiseptica displayed high survival (95.1 ± 6.2%) after 5 h treatments with 6.0 µM SPER/NO (constant [NO] ~ 300–400 nM). However, as the concentration of SPER/NO increased, B. bronchiseptica survival significantly decreased (69.1 ± 10.5%, 58.8 ± 7.3% and 4.4 ± 1.0% of initial inoculum were recovered with 62.5, 250 and 1,000 µM SPER/NO, respectively). Expired SPER/NO was not bacteriocidal confirming that the observed antimicrobial effects were due to NO production and not accumulation of decomposition products or autoxidation of NO (e.g., spermine and/or nitrite/nitrate).
Figure 1. Dose-dependent antimicrobial activity of prototypical airway redox species.
Approximately 5,000 CFU B. bronchiseptica were exposed to A) NO (generated from SPER/NO at the listed micromolar concentrations); B) H2O2 at final µM concentrations from diluted stock; or C) O2.− (reported as xanthine oxidase concentration in U/ml). All the redox species tested displayed dose-dependent antimicrobial activity against B. bronchiseptica. Bacterial survival was determined after a 5 h exposure period (± SEM) as compared to buffer controls and are representative of at least three independent experiments. “Exp” in A indicates experiment conducted with expired SPER/NO (1000 µM). “*” indicates statistical significance relative to matched controls (P < 0.05).
Incubation of B. bronchiseptica with H2O2 or O2.− also resulted in dose-dependent antimicrobial activity (Figure 1B, C). At the lowest H2O2 concentrations tested there were insignificant reductions in bacterial survival (83.3 ± 5.9%, and 85.4 ± 12.0% survival at 1.25 µM, and 2.5 µM, respectively). Significant reductions in B. bronchiseptica survival were observed after incubation with 5 or 10 µM H2O2 (63.4 ± 6.4% and 34.0 ± 3.4%, respectively). Despite an immediate reduction in B. bronchiseptica survival at the lowest O2.− concentration tested (68.7 ± 13.1% at 0.1 µM/min), the large variation between experiments prevented a significant change in survival except at 100 µM/min O2.− (32.6 ± 14.5% survival). Antimicrobial activity of NO, H2O2, and O2.− were observed against B. bronchiseptica within concentrations estimated to be relevant to mammalian ASL.
Combinations of redox species increase the antimicrobial activity toward B. bronchiseptica
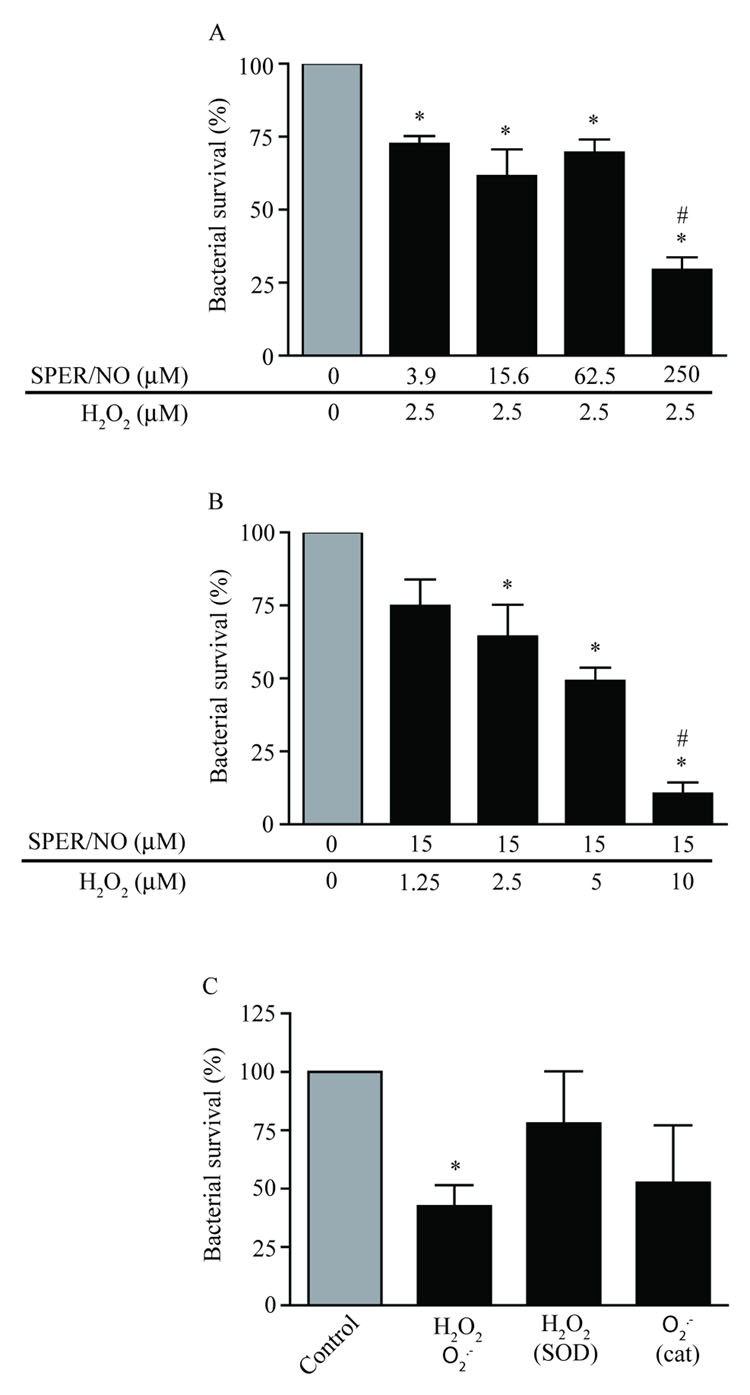
Because RNS and ROS are released continuously into ASL by airway epithelial cells, the total antimicrobial effect of redox species in vivo is likely the result of a synergistic effect. To determine whether NO augments the antimicrobial effect of H2O2 on B. bronchiseptica, challenges with SPER/NO were combined with a sub-antimicrobial concentration of H2O2 (2.5 µM). Survival of B. bronchiseptica after NO/H2O2 challenge was dose-dependent (Figure 2A), however, the decrease in bacterial survival was significant when compared to control, even at the lowest concentration of SPER/NO (72.7 ± 2.5%, 61.6 ± 9.1% and 69.6 ± 4.5% survival at 3.9, 15.6 and 62.5 µM, respectively). At 250 µM SPER/NO the combined antimicrobial effect of NO and H2O2 (29.4 ± 4.3% (Figure 2A)) was significantly increased over NO alone (58.8 ± 7.3% (Figure 1A)).
