Abstract
A mutant of Diplococcus pneumoniae that apparently does not require activator can become competent for uptake of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) when grown in dilute cultures or in the presence of trypsin. Development of competence in both mutant and wild strains is temperature dependent, being 10-fold greater at 30 C than at 37 C. Induction of competence on a shift from 37 to 30 C requires protein synthesis and the presence of Mg2+ and Ca2+; uptake of DNA does not require protein synthesis. Competence decays exponentially at higher temperatures. As well as taking up DNA, competent cells release oligonucleotide fragments of donor DNA in the medium external to the cells. Normal strains release fragments comparable in amount to the DNA taken up; but, in a mutant selected for inability to degrade DNA in agar, the amount of fragments formed external to the cells is only 40% of DNA uptake. Requirements for external deoxyribonuclease action are identical to those for DNA uptake: prior development of competence and the presence during treatment with DNA of Mg2+ ions and a source of energy.
Full text
PDF

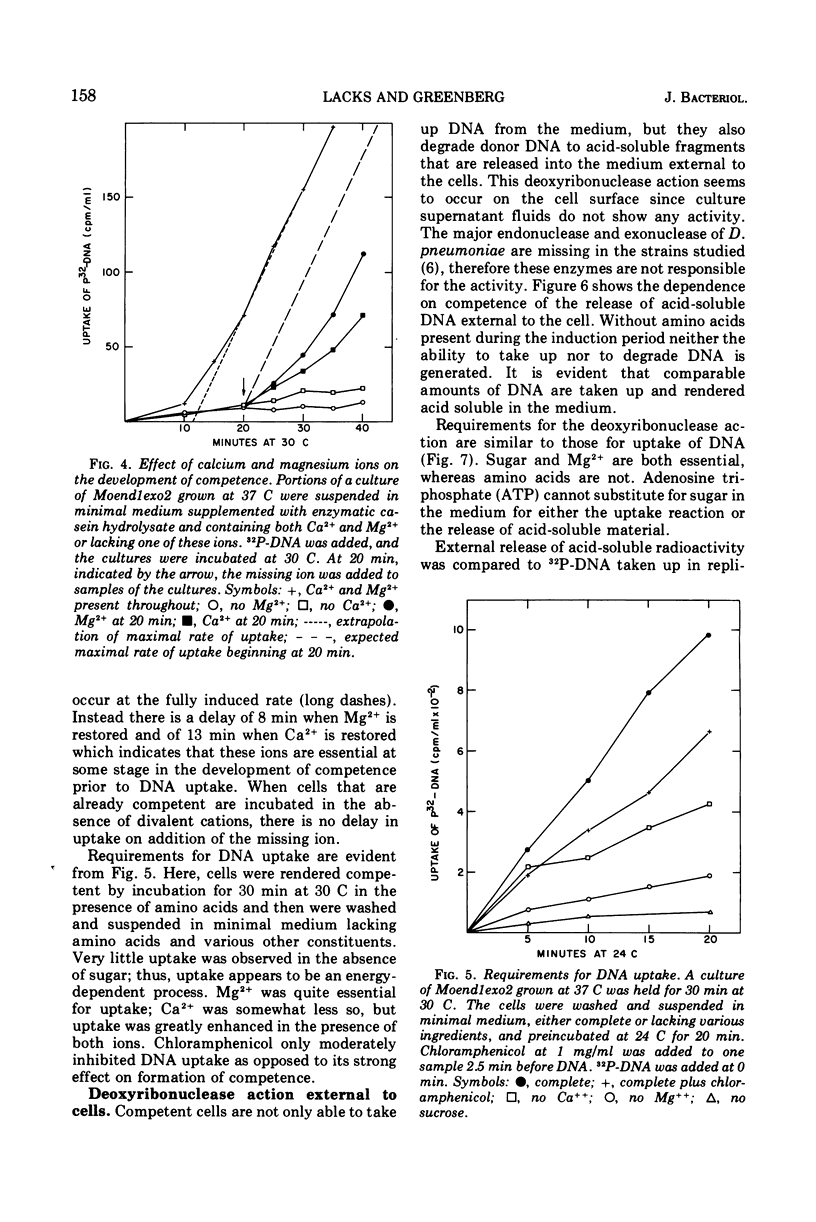


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
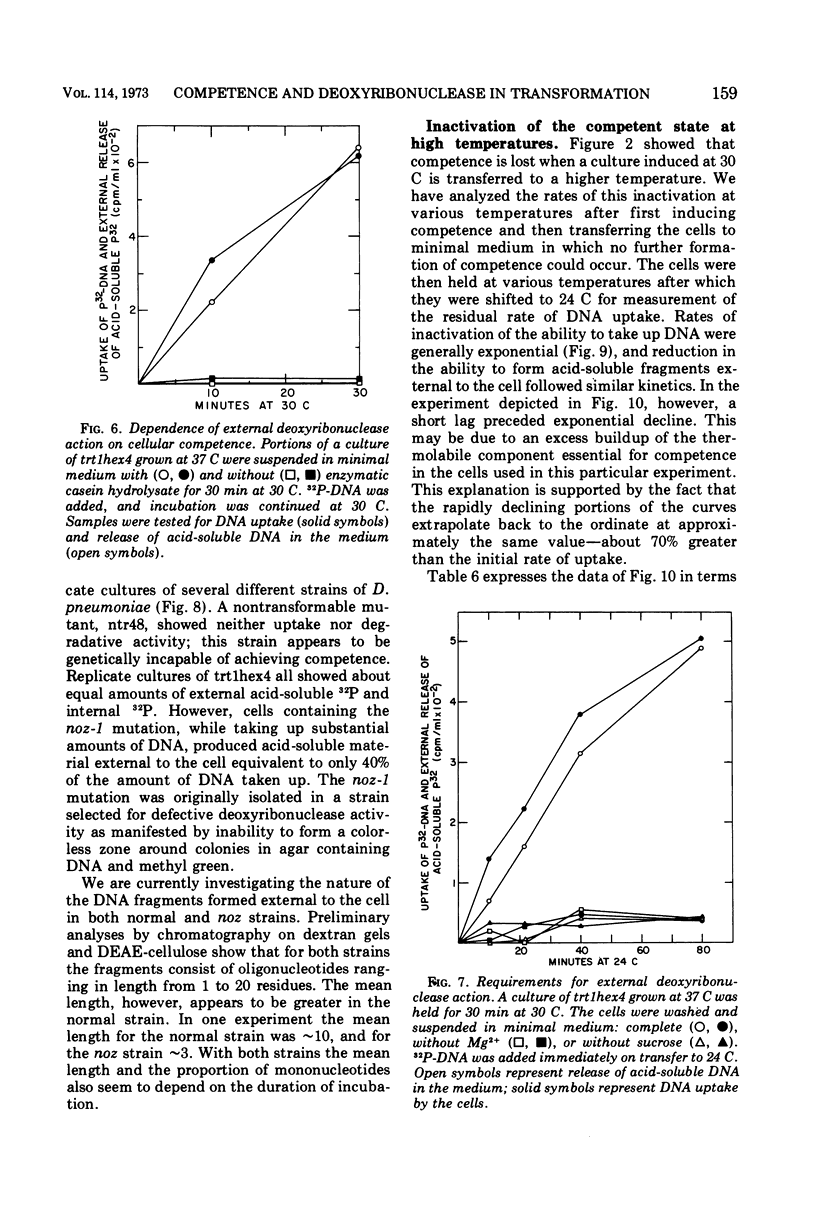
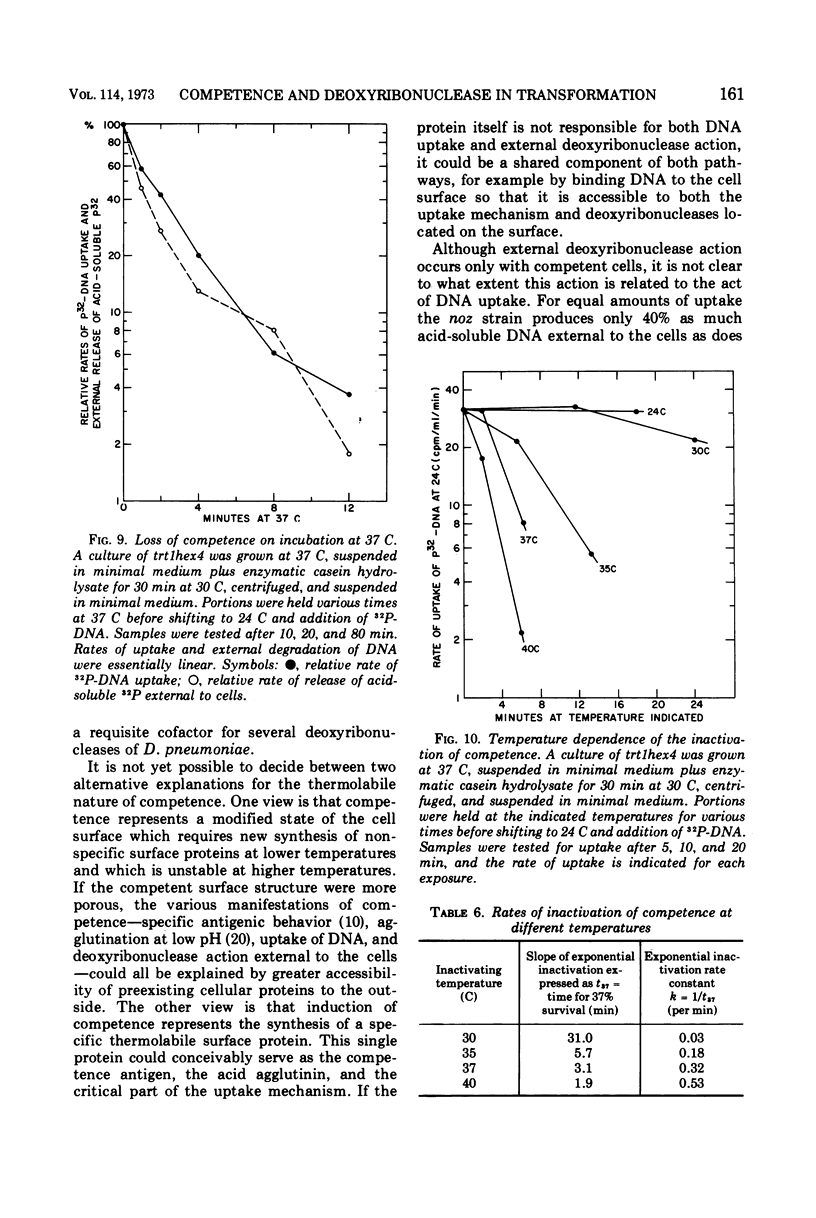
