Abstract
Chemosensation in the nervous system of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans depends on sensory cilia, whose assembly and maintenance requires the transport of components such as axonemal proteins and signal transduction machinery to their site of incorporation into ciliary structures. Members of the heteromeric kinesin family of microtubule motors are prime candidates for playing key roles in these transport events. Here we describe the molecular characterization and partial purification of two heteromeric kinesin complexes from C. elegans, heterotrimeric CeKinesin-II and dimeric CeOsm-3. Transgenic worms expressing green fluorescent protein driven by endogenous heteromeric kinesin promoters reveal that both CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 are expressed in amphid, inner labial, and phasmid chemosensory neurons. Additionally, immunolocalization experiments on fixed worms show an intense concentration of CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 polypeptides in the ciliated endings of these chemosensory neurons and a punctate localization pattern in the corresponding cell bodies and dendrites. These results, together with the phenotypes of known mutants in the pathway of sensory ciliary assembly, suggest that CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 drive the transport of ciliary components required for sequential steps in the assembly of chemosensory cilia.
INTRODUCTION
In the simple nervous system of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, sensory cilia play important roles in controlling behaviors that depend on chemosensory function. They do this by detecting environmental cues such as nutrients, odorants, pheromones, or high osmolarity, which can act as attractants, repellants, or regulators of mating, egg laying, development, feeding, or movement (Chou et al., 1996). Of the 302 neurons that make up the adult hermaphrodite nervous system, 60 have ciliated dendritic endings, and of these, 26 have chemosensory functions (Ward et al., 1975; Perkins et al., 1986; White et al., 1986; Bargmann et al., 1990; Chou et al., 1996). These chemosensory neurons are bipolar, and most have ciliated dendritic processes that contact the environment through openings in the cuticle. The chemosensory receptors that detect chemical cues are thought to be transmembrane proteins that reside on these sensory cilia, which act as specialized compartments for concentrating the sensory signal transduction machinery (Chou et al., 1996; Dwyer, 1998). Little is known of how sensory cilia are assembled or how sensory receptors are moved from their site of synthesis in cell bodies to the ciliary endings, but it is plausible to think that microtubule-based transport is involved (Perkins et al., 1986; Tabish et al., 1995; Scholey, 1996; Cole et al., 1998; Dwyer, 1998).
Sensory cilia, together with motile cilia and flagella, form a widespread group of related microtubule-based eukaryotic organelles that have evolved to function in motility and sensory transduction (Johnson, 1995; Stephens, 1995). Motile and sensory cilia have a similar design, consisting of a membrane-bounded cylinder surrounding nine doublet microtubules (MTs). In motile cilia, the concerted action of accessory structures such as dynein arms, radial spokes, and nexin links causes cilia to beat in a coherent manner (Johnson, 1995). In nonmotile sensory cilia, however, ciliary beating does not occur, and the cilia have a relatively simple structure lacking dynein and nexin arms, radial spokes, and the central pair apparatus (Perkins et al., 1986).
The assembly of ciliary axonemes involves the synthesis of axonemal precursors in the cytoplasm and the transport of preassembled complexes along cytoplasmic microtubules to the base of the axoneme, followed by their translocation to the distal tip of the ciliary axoneme where they are incorporated (Johnson and Rosenbaum, 1992; Johnson, 1995; Stephens, 1995). There is no protein synthesis or vesicle transport in cilia, so axonemal components are synthesized in the cell body, preassembled, and then transported as large protein complexes (Kozminski et al., 1995; Piperno and Mead, 1997). Recent work suggests that members of the heteromeric kinesin family of motors play key roles in delivering components required for ciliary assembly (Cole et al., 1992, 1993, 1998; Walther et al., 1994; Kozminski et al., 1995; Morris and Scholey, 1997).
The kinesins constitute a superfamily of microtubule-based motor proteins that drive various forms of intracellular transport (Vale and Fletterick, 1997), and some kinesin motors, including members of the heteromeric kinesin family, are known to be present in motile axonemes (Bernstein et al., 1994; Scholey, 1996). Heteromeric kinesins, as exemplified by heterotrimeric Kinesin-II from sea urchin, move to the plus ends of microtubules at ∼0.4 μm/s, and typically consist of two different heterodimerized, kinesin-related motor subunits (KRP85 and KRP95) linked by a coiled coil rod to a tail where an accessory subunit (KAP) of unknown function is localized (Cole et al., 1992, 1993, 1998; Rashid et al., 1995; reviewed by Scholey, 1996; Wedaman et al., 1996; Yamazaki et al., 1996; Hirokawa, 1998).
Immunolocalization and functional studies suggest that heteromeric kinesins may be multifunctional, participating in cytoplasmic vesicle transport as well as in the formation and function of axonemes (Kondo et al., 1994; Pesavento et al., 1994; Henson et al., 1995, 1997; Kozminski et al., 1995; Yamazaki et al., 1995, 1996; Vashishtha et al., 1996; Morris and Scholey, 1997; Piperno and Mead, 1997; Rogers et al., 1997; Muresan et al., 1998; Yang et al., 1998) (for review, see Scholey, 1996). For example, inhibiting the function of Kinesin-II using dominant negative constructs in Xenopus-derived cultured cells or melanophores disrupts the transport of membrane-bounded organelles (Le Bot et al., 1998; Tuma et al., 1998). On the other hand, inhibiting the function of Kinesin-II in sea urchin embryos with anti-Kinesin-II mAbs results in short, paralyzed cilia on blastulae, suggesting that Kinesin-II functions to elongate a short precursor “procilium” by driving the anterograde transport of ciliary components along the axoneme for delivery at the distal tip (Morris and Scholey, 1997). This model is consistent with studies done on the product of the Chlamydomonas FLA10 gene, which encodes a subunit of a heterotrimeric Kinesin-II motor that is required for the intraflagellar transport of electron-dense rafts beneath the flagellar membrane (Walther et al., 1994; Kozminski et al., 1995; Cole et al., 1998). These rafts have been shown to be assembled from 16S subunits composed of several polypeptides that display sequence homology with proteins that are required for sensory cilia formation in C. elegans, including the products of the osm-1 and osm-6 genes (Piperno et al., 1996; Piperno and Mead, 1997; Cole et al., 1998).
In C. elegans, mutations in the osm-1 and osm-6 genes result in defects in the structure and function of sensory cilia and corresponding defects in chemosensory behavior (Perkins et al., 1986; Starich et al., 1995; Collet et al., 1998). Similar phenotypic effects are displayed by worms carrying mutations in the osm-3 gene, which encodes a relative of one of the motor subunits of Kinesin-II (Perkins et al., 1986; Shakir et al., 1993; Tabish et al., 1995). Our own interest in heteromeric kinesins in C. elegans began with our observation that a close relative of the accessory subunit of sea urchin heterotrimeric Kinesin-II, CeKAP, was predicted to be encoded by an open reading frame located on a cosmid sequenced by the C. elegans genome sequencing consortium (Wedaman et al., 1996). These results suggested that OSM-3 and CeKAP were subunits of a heteromeric Kinesin-II motor that plays an important role in the assembly of sensory cilia in C. elegans, by transporting the OSM-1 and OSM-6 proteins into the sensory cilia where they contribute to axoneme assembly or maintenance (Wedaman et al., 1996; Cole et al., 1998).
Here we report that OSM-3 and CeKAP are in fact assembled into two distinct heteromeric kinesin holoenzymes: heterotrimeric CeKinesin-II, which contains CeKAP together with two distinct motor subunits, CeKRP95 and CeKRP85; and dimeric CeOsm-3, containing the OSM-3 polypeptide. Our data suggest that both heteromeric kinesins participate in sensory ciliogenesis and/or transport of chemosensory factors to the ciliated endings of amphid, inner labial, and phasmid chemosensory neurons.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cloning and Sequencing of CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 Polypeptides
CeKRP95.
Expressed sequence tag (EST) clone yk90a2 was obtained from Yuji Kohara (Gene Library Lab, National Institute of Genetics, Mishima, Japan). This clone was identified as a likely homologue of sea urchin SpKRP95 in a BLAST search using the deduced amino acid sequence of SpKRP95 against proteins listed in the C. elegans genome project database. The [lamba]-ZAP II phage clones were plaque purified using the XLI-Blue host strain, and the pBluescript-KS phagemid was excised using standard in vivo excision methods (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA). The cDNA clone was sequenced on both strands using automated sequencing methods.
CeKRP85 and CeKAP.
EST clones yk284b4 and yk94g1, which encode CeKRP85 and CeKAP, respectively, were obtained from Yuji Kohara and prepared as described above. Sequencing data revealed that clone yk94g1 did not contain the full-length cDNA for CeKAP, so the 5′ end was obtained by a PCR screen on cDNA made from mixed stage nematode cultures. Briefly, poly(A+) mRNA was prepared from 1 g of C. elegans using the Oligotex Direct mRNA kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA). cDNA was prepared by reverse transcription of mRNA using SuperScriptII reverse transcriptase (Life Technologies, Gaithersburg, MD) and CeKAP-specific primers. Nested PCR was performed on the cDNA using CeKAP-specific primers (3′ primer from known sequence, 5′ primer based on ORF data), and the PCR products were subcloned into pCR2.1 cloning vectors (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). To identify positive clones, colony hybridization was performed on transformants using CeKAP-specific probes generated by PCR and Klenow multiprime extension labeling.
osm-3.
The full-length cDNA predicted for osm-3 was amplified using nested PCR on C. elegans cDNA as described above for CeKAP. Multisequence alignments were performed using Pileup (Genetics Computer Group, Madison, WI; Devereux et al., 1984), Clustal W (Thompson et al., 1994), and SeqVu (Garvan Institute of Medical Research, Sydney, Australia).
