Abstract
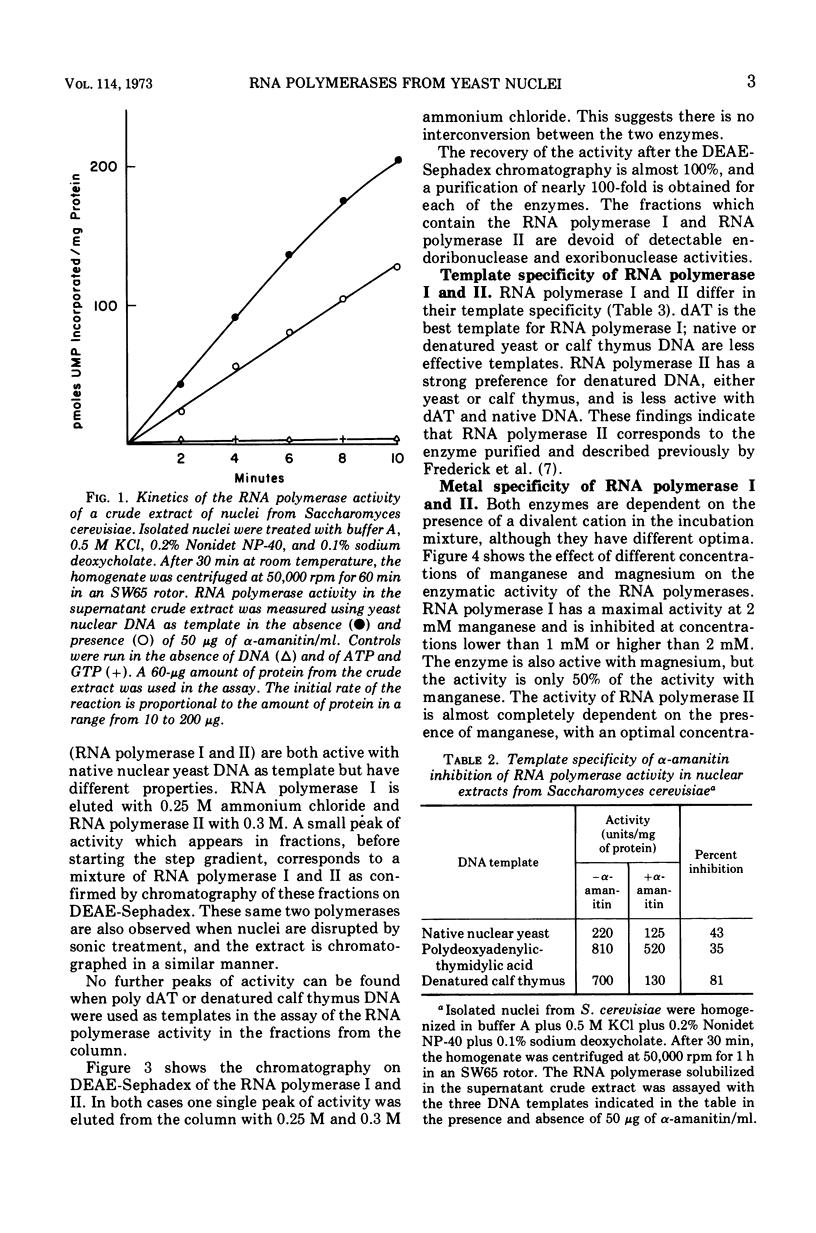
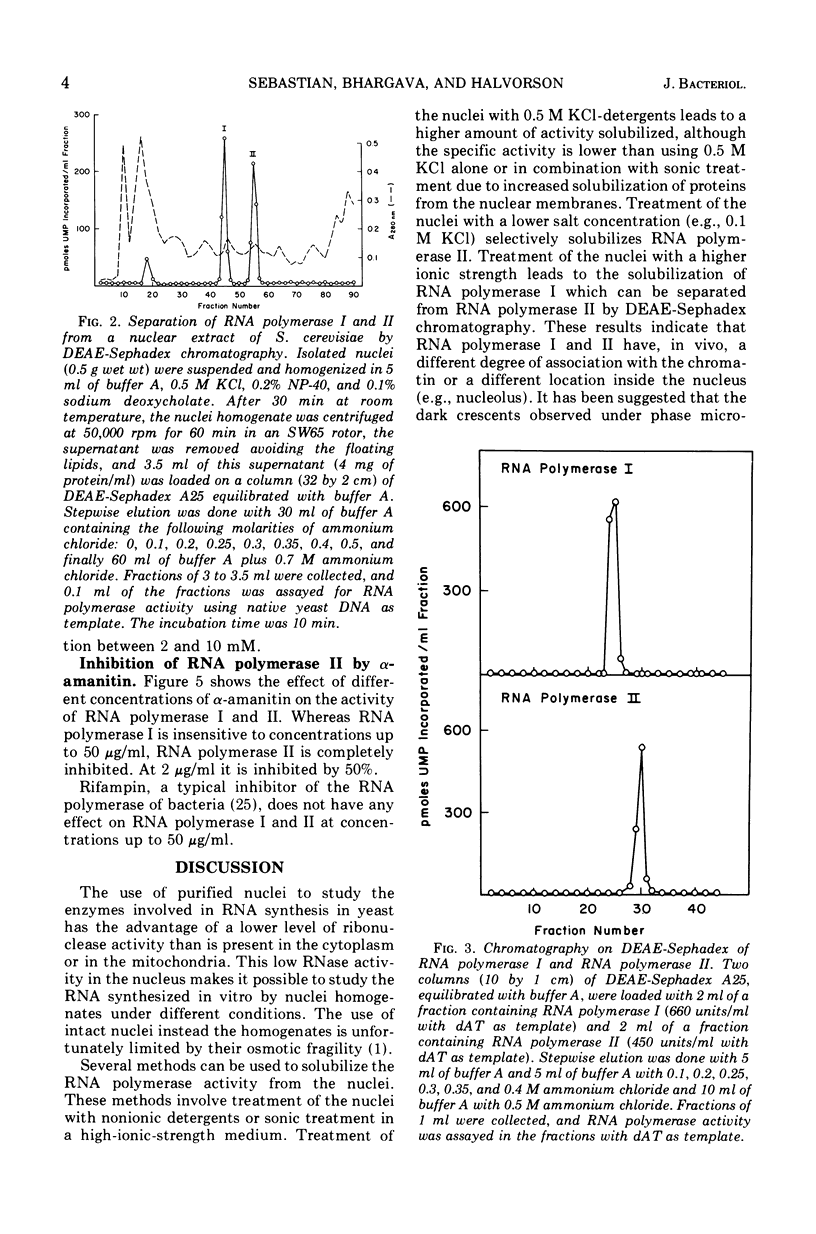
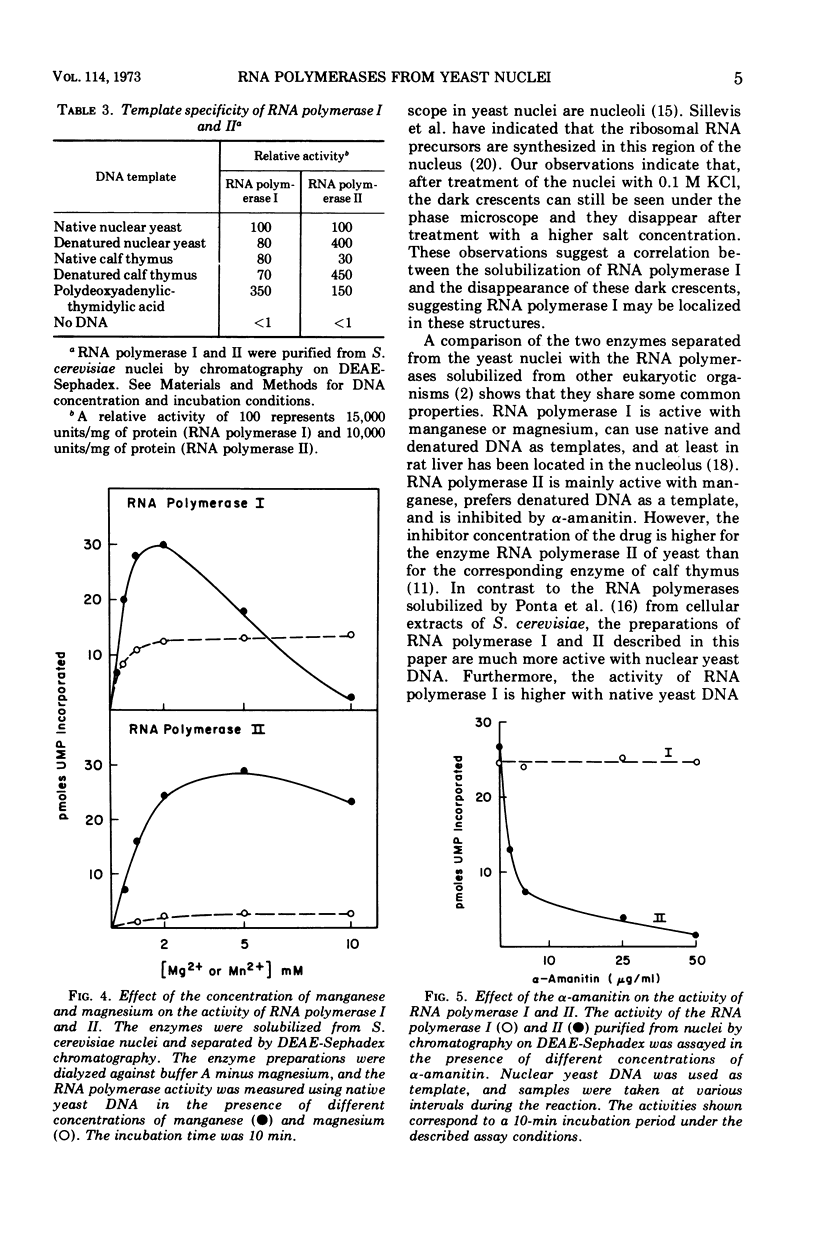
Two deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)-dependent ribonucleic acid (RNA) polymerases (I, II) have been solubilized from isolated Saccharomyces cerevisiae nuclei. The enzymes can be separated by chromatography on O-diethylaminoethyl Sephadex. Both enzymes are active with high-molecular-weight nuclear yeast DNA, although RNA polymerase I has a higher affinity for polydeoxy-adenylic-thymidylic acid and RNA polymerase II for denatured DNA. RNA polymerase I is active only with manganese. α-Amanitin inhibits only the activity of RNA polymerase II.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brogt T. M., Planta R. J. Characteristics of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity from isolated yeast nuclei. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jan 15;20(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R. A new method for the large scale purification of Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6160–6167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M., McGrath J., Waskell L. New RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T7. Nature. 1970 Oct 17;228(5268):227–231. doi: 10.1038/228227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederick E. W., Maitra U., Hurwitz J. The role of deoxyribonucleic acid in ribonucleic acid synthesis. XVI. The purification and properties of ribonucleic acid polymerase from yeast: preferential utilization of denatured deoxyribonucleic acid as template. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 25;244(2):413–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horgen P. A., Griffin D. H. RNA polymerase 3 of Blastocladiella emersonii is mitochondrial. Nat New Biol. 1971 Nov 3;234(44):17–18. doi: 10.1038/newbio234017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horgen P. A., Griffin D. H. Specific inhibitors of the three RNA polymerases from the aquatic fungus Blastocladiella emersonii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):338–341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Gniazdowski M., Mandel J. L., Jr, Gissinger F., Chambon P. Alpha-amanitin: a specific inhibitor of one of two DNA-pendent RNA polymerase activities from calf thymus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 6;38(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Shorenstein R. G., Sonenshein A. L. Structural alteration of RNA polymerase during sporulation. Nature. 1970 Aug 29;227(5261):910–913. doi: 10.1038/227910a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Sonenshein A. L. Change in the template specificity of RNA polymerase during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1969 Oct 4;224(5214):35–37. doi: 10.1038/224035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponta H., Ponta U., Wintersberger E. DNA-dependent RNA polymerases from yeast. Partial characterization of three nuclear enzyme activities. FEBS Lett. 1971 Nov 1;18(2):204–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80445-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Multiple forms of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in eukaryotic organisms. Nature. 1969 Oct 18;224(5216):234–237. doi: 10.1038/224234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific nucleolar and nucleoplasmic RNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):675–682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachner M., Seifert W., Zillig W. A correlation of changes in host and T 4 bacteriophage specific RNA synthesis with changes of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T 4 . Eur J Biochem. 1971 Oct 26;22(4):520–528. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smitt W. W., Vermeulen C. A., Vlak J. M., Rozijn T. H., Molenaar I. Electron microscopic autoradiographic study of RNA synthesis in yeast nucleus. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Jan;70(1):140–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90191-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain G. C., Mullinix K. P., Bogorad L. RNA polymerases of maize: nuclear RNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2647–2651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. C., Siegel R. B. Transcription of late phage RNA by T7 RNA polymerase. Nature. 1970 Dec 19;228(5277):1160–1162. doi: 10.1038/2281160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli W., Staehelin M. Actions of the rifamycins. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Sep;35(3):290–309. doi: 10.1128/br.35.3.290-309.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