- FOX M. S., HOTCHKISS R. D. Initiation of bacterial transformation. Nature. 1957 Jun 29;179(4574):1322–1325. doi: 10.1038/1791322a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotchkiss R. D. CYCLICAL BEHAVIOR IN PNEUMOCOCCAL GROWTH AND TRANSFORMABILITY OCCASIONED BY ENVIRONMENTAL CHANGES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1954 Feb;40(2):49–55. doi: 10.1073/pnas.40.2.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
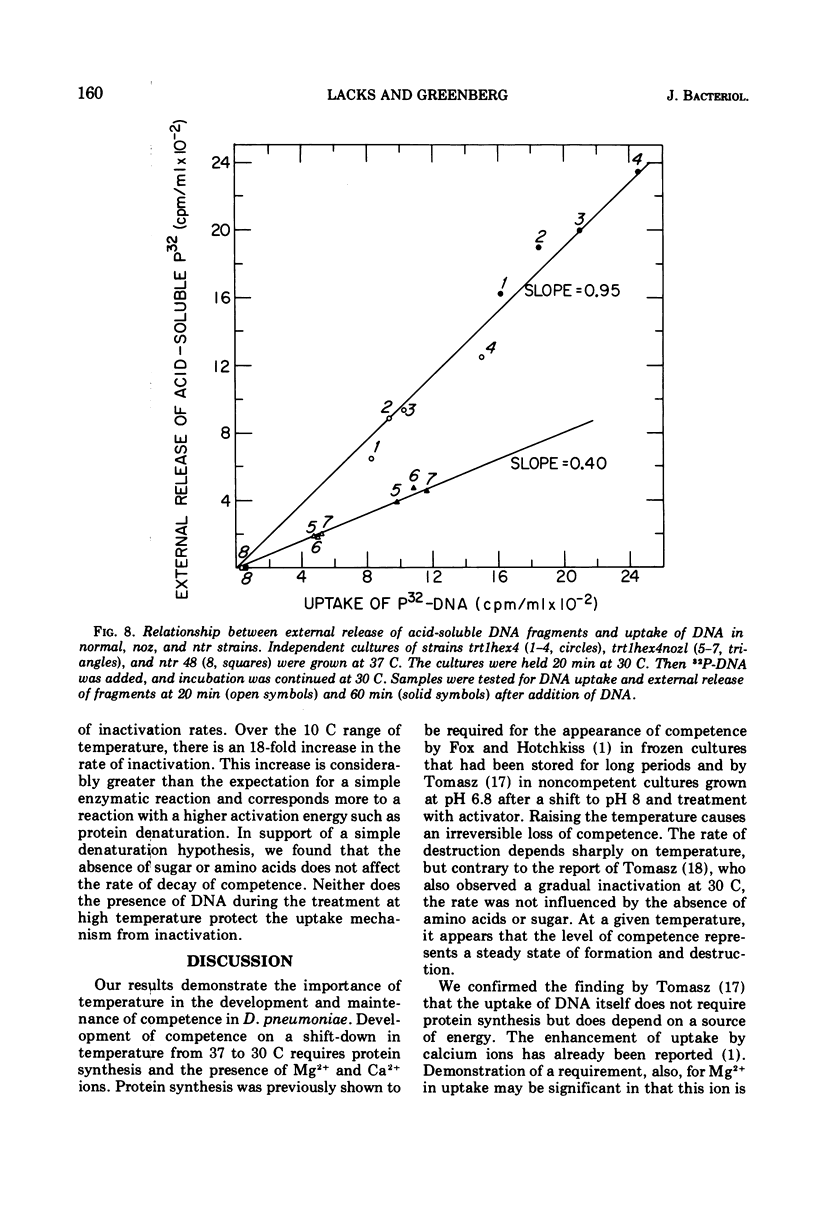
- LACKS S. Molecular fate of DNA in genetic transformation of Pneumococcus. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:119–131. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERMAN L. S., TOLMACH L. J. Genetic transformation. I. Cellular incorporation of DNA accompanying transformation in Pneumococcus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Oct;26(1):68–82. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. Integration efficiency and genetic recombination in pneumococcal transformation. Genetics. 1966 Jan;53(1):207–235. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. Mutants of Diplococcus pneumoniae that lack deoxyribonucleases and other activities possibly pertinent to genetic transformation. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):373–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.373-383.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A., Guild W. R. Transformation and deoxyribonucleic acid size: extent of degradation on entry varies with size of donor. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1157–1168. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1157-1168.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAVA G. C., GALIS A., BEISER S. M. Bacterial transformation: an antigen specific for 'competent' pneumococci. Nature. 1963 Mar 2;197:903–904. doi: 10.1038/197903b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKADA T., YANAGISAWA K., RYAN F. J. A method for securing thymineless mutants from strains of E. coli. Z Vererbungsl. 1961;92:403–412. doi: 10.1007/BF00890061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAKULA R., WALCZAK W. On the nature of competence of transformable streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Apr;31:125–133. doi: 10.1099/00221287-31-1-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothfield L., Pearlman M. The role of cell envelope phospholipid in the enzymatic synthesis of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Structural requirements of the phospholipid molecule. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 25;241(6):1386–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMASZ A., HOTCHKISS R. D. REGULATION OF THE TRANSFORMABILITY OF PHEUMOCOCCAL CULTURES BY MACROMOLECULAR CELL PRODUCTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Mar;51:480–487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.3.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Cellular metabolism in genetic transformation of pneumococci: requirement for protein synthesis during induction of competence. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):860–871. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.860-871.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Mosser J. L. On the nature of the pneumococcal activator substance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):58–66. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Zanati E., Ziegler R. DNA uptake during genetic transformation and the growing zone of the cell envelope. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1848–1852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Zanati E. ppearance of a protein "agglutinin" on the spheroplast membrane of pneumococci during induction of competence. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1213–1215. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1213-1215.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vovis G. F., Buttin G. An ATP-dependent deoxyribonuclease from diplococcus pneumoniae. I. Partial purification and some biochemical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 12;224(1):29–41. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90617-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


