Abstract
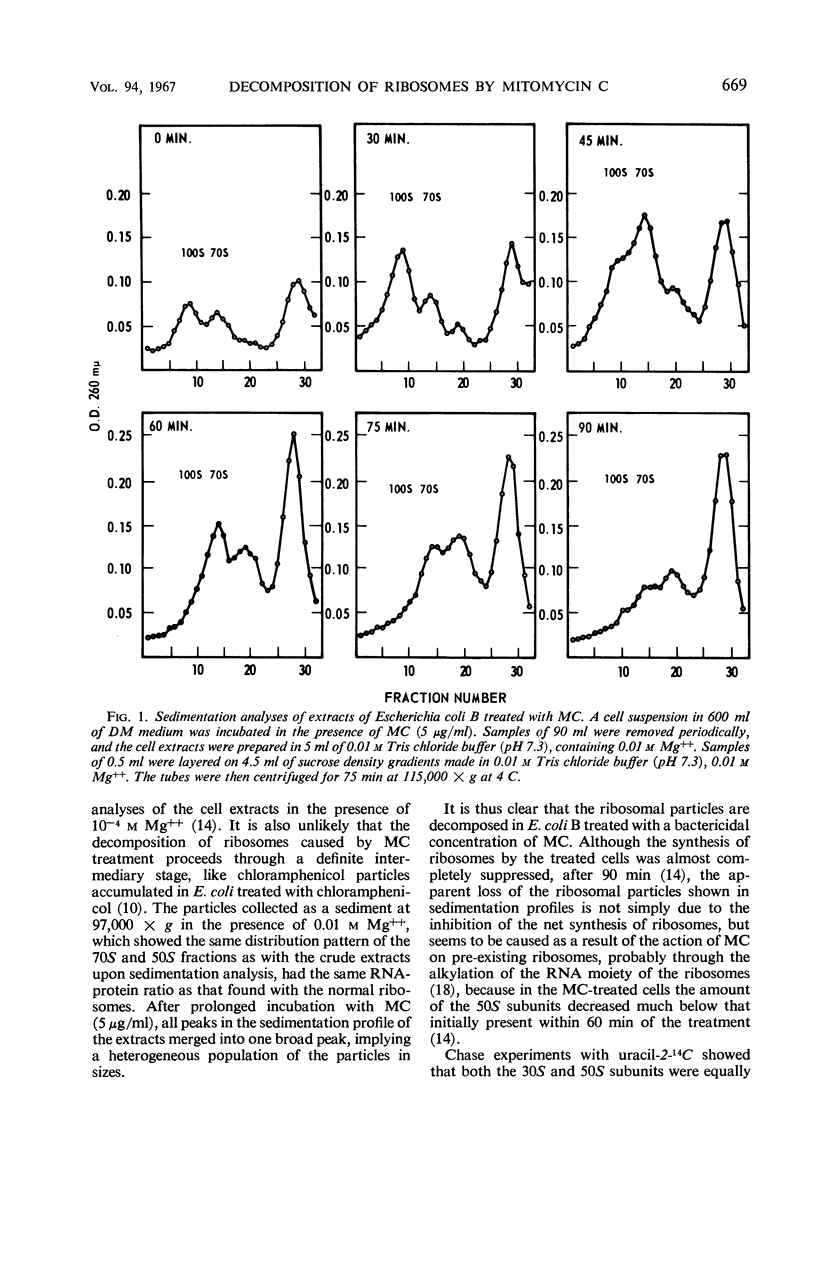
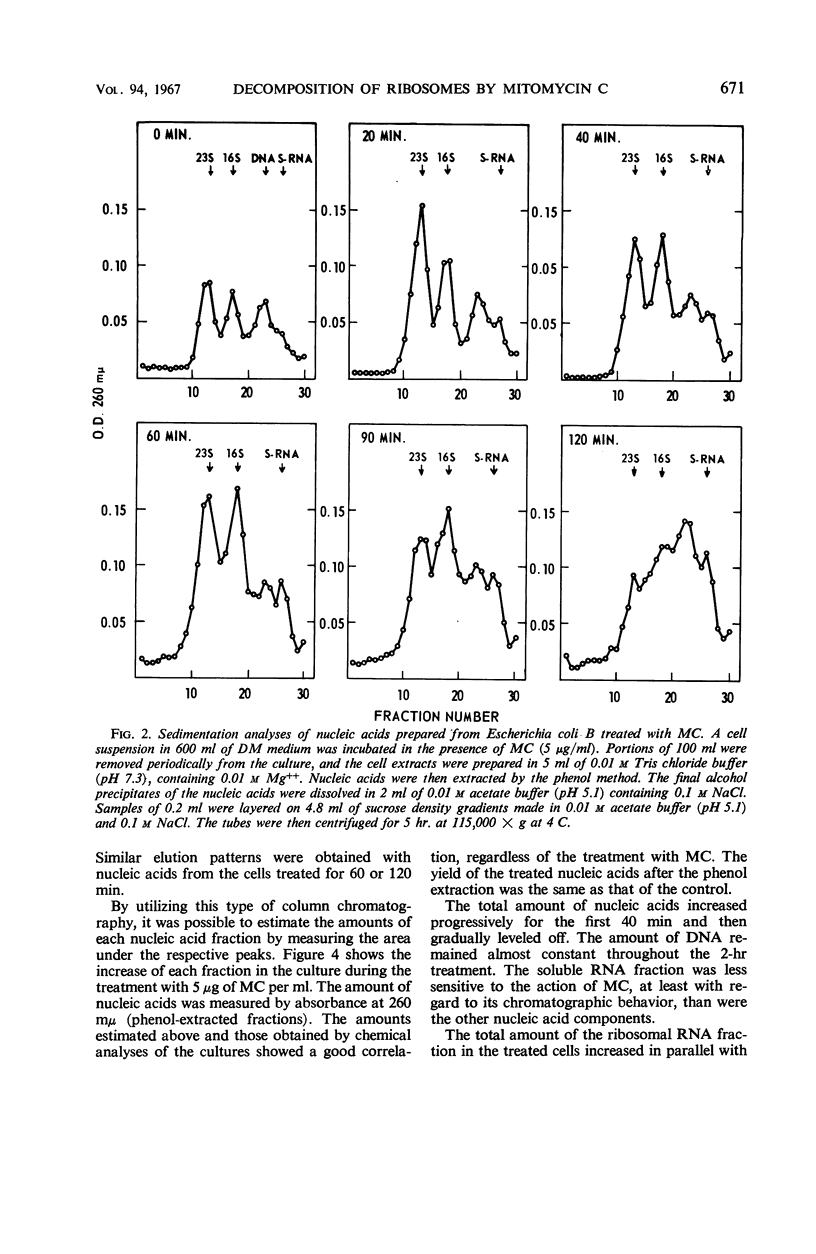
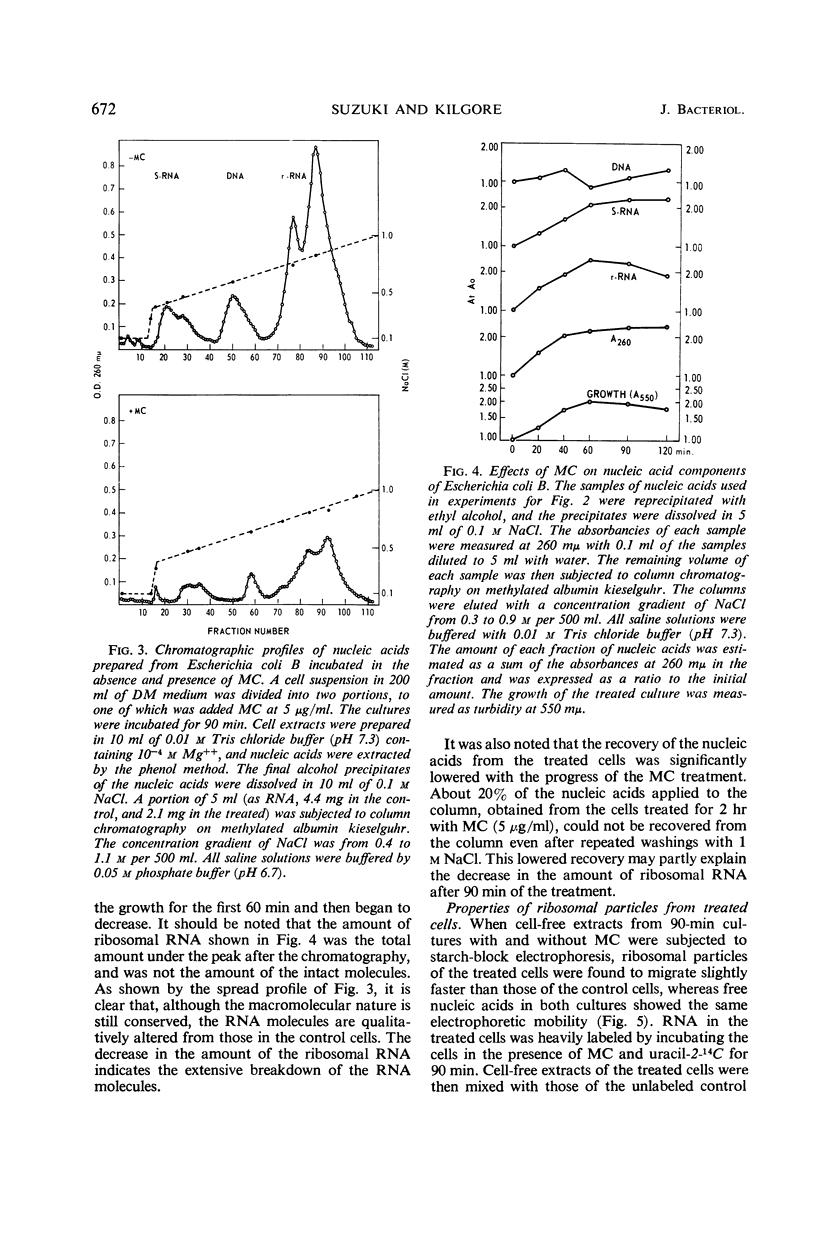
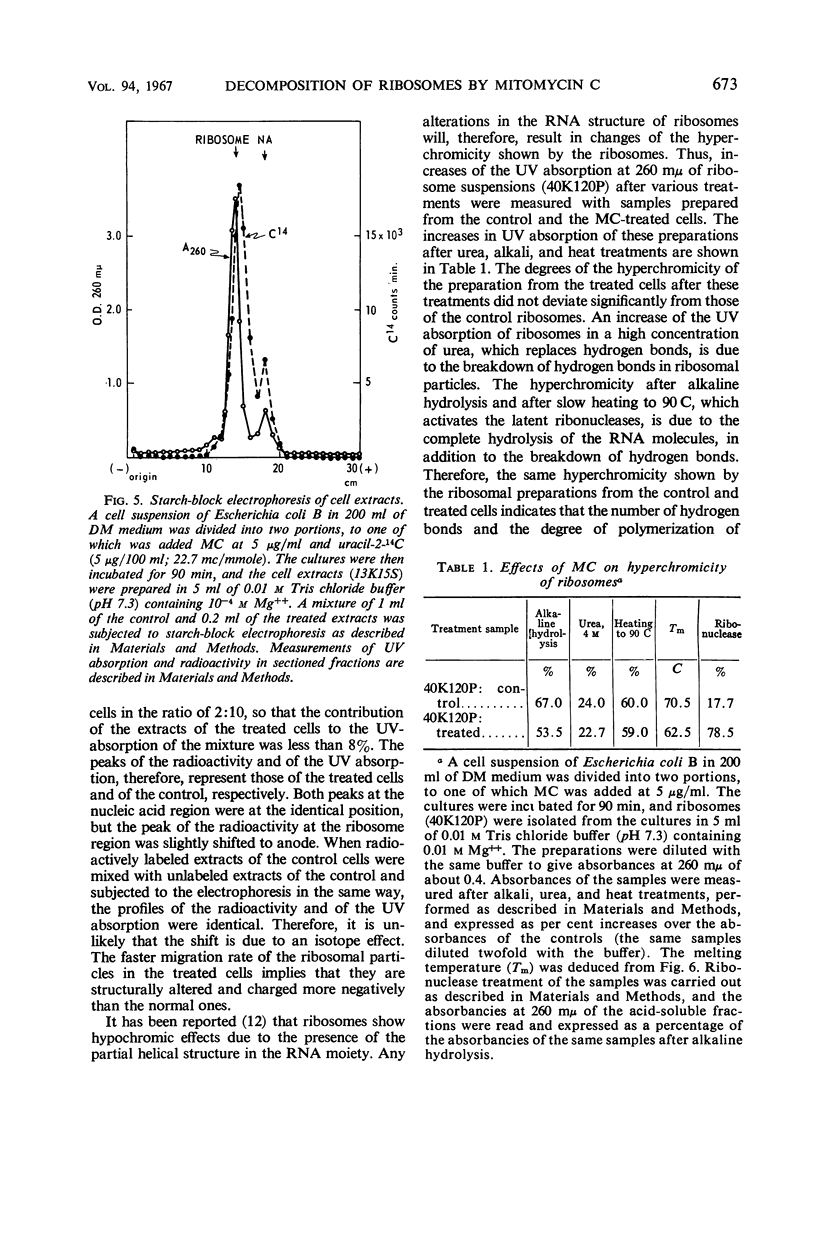
Exposure of cells of Escherichia coli to mitomycin C (5 μg/ml) resulted in a marked change in the sedimentation profiles of the cell-free extracts, indicating a specific decomposition of ribosomal particles. When the extracts were prepared in the presence of 0.01 m Mg++ and analyzed by sucrose density gradient centrifugations, the 100S fraction disappeared rapidly from the treated cells. The 70S ribosomes were also degraded, but more slowly, with a concomitant accumulation of a fraction having a sedimentation coefficient of about 50S. However, decomposition of the 70S ribosomes was preceded by an almost complete loss of the 50S ribosomal subunits, as revealed by sedimentation analyses in the presence of 10−4m Mg++. Synthesis of the ribosomes in the treated cells was also suppressed, being demonstrated by a lower incorporation of uracil-2-14C into the ribosomal fractions. However, the change in the ribosomal profile in the treated cells apparently resulted from the decomposition