Abstract
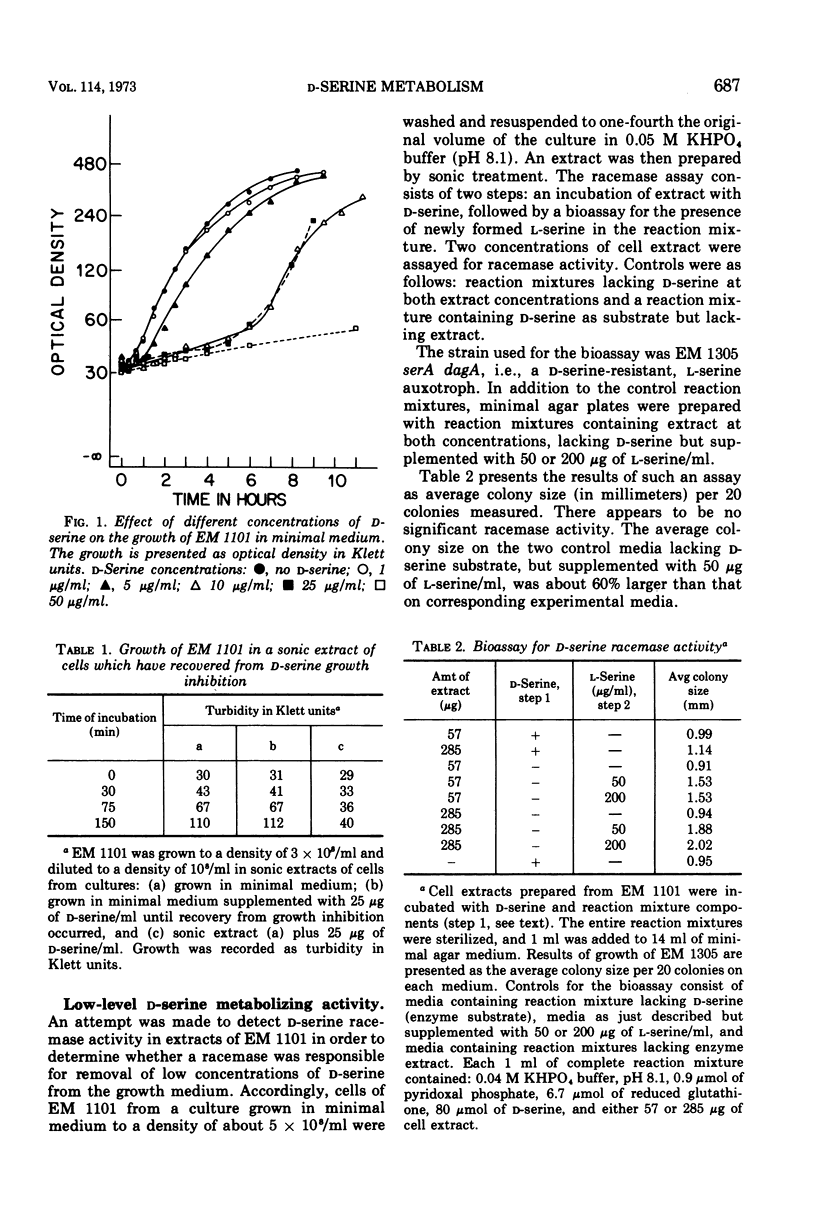
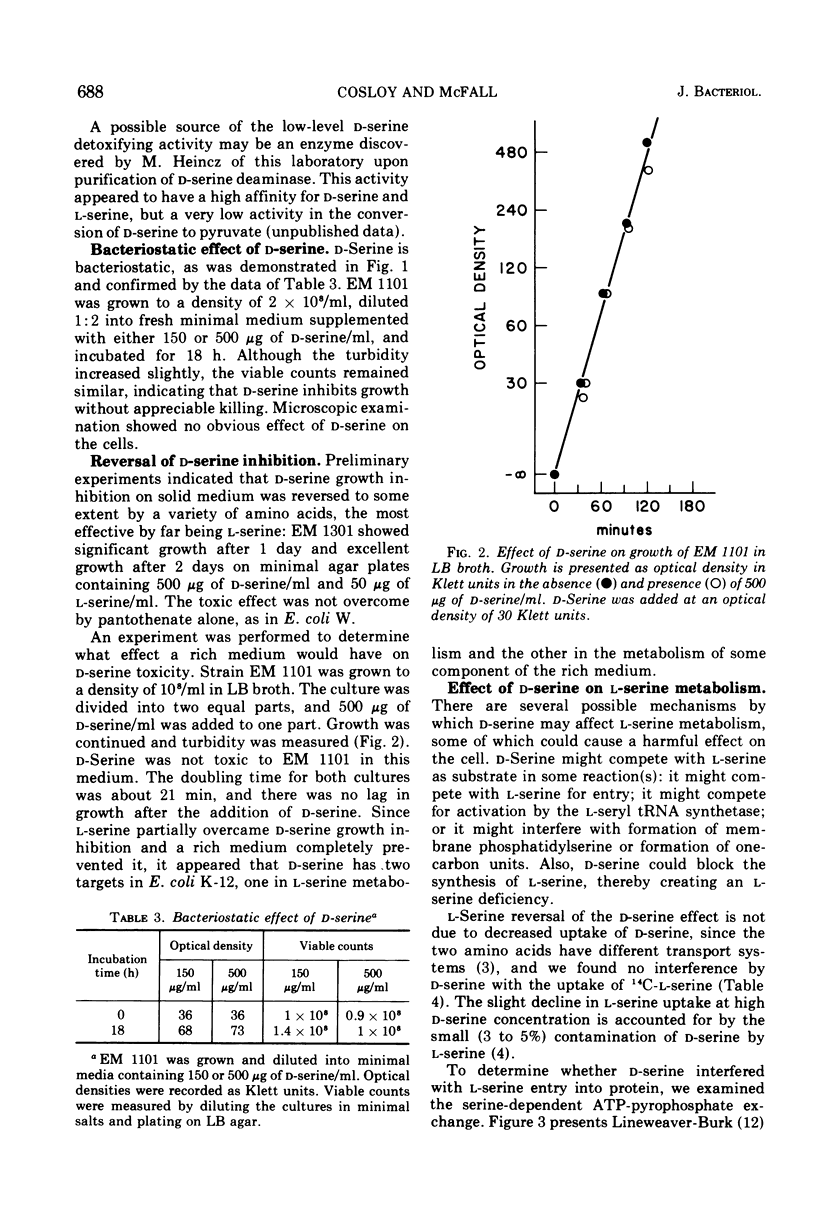
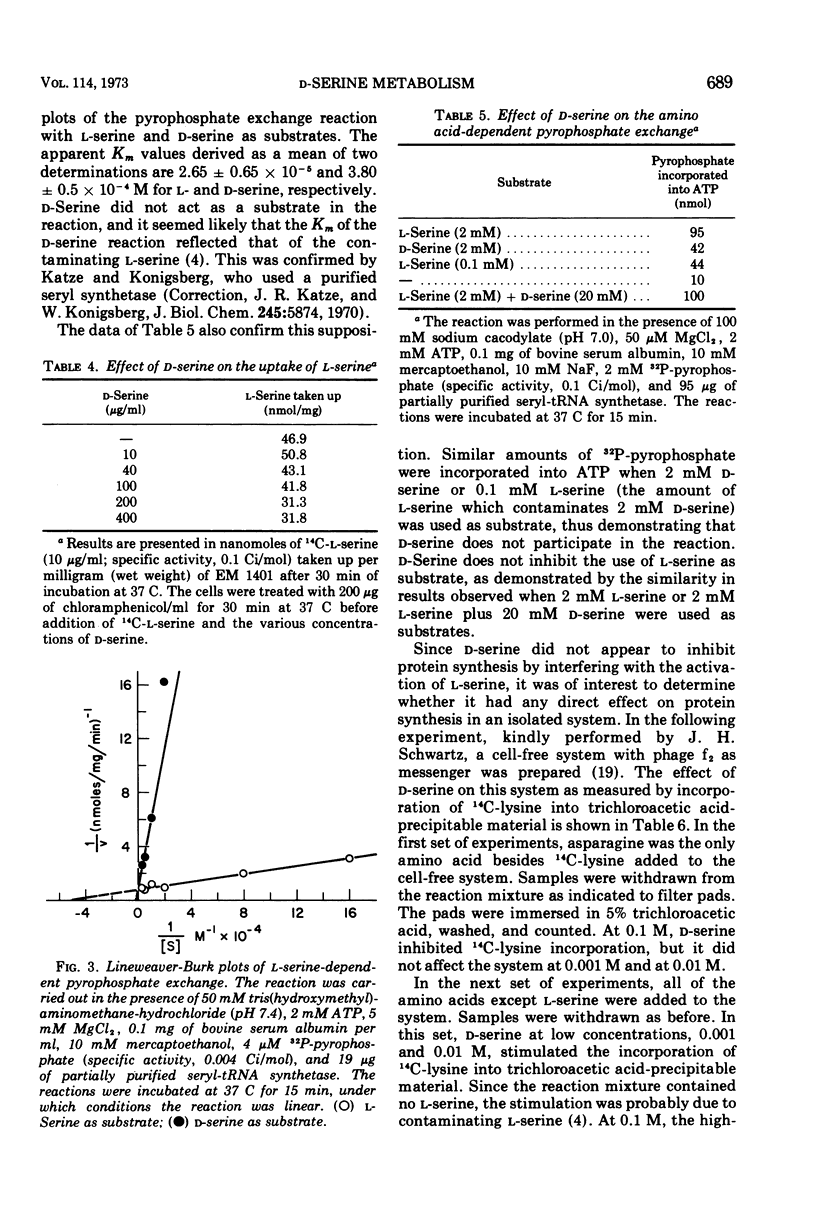
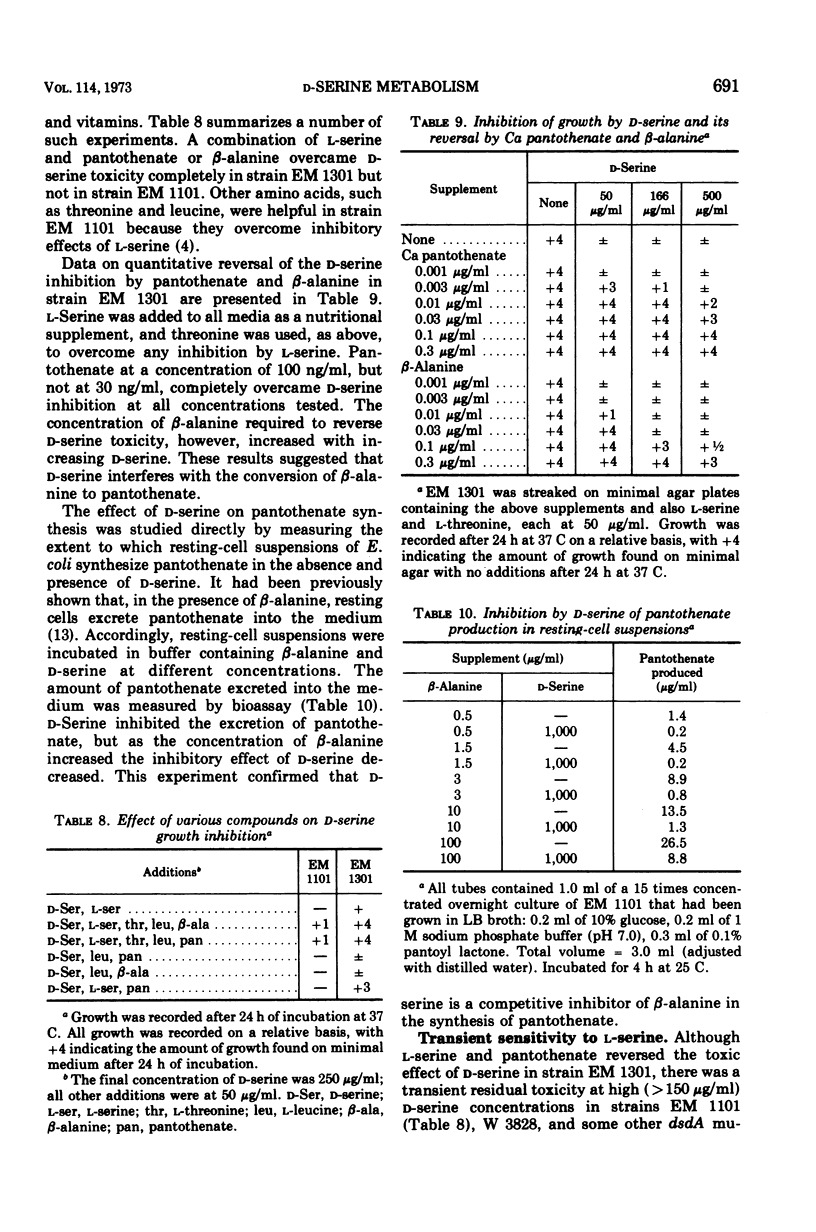
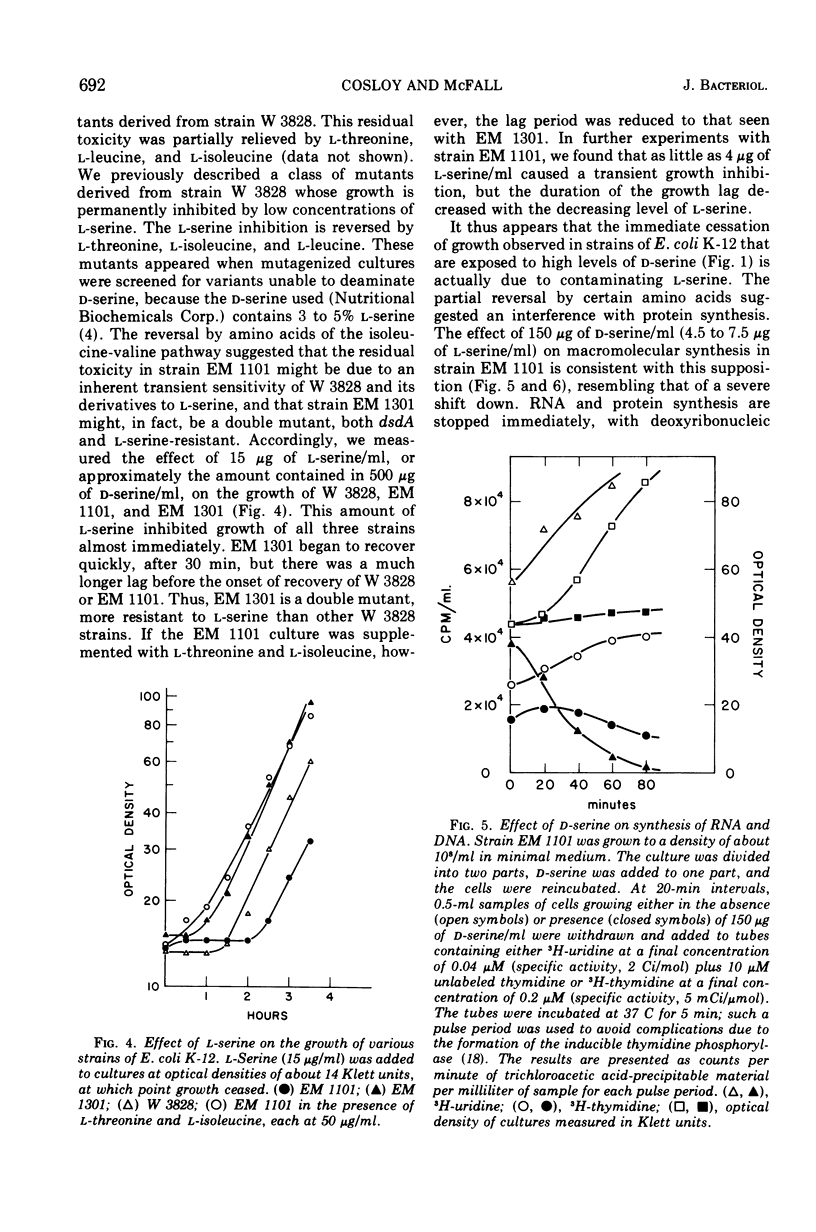
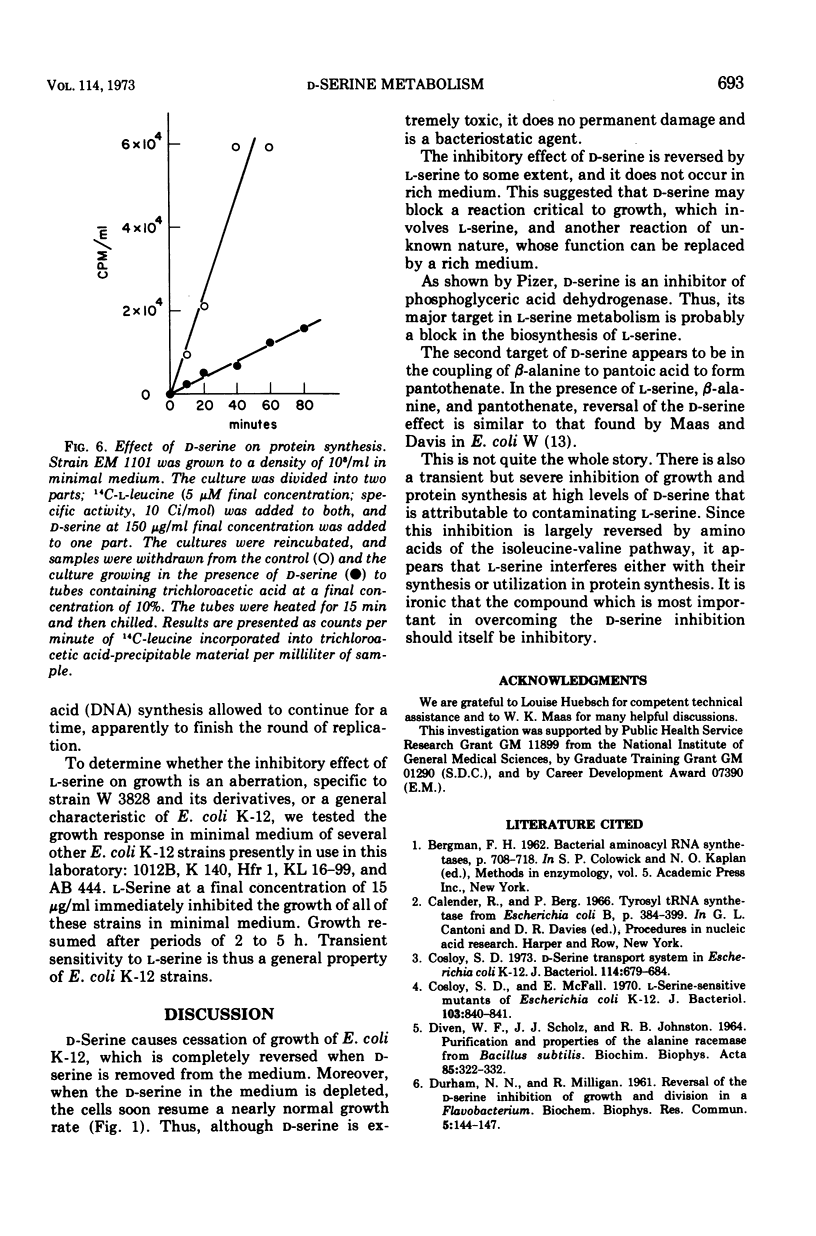
Without significant killing, d-serine at concentrations greater than 50 μg/ml inhibits growth in minimal media of mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 unable to form d-serine deaminase. The mutants eventually recover at lower concentrations. There is no evidence of d-serine toxicity in rich media. Toxicity is partially reversed by l-serine. d-Serine does not interfere with l-serine activation, one-carbon metabolism, or (Cronan, personal communication) formation of phosphatidylserine. Pizer (personal communication) finds, however, that it is a powerful feedback inhibitor of the first enzyme of l-serine