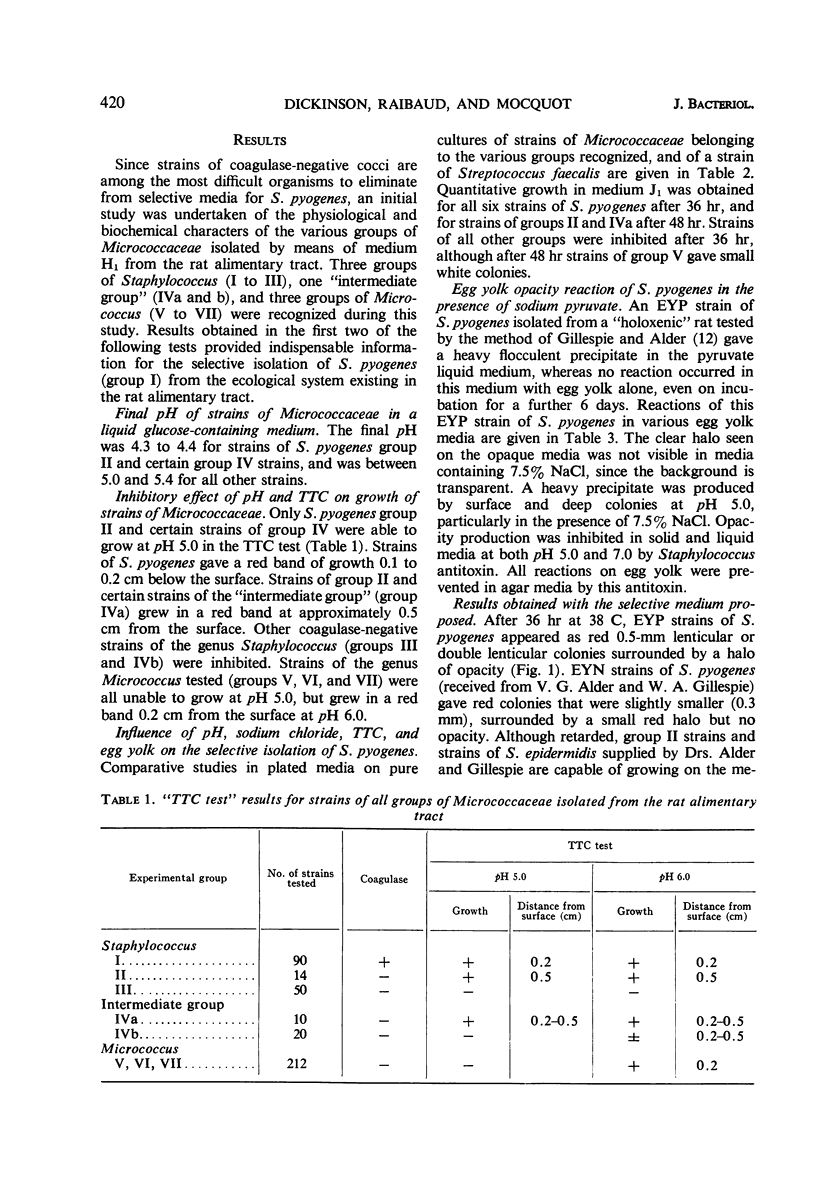
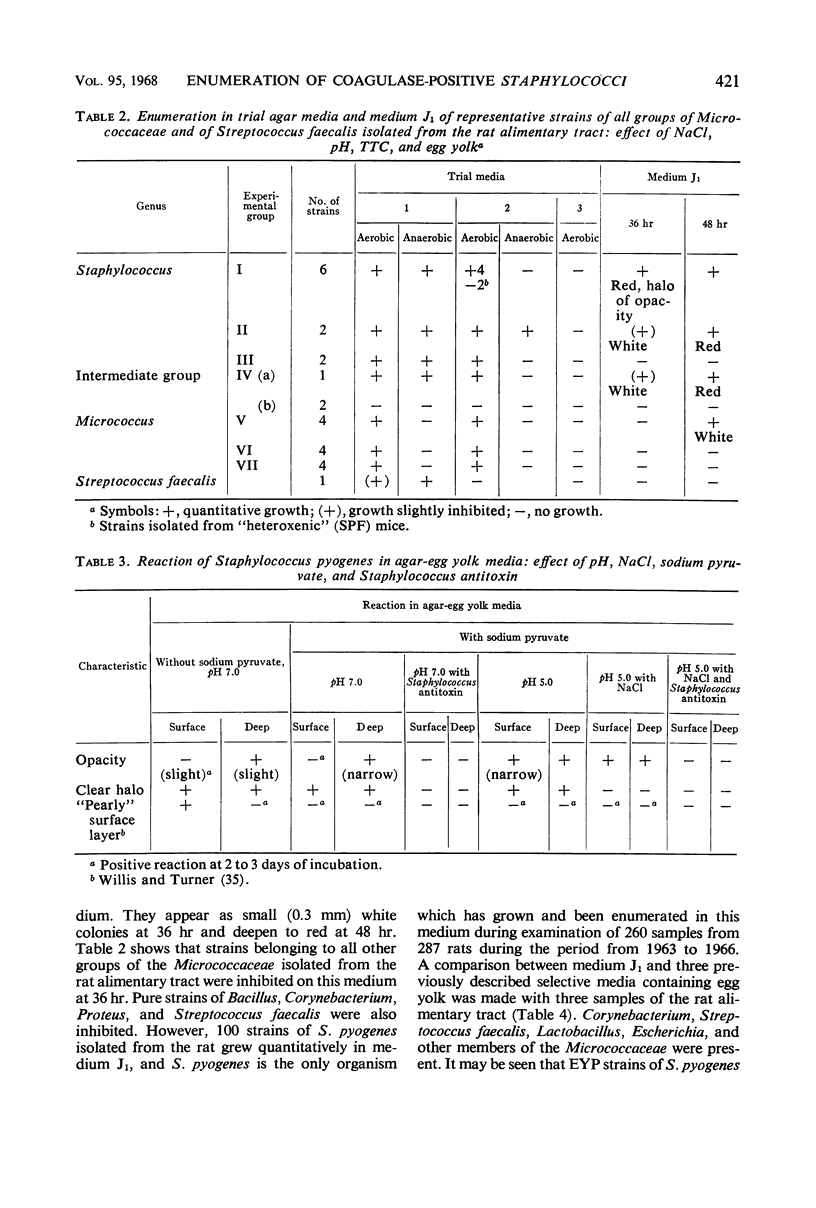
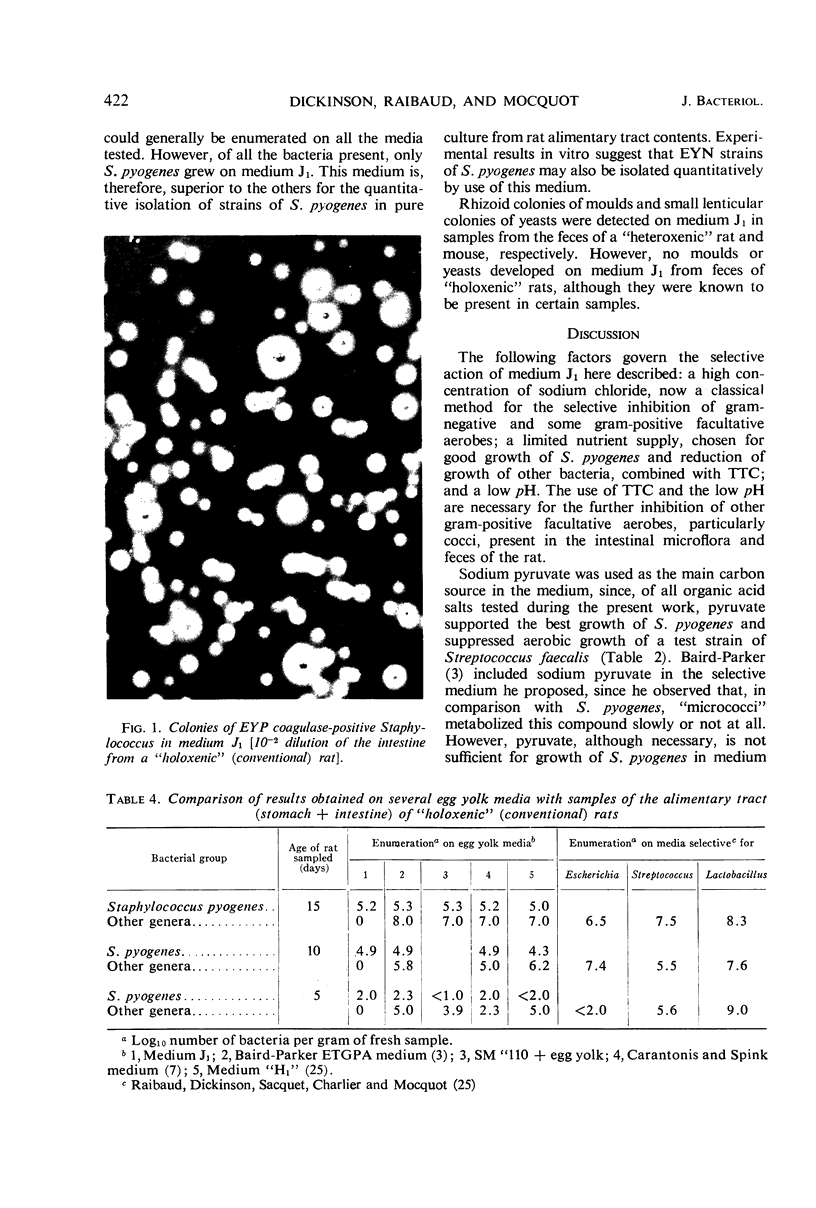
Abstract
A selective agar medium (medium J1) is proposed for the quantitative enumeration of egg yolk-positive (EYP) and egg yolk-negative (EYN) Staphylococcus pyogenes from the digestive tract and feces of the rat. This medium, buffered at pH 5.0, is composed of acid casein hydrolysate and yeast extract with 7.5% sodium chloride, 1.6% sodium pyruvate, 0.0008% 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC), and 6% egg yolk emulsion. Inoculation is by the pour-plate method and incubation is at 38 C in a water-jacketed incubator for 36 hr. Colonies of S. pyogenes reduce TTC; EYP strains are surrounded by a halo of opacity; and EYN strains may be surrounded by a red halo, but no opacity. Small, white colonies of S. epidermidis may develop, but Micrococcus, and all other groups of Staphylococcus recognized in the rat intestinal flora, are inhibited. Other bacterial genera, notably Bacillus, Corynebacterium, Proteus, and Streptococcus, are also inhibited.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDER V. G., GILLESPIE W. A., HERDAN G. Production of opacity in egg-yolk broth by Staphylococci from various sources. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):205–210. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAIRD-PARKER A. C. A classification of micrococci and staphylococci based on physiological and biochemical tests. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:409–427. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARANTONIS L. M., SPINK M. S. A selective salt egg agar medium for pathogenic staphylococci. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:217–220. doi: 10.1002/path.1700860127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman G. H., Lieb C. W., Berens C., Curcio L. The Isolation of Probable Pathogenic Staphylococci. J Bacteriol. 