Abstract
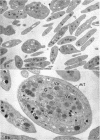
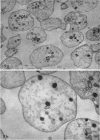
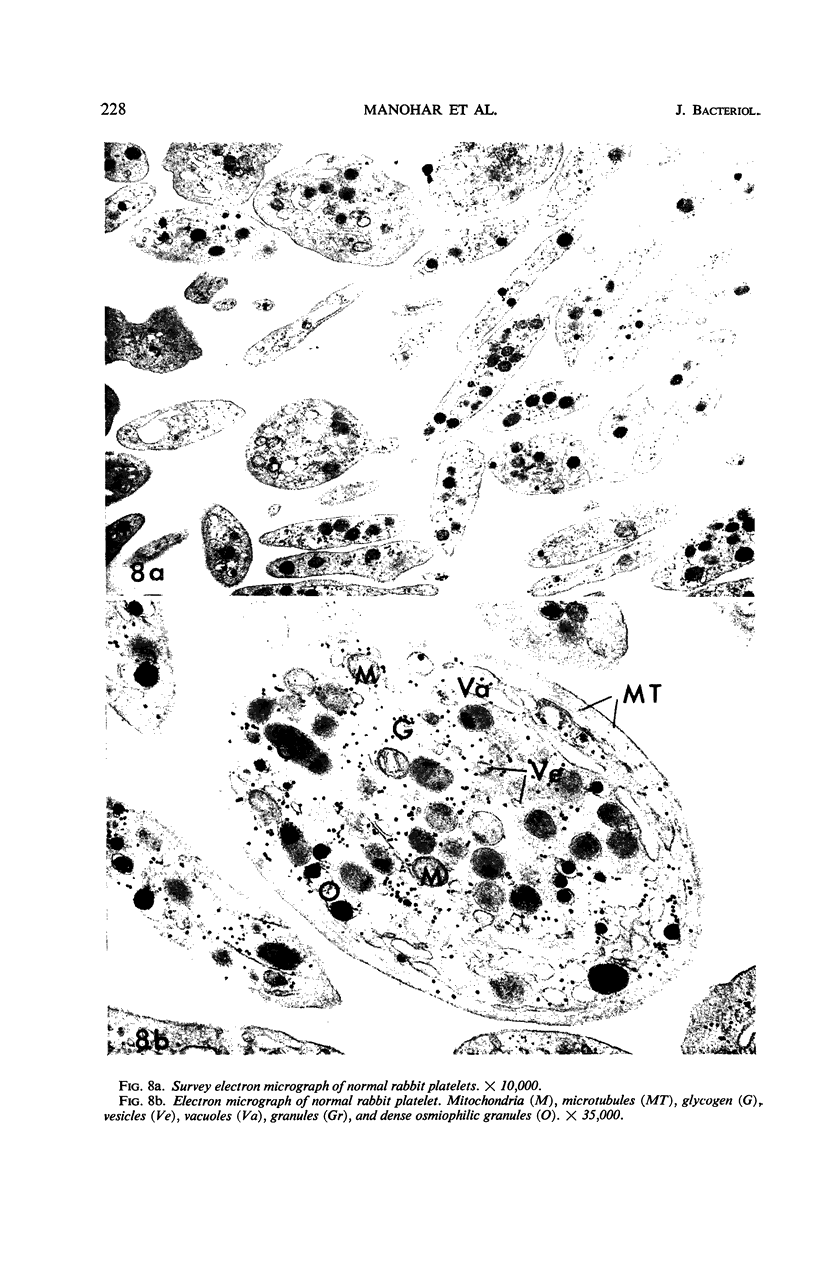
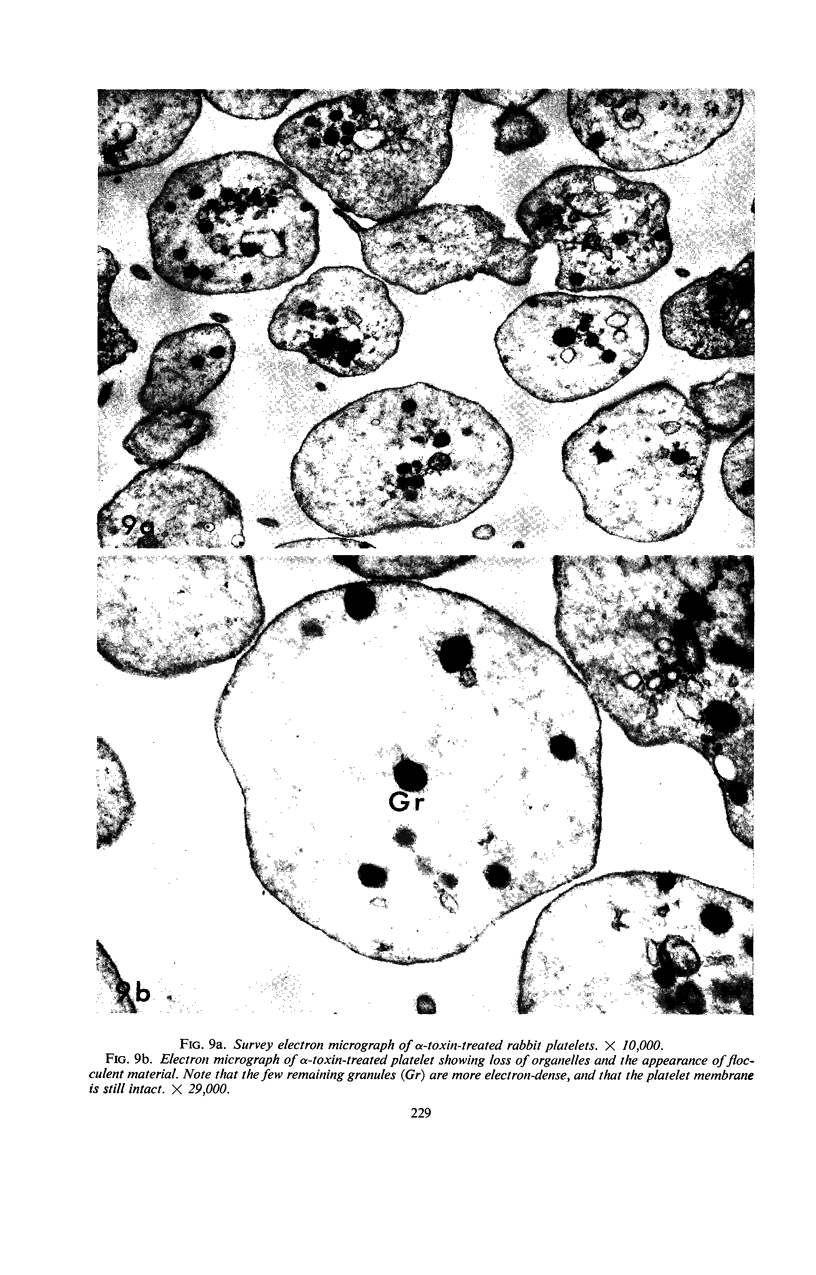
Crude and purified staphylococcal α-toxin were used to demonstrate that the platelet-damaging effect of crude α-toxin represents a fifth activity of the α-toxin molecule. The homogeneity of the purified toxin employed was demonstrated by ultracentrifugation, Ouchterlony, and immunoelectrophoretic methods. Continuous-flow electrophoretic migration studies demonstrated under a variety of conditions that the platelet-damaging and the α-hemolytic activities migrated as a unit. Fractionation studies with the use of Sephadex G-100, carboxymethyl cellulose, and diethylaminoethyl cellulose failed to separate these two activities. Further, when α-toxin of demonstrated purity and crude toxin were adjusted to the same hemolytic activity, they possessed the same platelet-damaging activity. In addition, heat-reactivation studies with crude α-toxin revealed that the platelet-damaging effect was inactivated and reactivated in parallel with α-hemolytic activity. Comparable studies with purified α-toxin showed parallel inactivation of both activities at 60 C. Additional heating at 100 C failed to reactivate either activity. Electron micrographs revealed that purified α-toxin produced distinct degenerative changes in rabbit platelets. These studies also provided definite evidence that purified α-toxin has a damaging effect on human platelets. Monovalent α-antisera prevented platelet damage.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. EFFECT OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL AND OTHER BACTERIAL TOXINS ON PLATELETS IN VITRO. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:209–223. doi: 10.1002/path.1700890121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOSHI K., CLUFF L. E., NORMAN P. S. Studies on the pathogenesis of staphylococcal infection. V. Purification and characterization of staphylococcal alpha hemolysin. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1963 Jan;112:15–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeljaszewicz J., Szmigielski S., Korbecki M., Zak C. Histochemical demonstration of changes in enzymatic activity of KB cells produced by staphylococcal alpha and beta hemolysins. J Infect Dis. 1965 Dec;115(5):421–428. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.5.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KITAMURA S., SHELTON J., THAL A. P. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS ALPHA-HEMOLYSIN. Ann Surg. 1964 Nov;160:926–935. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196411000-00023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUMAR S., LINDORFER R. K. The characterization of staphylococcal toxins. I. The electrophoretic migration of the alpha hemolytic, dermonecrotic, lethal, and leucocidal activities of crude toxin. J Exp Med. 1962 Jun 1;115:1095–1106. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.6.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN S. P., GREEN R. Methods for the study of surviving leukocytes: A. Preparation of cell suspension. Methods Med Res. 1958;7:136–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manohar M., Kumar S., Lindorfer R. K. Heat reactivation of the alpha-hemolytic, dermonecrotic, lethal activities of crude and purified staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1681–1685. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1681-1685.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEGEL I., COHEN S. ACTION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL TOXIN ON HUMAN PLATELETS. J Infect Dis. 1964 Dec;114:488–502. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.5.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver M. D. Cytoplasmic microtubules in rabbit platelets. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1965 Nov 15;68(4):474–480. doi: 10.1007/BF00347711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER A. F., MACK E. M., FROMMES S. A simple, rapid method for preparin glass knives for use in electron microscopy. Am J Vet Res. 1962 May;23:673–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]