Abstract
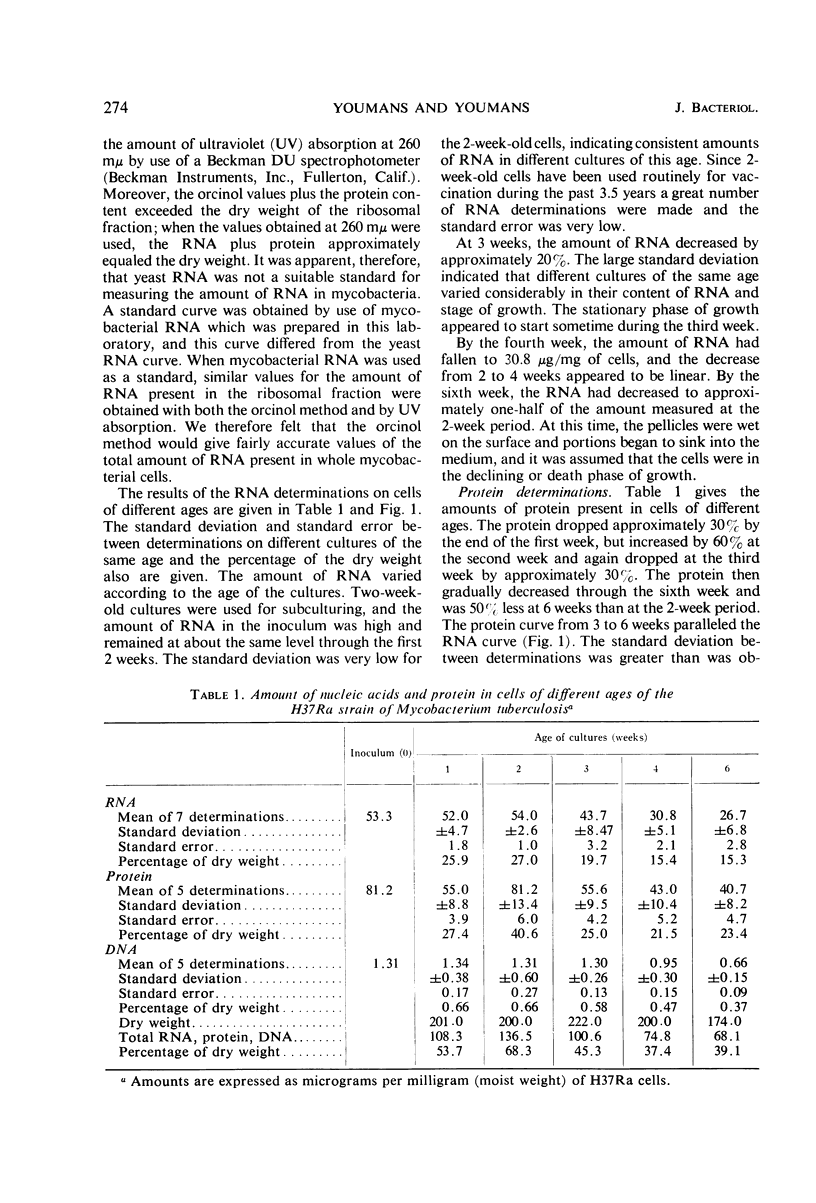
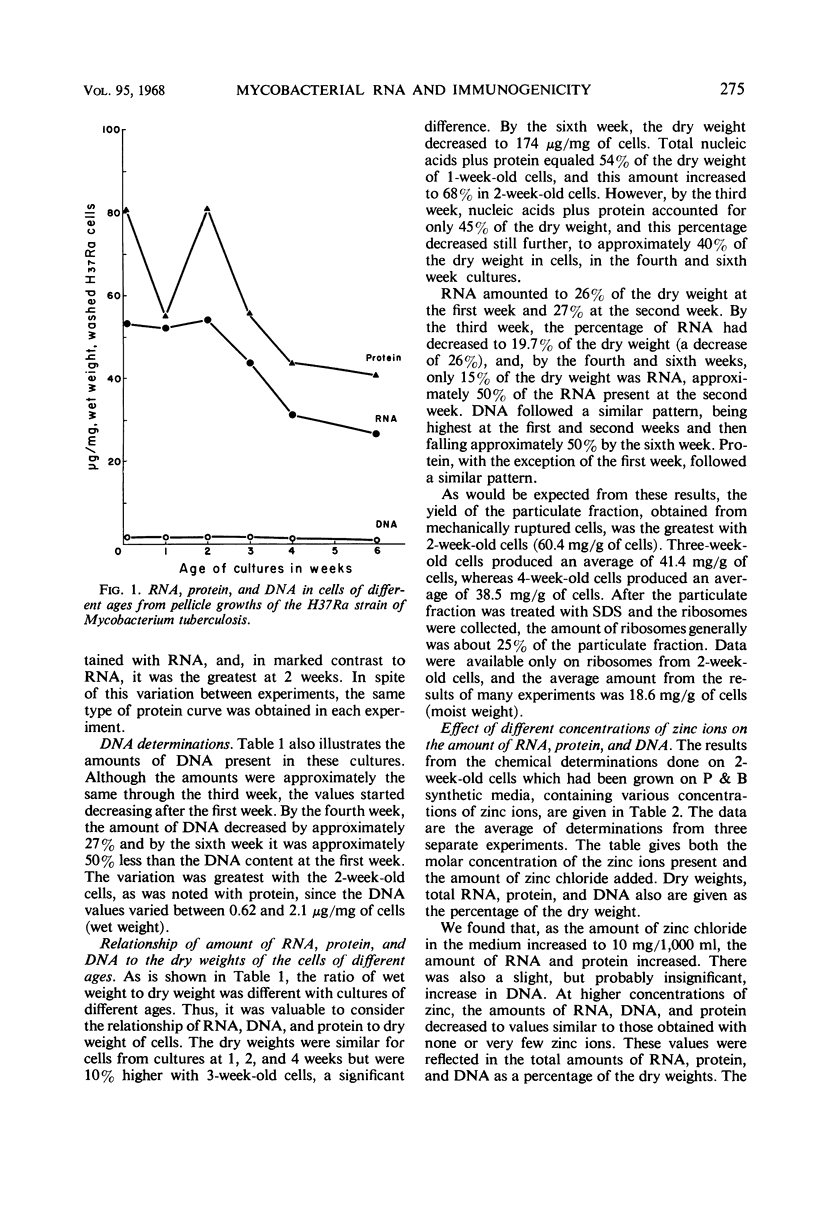
The amount of ribonucleic acid (RNA), protein, and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) was determined in pellicle cultures of different ages of the H37Ra strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, grown on a synthetic medium. We found that the highest content of RNA and protein was present in 2-week-old cultures, indicating that these cells were in the logarithmic phase of growth. DNA content was highest at 1 and 2 weeks. The amount of all three compounds then decreased about 50% during the following 6 weeks. Two-week-old cells should therefore be used for preparation of the immunogenic ribosomal fraction. The optimal concentration of zinc chloride increased RNA and protein synthesis, and also improved the appearance of the pellicle growth. Two-week-old cells, which contained the largest amount of RNA and protein, immunized mice significantly better than older cells. Since protein and DNA are not involved in the production of immunity, a correlation could be made between amount of RNA and the capacity of viable H37Ra cells to immunize mice. The immunizing capacity of these cells was not affected by ribonuclease, probably because the ribonuclease did not penetrate into the whole cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARNER H. D., COHEN S. S. Synchronization of division of a thymineless mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1956 Jul;72(1):115–123. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.1.115-123.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., SMITH K. C., ALLEN F. W. The preparation and characterization of ribonucleic acids from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1955 Sep;216(1):185–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWES E. A., RIBBONS D. W. SOME ASPECTS OF THE ENDOGENOUS METABOLISM OF BACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Jun;28:126–149. doi: 10.1128/br.28.2.126-149.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALE E. F., FOLKES J. P. The assimilation of amino-acids by bacteria. XIV. Nucleic acid and protein synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1953 Feb;53(3):483–492. doi: 10.1042/bj0530483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMGREN N. B., YOUMANS G. P. Studies on the metabolism of virulent and avirulent mycobacteria. Am Rev Tuberc. 1952 Oct;66(4):416–435. doi: 10.1164/art.1952.66.4.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARUYAMA Y. Biochemical aspects of the cell growth of Escherichia coli as studied by the method of synchronous culture. J Bacteriol. 1956 Dec;72(6):821–826. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.6.821-826.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P., MOYLE J. Relationships between cell growth, surface properties and nucleic acid production in normal and penicillin-treated Micrococcus pyogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Aug;5(3):421–438. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-3-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse M. L., Carter C. E. THE SYNTHESIS OF NUCLEIC ACIDS IN CULTURES OF ESCHERICHIA COLI, STRAINS B AND B/R. J Bacteriol. 1949 Sep;58(3):317–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.58.3.317-326.