Figure 2. Combinations of NO and H2O2 augment their antimicrobial activity.
A) Approximately 5,000 CFU of B. bronchiseptica were exposed to a sub-antimicrobial concentration of H2O2 (2.5 µM) in combination with a concentration gradient of SPER/NO. B) B. bronchiseptica were exposed to a sub-antimicrobial concentration of SPER/NO (15 µM) in combination with a concentration gradient of H2O2. The addition of a sub-antimicrobial concentration of either NO or H2O2 augmented the antimicrobial activity of the other redox agent. C) B. bronchiseptica were subjected to incubation in reaction buffer containing both H2O2 and O2.−. SOD and catalase were included as experimental controls to verify the augmentative effect of H2O2 and O2.− in combination. In each case significant antimicrobial activity was measured at concentrations of redox species that were not effective individually. Bacterial survival was determined after a 5 h exposure period (± SEM) as compared to buffer controls and are representative of at least three independent experiments. “*” indicates statistical significance relative to control (P < 0.05). “#” indicates a statistically significant difference as compared to either 250 µM SPER/NO alone (Figure 2A) or to 10 µM H2O2 alone (Figure 2B) (P < 0.05).
In complementary experiments SPER/NO was kept constant at a sub-antimicrobial concentration (15 µM) while the concentration of H2O2 was varied (Figure 2B). At the lowest supplemented concentration of H2O2 (1.25 µM), B. bronchiseptica survival was not significantly affected. All other concentrations of H2O2 reduced B. bronchiseptica survival when compared to controls (64.4 ± 10.7%, 49.3 ± 4.5% and 10.6 ± 3.8% survival at 2.5, 5.0 and 10.0 µM, respectively). Again, at the highest concentration of H2O2 tested (10.0 µM), the combined antimicrobial effect of NO and H2O2 (10.6 ± 3.8% (Figure 2B)) was significantly increased over H2O2 alone (34.0 ± 3.4 (Figure 1B)).
To examine the effects of exposure to combined ROS on B. bronchiseptica viability, bacterial survival was evaluated after challenge with continuous release of 0.1 µM/min of H2O2 and O2.−, (Figure 2C). This exposure significantly reduced the level of B. bronchiseptica survival to 42.7 ± 8.9% as compared to control. Addition of SOD resulted in partial rescue of B. bronchiseptica survival (78.1 ± 22.3%) whereas addition of catalase had a less robust effect (52.7 ± 24.6%).
