Abstract
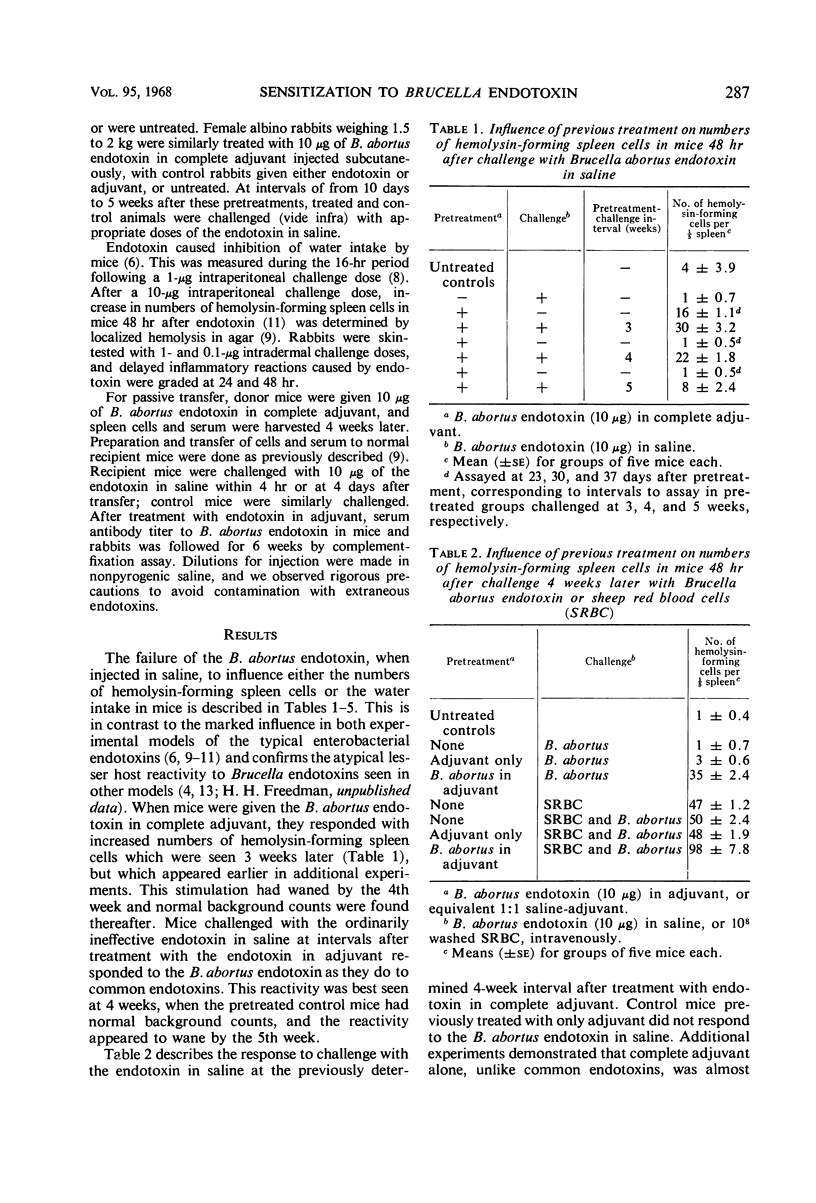
A Boivin preparation of Brucella abortus, unlike common enterobacterial endotoxins, failed to depress water intake or increase numbers of hemolysin-producing spleen cells in mice, or to cause delayed inflammatory reactions in rabbit skin. Reactivity to the B. abortus endotoxin was found only in animals which were previously given the endotoxin with, but not necessarily in, complete Freund's adjuvant. Previous treatment with the endotoxin in saline or with only the adjuvant was ineffective. Sensitization appeared within 10 days and waned after 5 weeks. Passive sensitization was obtained with sensitized donor spleen cells but not with serum. Serum antibody titers did not correlate with the appearance and disappearance of sensitization.
