Abstract
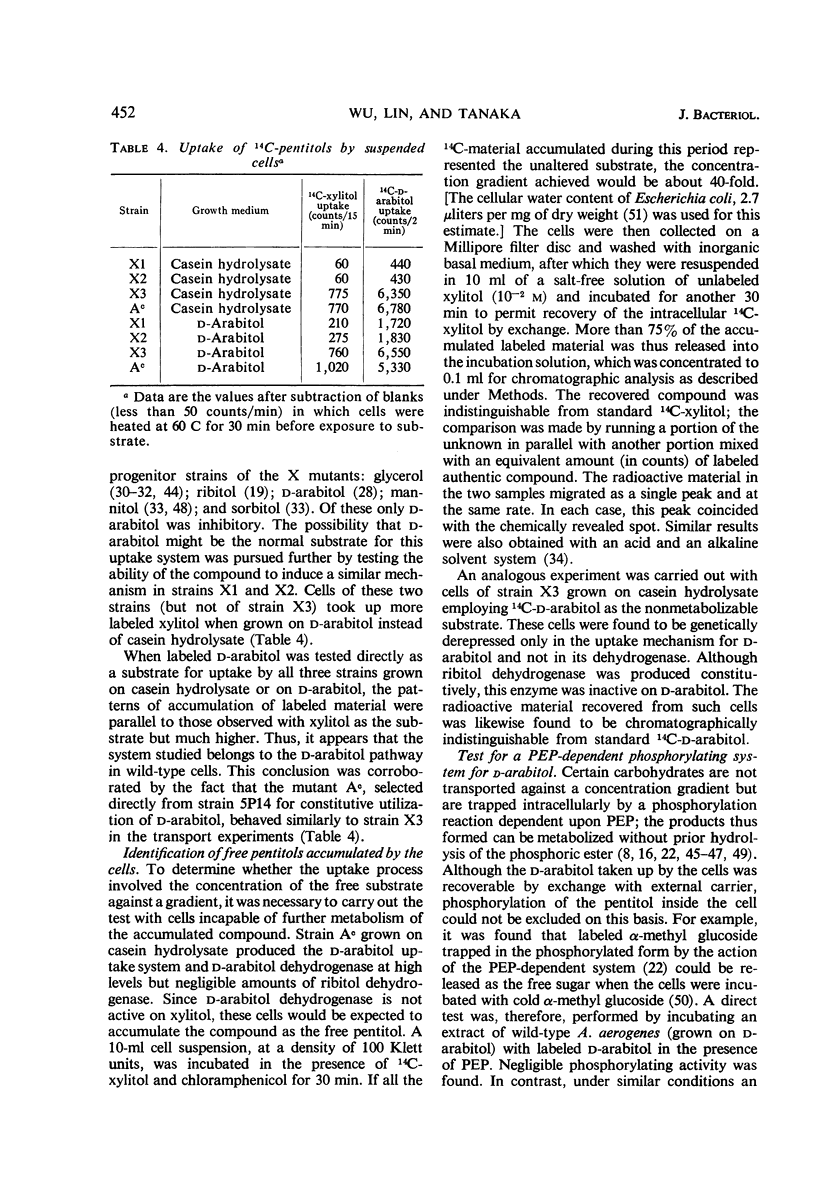
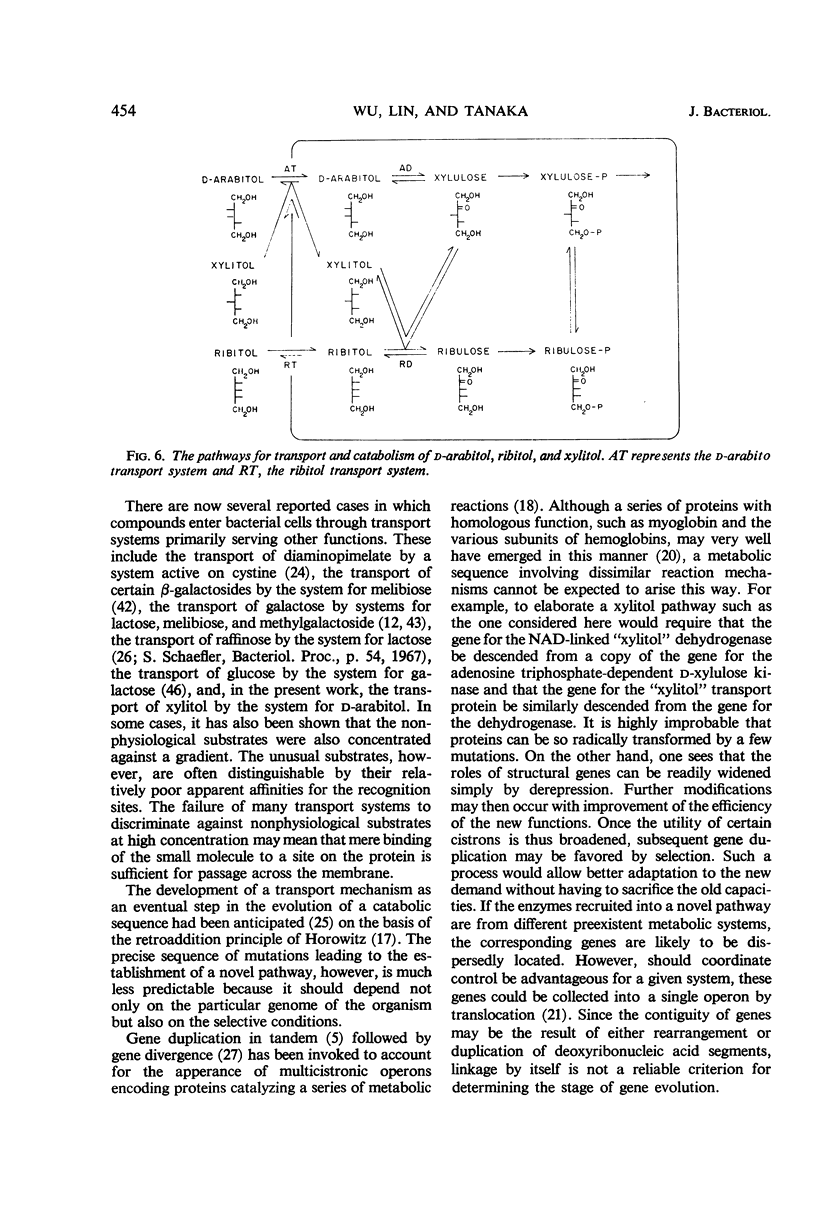
Wild-type Aerobacter aerogenes 1033 is unable to utilize xylitol. A succession of mutants was isolated capable of growth on this compound (0.2%) at progressively faster rates. Whereas the ability to utilize xylitol was achieved in the first-stage mutant (X1) by constitutive production of ribitol dehydrogenase (for which xylitol is a substrate but not an inducer), the basis for enhanced utilization of xylitol in the second-stage mutant (X2) was an alteration of ribitol dehydrogenase. This enzyme was purified from the various mutants. The apparent Km for xylitol was 0.12 m with X2 enzyme and 0.29 m with X1 enzyme. The X2 enzyme was also less heat stable and, at 0.05 m substrate concentration, had a higher ratio of activity with xylitol compared to ribitol than did the X1 enzyme. The third mutant (X3), with an even faster growth rate on xylitol, produced a ribitol dehydrogenase indistinguishable physically or kinetically from that of X2. However, X3 produced constitutively an active transport system which accepts xylitol. The usual function of this system is apparently for the transport of d-arabitol since the latter is not only a substrate but also an inducer of the transport system in parental strains of X3. The sequence of mutations described herein illustrates how genes belonging to different metabolic systems can be mobilized to serve a new biochemical pathway.