The antimicrobial activity of NO against B. bronchiseptica is in part bacteriostatic
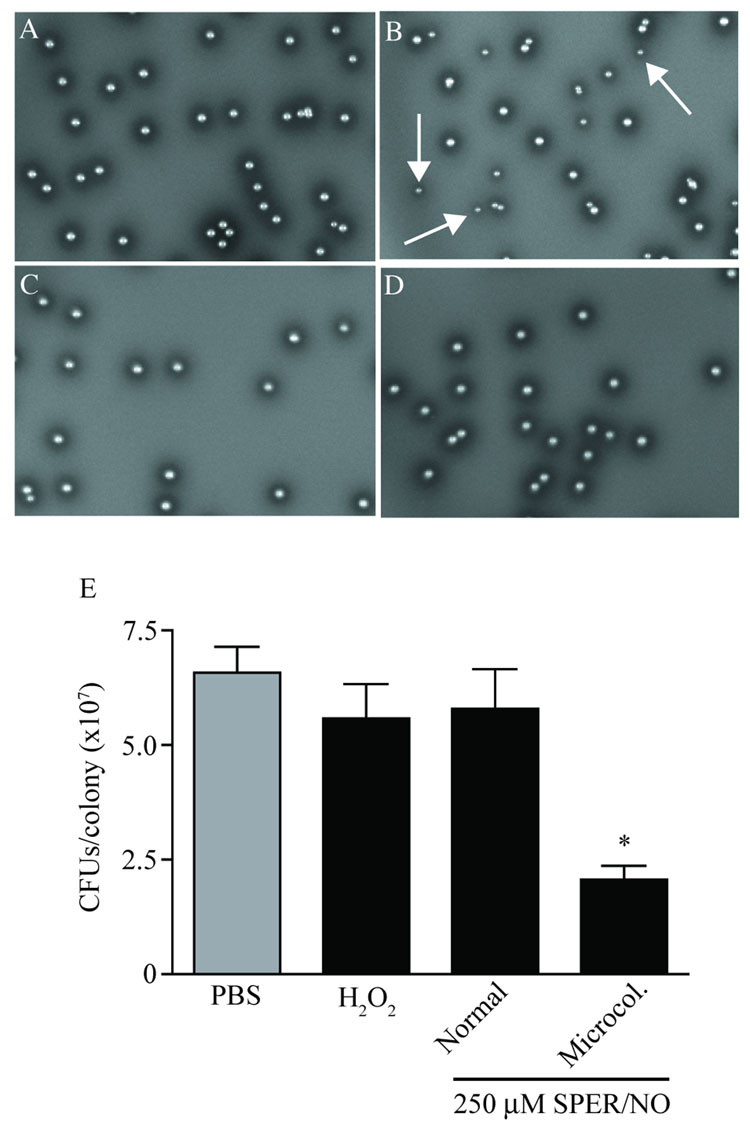
In an effort to determine whether NO and H2O2 differed in their anti-microbial capacities, B. bronchiseptica colony morphology was evaluated after exposure to either SPER/NO or H2O2. In order to normalize the physiological pressure exerted by each reagent, the LD50 (250 µM SPER/NO and 5 µM H2O2) as determined from experiments presented above was used. B. bronchiseptica exposed to PBS in mock challenge experiments displayed a consistent colony morphology (Figure 3A). Challenge with SPER/NO resulted in the generation of microcolonies in approximately 60% of colonies after growth on solid medium (Figure 3B). In contrast, there was no evidence of reduced colony size after exposure to an LD50 of H2O2 (Figure 3C) or to expired SPER/NO (Figure 3D). These data were consistent with NO being a necessary component for the generation of microcolonies.
Figure 3. Differential antimicrobial effects on B. bronchiseptica for NO and H2O2 at LD50.
B. bronchiseptica were cultured on BG agar for 48 h following exposure of ~5,000 CFU to A) PBS, B) 250 µM SPER/NO, C) 5 µM H2O2, or D) 250 µM expired SPER/NO. The production of microcolonies was observed only after exposure to SPER/NO (B, white arrows). E) Microcolonies contained a significantly reduced number of CFU as compared to normal size colonies when grown on BG agar plates. Values are presented ± SEM. Results represent data from a total of 40 colonies collected from at least two independent experiments. “*” indicates statistical significance relative to all other samples (P < 0.05).
The number of CFU within each colony was determined for NO-induced microcolonies and compared to that of normal sized colonies from SPER/NO, H2O2, and control (PBS) treatments (Figure 3E). The average number of CFU in 48 h colonies from samples exposed to PBS was 6.57 ± 0.56 × 107 CFU/colony. CFU from normal sized colonies obtained following exposure to 5.0 µM H2O2 or 250 µM SPER/NO were similar to that determined after exposure to PBS (5.58 ± 0.75 × 107 and 5.79 ± 0.86 × 107 CFU/colony, respectively). The NO-induced microcolonies contained a significantly reduced number of CFU as compared to that determined for all other samples (2.06 ± 0.30 × 107 CFU/colony).
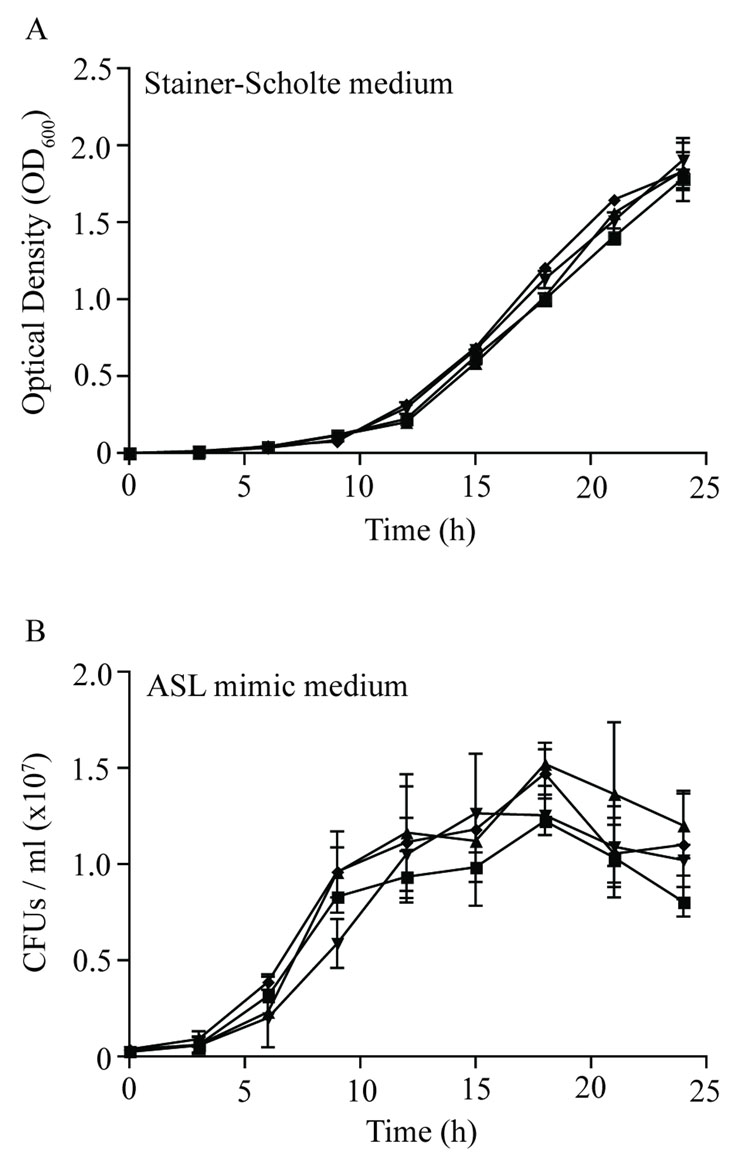
To determine if the reduced bacterial number in microcolonies was due to a permanent (e.g., DNA damage) or a transient (e.g., reversible metabolic inhibition) alteration, growth characteristics of bacteria recovered from each colony type were assessed in liquid culture with an optimal medium (Stainer-Scholte) and in an airway surface liquid-like medium (ASL mimic). In both cases, pre-exposure of B. bronchiseptica to redox stress did not adversely affect growth (Figure 4). Additionally, B. bronchiseptica sub-cultured from microcolonies resulted in normal sized colonies after subsequent plating onto solid medium (data not shown). These data are consistent with a transient bacteriostatic effect of NO in the development of B. bronchiseptica microcolonies.
