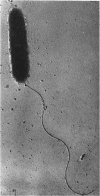
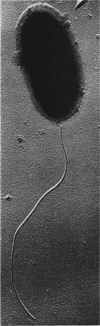
Abstract
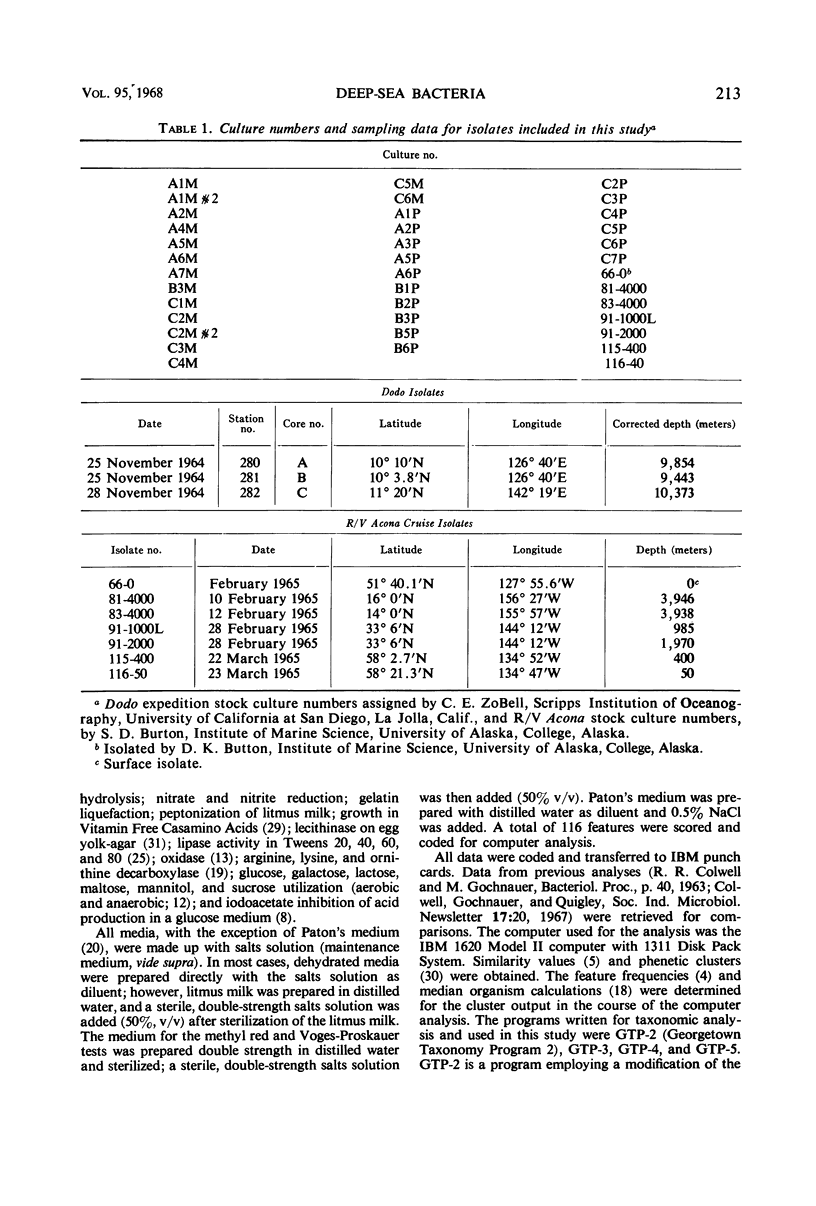
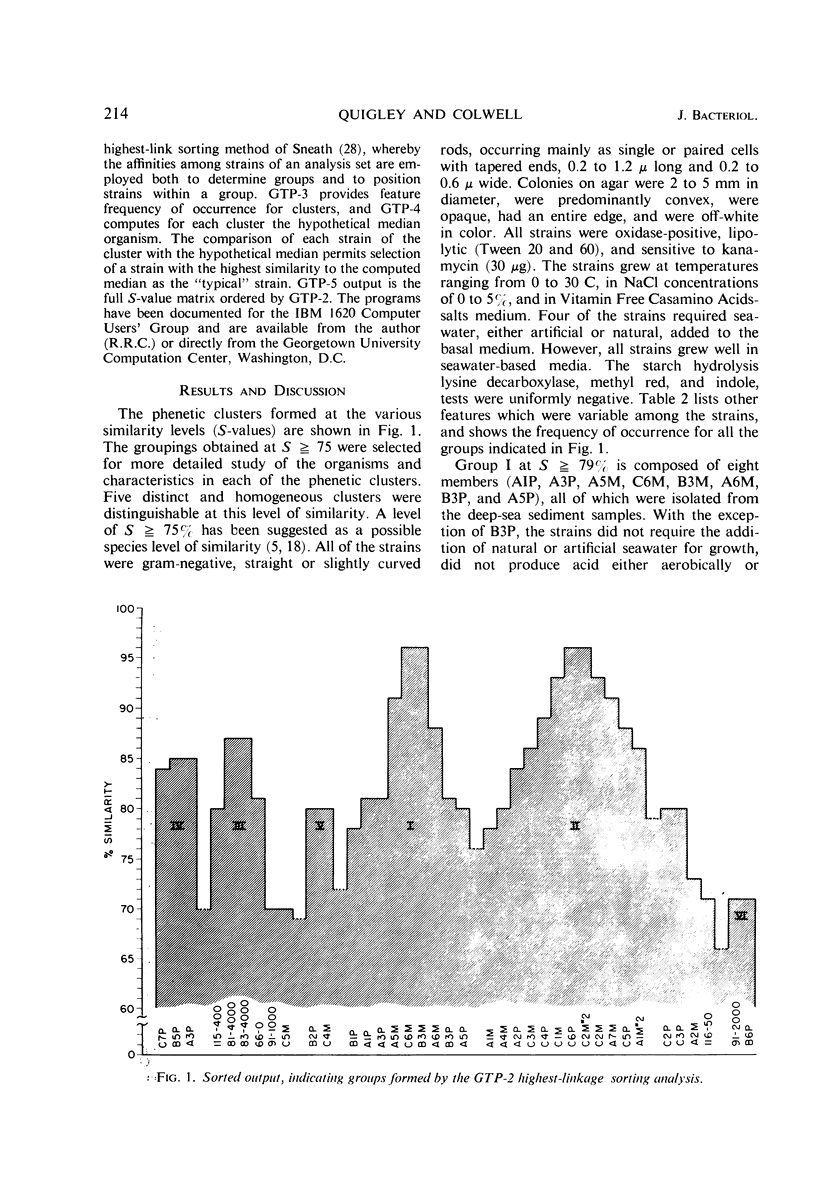
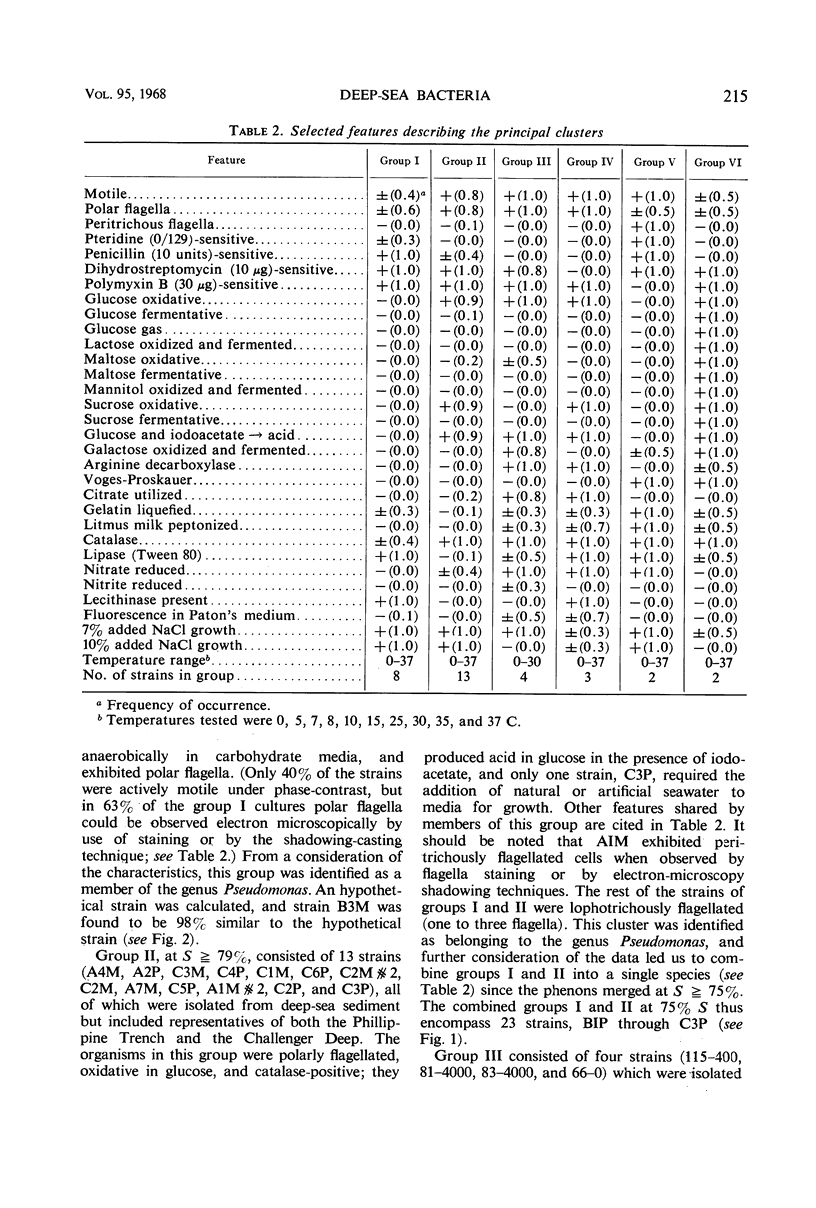
Thirty-eight isolates were subjected to taxonomic analysis by computer. Of the 38 isolates, 31 were from sediment samples collected at depths from 9,400 to 10,400 meters in the Philippine and Marianas Trenches of the Pacific Ocean, and 7 cultures were from seawater samples collected at various depths from surface to 4,000 meters and from several locations in the Pacific Ocean. A total of 116 characteristics were determined for each isolate, coded, and transferred to punch cards. Similarity values were obtained by computer analysis, with the use of two recently developed computer programs. Five distinct phenetic clusters were observed from the numerical analyses. Four of the clusters were identified as species of the genus Pseudomonas, and one, as an aerogenic species of Aeromonas. Group IV was identified as pigmented Pseudomonas fluorescens, and the major cluster, consisting of groups I and II, which merged at a species level of similarity, was treated as a new species of Pseudomonas. The 38 strain data were compared with data for 132 marine and nonmarine strains previously subjected to computer taxonomic analysis. The barotolerant deep-sea strains, with the exception of the deep-sea P. fluorescens isolates, clustered separately from all other marine strains.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEERS R. J., FISHER J., MEGRAW S., LOCKHART W. R. A comparison of methods for computer taxonomy. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Sep;28:641–652. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-4-641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLWELL R. R. A STUDY OF FEATURES USED IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Nov;37:181–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-37-2-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLWELL R. R., LISTON J. Taxonomic relationships among the pseudomonads. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jul;82:1–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.1.1-14.