of pre-existing ribosomes, rather than from the inhibition of the net synthesis of ribosomes. Sedimentation analyses and chromatography of the nucleic acids extracted from the treated cells indicated extensive but delayed degradation of the ribosomal ribonucleic acid (RNA), but not of the soluble RNA or deoxyribonucleic acid fractions. Altered structure of the ribosomes in the treated cells was also indicated by their lower melting temperature, broadened thermal profile, higher electrophoretic mobility, and extreme sensitivity to ribonuclease treatment, compared with normal ribosomes. The synthesis of messenger RNA was inhibited progressively with time in the treated cells.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FENWICK M. L. The influence of poliovirus infection of RNA synthesis in mammalian cells. Virology. 1963 Mar;19:241–249. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROS F., HIATT H., GILBERT W., KURLAND C. G., RISEBROUGH R. W., WATSON J. D. Unstable ribonucleic acid revealed by pulse labelling of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1961 May 13;190:581–585. doi: 10.1038/190581a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISHIHAMA A., MIZUNO N., TAKAI M., OTAKA E., OSAWA S. Molecular and metabolic properties of messenger RNA from normal and T2-infected Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1962 Sep;5:251–264. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80069-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERSTEN H. Action of mitomycin C on nucleic acid metabolism in tumor and bacterial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Apr 2;55:558–560. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90994-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERSTEN H., KERSTEN W., LEOPOLD G., SCHNIEDERS B. EFFECT OF MITOMYCIN C ON DNAASE AND RNA IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 23;80:521–523. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELL J. D., HERSHEY A. D. A fractionating column for analysis of nucleic acids. Anal Biochem. 1960 Jun;1:66–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(60)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy B. J., Britten R. J. The Synthesis of Ribosomes in E. coli: I. The Incorporation of C-Uracil into the Metabolic Pool and RNA. Biophys J. 1962 Jan;2(1):35–47. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(62)86839-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUZUKI H., KILGORE W. W. MITOMYCIN C: EFFECT ON RIBOSOMES OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. Science. 1964 Dec 18;146(3651):1585–1587. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3651.1585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZYBALSKI W., IYER V. N. CROSSLINKING OF DNA BY ENZYMATICALLY OR CHEMICALLY ACTIVATED MITOMYCINS AND PORFIROMYCINS, BIFUNCTIONALLY "ALKYLATING" ANTIBIOTICS. Fed Proc. 1964 Sep-Oct;23:946–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith-Kielland I. The effect of mitomycin C on ribonucleic acid synthesis in growing cultures of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 22;119(3):486–491. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90124-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Kilgore W. W. Effects of mitomycin C on macromolecular synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):675–682. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.675-682.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