Figure 4. B. bronchiseptica growth in optimal and sub-optimal medium following exposure to redox stress.
B. bronchiseptica cultured on BG agar following exposure to redox stress were resuspended in PBS to an OD600 of 0.3 and transferred to liquid medium for growth analysis in A) fully supplemented Stainer-Scholte medium or B) minimal medium representative of the ASL. ν - PBS; σ - microcolonies (250 µM SPER/NO); τ - normal sized colonies (250 µM SPER/NO); υ - H2O2. Growth in Stainer-Scholte medium was monitored spectrophotometrically (OD600) while growth in ASL mimic medium was monitored by determination of CFU/ml at 3 h intervals. Pre-exposure to redox agents did not adversely affect growth. These data are consistent with a transient bacteriostatic effect of NO to produce microcolonies that is not evident in the H2O2 challenge or control experiments.
DISCUSSION
For succesful colonization of the respiratory tract, pathogens must overcome innate immune defenses including mucociliary clearance and antimicrobial molecules that togther provide a non-specific, but robust, host defense (Ellerman & Bisgaard, 1997, Diamond, et al., 2000, Ganz, 2002, McCormack & Whitsett, 2002). In vivo analyses suggest RNS and ROS are important antimicrobial products in the airway. Loss of iNOS or the ROS-producing enzyme phagocyte oxidase in mice increases susceptibility to microbial infection (Nathan & Shiloh, 2000), including B. pertussis (Canthaboo, et al., 2002). The synergistic effects of these enzymes in immune defense are emphasized in double knockouts, where increased spontaneous infection by commensal microbes results in a high incidence of animal death (Shiloh, et al., 1999).
Both constitutive and inducible forms of NO synthases are expressed in the airway epithelium from a variety of Bordetella hosts (Asano, et al., 1994, Robbins, et al., 1994, Robbins, et al., 1994, Guo, et al., 1995, Rochelle, et al., 1998), allowing production of RNS near the cilia where bordetellae specifically bind in vitro and during colonization of the host airway (Goodnow, 1980, Soane, et al., 2000, Locht, et al., 2001, Edwards, et al., 2005). NO production has been measured in the proximity of a single endothelial cell in vitro at a concentration of 400–500 nM (Malinski & Taha, 1992). Because iNOS can predominate NOS species in respiratory epithelial cells, and the capacity of this isoform to produce NO is significantly higher than cNOS found in endothelial cells (Ricciardolo, 2003), we therefore considered 400 nM to be a lower concentration for NO in the ASL. Similarly, H2O2 has been measured in exhaled breath condensates at low micromolar levels (Jobsis, et al., 1998). Although sources for H2O2 are not as well defined as those for NO, airway epithelial cells can produce H2O2 for release into the ASL via nonphagocytic NADPH oxidases (Geiszt, et al., 2003, Lambeth, 2004, Moskwa, et al., 2007, Pantano, et al., 2007). The intimate interaction between bordetellae and ciliated epithelial cells of the host places this pathogen in an environmental niche enriched in redox species.