Full text
PDF
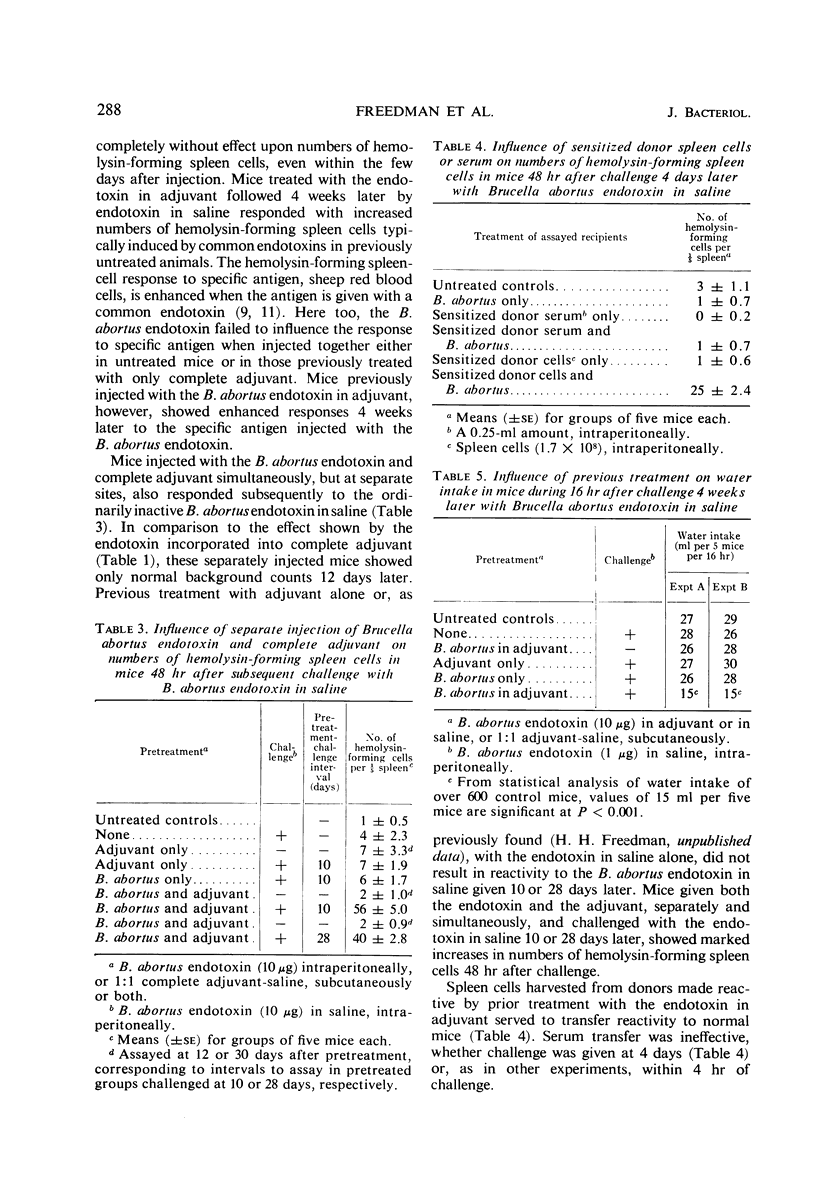


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABERNATHY R. S., BRADLEY G. M., SPINK W. W. Increased susceptibility of mice with brucellosis to bacterial endotoxins. J Immunol. 1958 Oct;81(4):271–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ABERNATHY R. S., SPINK W. W. Studies with Brucella endotoxin in humans: the significance of susceptibility to endotoxin in the pathogenesis of brucellosis. J Clin Invest. 1958 Feb;37(2):219–231. doi: 10.1172/JCI103601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Wilson J. B. Hypoferremia in mice and its application to the bioassay of endotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):903–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.903-910.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOS R. J., SCHAEDLER R. W. The effect of bacterial endotoxins on the water intake and body weight of mice. J Exp Med. 1961 May 1;113:921–934. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.5.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOSTER J. W., RIBI E. Immunological role of Brucella abortus cell walls. J Bacteriol. 1962 Aug;84:258–268. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.2.258-268.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. E., Schwartz B. S., Freedman H. H. Influence of an extract of Mycobacterium phlei on water intake and its neutralization by antibody. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1966 May;3(1):48–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman H. H., Fox A. E., Schwartz B. S. Antibody formation at various times after previous treatment of mice with endotoxin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jun;125(2):583–587. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman H. H., Fox A. E., Willis R. S., Schwartz B. S. Role of protein component of endotoxin in modification of host reactivity. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Aug-Sep;125(4):1316–1320. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman H. H., Nakano M., Braun W. Antibody formation in endotoxin-tolerant mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Apr;121(4):1228–1230. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-31012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel R. W., Braun W. Cytotoxicity of endotoxin in vitro. Effects on macrophages from normal guinea pigs. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1965 Aug;43(4):511–522. doi: 10.1038/icb.1965.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel R. W., Braun W., Plescia O. J. Endotoxin cytotoxicity: role of cell-associated antibody. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Feb;121(2):449–452. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARSON C. L., RIBI E., MILNER K. C., LIEBERMAN J. E. A method for titrating endotoxic activity in the skin of rabbits. J Exp Med. 1960 Jan 1;111:1–20. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAEDLER R. W., DUBOS R. J. The susceptibility of mice to bacterial endotoxins. J Exp Med. 1961 Mar 1;113:559–570. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.3.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPINK W. W., ANDERSON D. Experimental studies on the significance of endotoxin in the pathogenesis of brucellosis. J Clin Invest. 1954 Apr;33(4):540–548. doi: 10.1172/JCI102924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhr J. W. Delayed hypersensitivity. Physiol Rev. 1966 Jul;46(3):359–419. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1966.46.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