Antibody Production
Antibodies were raised against the nonconserved tail domains of CeKRP95 and OSM-3 and against nearly full-length CeKAP protein. cDNAs encoding the tail domains of CeKRP95 and OSM-3 were PCR amplified and subcloned into PET-28B (SacI–NotI) and PRSETB (EcoRI) expression vectors, respectively. Both vectors generate recombinant proteins with an amino-terminal (HIS)6 tag. EST clone yk94g1 was subcloned into the PRSETB (BamHI) expression vector, which drives the expression of a CeKAP-(HIS)6 fusion protein containing all but the first 33 amino acids of CeKAP. These constructs were transformed into Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) competent cells (Novagen, Madison, WI) for expression. The three recombinant fusion proteins were expressed and then purified on Ni-NTA Superflow resin under denaturing conditions as described by the manufacturer (Qiagen). Column fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, and peak fractions were dialyzed extensively into PBS (Sambrook et al., 1989).
Polyclonal antisera against CeKRP95, OSM-3, and CeKAP were raised in rabbits by Berkeley Antibody (Richmond, CA). Because of the common occurrence of preexisting antibodies against C. elegans proteins in naive rabbits, a total of 40 preimmune rabbits were screened for immunoreactivity by immunoblot analysis against C. elegans lysate and 5′-adenylyl-β,γ-imidodiphosphate (AMPPNP) MT pellet preparations. Rabbits that showed the least preinjection immunoreactivity against C. elegans proteins were chosen for injection. Two rabbits for each antigen were injected and bled by Berkeley Antibody using standard methods. Immune sera were screened by immunoblot analysis against C. elegans lysate, AMPPNP MTs, and ATP-eluted microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs). For affinity purification of antibodies, glutathione S-transferase (GST)-CeKRP95 and GST-OSM-3 fusion proteins were generated by subcloning cDNAs encoding the tail domains into pGEX-KG expression constructs. These fusion proteins were used to eliminate the copurification of contaminating anti-(HIS)6/T7 tag antibodies. The recombinant proteins were expressed and purified under native conditions on glutathione-Sepharose as described by the manufacturer (Pharmacia, Piscataway, NJ), and covalently coupled to Affigel-10 (GST-OSM-3) and Affigel-15 (GST-CeKRP95) affinity resin using standard methods (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA). CeKRP95 and OSM-3 antibodies were affinity purified by passing the antisera over the affinity columns, washing the column extensively with PBS, followed by elution with 0.2 M glycine (pH 2.8). Blot affinity purification was used to purify CeKAP-specific antibodies as described elsewhere (Harlow and Lane, 1988). All affinity-purified antibodies were tested for specificity by immunoblot analysis against their corresponding fusion protein, C. elegans lysate, AMPPNP MT pellets, and ATP-eluted MAPs.
Large-Scale Growth and Culture of C. elegans
C. elegans N2 wild-type worms were grown in large-scale liquid cultures using techniques modified from that described by Lye et al. (1987). Specifically, N2 worms were first grown to high density on 5–10 large NGM-agar plates seeded with the E. coli strain NA22. The worms were then used to inoculate a 16-l culture of S-basal media (19.3 mM K2HPO4, 25 mM KH2PO4, 100 mM NaCl, 2 mg/l cholesterol, pH 6.8) in a Belco spinner flask (Belco Glass, Vineland, NJ), which had been preaerated using house air supplies for several hours before inoculation. After inoculation, NA22 E. coli were added daily in 30- to 35-g quantities until the worms were ready for harvesting. The nematodes were cultured with aeration (house air and stirring) at room temperature until near saturation but without starving (monitored by dauer formation). The worms were settled by placing the culture at 4°C overnight, pelleted with low-speed centrifugation (1000 × g), and washed several times in PMEG buffer (100 mM piperazine-N,N′-bis[2-ethanesulfonic acid], 2.5 mM MgS04, 0.5 mM EDTA, 5 mM EGTA, 1 mM DTT, 0.9 M glycerol, pH 6.9, supplemented with protease inhibitors: 10 μg/ml leupeptin, 2 μg/ml aprotinin, 1 μg/ml pepstatin, 20 μg/ml benzamidine, 1 mg/ml Nα-p-tosyl-l-arginine methyl ester, 0.1 mM PMSF, and 0.1 mg/ml soybean trypsin inhibitor). The final worm pellet was frozen in LiN2 and stored at −80°C until further use. The NA22 E. coli used for food were grown in 16-l batches using Terrific Broth (Sambrook et al., 1989) stirred in a spinner flask with aeration overnight at room temperature. The saturated bacteria culture was pelleted and then resuspended in S-basal buffer and stored at 4°C until further use.
Biochemical Purification of Kinesin Holoenzymes
CeKinesin-II, CeOsm-3, and CeKinesin holoenzymes were partially purified using an MT affinity precipitation and purification scheme modified from that described by Cole et al. (1993). Specifically, frozen C. elegans pellets (80–100 g) were thawed on ice and then resuspended in 2× vol (wt/vol) of PMEG supplemented with protease inhibitors. The worm suspension was French press homogenized at 8000–10,000 psi, and the lysate was spun at 50,000 × g for 45 min. The supernatant was removed and spun for an additional 60 min at 150,000 × g. The high-speed supernatant was supplemented with 2 mM GTP, 20 μM Taxol, 10 U/ml hexokinase, and 50 mM glucose, and MTs were polymerized by incubating the extract at 16°C for 20 min. MAPs were bound to MTs with the addition of 2 mM AMPPNP and an additional incubation of 25 min at 16°C. The MTs and associated proteins were pelleted through a 15% sucrose cushion (in PMEG), and the MT pellet was washed in PMEG without MgSO4. The bound MT motors were eluted for 4–6 h at 4°C with the addition of 10 mM ATP, 10 mM MgS04, and 200 mM KCl in PMEG without glycerol (PME). The MTs were pelleted, and the motor-containing supernatant was fractionated using fast-performance liquid chromatography (FPLC)-Superose-6 gel filtration chromatography (Pharmacia). Fractions were analyzed for CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 by SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis using anti-CeKRP95, anti-CeKAP, and anti-OSM-3 antibodies. Peak fractions were pooled and dialyzed extensively into a low-ionic-strength buffer (20 mM Tris, 0.5 mM EDTA, 2.5 mM MgS04, 1 mM DTT), and the dialysate was fractionated by FPLC-Mono-Q anion exchange chromatography (Pharmacia), eluting in a salt gradient of 0–500 mM NaCl. Peak fractions for CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 were loaded separately onto 5–20% linear sucrose gradients and separated by ultracentrifugation, and the fractions were analyzed by immunoblot analysis.
Immunoprecipitation of CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 Motor Complexes
MAPs eluted from MT pellets with ATP were used to immunoprecipitate CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 polypeptides. ATP-eluted MAPs were separated into four aliquots and then precleared for 30 min on ice with the addition of preimmune sera from CeKRP95, OSM-3, and CeKAP rabbit and nonspecific mouse immunoglobulin G (for SUK-4 immunoprecipitations). The nonspecific antibody–antigen complexes were captured using protein A-Sepharose beads (Bio-Rad), and the precleared supernatant was immunoprecipitated for 1 h on ice using anti-CeKRP95, anti-OSM-3, anti-CeKAP, and anti-kinesin heavy chain (SUK-4) antibodies. The immune complexes were isolated with protein A beads that had been preblocked in 1 mg/ml soybean trypsin inhibitor and 10% BSA in PME. The beads were washed extensively in PME, and the immunoprecipitated proteins were eluted with Laemmli SDS-sample buffer (Sambrook et al., 1989) and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis.
Production of Promoter::GFP Transgenic Worms
Standard molecular biology techniques were used (Sambrook et al., 1989). The following fusion constructs were prepared for transformation into wild-type N2 worms: 1) CeKRP95 promoter::GFP constructs, which include a 4- or 1.5-kb Pfu-polymerase–amplified region immediately upstream of the CeKRP95 ORF (F20C5.2) in cosmid F20C5, inserted into the KpnI site of the GFP vector pPD95.75; this construct places the putative promoter immediately 5′ of the GFP gene; 2) osm3 promoter::GFP, which includes 2 kb of 5′ sequence directly upstream of the osm-3 gene in cosmid M02B7, also inserted into the KpnI site of pPD95.75; and 3) CeKAP promoter::GFP, which includes 1150 bp of 5′ sequence upstream from the CeKAP ORF F08F8.3, amplified from cosmid F56C9 and inserted into the KpnI site as described above. All cosmids were provided by Dr. Alan Coulson (Sanger Center, Cambridge, United Kingdom), and GFP vectors (including pPD95.75) were acquired from Dr. Andrew Fire’s Laboratory (Carnegie Institute of Washington, Baltimore, MD).
Wild-type N2 worms were maintained on MYOB nutrient agar plates containing OP50 E. coli at 20°C as described (Brenner, 1974). Germ line transformation was performed as previously described by microinjecting the recombinant DNA described above at 100 μg/ml into the germ cells of the adult gonad syncitium (Fire, 1986; Mello et al., 1991). As a cotransformation marker, plasmid pRF4, which contains the semidominant mutation rol-6 (su1006), was coinjected at a concentration of 100 μg/ml (Kramer et al., 1990). Transgenic roller hermaphrodites were picked from which stably transformed lines were recovered. Heritable roller lines were analyzed for GFP expression by epifluorescence microscopy, and images were collected by laser scanning confocal microscopy (Leica, Deerfield, IL; DM IRBE/TCS NT). The transformed lines were prepared for imaging by two different methods: 1) live worms were anesthetized using 1 mM levamisole in M9 buffer and then mounted onto 2% agarose pads as described elsewhere (Miller and Shakes, 1995); and (2) the worms were fixed briefly in 1% formaldehyde in M9 buffer and then mounted onto poly-l-lysine–coated slides.