During the initial phase of a respiratory tract infection the bacterial load can be extremely low; B. bronchiseptica airway infection can be established in healthy animals with doses below 20 CFU (Harvill, et al., 1999). The experiments outlined in this report, where low bacterial numbers (~5,000 CFU) were used to assess survival against physiological concentrations (nM-µM) of redox active species, represent at least a 20-fold reduction in the bacterial density as compared to studies in which high concentrations of RNS and/or ROS were used to induce logarithmic reductions in bacterial viability (Brunelli, et al., 1995, Pacelli, et al., 1995, Hurst & Lymar, 1997). However, the low bacterial load during the initial stage of an infection suggests the need for only a slight bias towards the host in the host-pathogen interplay for an effective innate immune function. Moreover, adverse effects of RNS and ROS on the airway mucosa prevent the release of high levels of redox active species into ASL as an innate immune mechanism. In fact, prolonged incubations (>24 h) of hamster tracheal organ cultures with B. pertussis induced sufficient NO production to damage the airway epithelium and favor bacterial colonization (Flak & Goldman, 1996, Flak & Goldman, 1999). Similarly, high concentrations of H2O2 in prolonged exposure experiments (>25 µM for 24 h) reduced the viability of cultured human airway epithelial cells (Spencer, et al., 1995). The synchronized production of NO and H2O2 to lower effective redox concentrations can limit damage to host cells and, as illustrated in Figure 2, simultaneously potentiate the antibacterial activity of the redox active species. In summary, the low CFU and physiologically relevant concentrations of redox-active species used herein may be more representative of the bacteria-to-reactant ratios found in the respiratory tract and thus allow for a more relevant evaluation of the actual contribution of RNS/ROS in airway innate immunity.
The mechanisms of antimicrobial activity induced by a particular redox species is dependent upon a number of factors including concentration, chemical stability, ability to cross hydrophobic membranes, reactivity, and spatio-temporal relationship with other redox species. Figure 5 illustrates some of the complexity of RNS and ROS reactions derived from enzymes known to be expressed in airway epithelial cells (Asano, et al., 1994, Rochelle, et al., 1998, Forteza, et al., 2005, Moskwa, et al., 2007). For example, in the presence of CO2 the reaction between NO and O2.− (Espey, et al., 2002) can give rise to the free radicals, NO2. and CO3.− (Squadrito & Pryor, 2002), which themselves can have antimicrobial activity. Furthermore, although NO and H2O2 do not directly react with each other, NO2−, the end product of aqueous NO autoxidation can be oxidized to NO2 by peroxidases as well as free heme and metals (Kono, et al., 1994, van der Vliet, et al., 1997, Sampson, et al., 1998, Wu, et al., 1999, Thomas, et al., 2002). At present, we cannot identify specific targets for bacteriocidal or bacteriostatic activity of individual redox-active species produced by airway epithelial cells. However, differences between NO and H2O2 in inducing microcolony formation indicate that NO is both bacteriocidal and bacteriostatic and thus that NO might have several targets within the bacterial cell.
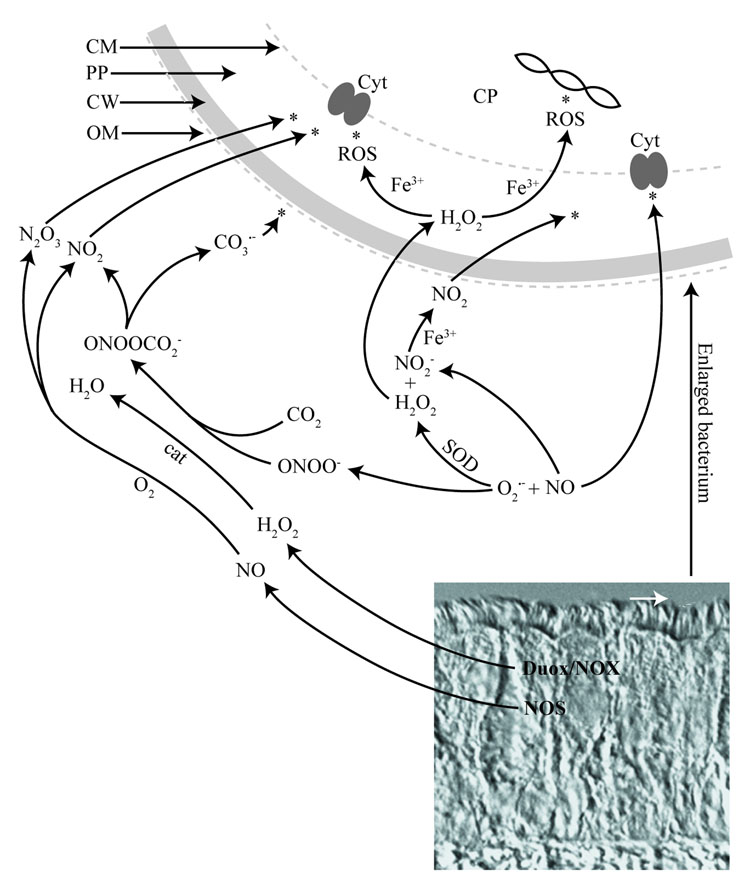
Figure 5. Role of RNS and ROS as antimicrobial agents at the airway mucosa.
