Figure 6.
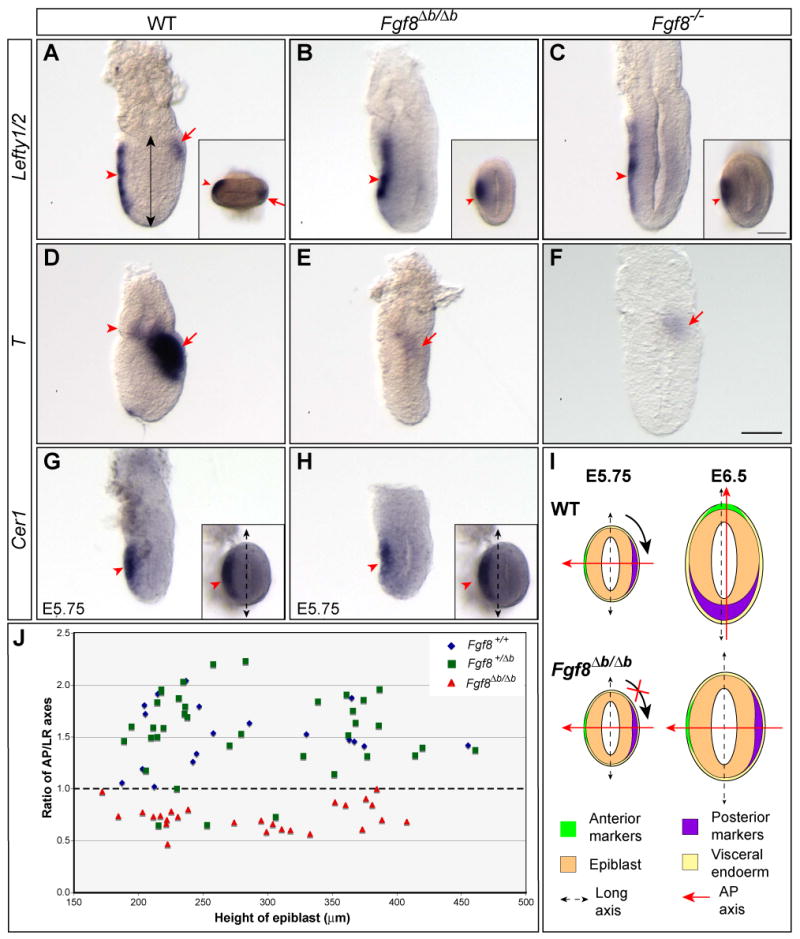
Fgf8b is required for normal induction of Lefty2 and T, and proper alignment between the AP axis and the shape of the embryo. (A-C) In situ hybridization with a RNA probe detecting both Lefty1 and Lefty2 in E6.5 embryos of indicated genotypes. Expression of Lefty1 in the AVE (marked by arrowhead) is unaffected in Fgf8Δb/Δb or Fgf8-/- embryos, whereas Lefty2 expression in the emerging primitive streak (arrow) is missing in the mutants. Insets show distal views of the embryos in A and C. (D-F) Analysis of T expression in E6.5 embryos of indicated genotype. Arrowhead marks T expression domain in the distal extraembryonic ectoderm, while arrow marks T expression in the posterior epiblast. (G-H) Expression of Cer1 in the AVE of WT (G) and Fgf8Δb/Δb embryos (H) at E5.75. Insets show distal views of the embryo. Dashed double-headed arrow marks the long axis of the embryo. (I) Schematic summary of the AP polarity with respect to the shape of WT and Fgf8Δb/Δb embryo at E5.75 and E6.5. Note that the shift of AP axis fails to occur in Fgf8Δb/Δb embryo. (J) Distribution of the ratio of AP and LR dimensions relating to the height of epiblast (indicated by double arrow in A) between E6.0 to E6.75 from intercrosses of Fgf8+/Δb mutants. Each dot represents one embryo. Scale bar in F that is equivalent to 50 μm is applicable to A-H, including insets in G and H. A different scale bar (50 μm) is used for the insets in A-C.
