Abstract
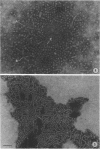
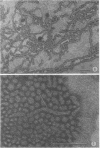
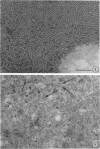
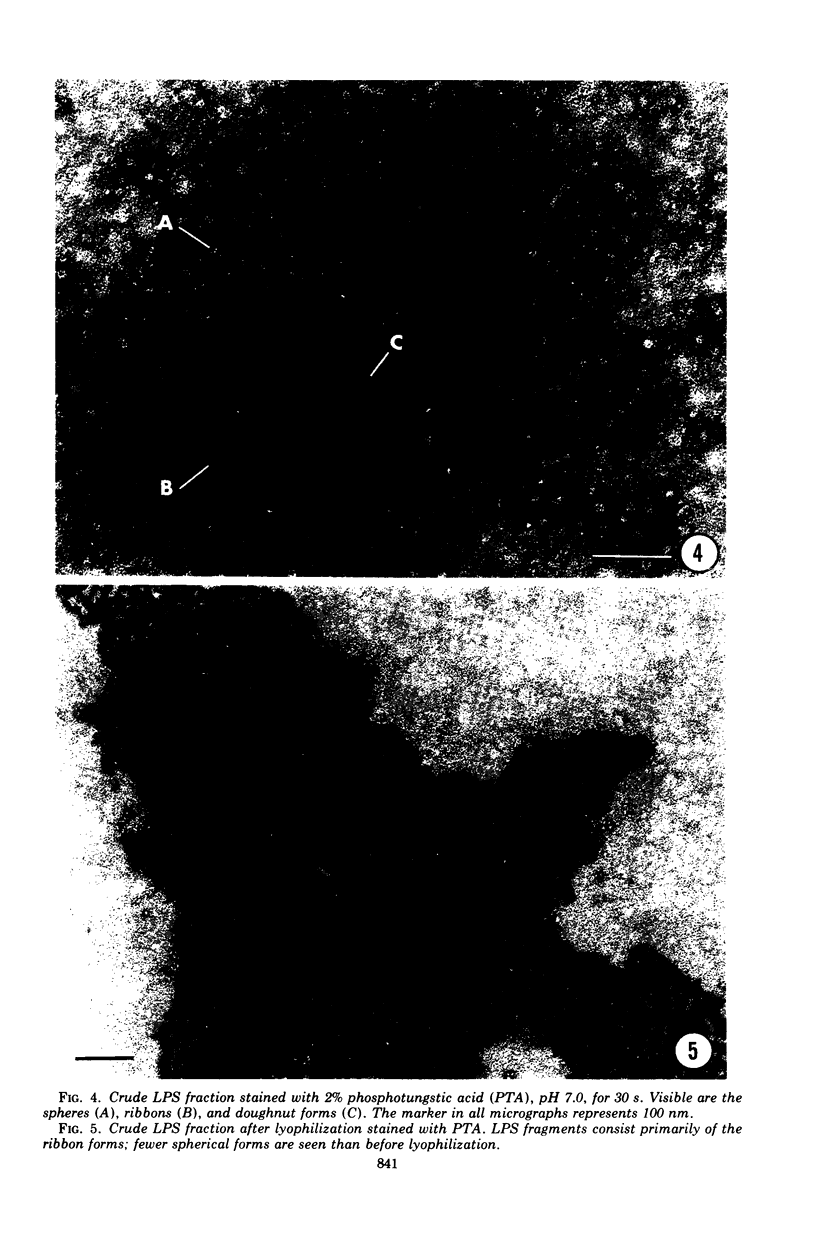
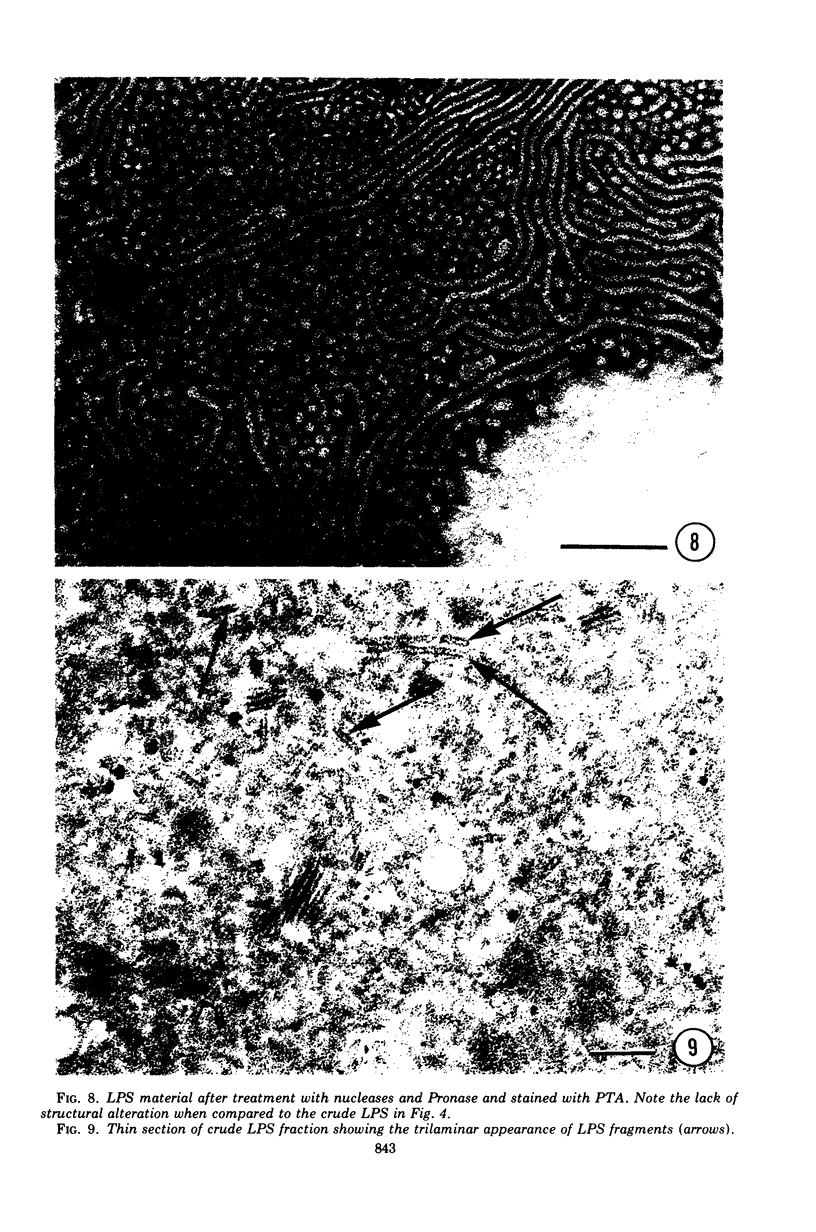
A lipopolysaccharide (LPS) fraction was extracted from Nichols, nonpathogenic Treponema pallidum by the hot, phenol-water procedure. The LPS was freed of nucleic acids and water-soluble proteins by successive exposures to ribonuclease, deoxyribonuclease, and Pronase. Purified LPS responded positively in a colorimetric assay for lipopolysaccharide. Electron microscope examination of the LPS both before and after purification demonstrated a heterogeneous mixture of forms including spheres, doughnuts, and ribbons. The trilaminar nature of the ribbon forms was observed by both negative staining and thin sectioning. Lyophilization of the LPS caused an increase in the number and length of ribbon forms seen. Results suggest that the surface layers of treponemes are similar to those of gram-negative bacteria.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHRISTIANSEN A. H. Studies on the antigenic structure of Treponema pallidum. 2. Isolation and purification of polysaccharides from Reiter's apathogenic strain. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1962;56:166–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'ALESSANDRO G., DEL CARPIO C. A lipopolysaccharide antigen of the Treponema. Nature. 1958 Apr 5;181(4614):991–992. doi: 10.1038/181991b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Dissociation and reassembly of Escherichia coli outer membrane and of lipopolysaccharide, and their reassembly onto flagellar basal bodies. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1184–1199. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1184-1199.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S., Black S. H. Ultrastructure of Treponema pallidum Nichols following lysis by physical and chemical methods. I. Envelope, wall, membrane and fibrils. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;76(4):308–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00408528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J., Work E. A colorimetric estimation of lipopolysaccharides. FEBS Lett. 1971 Sep 1;16(4):343–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jepsen O. B., Hougen K. H., Birch-Andersen A. Electron microscopy of treponema pallidum Nichols. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;74(2):241–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1968.tb03477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J., Inniss W. E. Electron microscopic study of lipopolysaccharide from an avian strain of Escherichia coli O18. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):238–243. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.238-243.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nell E. E., Hardy P. H. Studies on the chemical composition and immunologic properties of a polysaccharide from the Reiter treponeme. Immunochemistry. 1966 May;3(3):233–245. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(66)90187-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PILLOT J., DUPOUEY P. COMPOSITION ANTIG'ENIQUE DES TR'EPON'EMES V. ETUDE IMMUNOLOGIQUE DES ANTIG'ENES POLYOSIDIQUES DU TR'EPON'EME REITER. DISCUSSION. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Apr;106:617–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PILLOT J., DUPOUEY P. COMPOSITION ANTIG'ENIQUE DES TR'EPON'EMES. IV. SOLUBILISATION ET PURIFICATION DES ANTIG'ENES POLYOSIDIQUES DU TR'EPON'EME REITER. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Mar;106:456–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo D., Girard A., Rothfield L. Reconstitution of a functional membrane enzyme system in a monomolecular film. I. Formation of a mixed monolayer of lipopolysaccharide and phospholipid. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 14;53(3):475–490. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90078-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W., Jr, Graham J. A., Nath K. The morphologic structure of isolated bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]