Immunostaining
To immunolocalize CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 in C. elegans, mixed stage wild-type cultures were prepared for antibody staining using methods described by Finney and Ruvkun (1990) and Finney (1991; Fixation and Permeabilization Protocol, Comprehensive Protocol Collection C. elegans home page, http://www.dartmouth.edu/artsci/bio/ambros/protocols/worm_protocols.html). Briefly, worms were cultured on NGM-agar plates seeded with OP50 E. coli, washed off with M9 buffer, and then washed twice in M9 to remove contaminating bacteria. The washed worm pellet was resuspended in an ice-cold solution of 1× “Modified Ruvkun’s witches brew” (80 mM KCl, 20 mM NaCl, 10 mM EGTA, 5 mM spermidine-HCl, 15 mM Na-mM piperazine-N,N′-bis[2-ethanesulfonic acid], pH 7.4, 25% methanol) and 2% p-formaldehyde. The worms were incubated in fixative for 20 min on ice and then frozen on dry ice/ethanol, thawed, and rocked an additional 20 min at room temperature. The worms were pelleted and washed in Tris-Triton Buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 1% Triton X-100, 1 mM EDTA) and then incubated in 1% β-mercaptoethanol/Tris-Triton buffer for 1 h at room temperature to reduce disulfide linkages in the cuticle. The worms were washed once in borate buffer (25 mM H3BO3, 12.5 mM NaOH, pH 9.2) and then incubated in 10 mM DTT/borate buffer for 15 min at room temperature. The permeabilized worms were washed once in borate buffer and then incubated in 1% H202/borate buffer for 15 min at room temperature to oxidize free sulfhydryl groups. The H202 was washed away extensively with borate buffer, and the worms were processed for immunostaining. The worm samples were blocked for 1 h at room temperature with 10% normal goat serum in PBST-A (1× PBS, 1% BSA, 0.5% Triton X-100, 1 mM EDTA), settled by gravity, then incubated with immune antibodies diluted 1:200 in PBST-A for 2 h at room temperature. The worms were washed in PBST-B (1× PBS, 0.1% BSA, 0.5% Triton X-100, 1 mM EDTA) and then incubated in RITC-conjugated goat anti-rabbit antibodies (Jackson Immunoresearch Laboratories, West Grove, PA) diluted 1:200 in PBST-A. Secondary antibodies were preadsorbed against whole fixed worms before staining. The worms were washed and then mounted and visualized by confocal microscopy.
RESULTS
Molecular Analysis of C. elegans Heteromeric Kinesins
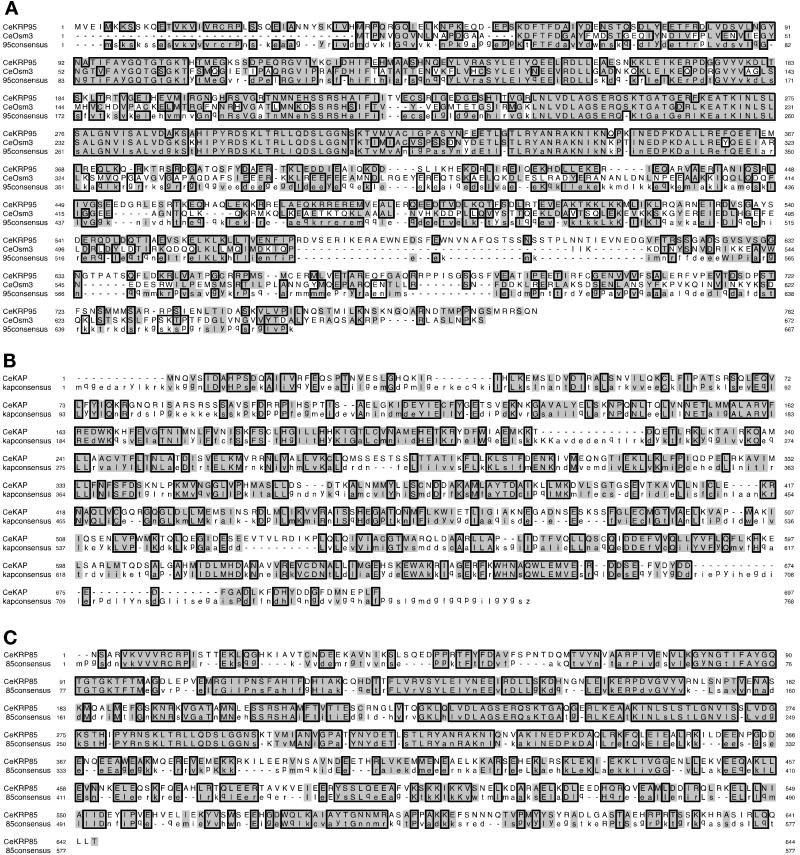
Using the deduced amino acid sequences of sea urchin heteromeric Kinesin-II motor polypeptides in BLAST searches into the C. elegans genome database, we identified sequences of two kinesin-related polypeptides, CeKRP85 and CeKRP95, which, like OSM-3 (Shakir et al., 1993), are members of the heteromeric kinesin subfamily. Additionally, in earlier attempts to identify Kinesin-II subunits in C. elegans, Wedaman et al. (1996) identified a likely C. elegans homologue of the urchin SpKAP accessory polypeptide encoded by an ORF provided by the C. elegans genome project. Collectively, these sequences in the C. elegans genome database suggested that there was indeed a Kinesin-II homologue in worms, and that it contained polypeptides with high sequence homology to their sea urchin counterparts. To further analyze these heteromeric kinesin polypeptides, we obtained cDNAs encoding full-length OSM-3, CeKRP95, and CeKAP and a partial clone encoding CeKRP85. We used their corresponding deduced amino acid sequences in alignments against consensus sequences generated from all known homologues (Figure 1). The deduced amino acid sequences for CeKRP95, CeKRP85, and OSM-3 suggest that these three motors contain an amino-terminal motor, internal stalk, and carboxy-terminal tail domain organization characteristic of other plus end–directed, kinesin-related motors (Figures 2 and 3A).
Figure 1.
Sequence analysis of C. elegans heteromeric kinesin polypeptides. Amino acid sequences deduced from full-length cDNAs encoding full-length CeKRP95 and Osm-3 (A), CeKAP (B), and nearly full-length CeKRP85 (C) were used in alignments against consensus sequences generated using the deduced amino acid sequences from all other known heteromeric kinesin subunits. Alignments and consensus sequences were generated using Clustal W (Thompson et al., 1994) and Lineup software (Genetics Computer Group analysis software; Devereux et al., 1984), and the figure was generated using SeqVu alignment software (Garvan Institute of Medical Research). Color blocks denote sequence homology; line blocks denote sequence identity; and dashes denote gaps in sequence or no consensus.
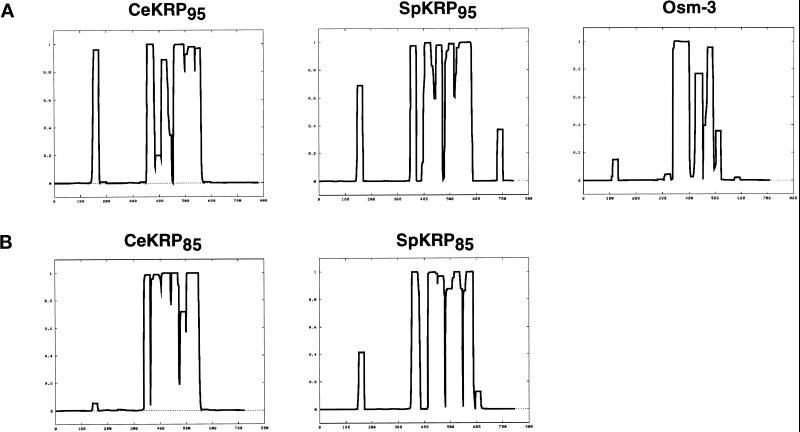
Figure 2.
Probability of α-helical coiled coil formation in the heteromeric kinesin polypeptides. The deduced amino acid sequences of C. elegans heteromeric motor polypeptides (CeKRP95, CeKRP85, and Osm-3) and, for comparison, sea urchin Kinesin-II motor polypeptides (SpKRP85 and SpKRP95) were analyzed for the probability of forming α-helical coiled coils using the Coils program (Lupas et al., 1991). The plots were generated using a window width of 21 and no weighing of a and d positions. (A) Comparison of coils outputs for KRP95-related polypeptides; (B) comparison of coils outputs for KRP85-related polypeptides. The predicted region of the coiled coil corresponds to the following spans of amino acids: 350–580 for CeKRP95; 340–560 for CeKRP85; 340–510 for Osm-3; 350–590 for SpKRP95; and 350–600 for SpKRP85. The results predict that CeKRP85 and CeKRP95 form similar-sized coiled coils that are 33–35 nm long, SpKRP85 and SpKRP95 form similar-sized coiled coils 36–38 nm long, and Osm-3 forms a shorter coiled coil only 26 nm in length.
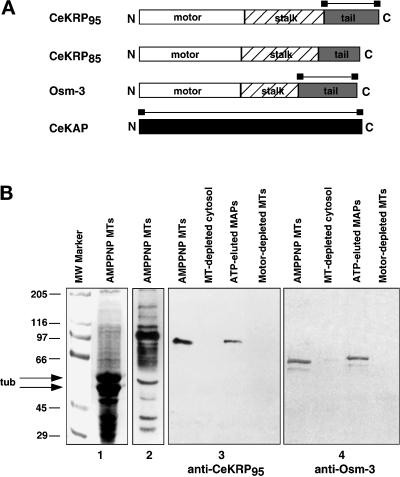
Figure 3.
