Abstract
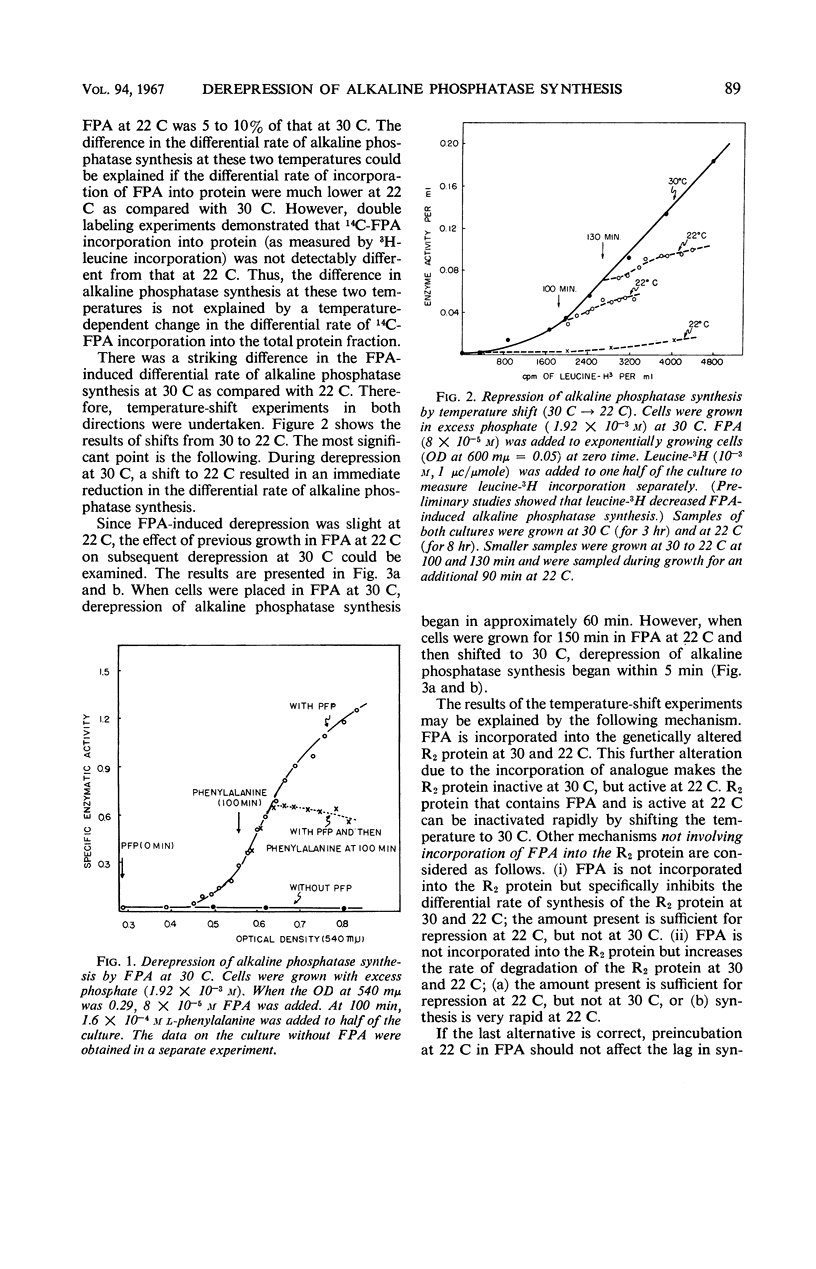
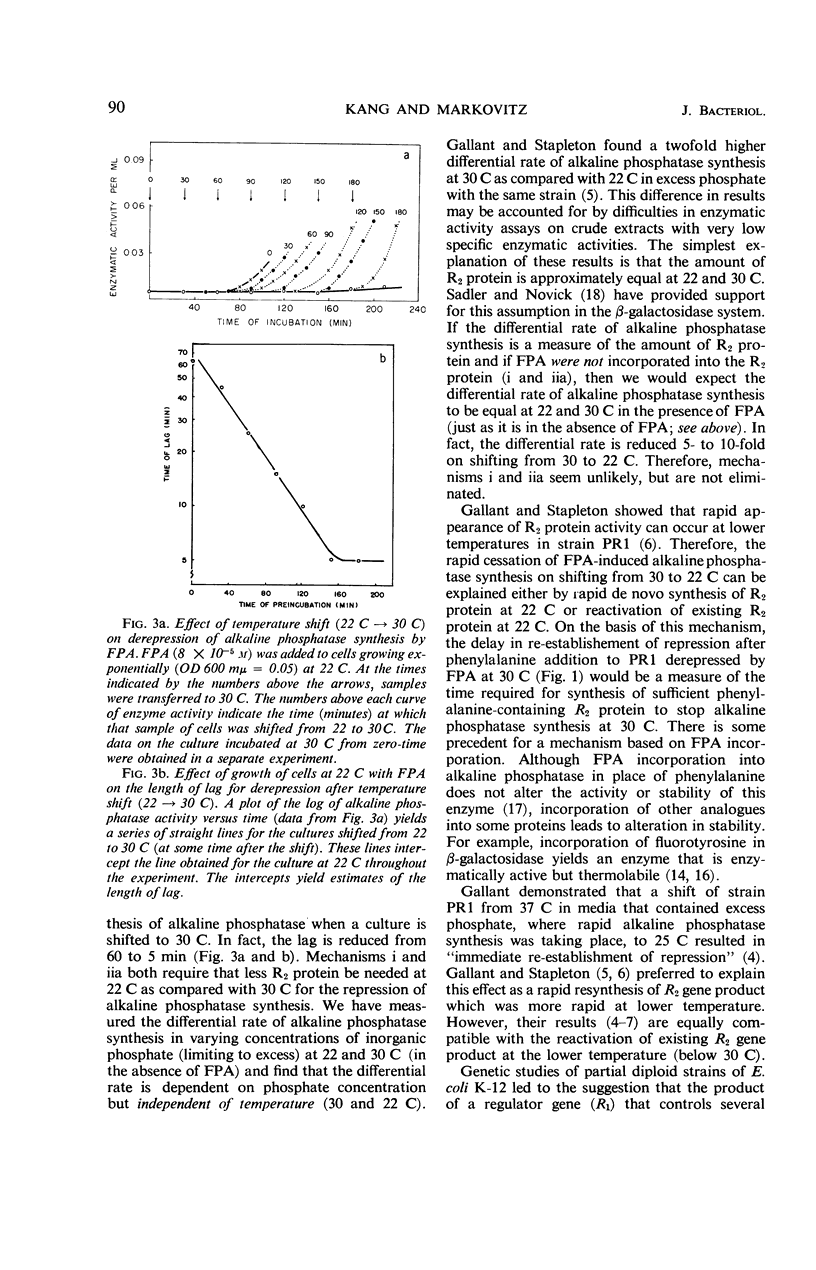
p-Fluorophenylalanine (FPA) causes a 100-fold increase in alkaline phosphatase in Escherichia coli B, strain PR1 at 30 C in minimal medium that contains excess inorganic phosphate (1.92 × 10−3m). Little increase in alkaline phosphatase synthesis occurs under these conditions at 22 C. [This strain is known to have a mutation in a regulator gene (R2) that, in the absence of FPA, permits derepression of alkaline phosphatase synthesis at 37 C, but not at 30 C or below.] In contrast, E. coli B3 (the strain from which E. coli B strain PR1 was derived) is not derepressed at 30 C by FPA. 14C-FPA is incorporated into bacterial proteins. Temperature-shift experiments (30 C⇌22 C) in the presence of FPA are consistent with the following mechanism. FPA is incorporated into the genetically altered R2 protein at 30 and 22 C. This further alteration due to the incorporation of analogue makes the R2 protein inactive at 30 C, but active at 22 C.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENZER S., CHAMPE S. P. A change from nonsense to sense in the genetic code. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1114–1121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R., Gussin G. N. Suppression in vitro: Identification of a Serine-sRNA as a "Nonsense" Suppressor. Science. 1965 Jul 23;149(3682):417–422. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3682.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECHOLS H., GAREN A., GAREN S., TORRIANI A. Genetic control of repression of alkaline phosphatase in E. coli. J Mol Biol. 1961 Aug;3:425–438. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALLANT J. A. Thermal derepression of alkaline phosphatase synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Aug 31;8:506–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALLANT J., STAPLETON R. DEREPRESSION OF ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE SYNTHESIS BY CHLORAMPHENICOL AND CANAVANINE INHIBITION. J Mol Biol. 1964 Apr;8:442–451. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALLANT J., STAPLETON R. PHYSIOLOGICAL EVIDENCE ON THE NATURE OF THE REPRESSOR OF ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE SYNTHESIS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Mol Biol. 1964 Apr;8:431–441. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALLANT J., STAPLETON R. PROPERTIES OF A TEMPERATURE-SENSITIVE REGULATORY SYSTEM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Aug;50:348–355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.2.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., ECHOLS H. Genetic control of induction of alkaline phosphatase synthesis in E. coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Aug;48:1398–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.8.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., GAREN S. Genetic evidence on the nature of the repressor for alkaline phosphatase in E. coli. J Mol Biol. 1963 May;6:433–438. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., LEVINTHAL C. A fine-structure genetic and chemical study of the enzyme alkaline phosphatase of E. coli. I. Purification and characterization of alkaline phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:470–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., OTSUJI N. ISOLATION OF A PROTEIN SPECIFIED BY A REGULATOR GENE. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jun;8:841–852. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80165-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., SIDDIQI O. Suppression of mutations in the alkaline phosphatase structural cistron of E. coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1121–1127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEPES A., BEGUIN S. HYDROXYLAMINE, AN INHIBITOR OF PEPTIDE CHAIN INITIATION. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Feb 3;18:377–383. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90717-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang S., Markovitz A. Induction of capsular polysaccharide synthesis by rho-fluorophenylalanine in Escherichia coli wild type and strains with altered phenylalanyl soluble ribonucleic acid synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):584–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.584-591.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNIER R. L., SARRAZIN G. ETUDE DE L'ORIGINE DES DIFF'ERENCES DE STABILIT'E PR'ESENT'EES PAR LA BETA-GALACTOSIDASE NORMALE ET LA BETA-GALACTOSIDASE DONT TOUS LES GROUPES TYROSINE SONT REMPLAC'ES PAR LA 3-FLUOROTYROSINE. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1964 Jul 27;259:937–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markovitz A., Rosenbaum N. A regulator gene that is dominant on an episome and recessive on a chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1084–1091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H. Random replacement of phenylalanine by p-fluorophenylalanine in alkaline phosphatase(s) formed during biosynthesis by E. coli. J Mol Biol. 1963 Apr;6:284–294. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80089-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SADLER J. R., NOVICK A. THE PROPERTIES OF REPRESSOR AND THE KINETICS OF ITS ACTION. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:305–327. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80255-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARABHAI A. S., STRETTON A. O., BRENNER S., BOLLE A. CO-LINEARITY OF THE GENE WITH THE POLYPEPTIDE CHAIN. Nature. 1964 Jan 4;201:13–17. doi: 10.1038/201013a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIGERT M. G., GAREN A. AMINO ACID SUBSTITUTIONS RESULTING FROM SUPPRESSION OF NONSENSE MUTATIONS. I. SERINE INSERTION BY THE SU-1 SUPPRESSOR GENE. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:448–455. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


