Abstract
Strains of type 6 (S 43) and type 14 group A streptococci were grown with M-protein production in the presence of chemically defined synthetic media slightly modified from that previously employed for the growth of a nonproducer of M protein (type 4). The M protein, which is associated with virulence in group A streptococcus, was previously produced in growing cultures only with complex media. The bacterial growth with the biosynthesis of M protein in synthetic medium was obtained by successive adaptation in steady-state culture with decreasing amounts of Todd-Hewitt broth. The synthesis continued for at least 480 generations at pH 7.3 and with a generation time of 84 min. Glucose was the limiting nutrilite and the concentration of reducing agents in the medium was critical. The M protein was identified by gel diffusion against type-specific antisera from the Communicable Disease Center and from R. Lancefield. The yield of M protein obtained from organisms grown in the continuous-culture device was comparable to that from standard broth stationary cultures.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHANCE B. The reactions of catalase in the presence of the notatin system. Biochem J. 1950 Apr;46(4):387–402. doi: 10.1042/bj0460387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALE W. M., RUSSELL C. A study of the irradiation of catalase by ionizing radiations in the presence of cysteine, cystine and glutathione. Biochem J. 1956 Jan;62(1):50–57. doi: 10.1042/bj0620050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES H. C., KARUSH F., RUDD J. H. EFFECT OF AMINO ACIDS ON STEADY-STATE GROWTH OF A GROUP A HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCUS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Feb;89:421–427. doi: 10.1002/path.1700890156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott S. D. A PROTEOLYTIC ENZYME PRODUCED BY GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO ITS EFFECT ON THE TYPE-SPECIFIC M ANTIGEN. J Exp Med. 1945 Jun 1;81(6):573–592. doi: 10.1084/jem.81.6.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX E. N., KRAMPITZ L. O. Studies on the biosynthesis of the M-protein of group A hemolytic streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1956 Apr;71(4):454–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.4.454-461.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Wittner M. K., Dorfman A. Antigenicity of the M proteins of group A hemolytic streptococci. 3. Antibody responses and cutaneous hypersensitivity in humans. J Exp Med. 1966 Dec 1;124(6):1135–1151. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.6.1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Wittner M. K. The multiple molecular structure of the M proteins of group A streptococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1118–1125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILBERT D. L. The role of pro-oxidants and antioxidants in oxygen toxicity. Radiat Res. 1963;Suppl 3:44–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb S. F. Bacterial nutritional approach to mechanisms of oxygen toxicity. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1021–1027. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1021-1027.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS T. N., IACOCCA V. F., KARUSH F. Growth of group A hemolytic streptococcus in the steady state. J Bacteriol. 1956 Sep;72(3):283–294. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.3.283-294.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEILIN D., HARTREE E. F. Purification of horse-radish peroxidase and comparison of its properties with those of catalase and methaemoglobin. Biochem J. 1951 Jun;49(1):88–104. doi: 10.1042/bj0490088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C., PERLMANN G. E. Preparation and properties of type-specific M antigen isolated from a group A, type 1 hemolytic streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1952 Jul;96(1):71–82. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICKELSON M. N. CHEMICALLY DEFINED MEDIUM FOR GROWTH STREPTOCOCCUS PYOGENES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:158–164. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.158-164.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlwain H. The metabolism and functioning of vitamin-like compounds: 1. Ammonia formation from glutamine by haemolytic streptococci; its reciprocal connexion with glycolysis. Biochem J. 1946;40(1):67–78. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlwain H. The metabolism and functioning of vitamin-like compounds: 3. Products of the decomposition of glutamine during streptococcal glycolysis. Biochem J. 1946;40(4):460–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelson M. N., Slade H. D. Absence of type specific M antigen from group A streptococci grown in a chemically defined medium. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1251–1251. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1251-.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
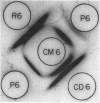
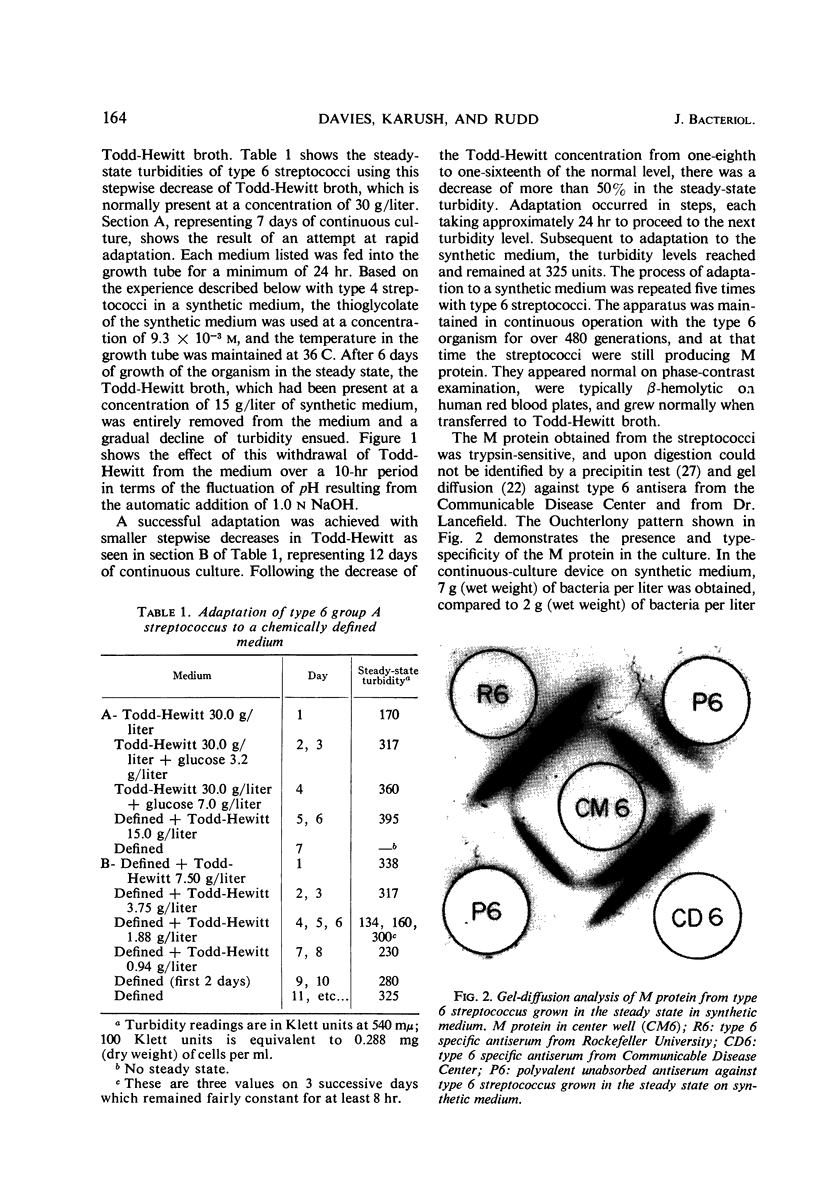
- OUCHTERLONY O. Antigen-antibody reactions in gels. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1949;26(4):507–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1949.tb00751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panos C., Cohen B. Growth rates of Streptococcus pyogenes and derived L form at various temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1242–1243. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1242-1243.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLADE H. D., KNOX G. A. Nutrition and the role of reducing agents in the formation of streptolysin O by a group A hemolytic streptococcus. J Bacteriol. 1950 Sep;60(3):301–310. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.3.301-310.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLADE H. D., SLAMP W. C. The requirement of ovalbumin for the growth of group A hemolytic Streptococcus in a synthetic medium. J Exp Med. 1955 Sep 1;102(3):291–305. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.3.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]