Maps of heteromeric kinesin polypeptides and demonstration of antibody specificity. (A) Schematic representation of C. elegans heteromeric kinesin polypeptides. Maps of CeKRP95, CeKRP85 and Osm-3, demonstrate the predicted organization of these heteromeric kinesin polypeptides into motor, stalk, and tail domains, which are characteristic of kinesin-related motor proteins. CeKAP has no obvious domains or motifs. Bars indicate regions used to generate CeKRP95-, Osm-3-, and CeKAP-specific antibodies. (B) Immunoblots of C. elegans MTs and associated motors demonstrating antibody specificity. (1) Coomassie Blue–stained gel of AMPPNP MTs; (2) corresponding immunoblot probed with pan-kinesin antibodies; (3) immunoblot using anti-CeKRP95 antibodies against AMPPNP MT pellets, MT-depleted supernatant, ATP-eluted MAPs, and MT pellet after ATP elution; (4) immunoblot using anti-CeOsm-3 antibodies against the same samples. These blots demonstrate that there are several kinesin-related motors that cosediment with MTs with the addition of AMPPNP, and that two of these motors, CeKRP95 and Osm-3, show enrichment with AMPPNP MTs and effective elution from these MTs with ATP.
The CeKRP95 and CeKAP sequences (Figure 1) diverged significantly from their corresponding ORFs predicted by GeneFinder through the genome project. For example, the ORF for CeKRP95 was predicted to encode a 1130-amino acid polypeptide with a theoretical molecular weight of 129 kDa, whereas our clone indicates that CeKRP95 is actually a 782 amino acid polypeptide with a theoretical molecular mass of 89 kDa (running at 97.3 kDa by SDS-PAGE). CeKRP95 displays greatest homology to sea urchin SpKRP95, with 73 and 55% identity in the motor and full-length protein, respectively. Sequencing data from two overlapping cDNA clones for CeKAP predicts that it is a 690-amino acid polypeptide with a theoretical molecular mass of 78 kDa (running at 82.6 kDa by SDS-PAGE), which is different from the 930-amino acid, 104-kDa polypeptide predicted by GeneFinder. CeKAP displays the greatest homology to mouse KAP3A with 34% identity overall.
The EST clone encoding CeKRP85 is not quite full length; although no genomic sequence is available at this time for CeKRP85, sequence alignments against other known homologues suggest we are missing only ∼10–20 bp at its 5′ end. Our data indicate that CeKRP85 is likely to be a 644-amino acid polypeptide with a theoretical molecular mass of 74 kDa, displaying greatest homology to KIF3A with 65 and 54% identity in the motor and overall, respectively.
Finally, sequence data from our osm-3 cDNA clone revealed, to our surprise, significant deviation from that published by Shakir et al. (1993). The differences are most extensive in regions encoding the stalk and tail domains of the protein, starting at amino acid position 321 and continuing to amino acid 564. The sequences then reunite at amino acid position 565 and match identically through the end of the protein. The deduced amino acid sequence from our clone displays 98% identity in the motor domain with the OSM-3 amino acid sequence published by Shakir et al. (1993) but only 68% identity overall. Our clone encodes an OSM-3 polypeptide that is 671 amino acids in length with a theoretical molecular mass of 76 kDa (running at 75.4 kDa by SDS-PAGE) and displays greatest homology to sea urchin SpKRP95. Although OSM-3 is placed in the heteromeric subfamily of kinesin-related proteins (L. Greene and S. Henikoff [1996] Kinesin home page, http://www.blocks.fhcrc.org./∼kinesin/), it displays only 64 and 41% identity in the motor and overall with SpKRP95, respectively.
In other systems, heteromeric kinesin holoenzymes are proposed to assemble from two distinct motor subunits that are predicted to have similar lengths and distribution of coiled coil in their stalks. Thus, dimerization occurs by forming heterodimeric coiled coils between these regions (Rashid et al., 1995). This is exemplified by SpKRP95 and SpKRP85 of sea urchin heterotrimeric Kinesin-II (Figure 2). The deduced amino acid sequences of CeKRP95 and CeKRP85 predict that they may form similar-sized coiled coils, 230 and 220 residues long, respectively; however, OSM-3 is predicted to have a less extensive coiled coil, only 170 amino acids in length (Figure 2). Assuming each coiled-coil rises 0.15 nm per residue, the simplest interpretation of these data is that CeKRP95 and CeKRP85 heterodimerize to form a 33- to 35-nm coiled coil stalk, whereas OSM-3 dimerizes with itself or with a currently unidentified motor polypeptide to form a coiled coil that is ∼26 nm long.
Partial Purification and Hydrodynamic Properties of Two Heteromeric Kinesin Holoenzymes, CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3
The aforementioned sequence analysis suggested that C. elegans contains two heteromeric kinesin complexes, one containing CeKRP85/95 and the other containing OSM-3. To test this hypothesis and to determine whether CeKAP is an accessory subunit of one or both of these complexes, we used immunoblotting to monitor the behavior of the CeKRP95, OSM-3, and CeKAP polypeptides during the fractionation of cytosolic extracts of C. elegans. Polyclonal antibodies were raised against the nonconserved tail domains of OSM-3 and CeKRP95 and against full-length CeKAP (Figure 3A). These antibodies react specifically with polypeptides of the appropriate molecular mass on immunoblots of MT proteins prepared from mixed stage C. elegans cultures and clearly show that these polypeptides cosediment with MTs with the addition of AMPPNP and elute from MTs with ATP as expected for kinesin-related motors (Figure 3B). In addition to the OSM-3 and CeKRP95 polypeptides, there are other kinesin-related proteins that cosediment with AMPPNP MTs and are detected using pankinesin antibodies (Figure 3B); these are likely to include conventional kinesin heavy chain (UNC-116) and the monomeric kinesin UNC-104 (Otsuka et al., 1991; Patel et al., 1993).
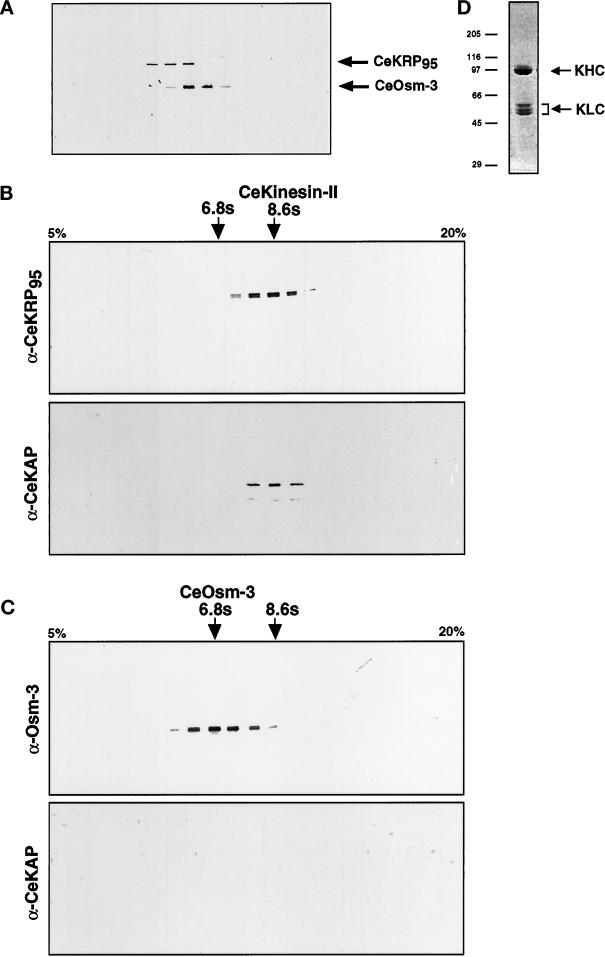
Although OSM-3, CeKRP95, and CeKAP (our unpublished results) all enrich by MT affinity, OSM-3 behaves differently from the other polypeptides during subsequent fractionation. For example, the two motor subunits, OSM-3 and CeKRP95, are separable on gel filtration columns (Figure 4A), anion exchange columns (our unpublished results), and sucrose density gradients (Figure 4, B and C), suggesting that they are components of different holoenzymes. Additionally, CeKAP copurifies exactly with CeKRP95 but not OSM-3 throughout the entire fractionation procedure (e.g., compare gradients in Figure 4, B and C).
Figure 4.
CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 are separable holoenzymes. (A) Immunoblot of a Superose-6 FPLC gel filtration run, probed with a mixture of anti-CeKRP95 and anti-Osm-3 antibodies. CeKinesin-II elutes as a single peak in fraction 29 (Stokes radius of 6.4 nm), and CeOsm-3 elutes as a single peak in fraction 31 (Stokes radius of 5.0 nm). (B and C) The peak fractions of CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 from MonoQ anion exchange chromatography were loaded onto separate 5–20% linear sucrose gradients, and the fractions were analyzed by immunoblot analysis using CeKinesin-II– and CeOsm-3–specific antibodies. (B) CeKinesin-II sucrose gradient fractions probed with anti-CeKRP95 and anti-CeKAP antibodies, showing exact cofractionation of these polypeptides at fraction 14 (8.6S). (C) CeOsm-3 sucrose gradient fractions probed with anti-Osm-3 and anti-CeKAP antibodies, showing that although CeOsm-3 peaks at fraction 11 (6.8S), CeKAP cannot be detected in these gradients. (D) Coomassie Blue–stained gel of purified C. elegans conventional kinesin, obtained using the same protocol as that described for CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3. C. elegans conventional kinesin is highly purified in a monodisperse peak after sucrose gradient centrifugation.