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLWELL R. R., MANDEL M. ADANSONIAN ANALYSIS AND DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID BASE COMPOSITION OF SERRATIA MARCESCENS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Feb;89:454–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.2.454-461.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLWELL R. R., MANDEL M. ADANSONIAN ANALYSIS AND DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID BASE COMPOSITION OF SOME GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1412–1422. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1412-1422.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLWELL R. R., MORITA R. Y. REISOLATION AND EMENDATION OF DESCRIPTION OF VIBRIO MARINUS (RUSSELL) FORD. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:831–837. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.831-837.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSEN A. J., WEEKS O. B., COLWELL R. R. TAXONOMY OF PSEUDOMONAS PISCICIDA (BEIN) BUCK, MEYERS, AND LEIFSON. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:752–761. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.752-761.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGH R., LEIFSON E. The taxonomic significance of fermentative versus oxidative metabolism of carbohydrates by various gram negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):24–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.1.24-26.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haight R. D., Morita R. Y. Thermally induced leakage from Vibrio marinus, an obligately psychrophilic marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1388–1393. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1388-1393.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOVACS N. Identification of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by the oxidase reaction. Nature. 1956 Sep 29;178(4535):703–703. doi: 10.1038/178703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIFSON E., COSENZA B. J., MURCHELANO R., CLEVERDON R. C. MOTILE MARINE BACTERIA. I. TECHNIQUES, ECOLOGY, AND GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:652–666. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.652-666.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIFSON E. MIXED POLAR AND PERITRICHOUS FLAGELLATION OF MARINE BACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:166–167. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.166-167.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LISTON J., WIEBE W., COLWELL R. R. QUANTITATIVE APPROACH TO THE STUDY OF BACTERIAL SPECIES. J Bacteriol. 1963 May;85:1061–1070. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.5.1061-1070.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON A. M. Enhancement of pigment production by Pseudomonas. Nature. 1959 Oct 17;184(Suppl 16):1254–1254. doi: 10.1038/1841254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister R. M., Burkholder P. R. Numerical taxonomy of some bacteria isolated from antarctic and tropical seawaters. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):863–872. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.863-872.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEWAN J. M., HODGKISS W. A method for the rapid differentiation of certain nonpathogenic, asporogenous bacilli. Nature. 1954 Jan 30;173(4396):208–209. doi: 10.1038/173208b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIERRA G. A simple method for the detection of lipolytic activity of micro-organisms and some observations on the influence of the contact between cells and fatty substrates. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1957;23(1):15–22. doi: 10.1007/BF02545855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNEATH P. H. The application of computers to taxonomy. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Aug;17(1):201–226. doi: 10.1099/00221287-17-1-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvestri L. G., Hill L. R. Agreement Between Deoxyribonucleic Acid Base Composition and Taxometric Classification of Gram-Positive Cocci. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):136–140. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.136-140.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIS A. T., GOWLAND G. Egg-yolk reactions of Pseudomonas species. Nature. 1960 Jul 30;187:432–433. doi: 10.1038/187432b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zobell C. E. Bacterial Life at the Bottom of the Philippine Trench. Science. 1952 May 9;115(2993):507–508. doi: 10.1126/science.115.2993.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]