Abstract
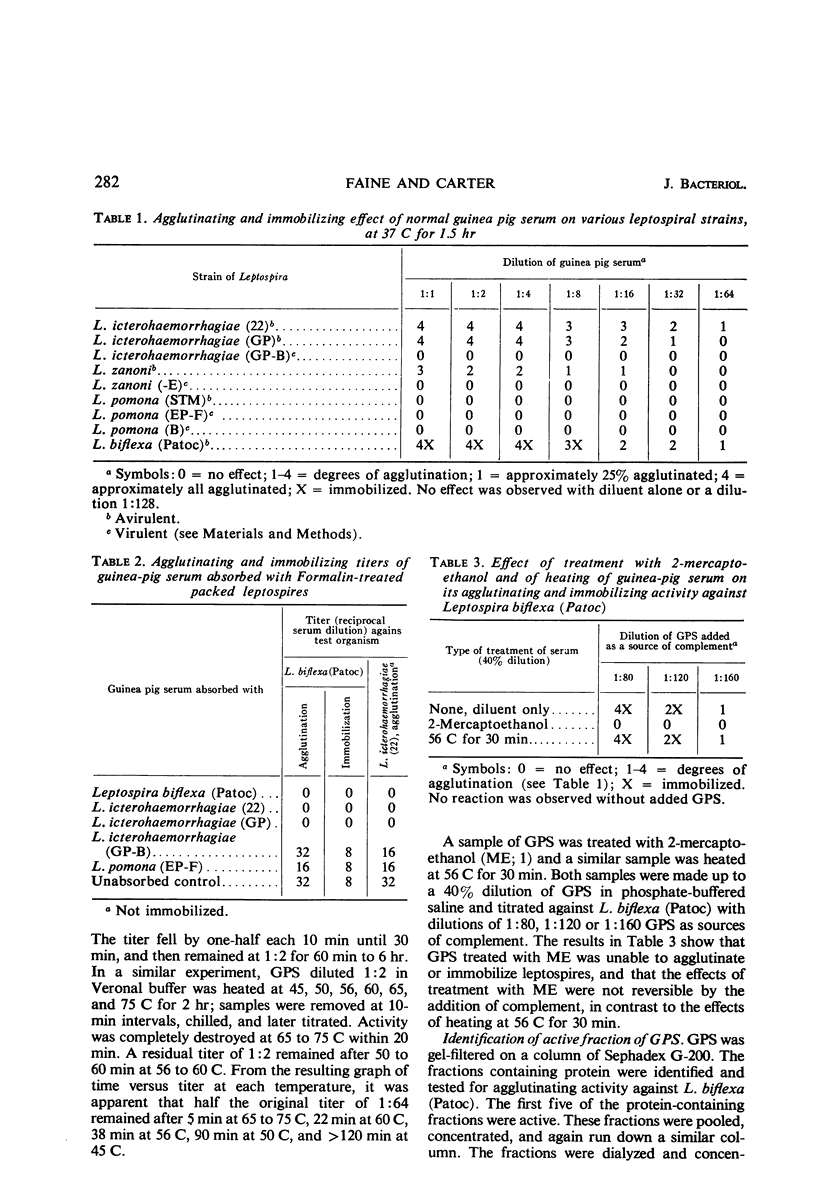
Serum from normal mammals agglutinated and immobilized nonpathogenic Leptospira biflexa and agglutinated avirulent lines of pathogenic serotypes L. icterohaemorrhagiae and L. zanoni. Virulent lines of L. icterohaemorrhagiae and L. zanoni were not affected, nor were any of three strains of L. pomona, one of which was avirulent. The active principle in serum was a β-macroglobulin which was heat-labile and reduced by 2-mercaptoethanol, and acted in conjunction with complement and lysozyme; it was absorbable from serum by Formalin-treated susceptible leptospires. The Formalin-stable receptor antigen, named “Z antigen,” is associated with virulence rather than pathogenicity, but may not be a determinant of virulence.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADLER F. L. STUDIES ON MOUSE ANTIBODIES. II. MERCAPTOETHANOL-SENSITIVE 7 S ANTIBODIES IN MOUSE ANTISERA TO PROTEIN ANTIGENS. J Immunol. 1965 Jul;95:39–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAINE S. Catalase activity in pathogenic Leptospira. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Feb;22:1–9. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAINE S., VANDERHOEDEN J. VIRULENCE-LINKED COLONIAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL VARIATION IN LEPTOSPIRA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1493–1496. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1493-1496.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTMANN L., FILITTI WURMSER S., JACQUOT ARMAN Y., MAILLOUX M., HUREZ D., FAUVERT R. NATURE MACROMOL'ECULAIRE D'UN ANTICORPS DE LA LEPTOSPIROSE AUSTRALIS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Feb 10;82:249–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocker N. D., Bauer D. C. The nature of antibodies synthesized during the immune response to Leptospira biflexa. J Immunol. 1965 Nov;95(5):887–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON R. C., MUSCHEL L. H. ANTILEPTOSPIRAL ACTIVITY OF NORMAL SERUM. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1625–1626. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1625-1626.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Harris V. G. Antileptospiral activity of serum. II. Leptospiral virulence factor. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):513–519. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.513-519.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Harris V. G. Differentiation of pathogenic and saprophytic letospires. I. Growth at low temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):27–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.27-31.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Muschel L. H. Antileptospiral activity of serum. I. Normal and immune serum. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1403–1409. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1403-1409.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LATASTE-DOROLLE C., EYQUEM A., BURI J. F. ANALYSE IMMUNO-'ELECTROPHOR'ETIQUE, EN MILIEU G'ELOS'E, DES PROT'EINES S'ERIQUES DANS LES LEPTOSPIROSES. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Apr;106:646–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike R. M., McBrayer H. L., Schulze M. L., Chandler C. H. Chromatographic analysis and sulfhydryl sensitivity of antileptospira agglutinins in rabbit and human sera. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Dec;120(3):786–789. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]