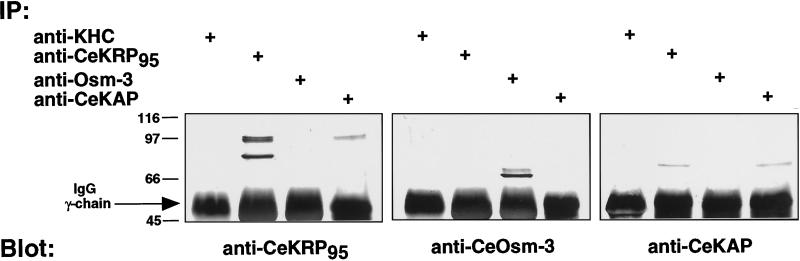
Immunoprecipitation experiments performed on ATP-eluted MAPs support the hypothesis that CeKRP95 and CeKAP are components of one heteromeric kinesin complex that is distinct from OSM-3 (Figure 5). CeKRP95 and CeKAP polypeptides were both immunoprecipitated using anti-CeKRP95 and anti-CeKAP antibodies, but neither peptide was precipitated by anti-OSM-3 or anti-kinesin heavy-chain antibodies. Conversely, the OSM-3 polypeptide is only immunoprecipitated using anti-OSM-3 antibodies. The anti-CeKRP95 antibody also immunoprecipitated a smaller polypeptide of unknown identity, which may represent a proteolytic fragment or isotype of CeKRP95 (Figure 5, left panel). We consider the former explanation to be more likely, because the protein demonstrates unpredictability during fractionation procedures, fails to copurify with CeKRP95, OSM-3, or CeKAP, and appears suddenly in fractions and samples where it had been previously absent. Indeed, we encountered significant problems with proteolysis in C. elegans lysates, which has been previously described by Aamodt and Cullotti (1986).
Figure 5.
Immunoprecipitation of CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 polypeptides. Motors eluted from MTs by the addition of ATP were immunoprecipitated with antibodies against conventional kinesin heavy chain (SUK4 mAb), CeKRP95, Osm-3, and CeKAP. Immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose, and immunoblotted separately with the same antibodies. Antibodies used for immunoprecipitation are indicated by + at the top, and panels 1–3 are blots of immunoprecipitates probed with anti-CeKRP95, anti-Osm-3, and anti-CeKAP antibodies, respectively. These experiments effectively demonstrate coimmunoprecipitation of CeKRP95 and CeKAP with anti-CeKRP95 or anti-CeKAP antibodies but not with anti-Osm-3 antibodies, whereas Osm-3 is only precipitated using anti-Osm-3 antibodies.
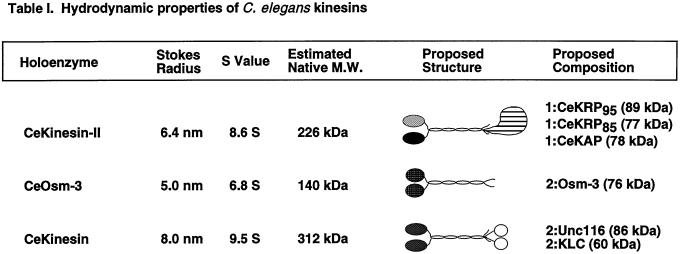
Based on these biochemical fractionation and immunoprecipitation results, it is plausible to hypothesize that C. elegans contains two distinct heteromeric kinesin complexes. In an effort to predict the subunit composition of these two motor complexes, we estimated the native molecular masses of the holoenzymes by characterizing their hydrodynamic properties. We used antibodies to detect the corresponding peak fractions of each polypeptide from gel filtration chromatography and sucrose density gradients, which allowed us to estimate the Stokes radii and sedimentation coefficients of the complexes, respectively (Table 1). We estimated the native molecular mass of the complex containing CeKRP95 and CeKAP at 226 kDa, which is consistent with it being a heterotrimeric structure composed of CeKRP95, CeKRP85, and CeKAP in a 1:1:1 M stoichiometry, similar to the heterotrimeric kinesins that have been characterized in sea urchin, mouse, Chlamydomonas, and Xenopus (Cole et al., 1993, 1998; Wedaman et al., 1996; Yamazaki et al., 1996; Le Bot et al., 1998; Tuma et al., 1998). In contrast, we estimated the native molecular mass of the complex containing OSM-3 to be 140 kDa, which is consistent with it being either a homodimer of two OSM-3 polypeptides or a heterodimer of OSM-3 and an unidentified second motor subunit.
Table 1.
To definitively determine the subunit composition of these two holoenzymes, it will ultimately be important to purify them to homogeneity; however, the low abundance of these proteins in C. elegans has so far precluded us from doing so. Although we were able to accomplish the first purification of the C. elegans conventional kinesin heterotetramer quite easily (Figure 4D and Table 1), we have found the purification of the heteromeric kinesins to be unfeasible using our current methods and starting volumes. For example, from a starting sample of high-speed supernatant containing ∼2.6 g of total protein, we are able to obtain an AMPPNP MT/MAP pellet containing ∼50 mg of total protein, from which ∼3.7 mg of total protein are eluted by ATP. In this ATP eluate, conventional kinesin represents ∼1 mg (or 25%). The last step of purification yields ∼0.4 mg of highly purified C. elegans conventional kinesin, which is active in an MT gliding assay (moving at 2.1 μm/s; our unpublished results). Conversely, we estimate that CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 comprise only ∼2.4 and 1.8% (90 and 65 μg) of the total protein in ATP-eluted MAPs, respectively, and their concentrations during subsequent fractionations are too low to measure accurately. Indeed, we estimate that to purify CeKinesin-II in yields comparable with those obtained from sea urchin (0.1 mg/100 ml of starting cytosol; Wedaman et al., 1996) would require starting with ∼200 l of liquid worm culture.
Expression of GFP by Heteromeric Kinesin Promoters
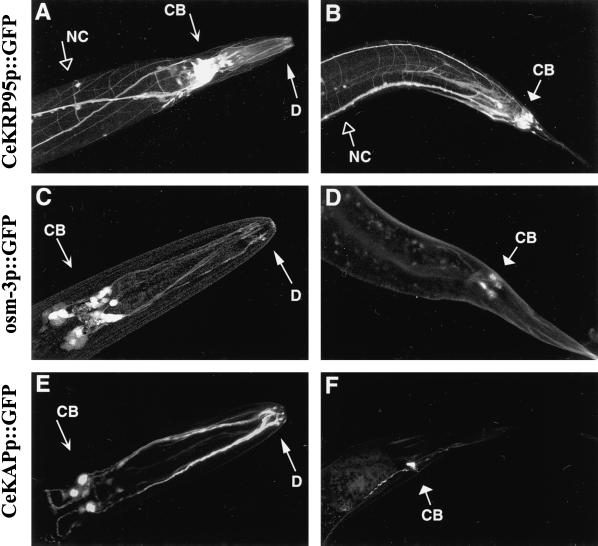
To determine the cell-specific expression of CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3, we monitored the expression of GFP driven by endogenous CeKRP95, CeKAP, and osm-3 promoter sequences. We used germ line transformation to create transgenic worms carrying heritable, extrachromosomal arrays of CeKRP95promoter::GFP, CeKAPpromoter::GFP, and osm-3promoter::GFP constructs (Mello and Fire, 1995). We observed that osm-3promoter::GFP is expressed exclusively in a small subset of neurons; specifically, the amphid, phasmid, and inner labial neurons, which constitute the 26 cells of the chemosensory nervous system (Figure 6, C and D). This result is in agreement with previous results obtained and described by Tabish et al. (1995) using an osm-3promoter::lacZ reporter construct. We observed osm-3promoter::GFP expression in both the cell bodies and dendrites of these chemosensory neurons, with highest expression during L1–L3 larval stages and declining expression in L4 and adult hermaphrodites. However, the expression of this transgene was quite low overall.
Figure 6.
Expression of heteromeric kinesin promoter::GFP constructs in the C. elegans nervous system. Heritable lines of worms carrying extrachromosomal arrays of CeKRP95 promoter::GFP, osm-3 promoter::GFP, or CeKAP promoter::GFP fusion constructs were created and imaged by laser scanning confocal microscopy. Genomic sequences upstream from the CeKRP95, Osm-3, and CeKAP genes were fused to a GFP reporter, and the constructs were singularly coinjected into hermaphrodite gonads of N2 wild-type worms with the dominant rol-6 marker. Heritable lines of worms displaying the roller phenotype were isolated and analyzed for GFP expression. Shown are the head (left) and tail (right) regions of CeKRP95 promoter-GFP transgenics (A and B), osm-3 promoter::GFP transgenics (C and D), and CeKAP promoter::GFP transgenics (E and F). CB, cell body; D, dendrite; NC, nerve cords and associated commissures. (B, D, and F) GFP expression in the phasmid chemosensory neurons of the tail; (A, C, and E) GFP expression in the cell bodies and dendrites of the amphid and inner labial chemosensory neurons in the head. A and B also indicate widespread neuronal expression in CeKRP95 promoter::GFP worms, with GFP being expressed in the nerve ring and the dorsal and ventral nerve cords and associated commissures.
Promoter::GFP constructs for one of the two motor subunits of CeKinesin-II, namely CeKRP95, as well as the presumptive accessory subunit, CeKAP, also revealed that these promoters drive the expression of GFP in the cell bodies and dendrites of all 26 chemosensory neurons in the head and tail of the worm (Figure 6, A, B, E, and F). In addition, the CeKRP95promoter::GFP was also expressed throughout the nervous system, displaying a striking GFP pattern in the neuronal processes of the major nerve cords and associated commissures (Figure 6, A and B). Although the majority of CeKAPpromoter::GFP expression was seen in the chemosensory neurons, light GFP expression was also seen in the dorsal and ventral nerve cords in a pattern similar to that displayed by CeKRP95promoter::GFP transgenic worms. However, because of the low level of GFP expression outside the chemosensory nervous system, these images were difficult to capture. Both CeKRP95promoter::GFP and CeKAPpromoter::GFP transgenics showed early GFP expression, but in contrast to osm-3 transgenic worms, the intensity of GFP expression seemed to increase with age. Overall, the data provide strong evidence that the two heteromeric kinesin complexes are expressed in the chemosensory nervous system and, specifically, in the amphid, inner labial, and phasmid chemosensory neurons. Our data also raise the possibility that CeKinesin-II may be expressed in other neurons as well.