DIC of tracheal section (Rabbit) showing pseudostratified airway epithelium with ciliated lining oriented toward the tracheal lumen. The white arrow points to the area where bacteria (in white) first interact with airway host cells on the ciliated surface. Theoretical reactions based on release of NO and H2O2 and potential targets (asterisks) within an invading bacterium (enlarged) are illustrated. The site of activity for individual redox species depends in part on their ability to cross biological membranes. NO can arise from NOS while H2O2/O2.− can be produced from NOX or Duox in airway epithelial cells. Release of RNS and ROS into the ASL can support generation of numerous redox species with potential antibacterial activity. In addition to the antibacterial potential of redox species, ASL components including surfactant and mucins also contribute to the antibacterial defense of the airway (not shown). The combined effects of all antibacterial components (not shown) at the airway mucosa constitute the full chemical barrier of the airway innate immune system. In vitro analysis shows that NO and H2O2 dependent antimicrobial activity can contribute significantly to the chemical barrier against B. bronchiseptica. Abbreviations: CP, cytoplasm; CM. cytoplasmic membrane; PP, periplasm; CW, cell wall; OM, outer membrane; Cyt, cytochrome.
In this study, the responses of low CFU of B. bronchiseptica to redox species at physiologically relevant doses have been established, and the data show that minor alterations in redox stress level can result in significant antibacterial effects. Our model for the analysis of RNS and ROS is, to our knowledge, the first such model established using a pathogen highly adapted to colonization of the healthy conducting airway. Further, the established antibacterial effects of low concentrations of redox active species together with the complexity of reactions involving redox active species in ASL encourages analyses to identify specific effector molecules and their targets within the bacterial cells during in vitro exposure or following controlled production by the airway epithelium in vivo.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank Dr. Jessica A. Edwards for providing the DIC image incorporated into Figure 5 and for manuscript review; Dr. Peggy A. Cotter for her supply of and help in working with Bordetella bronchiseptica; and Terri Boitano for manuscript editing. This work was supported by NIH grants HL64039, AI1061811, ALA Grant C1350-N (SB) and an award through The University of Arizona Institute for Collaborative Research (BIO5 to SB, KMM and RLF).
REFERENCES
- 1.Asano K, Chee CB, Gaston B, Lilly CM, Gerard C, Drazen JM, Stamler JS. Constitutive and inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression, regulation, and activity in human lung epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91:10089–10093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.10089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bjornstad ON, Harvill ET. Evolution and emergence of Bordetella in humans. Trends Microbiol. 2005;13:355–359. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2005.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Borisov VB, Forte E, Konstantinov AA, Poole RK, Sarti P, Giuffre A. Interaction of the bacterial terminal oxidase cytochrome bd with nitric oxide. FEBS Lett. 2004;576:201–204. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Brunelli L, Crow JP, Beckman JS. The comparative toxicity of nitric oxide and peroxynitrite to Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1995;316:327–334. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1995.1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bryk R, Griffin P, Nathan C. Peroxynitrite reductase activity of bacterial peroxiredoxins. Nature. 2000;407:211–215. doi: 10.1038/35025109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Canthaboo C, Xing D, Wei XQ, Corbel MJ. Investigation of role of nitric oxide in protection from Bordetella pertussis respiratory challenge. Infect Immun. 2002;70:679–684. doi: 10.1128/iai.70.2.679-684.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cotter PA, Miller JF. BvgAS-mediated signal transduction: analysis of phase-locked regulatory mutants of Bordetella bronchiseptica in a rabbit model. Infect Immun. 1994;62:3381–3390. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.8.3381-3390.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cotter PA, Jones AM. Phosphorelay control of virulence gene expression in Bordetella. Trends Microbiol. 2003;11:367–373. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(03)00156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cowley EA, Govindaraju K, Lloyd DK, Eidelman DH. Airway surface fluid composition in the rat determined by capillary electrophoresis. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:L895–L899. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1997.273.4.L895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.DeShazer D, Wood GE, Friedman RL. Molecular characterization of catalase from Bordetella pertussis: identification of the katA promoter in an upstream insertion sequence. Mol Microbiol. 1994;14:123–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Diamond G, Legarda D, Ryan LK. The innate immune response of the respiratory epithelium. Immunol Rev. 2000;173:27–38. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2000.917304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Donaldson SH, Lazarowski ER, Picher M, Knowles MR, Stutts MJ, Boucher RC. Basal nucleotide levels, release, and metabolism in normal and cystic fibrosis airways. Mol Med. 2000;6:969–982. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Donnelly LE, Barnes PJ. Expression and regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase from human primary airway epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002;26:144–151. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.26.1.4477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Edwards JA, Groathouse NA, Boitano S. Bordetella bronchiseptica adherence to cilia is mediated by multiple adhesin factors and blocked by surfactant protein A. Infect Immun. 2005;73:3618–3626. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.6.3618-3626.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ellerman A, Bisgaard H. Longitudinal study of lung function in a cohort of primary ciliary dyskinesia. Eur Respir J. 1997;10:2376–2379. doi: 10.1183/09031936.97.10102376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Espey MG, Thomas DD, Miranda KM, Wink DA. Focusing of nitric oxide mediated nitrosation and oxidative nitrosylation as a consequence of reaction with superoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:11127–11132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.152157599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Fang FC. Perspectives series: host/pathogen interactions. Mechanisms of nitric oxide-related antimicrobial activity. J Clin Invest. 1997;99:2818–2825. doi: 10.1172/JCI119473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Flak TA, Goldman WE. Autotoxicity of nitric oxide in airway disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996;154:S202–S206. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/154.4_Pt_2.S202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Flak TA, Goldman WE. Signalling and cellular specificity of airway nitric oxide production in pertussis. Cell Microbiol. 1999;1:51–60. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.1999.00004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Forteza R, Salathe M, Miot F, Conner GE. Regulated hydrogen peroxide production by Duox in human airway epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2005;32:462–469. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2004-0302OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ganz T. Antimicrobial polypeptides in host defense of the respiratory tract. J Clin Invest. 2002;109:693–697. doi: 10.1172/JCI15218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gardner PR, Gardner AM, Martin LA, Salzman AL. Nitric oxide dioxygenase: an enzymic function for flavohemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:10378–10383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.18.10378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Geiszt M, Witta J, Baffi J, Lekstrom K, Leto TL. Dual oxidases represent novel hydrogen peroxide sources supporting mucosal surface host defense. Faseb J. 2003;17:1502–1504. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-1104fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gonzalez-Flecha B, Demple B. Transcriptional regulation of the Escherichia coli oxyR gene as a function of cell growth. J Bacteriol. 1997;179:6181–6186. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.19.6181-6186.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Goodnow RA. Biology of Bordetella bronchiseptica. Microbiol Rev. 1980;44:722–738. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.4.722-738.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Greenberg DP, von Konig CH, Heininger U. Health burden of pertussis in infants and children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005;24:S39–S43. doi: 10.1097/01.inf.0000160911.65632.e1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Guo FH, De Raeve HR, Rice TW, Stuehr DJ, Thunnissen FB, Erzurum SC. Continuous nitric oxide synthesis by inducible nitric oxide synthase in normal human airway epithelium in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92:7809–7813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.17.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hampton MB, Kettle AJ, Winterbourn CC. Involvement of superoxide and myeloperoxidase in oxygen-dependent killing of Staphylococcus aureus by neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1996;64:3512–3517. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.9.3512-3517.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Harvill ET, Cotter PA, Yuk MH, Miller JF. Probing the function of Bordetella bronchiseptica adenylate cyclase toxin by manipulating host immunity. Infect Immun. 1999;67:1493–1500. doi: 10.1128/iai.67.3.1493-1500.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hrabie JA, Klose JR, Wink DA, Keefer LK. New nitric oxide-releasing zwitterions derived from polyamines. J. Org. Chem. 1993;58:1472–1476. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hurst JK, Lymar SV. Toxicity of peroxynitrite and related reactive nitrogen species toward Escherichia coli. Chem Res Toxicol. 1997;10:802–810. doi: 10.1021/tx970008v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Imlay JA. Pathways of oxidative damage. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2003;57:395–418. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.57.030502.090938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ischiropoulos H, Zhu L, Beckman JS. Peroxynitrite formation from macrophage-derived nitric oxide. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992;298:446–451. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90433-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jobsis Q, Raatgeep HC, Schellekens SL, Hop WC, Hermans PW, de Jongste JC. Hydrogen peroxide in exhaled air of healthy children: reference values. Eur Respir J. 1998;12:483–485. doi: 10.1183/09031936.98.12020483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Joris L, Dab I, Quinton PM. Elemental composition of human airway surface fluid in healthy and diseased airways. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993;148:1633–1637. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.6_Pt_1.1633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Keefer LK, Nims RW, Davies KM, Wink DA. "NONOates" (1-substituted diazen-1-ium-1,2-diolates) as nitric oxide donors: convenient nitric oxide dosage forms. Methods Enzymol. 1996;268:281–293. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(96)68030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Khelef N, DeShazer D, Friedman RL, Guiso N. In vivo and in vitro analysis of Bordetella pertussis catalase and Fe-superoxide dismutase mutants. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1996;142:231–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1996.tb08435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kono Y, Shibata H, Adachi K, Tanaka K. Lactate-dependent killing of Escherichia coli by nitrite plus hydrogen peroxide: a possible role of nitrogen dioxide. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994;311:153–159. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1994.1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kozlova I, Vanthanouvong V, Almgren B, Hogman M, Roomans GM. Elemental composition of airway surface liquid in the pig determined by x-ray microanalysis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2005;32:59–64. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2003-0456OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lambeth JD. NOX enzymes and the biology of reactive oxygen. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:181–189. doi: 10.1038/nri1312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Locht C, Antoine R, Jacob-Dubuisson F. Bordetella pertussis, molecular pathogenesis under multiple aspects. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2001;4:82–89. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(00)00169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Malinski T, Taha Z. Nitric oxide release from a single cell measured in situ by a porphyrinic-based microsensor. Nature. 1992;358:676–678. doi: 10.1038/358676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Maragos CM, Morley D, Wink DA, Dunams TM, Saavedra JE, Hoffman A, Bove AA, Isaac L, Hrabie JA, Keefer LK. Complexes of NO with nucleophiles as agents for the controlled biological release of nitric oxide. Vasorelaxant effects. J Med Chem. 1991;34:3242–3247. doi: 10.1021/jm00115a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Martinez de Tejada G, Miller JF, Cotter PA. Comparative analysis of the virulence control systems of Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica. Mol Microbiol. 1996;22:895–908. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1996.01538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.McCord JM, Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein) J Biol Chem. 1969;244:6049–6055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.McCormack FX, Whitsett JA. The pulmonary collectins, SP-A and SP-D, orchestrate innate immunity in the lung. J Clin Invest. 