1937 May;33(5):533–543. doi: 10.1128/jb.33.5.533-543.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS J. B., NIVEN C. F., Jr A comparative study of known food-poisoning staphylococci and related varieties. J Bacteriol. 1950 Apr;59(4):545–550. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.4.545-550.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLESPIE W. A., ALDER V. G. Production of opacity in egg-yolk media by coagulase-positive staphylococci. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1952 Jan;64(1):187–200. doi: 10.1002/path.1700640119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRABER C. D., LATTA R., FAIRCHILD J. P., VOGEL E. H., Jr Production of opalescence by staphylococci in egg yolk medium, as an index to bacteriophage typability. Am J Clin Pathol. 1958 Oct;30(4):314–317. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/30.4.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JESSEN O., FABER V., ROSENDAL K., ERIKSEN K. R. Some properties of Staphylococcus aureus, possibly related to pathogenicity. Part 1. A study of 446 strains from different types of human infection. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1959;47:316–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JESSEN O., FABER V., ROSENDAL K., ERIKSEN K. R. Some properties of Staphylococcus aureus, possibly related to pathogenicity. Part 2. In-vitro properties and origin of the infecting strains correlated to mortality in 190 patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1959;47:327–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JESSEN O., ROSENDAL K., FABER V., HOVE K., ERIKSEN K. R. Some properties of Staphylococcus aureus, possibly related to pathogenicity. 3. Bacteriological investigations of Staphylococcus aureus strains from 462 cases of bacteraemia. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1963;58:85–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1963.tb04830.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY E. R., BARBARO J. F. The inhibitory effect of triphenyltetrazolium on some strains of micrococci. J Bacteriol. 1952 Feb;63(2):297–298. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.2.297-298.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCDIVITT M. E., JEROME N. W. LIMITATIONS OF FIBRINOGEN-POLYMYXIN MEDIUM IN DETECTING COAGULASE-POSITIVE STAPHYLOCOCCI IN RAW MILK. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:157–159. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.157-159.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER M. T. Some cultural characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus strains from superficial skin infections. J Hyg (Lond) 1958 Jun;56(2):238–253. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400037712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERNICE A., MACRI N. [Influence of pH on the enzymatic activity of Staphylococcus in egg yolk media. I. Behavior on solid media]. G Batteriol Virol Immunol. 1962 Jul-Aug;55:227–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REID W. B., WILSON J. B. A study of the staphylococci associated with the bovine udder. Am J Vet Res. 1959 Sep;20:825–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud P., Dickinson A. B., Sacquet E., Charlier H., Mocquot G. La microflore du tube digestif du rat. 3. Implantation fortuite de différents genres microbiens chez le rat indemne de microbes pathogènes spécifiques (rat "SPF") Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Jul;111(1):46–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud P., Dickinson A. B., Sacquet E., Charlier H., Mocquot G. La microflore du tube digestif du rat. I. Techniques d'étude et milieux de culture proposés. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Apr;110(4):568–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud P., Dickinson A. B., Sacquet E., Charlier H., Mocquot G. La microflore du tube digestif du rat. II. Dénombrement de différents genres microbiens dans l'estomac et l'intestin de rats conventionnels. Variation quantitiatives individuelles et en fonction de l'age. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Jun;110(6):861–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud P., Dickinson A. B., Sacquet E., Charlier H., Mocquot G. La microflore du tube digestif du rat. IV.-Implantation controlée chez le rat gnotobiotique de différents genres microbiens isolés du rat conventionnel. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Aug;111(2):193–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAH D. B., RUSSELL K. E., WILSON J. B. COMPARISON OF TWO MEDIA FOR THE DETECTION OF THE EGG YOLK FACTOR OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 May;85:1181–1182. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.5.1181-1182.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAH D. B., WILSON J. B. EGG YOLK FACTOR OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. I. NATURE OF THE SUBSTRATE AND ENZYME INVOLVED IN THE EGG YOLK OPACITY REACTION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Mar;85:516–521. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.3.516-521.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMUCKLER S. A., APPLEMAN M. D. IMPROVED STAPHYLOCOCCUS MEDIUM NO. 110. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jul;12:355–359. doi: 10.1128/am.12.4.355-359.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIS A. T., TURNER G. C. Staphylococcal lipolysis and pigmentation. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:337–347. doi: 10.1002/path.1700840208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]