Immunolocalization of CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 Polypeptides in the C. elegans Nervous System
We used affinity-purified antibodies specific for the CeKRP95, CeKAP, and OSM-3 polypeptides in immunofluorescence microscopy experiments to determine the cell-specific and subcellular localization of CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3. Confocal images of fixed and stained nematodes are shown in Figure 7. Because of stage-specific differences in promoter::GFP expression for CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3, we chose to provide images of L2–L4 stage worms for comparison, because these stages provide the clearest examples of the spatial localization for all three polypeptides.
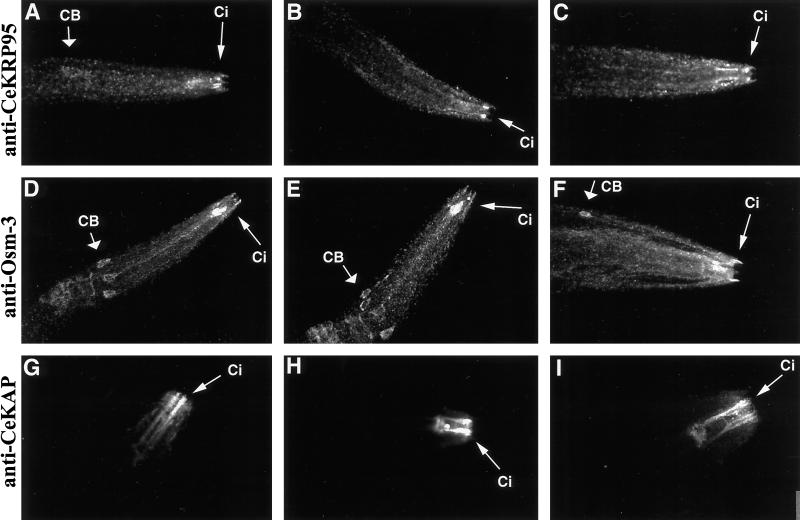
Figure 7.
CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 polypeptides immunolocalize to and concentrate in the ciliated endings of chemosensory neurons. Growing cultures of mixed stage N2 wild-type worms were fixed and permeabilized, then used to immunolocalize the CeKRP95, Osm-3, and CeKAP polypeptides. Shown are confocal projections of L2–L4 stage worms stained with anti-CeKRP95 antibodies (A–C), anti-Osm-3 antibodies (D–F), and anti-CeKAP antibodies (G–I). CB, cell body; Ci, sensory cilia. (A–F) Perinuclear, punctate staining of the polypeptides is observed in the cell bodies and along dendrites of the amphid chemosensory neurons. This pattern is seen in immunolocalization experiments using all three antibodies but is most obvious in anti-Osm-3– and anti-CeKRP95–stained worms. All antibodies demonstrate intense staining in the ciliated endings of the chemosensory neurons (A-I). Although all three antibodies stain the cell bodies and dendrites of these neurons in a punctate manner, the most intense staining is seen in the ciliated endings, suggesting a concentration of the CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 holoenzymes in these structures.
Antibodies to CeKRP95, CeKAP, and OSM-3 all stained the cell body cytoplasm, dendrites, and ciliated endings of the amphid, inner labial, and phasmid chemosensory neurons. Cell body staining was most dramatic in anti-OSM-3– and anti-CeKRP95–stained worms (Figure 7, A–F). In addition, worms stained with anti-CeKRP95 and anti-OSM-3 antibodies demonstrated a perinuclear, punctate staining in cell bodies and a punctate staining along corresponding dendrites of amphid neurons (Figure 7, A–F). These punctae clearly align along neuronal processes in single confocal optical sections, although this is slightly obscured because of the abundance of overlapping punctae in the confocal projections provided in Figure 7. This punctate staining pattern suggests an association with vesicles or macromolecular complexes and is similar to that reported for mouse KIF3A in nerve axons (Kondo et al., 1994), for Kinesin-II in sea urchin sperm flagellar axonemes (Henson et al., 1997), and for FLA-10 in the basal body and flagella of Chlamydomonas (Vashishtha et al., 1996; Cole et al., 1998).
The most striking feature of the anti-CeKRP95–, anti-CeKAP–, and anti-OSM-3–stained nematodes is the high intensity of staining of the sensory cilia themselves, suggesting that the polypeptides concentrate in these structures. Although all three antibodies showed staining in the ciliated endings, worms stained with anti-CeKAP antibodies demonstrated the most dramatic localization to sensory cilia, as shown by the intense immunofluorescence in the amphid and inner labial chemosensory cilia in Figure 7, G–I.
The immunolocalization of CeKRP95 to the cell bodies, dendrites, and ciliated endings of chemosensory neurons in the head of the worm (Figure 7, A–C) is consistent with CeKRP95 promoter::GFP expression. However, unlike the transgenic worms, anti-CeKRP95 immunostaining shows only faint localization in the general nervous system, with light punctate staining in the dorsal and ventral nerve cords and motor commissures. This faint staining was less consistent than the staining of the chemosensory neurons and hard to document in confocal projections; however, this pattern was not seen in preimmune stained worms or in secondary-antibody controls (our unpublished results).
Together, the promoter::GFP and immunolocalization data for OSM-3, CeKRP95, and CeKAP strongly suggest that the CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 holoenzymes both function in the subset of neurons responsible for chemosensation, where they concentrate in the ciliated endings of these neurons and may play roles in sensory ciliary assembly and function. However, the data also raise the possibility that CeKinesin-II polypeptides may function more broadly throughout the C. elegans nervous system as well, as suggested by the faint antibody staining and promoter::GFP expression.
DISCUSSION
Here we report the initial characterization of two heteromeric kinesin holoenzymes, CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3, which are present in the C. elegans nervous system and are concentrated in sensory cilia. Our data are consistent with the hypothesis that these two motor protein complexes play important roles in sensory ciliary formation and function.
Oligomeric State of CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3
The data obtained from sequence and biochemical analyses suggest that one heteromeric kinesin, CeKinesin-II, is a 226-kDa heterotrimer of two motor subunits, CeKRP85 and CeKRP95, which heterodimerize to form a 33- to 35-nm coiled coil rod, plus an accessory subunit CeKAP. The second heteromeric kinesin, CeOsm-3, behaves as a 140-kDa dimer containing the previously described OSM-3 motor subunit (Shakir et al., 1993; Tabish et al., 1995). Osm-3 sequence analysis suggests that the stalk domain should form a 26-nm coiled coil rod, but whether the CeOsm-3 holoenzyme is a homodimer or a heterodimer is unclear. The differences in subunit composition of these two heteromeric motor complexes may represent adaptations that allow them to perform specific and distinct functions within the chemosensory nervous system of C. elegans.
The protein sequence deduced from our osm-3 cDNA clone differed from that published by Shakir et al. (1993). This is especially obvious in the stalk domain, which is predicted to have a more extensive coiled coil than that predicted by Tabish et al. (1995). Although these differences may be due to errors in sequencing or cDNA synthesis, they may also represent isoforms of the OSM-3 polypeptide that could potentially heterodimerize within the CeOsm-3 holoenzyme. Indeed, our anti-OSM-3 antibodies detect two closely migrating bands that exactly cofractionate in all steps of purification and are often difficult to resolve by 8% SDS-PAGE. These bands may result from proteolysis or may represent alternative splice forms, posttranslational modifications of the OSM-3 polypeptide, or the product of a different, albeit closely related, gene. However, it should be noted that we isolated five independent cDNA clones encoding OSM-3, and all shared identical amino acid sequence.
Expression and Localization of the Two Heteromeric Kinesin Complexes
Using promoter::GFP reporter constructs and immunofluorescence microscopy, we determined that CeOsm-3 and CeKinesin-II are expressed in the cell bodies and dendrites of amphid, inner labial, and phasmid chemosensory neurons and concentrate in sensory cilia. Together these results provide concordant data in strong support of the hypothesis that both complexes participate in transporting material along sensory dendrites to the cilia for sensory ciliogenesis (next section). The punctate staining suggests that they may transport vesicles and/or macromolecular complexes along dendrites and cilia, which may include structural components of axonemes and/or sensory receptors that accumulate in the ciliated endings of chemosensory neurons.
The promoter::GFP experiments also raise the possibility that CeKinesin-II functions throughout the entire nervous system, but this is not entirely clear. For example, CeKRP95 promoter::GFP worms display high GFP expression in the nerve cords and associated commissures; however, only weak (but detectable) immunofluorescence signals in this region of the nervous system were observed. Additionally, CeKAPpromoter::GFP worms showed only very light expression in the dorsal and ventral nerve cords, which was not seen by immunofluorescence microscopy. Several possibilities may be considered to explain this: 1) the genomic sequence upstream from the CeKRP95 gene that was used in promoter::GFP experiments may contain cis-acting sequences that result in a more broad, or ectopic, expression pattern when used in reporter assays (although two different-sized promoters were used, and both show the same pattern of expression); 2) immunolocalization experiments may actually underrepresent the localization of CeKinesin-II throughout the nervous system because of problems with permeabilization of the outer cuticle and antibody penetration; 3) the levels of protein in other neurons is quite low compared with that concentrated in chemosensory neurons and sensory cilia and is therefore hard to image; and 4) there may be an additional CeKAP protein that assembles with CeKRP95 and is involved in general neuronal transport. Indeed, at least two KAPs have been found in mouse (Yamazaki et al., 1996). It is possible that a second accessory polypeptide exists that is not recognized by our anti-CeKAP antibody but is nearly the same molecular mass as CeKAP, which could result in similar hydrodynamic properties of CeKinesin-II regardless of the CeKAP it associates with.
The promoter::GFP expression data provide complementary evidence for expression of these holoenzymes in the C. elegans chemosensory nervous system; however, we cannot draw firm conclusions about the expression and function of CeKinesin-II in other neurons without functional data from the analysis of mutants. We anticipate that the isolation and detailed phenotypic analysis of CeKinesin-II mutants will address the biological functions of CeKinesin-II in chemosensory neurons and other cells of the nervous system. Given the multifunctional nature of Kinesin-II in other systems (Scholey, 1996), it is reasonable to hypothesize that CeKinesin-II has neuronal functions that extend beyond its role in chemosensory neurons. The simple, extensively characterized nervous system of C. elegans and its well-developed genetics make it an appealing system to address the roles of heteromeric kinesins in the nervous system.