biosynthesis. In the presence of l-serine, the residual toxicity is largely and noncompetitively over come by pantothenate, indicating that d-serine inhibits growth by affecting two targets: pantothenate biosynthesis and l-serine biosynthesis. l-Serine causes transient growth inhibition in E. coli K-12. Contaminating l-serine in d-serine preparations contributes to the d-serine inhibitory response.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cosloy S. D. D-serine transport system in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):679–684. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.679-684.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosloy S. D., McFall E. L-Serine-sensitive mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):840–841. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.840-841.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIVEN W. F., SCHOLZ J. J., JOHNSTON R. B. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF THE ALANINE RACEMASE FROM BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 4;85:322–332. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90253-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DURHAM N. N., MILLIGAN R. A mechanism of growth inhibition by D-serine in a Flavobacterium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 11;7:342–345. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90311-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DURHAM N. N., MILLIGAN R. Reversal of the D-serine inhibition of growth and division in a Flavobacterium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1961 Jun 2;5:144–147. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(61)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRULA E. A., GRULA M. M. INHIBITION IN SYNTHESIS OF BETA-ALANINE BY D-SERINE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 10;74:776–778. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91430-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRULA M. M., GRULA E. A. Cell division in a species of Erwinia IV. Metabolic blocks in panothenate biosynthesis and their relationship to inhibition of cell division. J Bacteriol. 1962 May;83:989–997. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.5.989-997.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANFER J. N., KENNEDY E. P. Synthesis of phosphatidylserine by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jan;237:PC270–PC271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze J. R., Konigsberg W. Purification and properties of seryl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 10;245(5):923–930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAAS W. K., DAVIS B. D. Pantothenate studies. I. Interference by D-serine and L-aspartic acid with pantothenate synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1950 Dec;60(6):733–745. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.6.733-745.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCFALL E. GENETIC STRUCTURE OF THE D-SERINE DEAMINASE SYSTEM OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Mol Biol. 1964 Sep;9:746–753. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80179-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFall E. Mapping of the d-serine deaminase region in Escherichia coli K-12. Genetics. 1967 Jan;55(1):91–99. doi: 10.1093/genetics/55.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIZER L. I. THE PATHWAY AND CONTROL OF SERINE BIOSYNTHESIS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1963 Dec;238:3934–3944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACHMELER M., GERHART J., ROSNER J. Limited thymidine uptake in Escherichia coli due to an inducible thymidine phosphorylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 29;49:222–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90888-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. H. Initiation of protein synthesis under the direction of tobacco mosaic virus RNA in cell-free extracts of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1967 Dec 14;30(2):309–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney J. G., Grula E. A. Incorporation of D-serine into the cell wall mucopeptide of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:375–381. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(64)80013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