2002;109:707–712. doi: 10.1172/JCI15293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Michan C, Manchado M, Dorado G, Pueyo C. In vivo transcription of the Escherichia coli oxyR regulon as a function of growth phase and in response to oxidative stress. J Bacteriol. 1999;181:2759–2764. doi: 10.1128/jb.181.9.2759-2764.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Morris SL, Walsh RC, Hansen JN. Identification and characterization of some bacterial membrane sulfhydryl groups which are targets of bacteriostatic and antibiotic action. J Biol Chem. 1984;259:13590–13594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Moskwa P, Lorentzen D, Excoffon KJ, Zabner J, McCray PB, Jr, Nauseef WM, Dupuy C, Banfi B. A novel host defense system of airways is defective in cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:174–183. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200607-1029OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Nathan C, Shiloh MU. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates in the relationship between mammalian hosts and microbial pathogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:8841–8848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.16.8841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Pacelli R, Wink DA, Cook JA, Krishna MC, DeGraff W, Friedman N, Tsokos M, Samuni A, Mitchell JB. Nitric oxide potentiates hydrogen peroxide-induced killing of Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1995;182:1469–1479. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.5.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Pantano C, Anathy V, Ranjan P, Heintz NH, Janssen-Heininger YM. Nonphagocytic oxidase 1 causes death in lung epithelial cells via a TNF-RI-JNK signaling axis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2007;36:473–479. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2006-0109OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Parkhill J, Sebaihia M, Preston A, et al. Comparative analysis of the genome sequences of Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica. Nat Genet. 2003;35:32–40. doi: 10.1038/ng1227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ricciardolo F. Multiple roles of nitric oxide in the airways. Thorax. 2003;58:175–182. doi: 10.1136/thorax.58.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Riley DP, Rivers WJ, Weiss RH. Stopped-flow kinetic analysis for monitoring superoxide decay in aqueous systems. Anal Biochem. 1991;196:344–349. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90476-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Robbins RA, Barnes PJ, Springall DR, Warren JB, Kwon OJ, Buttery LD, Wilson AJ, Geller DA, Polak JM. Expression of inducible nitric oxide in human lung epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994;203:209–218. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Robbins RA, Springall DR, Warren JB, et al. Inducible nitric oxide synthase is increased in murine lung epithelial cells by cytokine stimulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994;198:835–843. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Robinson NP, Kyle H, Webber SE, Widdicombe JG. Electrolyte and other chemical concentrations in tracheal airway surface liquid and mucus. J Appl Physiol. 1989;66:2129–2135. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.5.2129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Rochelle LG, Fischer BM, Adler KB. Concurrent production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species by airway epithelial cells in vitro. Free Radic Biol Med. 1998;24:863–868. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(97)00375-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Sampson JB, Ye Y, Rosen H, Beckman JS. Myeloperoxidase and horseradish peroxidase catalyze tyrosine nitration in proteins from nitrite and hydrogen peroxide. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1998;356:207–213. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1998.0772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Schmidt HH, Walter U. NO at work. Cell. 1994;78:919–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Shiloh MU, MacMicking JD, Nicholson S, Brause JE, Potter S, Marino M, Fang F, Dinauer M, Nathan C. Phenotype of mice and macrophages deficient in both phagocyte oxidase and inducible nitric oxide synthase. Immunity. 1999;10:29–38. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Soane MC, Jackson A, Maskell D, Allen A, Keig P, Dewar A, Dougan G, Wilson R. Interaction of Bordetella pertussis with human respiratory mucosa in vitro. Respir Med. 2000;94:791–799. doi: 10.1053/rmed.2000.0823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Spencer JP, Jenner A, Chimel K, Aruoma OI, Cross CE, Wu R, Halliwell B. DNA strand breakage and base modification induced by hydrogen peroxide treatment of human respiratory tract epithelial cells. FEBS Lett. 1995;374:233–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01117-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Squadrito GL, Pryor WA. Mapping the reaction of peroxynitrite with CO2: energetics, reactive species, and biological implications. Chem Res Toxicol. 2002;15:885–895. doi: 10.1021/tx020004c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Stainer DW, Scholte MJ. A simple chemically defined medium for the production of phase I Bordetella pertussis. J Gen Microbiol. 1970;63:211–220. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-2-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Thomas DD, Espey MG, Vitek MP, Miranda KM, Wink DA. Protein nitration is mediated by heme and free metals through Fenton-type chemistry: an alternative to the NO/O2− reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:12691–12696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.202312699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.van der Vliet A, Eiserich JP, Halliwell B, Cross CE. Formation of reactive nitrogen species during peroxidase-catalyzed oxidation of nitrite. A potential additional mechanism of nitric oxide-dependent toxicity. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:7617–7625. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.12.7617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Weber H, Engelmann S, Becher D, Hecker M. Oxidative stress triggers thiol oxidation in the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase of Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Microbiol. 2004;52:133–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.03971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Wilson R, Dowling RB, Jackson AD. The biology of bacterial colonization and invasion of the respiratory mucosa. Eur Respir J. 1996;9:1523–1530. doi: 10.1183/09031936.96.09071523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Wu W, Chen Y, Hazen SL. Eosinophil peroxidase nitrates protein tyrosyl residues. Implications for oxidative damage by nitrating intermediates in eosinophilic inflammatory disorders. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:25933–25944. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.36.25933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]