Functions of Heteromeric Kinesins in Sensory Cilia
Our data clearly demonstrate that both CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 are localized in the cell bodies, dendrites, and ciliated endings of chemosensory neurons. In other systems, heteromeric kinesins are thought to participate in the assembly, maintenance, and function of motile cilia (Cole et al., 1993, 1998; Walther et al., 1994; Kozminski et al., 1995; Morris and Scholey, 1997), sensory cilia (Beech et al., 1996; Telford et al., 1998), and neurons (Kondo et al., 1994; Pesavento et al., 1994). Our immunolocalization results are consistent with the hypothesis that these two C. elegans heteromeric kinesins participate in the assembly of sensory cilia, suggesting that ciliary assembly is a conserved function of heteromeric kinesins, but direct functional evidence is required to test this hypothesis.
One powerful approach to the identification of protein function is through the analysis of mutants. There are multiple mutants displaying defects in the formation and function of sensory cilia in C. elegans (Perkins et al., 1986; Bargmann et al., 1990; Starich et al., 1995; Collet et al., 1998). The ciliated endings of sensory neurons in wild-type C. elegans take up dyes such as FITC from the environment, but mutants with defects in sensory cilia exclude the dye and display a “dye-filling” or dyf phenotype (Perkins et al., 1986; Bargmann et al., 1990; Starich et al., 1995). So far, ∼100 dye-filling mutants have been isolated (Starich et al., 1995), and they define 25 genes: 6 chemotaxis (che) genes, 4 osmotic avoidance (osm) genes, 2 dauer larva-defective (daf) genes, and 13 new genes (dyf1–13). Most of these mutants that have been analyzed at the ultrastructural level were found to display defects in the morphology of sensory cilia (Perkins et al., 1986). Additional che, osm, and daf mutants have been isolated in independent screens, many of which also display structural defects in their sensory cilia, suggesting that the analysis of these mutants will provide a powerful route to the analysis of the mechanism of sensory ciliary assembly, including the roles of heteromeric kinesins in the process.
Three dye-filling mutants are already known to be particularly relevant to the heteromeric kinesins’ roles in sensory ciliary assembly, namely the osm-1, osm-3, and osm-6 mutants (Perkins et al., 1986; Tabish et al., 1995; Collet et al., 1998). Elegant studies have shown that the activity of the heterotrimeric FLA-10 kinesin in Chlamydomonas is required for the intraflagellar transport of rafts that contain OSM-1 and OSM-6 homologues (Cole et al., 1998). This observation led to the proposal that OSM-3, a close relative of FLA-10, might be a subunit of a C. elegans heterotrimeric kinesin that transports the OSM-1 and OSM-6 proteins required for axonemal assembly (Cole et al., 1998). However, our discovery of a second heteromeric kinesin complex in C. elegans, heterotrimeric CeKinesin-II, which is far more similar in the sequences of its subunits as well as in its oligomeric state to FLA-10 kinesin, leads us to propose that this motor is more likely than dimeric CeOsm-3 to function as a motor for transporting the OSM-1 and OSM-6 proteins into sensory cilia.
osm-3 mutants lack the distal segments of their sensory cilia, which in wild-type worms consist of nine singlet microtubules surrounded by a membrane (Perkins et al., 1986). In contrast, osm-1 and osm-6 mutants lack both the middle and distal segments of their amphid sensory cilia and show ectopic expression of membrane-linked doublet MTs that assemble beneath normal transition zones (Perkins et al., 1986). These phenotypes suggest that OSM-1 and OSM-6 are required for the proper assembly of the middle segments of sensory cilia, whereas OSM-3 is required to assemble the distal segments (Perkins et al., 1986). Thus, we propose that CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3 are required for two sequential steps in the assembly of sensory cilia: CeKinesin-II moves from the cell bodies and out along dendrites to the sensory cilia, carrying a cargo consisting of the OSM-1 and OSM-6 proteins (and very likely additional components as well). The delivery of OSM-1 and OSM-6 would ensure that the doublet microtubules of the middle segment of the sensory cilia is correctly assembled on the transition zone at the base of the axoneme, which would then serve as tracks for the movement of CeOsm-3 to deliver some additional component(s) that is required for the correct assembly of the singlet microtubules that form the distal segments of the cilia. Further analysis of existing dyf mutants, together with the analysis of CeKinesin-II mutants isolated using reverse genetic procedures, should allow this model to be tested and should reveal additional components of the heteromeric kinesin ciliary assembly pathway.
The punctate neuronal staining seen in anti-CeKRP95– and anti-CeOsm-3–stained worms suggest they may also be involved in transporting sensory receptors and other Golgi-derived, membrane-associated factors from their site of synthesis in the cell body to the endings of chemosensory dendrites. Various different receptors and signaling molecules are known to localize to chemosensory cilia, including G-protein–coupled receptors, G-proteins, and ion channels (Dwyer, 1998). In fact, >40 highly divergent members of the G-protein–coupled receptor family have been identified and are thought to contribute to the wide range of chemical stimuli recognized by C. elegans, which have only 14 different types of chemosensory neurons (Troemel et al., 1995). It is unknown how sensory receptors are localized to the ciliated endings of sensory neurons, although recent evidence suggests an active transport mechanism for at least one receptor, the diacetyl receptor ODR-10 (Dwyer, 1998). ODR-10 is a G-protein–coupled odorant receptor that localizes to the ciliated endings of AWA olfactory neurons. Dwyer (1998) has used odr-10::GFP fusions to visualize the receptors being rapidly transported in vesicles along dendrites to nerve endings at a rate of 1 μm/s in an ATP-dependent manner. This rate is consistent with an active transport mechanism mediated by kinesin related proteins, including those of the heteromeric kinesins.
Interestingly, Kinesin-II has also been linked to signal transduction pathways in other organisms. Specifically, SMAP, the human homologue of the Kinesin-II accessory polypeptide, was identified in a two-hybrid screen for proteins that interact with Smg-GDS, a guanine-nucleotide exchange factor (Shimizu et al., 1996). The regulation of SMAP binding to Smg-GDS was shown to be dependent on phosphorylation of SMAP by v-src kinase in vitro, perhaps linking Kinesin-II transport functions with src-tyrosine signaling processes in human cells (Shimizu et al., 1996). It is possible that CeKinesin-II is also linked to G-protein–mediated signaling pathways during chemosensation through its associated CeKAP.
Conclusion
In summary, we have reported the presence of two heteromeric kinesin complexes in the nervous system of C. elegans: CeKinesin-II and CeOsm-3. Our results strongly support a role for both these motors in the formation and function of chemosensory cilia, and raise the possibility that CeKinesin-II may have additional functions in the nervous system as well. The isolation of mutants displaying defects in CeKinesin-II function should allow us to test this directly, by performing a detailed characterization of the mutant phenotype, then using said mutants in genetic crosses with known mutants in chemosensory function and against transgenic lines carrying GFP reporters fused to genes encoding putative cargo.
In a broader context, the study of intracellular transport in the C. elegans nervous system will illuminate the roles of multiple motors including the heteromeric kinesins (this report), conventional kinesin (Patel et al., 1993), monomeric kinesins (Otsuka et al., 1991), cytoplasmic dynein (Lye et al., 1987), and multiple myosins (Baker and Titus, 1997) in the assembly of neuronal structures and the delivery of transmembrane receptors and other components of the sensory signaling machinery to their site of action. C. elegans represents an elegant, genetically pliable system that is amenable to biochemistry and cytology for studying the concerted functions of these and other motors in neuronal and axonemal transport within a single cell, namely, the chemosensory neuron.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Drs. Cori Bargmann and Noelle Dwyer for discussion, advice, and encouragement, Dr. Joel Rosenbaum for helpful comments on the manuscript, Drs. Bill Saxton and Susan Strome for pointing out the presence of CeKRP85 in the EST database, Dr. Yuji Kohara (National Institute of Genetics of Japan) for EST clones, Dr. Alan Coulson (Sanger Center, Cambridge, United Kingdom) for genomic cosmid clones, Jose Orozco for help in cloning full-length Osm-3, and members of the Scholey and Rose laboratories for encouragement and discussion. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grant GM50718 to J.M.S.
