Abstract
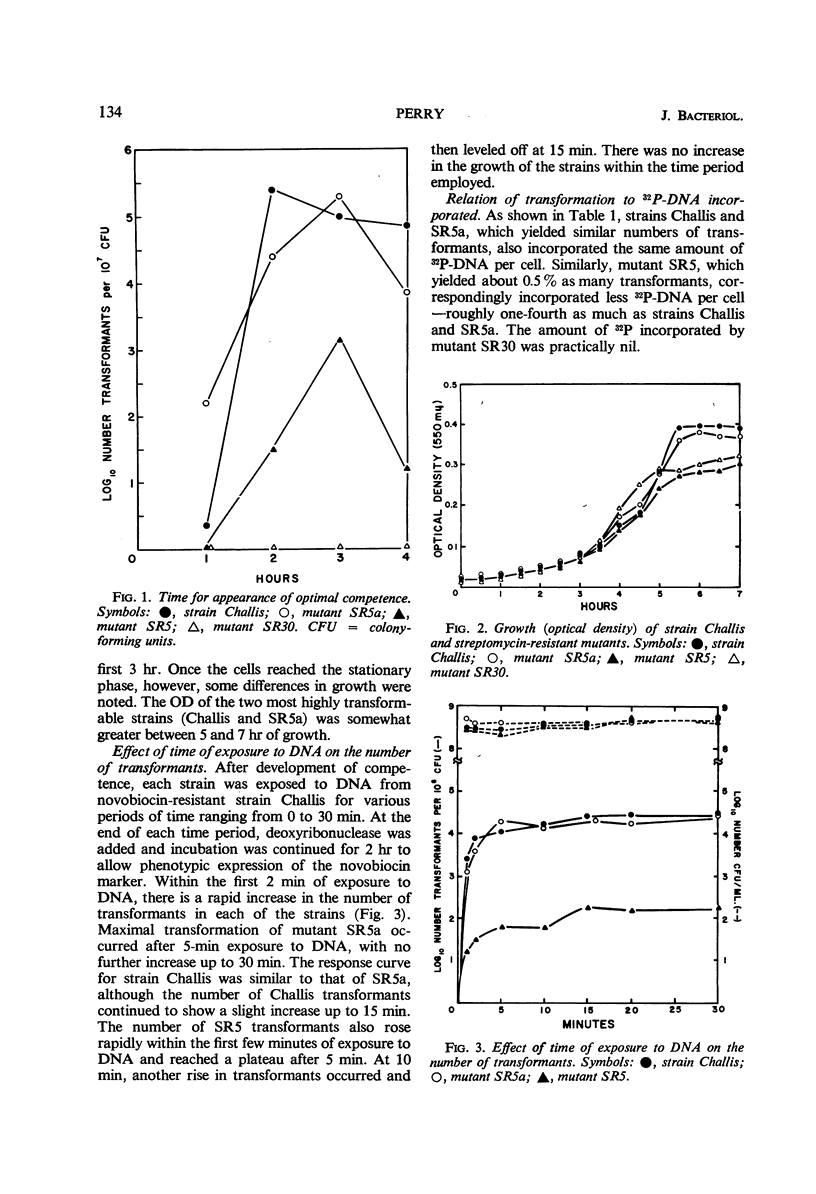
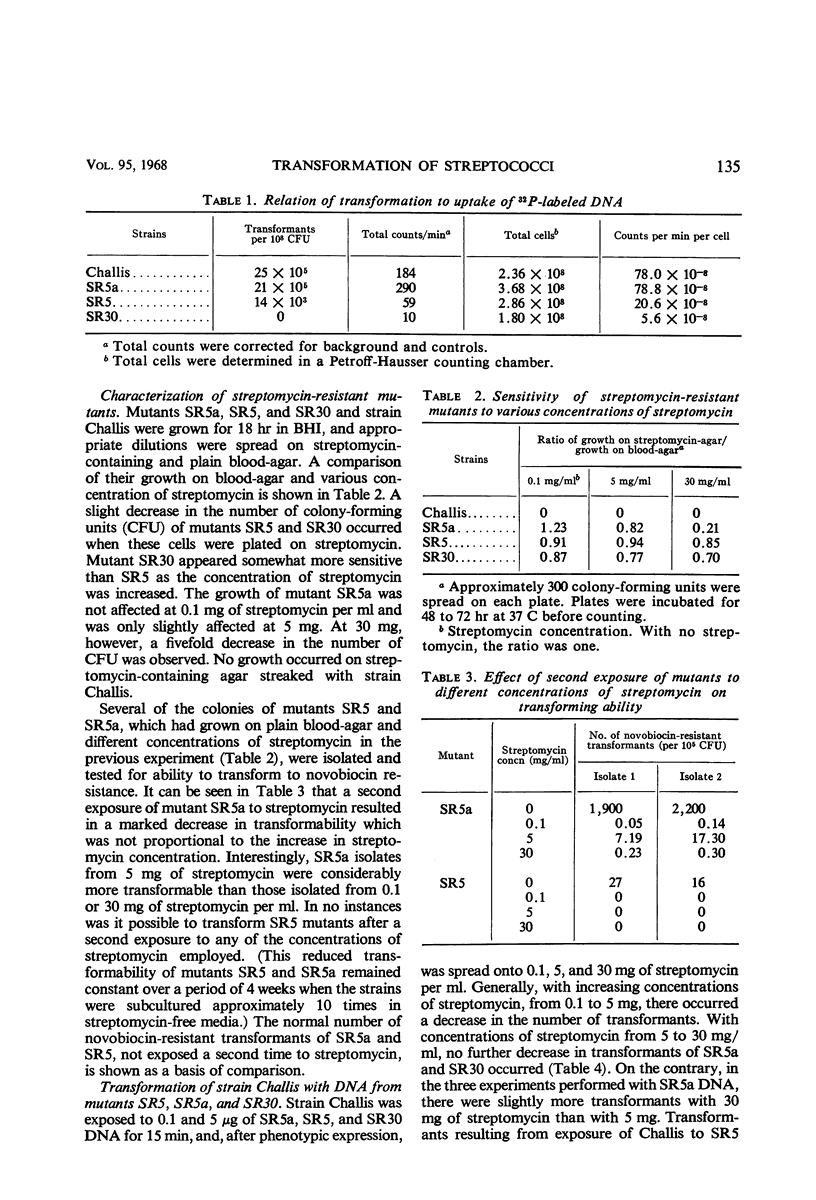
Several resistant mutants of a transformable group H streptococcus, strain Challis, were isolated from media containing high concentrations of streptomycin. Mutants SR5a and SR5 exhibited high and low transformability, respectively, when exposed to deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) from a novobiocin-resistant Challis strain. With similar exposure, mutant SR30 exhibited loss of transformability. The mutants further differed from the parent strain in time of appearance of optimal competence, and, in the case of SR5 and SR30, total growth was somewhat less than that of the parent. The rapidity with which transformants appeared upon initial exposure to DNA was approximately the same in the mutants and the parent strain. The decrease or loss of transformability of mutants SR5 and SR30 was found to be due to an alteration in capacity to take up DNA. Mutant SR5a (highly transformable) was further differentiated from mutants SR5 and SR30 in that it was somewhat more sensitive to high concentrations of streptomycin. Transformants obtained by treating strain Challis with the three types of mutant DNA, on the other hand, exhibited similar degrees of resistance to increasing concentrations of streptomycin. The additional decrease in transforming ability of mutant SR5a and the loss of transforming ability of mutant SR5 after a second exposure to streptomycin may indicate a stepwise process in the change from transformability to nontransformability. Although streptomycin resistance may not be directly related to inability to transform, results indicate that streptomycin greatly increases the chances of selecting these mutants and also can be of value in serving as a marker in studies of this nature.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAVIES J., GILBERT W., GORINI L. STREPTOMYCIN, SUPPRESSION, AND THE CODE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 May;51:883–890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.5.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPHRATI-ELIZUR E. RESISTANCE TO ACTINOMYCIN D AND TRANSFORMABILITY IN B.SUBTILIS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 4;18:103–107. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90890-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLAKS J. G., COX E. C., WITTING M. L., WHITE J. R. Polypeptide synthesis with ribosomes from streptomycin-resistant and dependent E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 11;7:390–393. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90321-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX M. S. Deoxyribonucleic acid incorporation by transformed bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Oct;26(1):83–85. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANCOCK R. Uptake of 14C-streptomycin by some microorganisms and its relation to their streptomycin sensitivity. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Jul;28:493–501. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-3-493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTY M. The lysis of group A hemolytic streptococci by extracellular enzymes of Streptomyces albus. I. Production and fractionation of the lytic enzymes. J Exp Med. 1952 Dec;96(6):555–568. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.6.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY D., SLADE H. D. Transformation of streptococci to streptomycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1962 Mar;83:443–449. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.3.443-449.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLSINELLI M., CIFERRI O., CASSANI G., ALBERTINI A. MECHANISM OF RESISTANCE TO ACTINOMYCIN IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1567–1572. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1567-1572.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry D., Slade H. D. Effect of filtrates from transformable and nontransformable streptococci on the transformation of streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2216–2222. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2216-2222.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAVIN A. W. The genetics of transformation. Adv Genet. 1961;10:61–163. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIROTNAK F. M., LUNT R. B., HUTCHISON D. J. ALTERATION IN TRANSFORMABILITY OF DIPLOCOCCUS PNEUMONIAE AFTER THE ACQUISITION OF GENETIC DETERMINANTS INDUCING RESISTANCE TO ERYTHROMYCIN. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:735–739. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.735-739.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPEYER J. F., LENGYEL P., BASILIO C. Ribosomal localization of streptomycin sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Apr 15;48:684–686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.4.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J., Reilly B. E., Evans A. H. Microbial transformation and transfection. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1966;20:371–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.20.100166.002103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