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SATO H. Comparison of nucleic acid contents of streptomycin-resistant and-dependent and chloramphenicol-resistant strain induced from E. coli. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1954 Oct 25;60(3-4):375–386. doi: 10.1620/tjem.60.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLENK F., DAINKO J. L. ACTION OF RIBONUCLEASE PREPARATIONS ON VIABLE YEAST CELLS AND SPHEROPLASTS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Feb;89:428–436. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.2.428-436.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L., YOUMANS G. P. The enumeration of nonpathogenic viable tubercle bacilli from the organs of mice. Am Rev Tuberc. 1957 Feb;75(2):280–294. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1957.75.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUY J. H. The nucleic acids of Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1958 Aug;76(2):179–184. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.2.179-184.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUMITA T., CHARGAFF E. Studies on nucleoproteins. VI. The deoxyribonucleoprotien and the deoxyribonucleic acid of bovine tubercle bacilli. (BCG). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Sep;29(3):568–578. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADE H. E., MORGAN D. M. The nature of the fluctuating ribonucleic acid in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1957 Feb;65(2):321–331. doi: 10.1042/bj0650321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBB M. Effects of magnesium on cellular division in bacteria. Science. 1953 Nov 20;118(3073):607–611. doi: 10.1126/science.118.3073.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEGENER W. S., ROMANO A. H. ZINC STIMULATION OF RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN RHIZOPUS NIGRICANS. Science. 1963 Dec 27;142(3600):1669–1670. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3600.1669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLISTON E. H., BINGENHEIMER J., ROSENTHAL S. R. Trace elements and BCG cultures. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1958 Jan;94(1):49–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS A. S., YOUMANS G. P. IMMUNOGENIC ACTIVITY OF A RIBOSOMAL FRACTION OBTAINED FROM MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1291–1298. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1291-1298.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS G. P., YOUMANS A. S. The measurement of the response of immunized mice to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis va. hominis. J Immunol. 1957 May;78(5):318–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Effect of trypsin and ribonuclease on the immunogenic activity of ribosomes and ribonucleic acid isolated from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2146–2154. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2146-2154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Preparation of highly immunogenic ribosomal fractions of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by use of sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2139–2145. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2139-2145.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