REFERENCES
- Aamodt EJ, Cullotti JC. Microtubules and microtubule associated proteins from the nematode C. elegans: periodic cross-links connect microtubules in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1986;103:23–32. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker JP, Titus MA. A family of unconventional myosins from the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1997;272:523–535. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1997.1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann CI, Thomas JH, Horvitz HR. Chemosensory cell function in the behavior and development of C. elegans. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol. 1990;55:529–538. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1990.055.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beech PL, Pagh-Roehl K, Noda Y, Hirokawa N, Burnside B, Rosenbaum JL. Localization of kinesin superfamily proteins to the connecting cilium of fish photoreceptors. J Cell Sci. 1996;109:889–897. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.4.889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein M, Beech PL, Katz SG, Rosenbaum JL. A new kinesin-like protein (Klp1) localized to a single microtubule of the Chlamydomonas flagellum. J Cell Biol. 1994;125:1313–1326. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.6.1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974;77:71–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou JH, Troemel E, Sengupta P, Colbert H, Tong L, Tobin D, Roayaie K, Crump J, Dwyer N, Bargmann CI. Olfactory recognition and discrimination in Caenorhabditis elegans. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quantit Biol. 1996;61:57–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole DG, Cande WZ, Baskin RJ, Skoufias DA, Hogan CJ, Scholey JM. Isolation of a sea urchin egg kinesin-related protein using peptide antibodies. J Cell Sci. 1992;101:291–301. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.2.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole DG, Chinn SW, Wedaman KP, Hall K, Vuong T, Scholey JM. Novel heterotrimeric kinesin-related protein purified from sea urchin eggs. Nature. 1993;366:268–270. doi: 10.1038/366268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole DG, Diener DR, Himelblau AL, Beech PL, Fuster JC, Rosenbaum JL. Chlamydomonas kinesin-II-dependent intraflagellar transport (IFT): IFT particles contain proteins required for ciliary assembly in Caenorhabditis elegans sensory neurons. J Cell Biol. 1998;141:993–1008. doi: 10.1083/jcb.141.4.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collet J, Spike CA, Lundquist EA, Shaw JE, Herman RK. Analysis of osm-6, a gene that affects sensory cilium structure and sensory neuron function in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1998;148:187–200. doi: 10.1093/genetics/148.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J, Haeberli P, Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984;12:387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer, N.D. (1998). Odorant receptor localization to olfactory cilia is mediated by Odr-4 and Unc-101. Ph.D Thesis. San Francisco, CA: University of California. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Finney M, Ruvkun GB. The unc-86 gene product couples cell lineage and cell identity in C. elegans. Cell. 1990;63:895–905. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90493-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fire A. Integrative transformation of Caenorhabditis elegans. EMBO J. 1986;5:2673–2680. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04550.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E, Lane D. In: Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual ed. E. Harlow and D. Lane. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 1988. pp. 516–552. [Google Scholar]
- Henson JH, Cole DG, Roesener CD, Capuano S, Mendola RJ, Scholey JM. The heterotrimeric motor protein kinesin-II localizes to the midpiece and flagellum of sea urchin and sand dollar sperm. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1997;38:29–37. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0169(1997)38:1<29::AID-CM4>3.0.CO;2-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson JH, Cole DF, Terasaki M, Rashid D, Scholey JM. Immunolocalization of the heterotrimeric kinesin related protein KRP85,95 in the mitotic apparatus of sea urchin embryos. Dev Biol. 1995;171:182–194. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.1270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N. Kinesin and dynein superfamily proteins and the mechanism of organelle transport. Science. 1998;279:519–526. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5350.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson KA. Keeping the beat: form meets function in the Chlamydomonas flagellum. Bioessays. 1995;17:847–854. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson KA, Rosenbaum JL. Polarity of flagellar assembly in Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol. 1992;119:1605–1611. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo S, Sato-Yoshitake R, Noda Y, Aizawa H, Nakata T, Matsuura Y, Hirokawa N. Kif3A is a new microtubule-based motor in the nerve axon. J Cell Biol. 1994;125:1095–1107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.5.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozminski KG, Beech PL, Rosenbaum JL. The Chlamydomonas kinesin-like protein FLA10 is involved in motility associated with the flagellar membrane. J Cell Biol. 1995;131:1517–1527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J, French RP, Park E, Johnson JJ. The Caenorhabditis elegans rol-6 gene, which interacts with the sqt-1 collagen gene to determine organismal morphology, encodes a collagen. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10:2081–2090. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bot N, White AC, Karsenti E, Vernos I. Role of Xklp3, a subunit of the Xenopus kinesin-II heterotrimeric complex, in membrane transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and the golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1998;143:1559–1573. doi: 10.1083/jcb.143.6.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupas A, Van Dyke M, Stock J. Predicting coiled coils from protein sequences. Science. 1991;252:1162–1164. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lye RJ, Porter ME, Scholey JM, McIntosh JR. Identification of a microtubule-based cytoplasmic motor in the nematode C. elegans. Cell. 1987;51:309–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mello CC, Fire A. DNA transformation. In: Epstein HF, Shakes DC, editors. Caenorhabditis elegans: Modern Biological Analysis of an Organism. San Diego: Academic Press; 1995. pp. 452–482. [Google Scholar]
- Mello CC, Kramer JM, Stinchcomb D, Ambros V. Efficient gene transfer in C. elegans: extrachromosomal maintenance and integration of transforming sequences. EMBO J. 1991;10:3959–3970. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04966.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller DM, Shakes DC. Immunofluorescence microscopy. In: Epstiein HF, Shakes DC, editors. Caenorhabditis elegans: Modern Biological Analysis of an Organism. San Diego: Academic Press; 1995. pp. 365–394. [Google Scholar]
- Morris RL, Scholey JM. Heterotrimeric kinesin-II is required for the assembly of motile 9 + 2 ciliary axonemes in sea urchin embryos. J Cell Biol. 1997;138:1009–1022. doi: 10.1083/jcb.138.5.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muresan V, Abramson T, Lyass A, Winter D, Porro E, Hong F, Chamberlin NL, Schnapp BJ. Kif3C and Kif3A form a novel neuronal heteromeric kinesin that associates with membrane vesicles. Mol Biol Cell. 1998;9:637–652. doi: 10.1091/mbc.9.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka AJ, Jeyprakesh A, Garcia-Anoveros J, Tang LZ, Fish G, Hartshorne T, Franco R, Born T. The C. elegans unc-104 gene encodes a putative kinesin heavy chain-like protein. Neuron. 1991;6:113–122. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90126-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel N, Thierry-Mieg D, Mancillas JR. Cloning by insertional mutagenesis of a cDNA encoding Caenorhabditis elegans kinesin heavy chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:9181–9185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins LA, Hedgecock EM, Thomson JN, Cullotti JG. Mutant sensory cilia in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1986;117:456–487. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesavento PA, Stewart RJ, Goldstein LS. Characterization of the Klp68D kinesin-like protein in Drosophila: possible roles in axonal transport. J Cell Biol. 1994;127:1041–1048. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.4.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G, Mead K. Transport of a novel complex in the cytoplasmic matrix of Chlamydomonas flagella. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:4457–4462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.9.4457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G, Mead K, Henderson S. Inner dynein arms require the activity of the kinesin homologous protein, KHP1, to reach the tip of flagella in Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol. 1996;133:371–380. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashid DJ, Wedaman KP, Scholey JM. Heterodimerization of the two motor subunits of the heterotrimeric kinesin, KRP85/95. J Mol Biol. 1995;252:157–162. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers SL, Tint IS, Fanapour PC, Gelfand VI. Regulated bidirectional motility of melanophore pigment granules along microtubules in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:3720–3725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.8.3720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Scholey JM. Kinesin-II, a membrane traffic motor in axons, axonemes, and spindles. J Cell Biol. 1996;133:1–4. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakir M, Fukushige T, Yasuda H, Miwa J, Siddiqui SS. C. elegans osm-3 gene mediating osmotic avoidance behavior encodes a kinesin-like protein. NeuroReport. 1993;4:891–894. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199307000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K, Kawabe H, Minami S, Honda T, Takaishi K, Shirataki H, Takai Y. SMAP, an Smg GDS-associating protein having arm repeats and phosphorylated by SRC tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:27013–27017. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.43.27013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starich TA, Herman RK, Kari CK, Yeh WH, Schackwitz WS, Schulyler M, Collet J, Thomas J, Riddle D. Mutations affecting chemosensory neurons of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1995;139:171–188. doi: 10.1093/genetics/139.1.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens RE. Ciliogenesis in sea urchin embryos—a subroutine in the program of development. Bioessays. 1995;17:331–340. doi: 10.1002/bies.950170409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabish M, Siddiqui ZK, Nishikawa K, Siddiqui SS. Exclusive expression of C. elegans osm-3 kinesin gene in chemosensory neurons open to the external environment. J Mol Biol. 1995;247:377–389. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.0146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telford EAR, Wightman P, Leek J, Markham AF, Lench NJ, Bonthron DT. cDNA cloning, genomic organization, and chromosomal localization of a novel human gene that encodes a kinesin-related protein highly similar to KIF3C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;242:407–412. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1997.7977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position specific gap penalties, and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994;22:4673–4680. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.22.4673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuma MC, Zill A, Le Bot N, Vernos I, Gelfand V. Kinesin II is the microtubule motor protein responsible for pigment dispersion in Xenopus melanophores. J Cell Biol. 1998;143:1547–1558. doi: 10.1083/jcb.143.6.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale RD, Fletterick R. The design plan of kinesin motors. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1997;13:745–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.13.1.745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vashishtha M, Walther Z, Hall JL. The kinesin homologous protein encoded by the Chlamydomonas Fla 10 gene is associated with basal bodies and centrioles. J Cell Sci. 1996;109:541–549. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.3.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther Z, Vashishtha M, Hall JL. The Chlamydomonas Fla10 gene encodes a novel kinesin homologous protein. J Cell Biol. 1994;126:175–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S, Thompson N, White JG, Brenner S. Electron microscopic reconstruction of the anterior sensory anatomy of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J Comp Neurol. 1975;160:313–317. doi: 10.1002/cne.901600305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedaman KP, Meyer DW, Rashid DJ, Cole DG, Scholey JM. Sequence and submolecular localization of the 115-kDa accessory subunit of the heterotrimeric kinesin-II (KRP85/95) complex. J Cell Biol. 1996;132:371–380. doi: 10.1083/jcb.132.3.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White JG, Southgate E, Thompson JN, Brenner S. The structure of the nervous system of the nematode C. elegans. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986;314:1–340. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1986.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki H, Nakata T, Okada Y, Hirokawa N. KIF3A/3B: a heterodimeric kinesin superfamily protein that works as a microtubule plus end-directed motor for membrane organelle transport. J Cell Biol. 1995;130:1387–1399. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.6.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki H, Nakata T, Okada Y, Hirokawa N. Cloning and characterization of KAP3: a novel kinesin-superfamily-associated protein of Kif3A/3B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:8443–8448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.16.8443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z, Goldstein LS. Characterization of the KIF3C neural kinesin-like motor from mouse. Mol Biol Cell. 1998;9:249–261. doi: 10.1091/mbc.9.2.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]