Full text
PDF


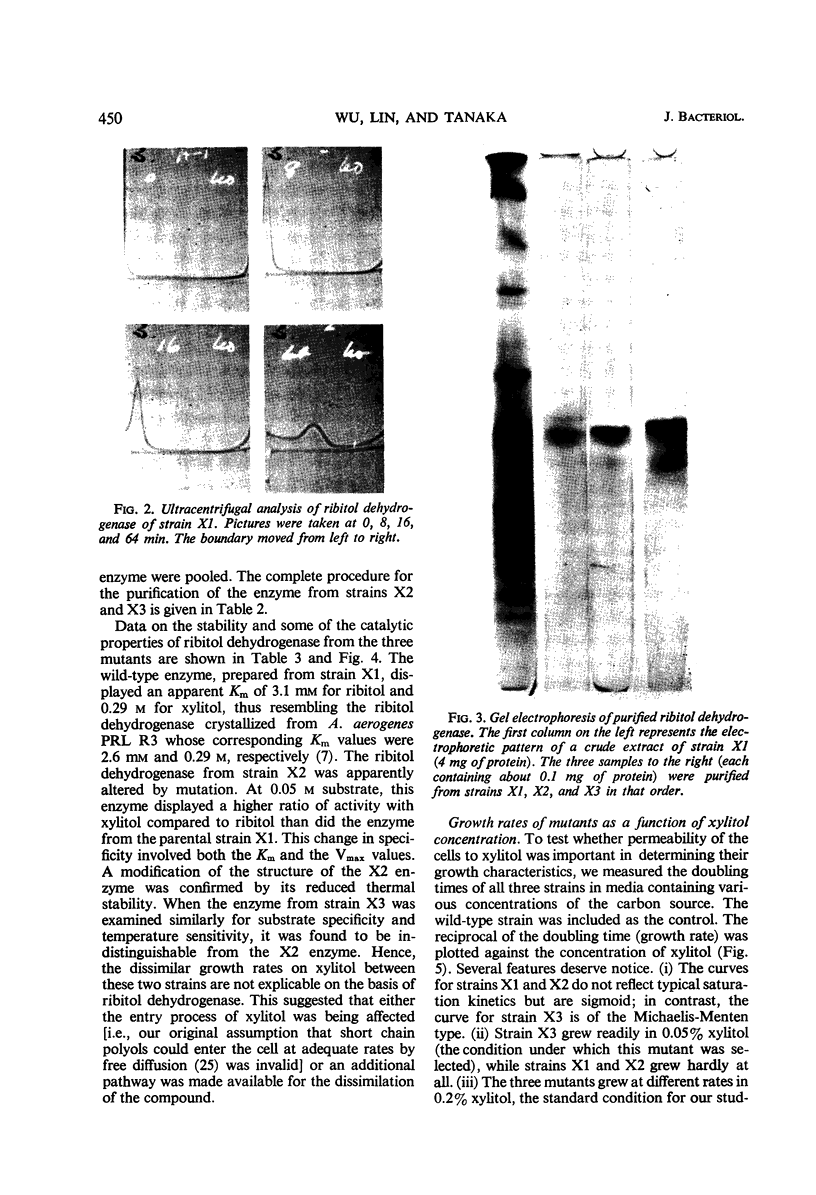
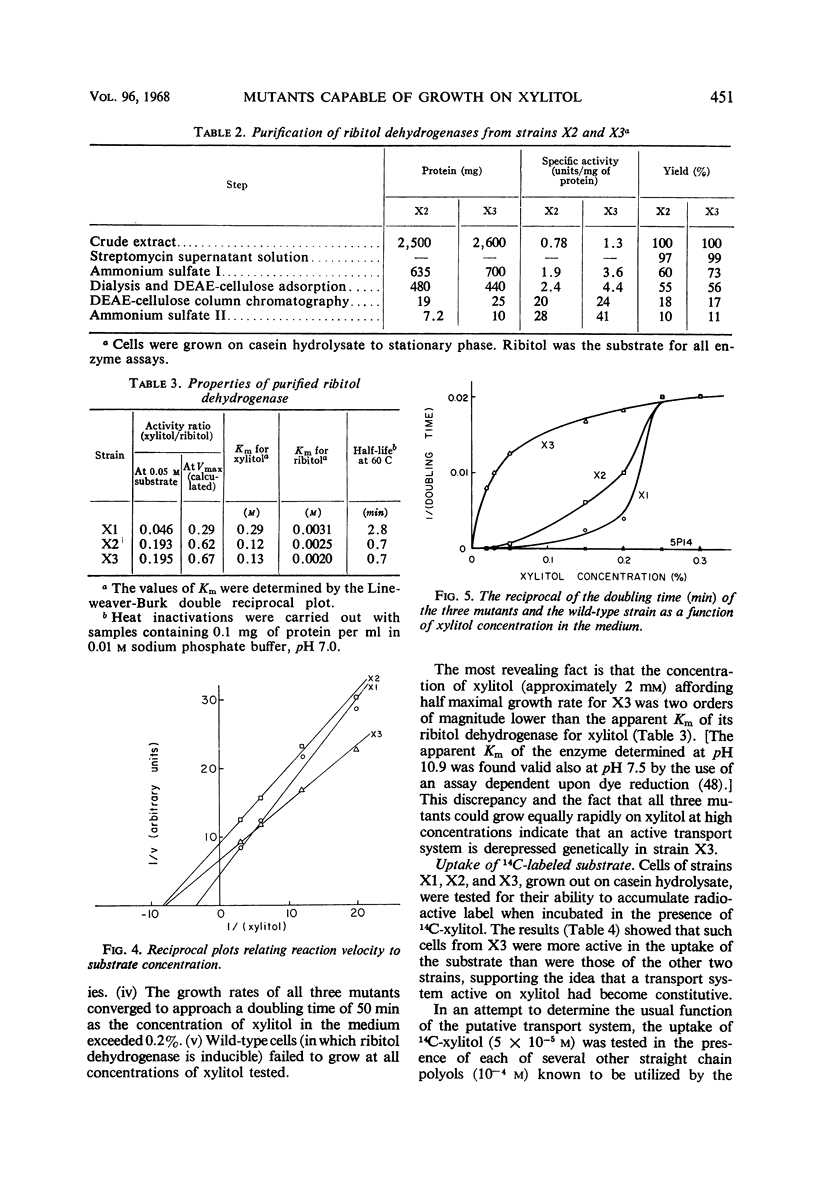



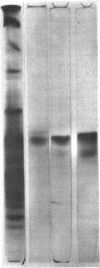
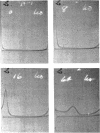
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALTERMATT H. A., SIMPSON F. J., NEISH A. C. The anaerobic dissimilation of D-ribose-1-C14, D-xylose-1-C14, D-xylose-2-C14, and D-xylose-5-C14 by Aerobacter aerogenes. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1955 Jul;33(4):615–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENZER S. Induced synthesis of enzymes in bacteria analyzed at the cellular level. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Jul;11(3):383–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges C. B. THE BAR "GENE" A DUPLICATION. Science. 1936 Feb 28;83(2148):210–211. doi: 10.1126/science.83.2148.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOSSITT D., MORTLOCK R. P., ANDERSON R. L., WOOD W. A. PATHWAYS OF L-ARABITOL AND XYLITOL METABOLISM IN AEROBACTER AEROGENES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2110–2115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROMM H. J., NELSON D. R. Ribitol dehydrogenase. III. Kinetic studies with product inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jan;237:215–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROMM H. J. Ribitol dehydrogenase. I. Purification and properties of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1958 Nov;233(5):1049–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. F., Wilson G. The role of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent kinase system in beta-glucoside catabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):988–995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm H. J., Bietz J. A. Ribitol dehydrogenase. IV. Purification and crystallization of the enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 9;115(3):510–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan A. K., Rotman B. Transport systems for galactose and galactosides in Escherichia coli. I. Genetic determination and regulation of the methyl-galactoside permease. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):42–50. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYASHI S., KOCH J. P., LIN E. C. ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF L-ALPHA-GLYCEROPHOSPHATE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:3098–3105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULLEY S. B., JORGENSEN S. B., LIN E. C. Ribitol dehydrogenase in Aerobacter aerogenes 1033. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Feb 12;67:219–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91819-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengstenberg W., Egan J. B., Morse M. L. Carbohydrate transport in Staphylococcus aureus. V. The accumulation of phosphorylated carbohydrate derivatives, and evidence for a new enzyme-splitting lactose phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):274–279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz N. H. On the Evolution of Biochemical Syntheses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1945 Jun;31(6):153–157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.31.6.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNDIG W., GHOSH S., ROSEMAN S. PHOSPHATE BOUND TO HISTIDINE IN A PROTEIN AS AN INTERMEDIATE IN A NOVEL PHOSPHO-TRANSFERASE SYSTEM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:1067–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy E. P., Scarborough G. A. Mechanism of hydrolysis of O-nitrophenyl-beta-galactoside in Staphylococcus aureus and its significance for theories of sugar transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):225–228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERNER S. A., WU T. T., LIN E. C. EVOLUTION OF A CATABOLIC PATHWAY IN BACTERIA. Science. 1964 Dec 4;146(3649):1313–1315. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3649.1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESTER G., BONNER D. M. Genetic control of raffinose utilization in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1957 Apr;73(4):544–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.4.544-552.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS E. B. Pseudoallelism and gene evolution. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1951;16:159–174. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1951.016.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIN E. C. An inducible D-arabitol dehydrogenase from Aerobacter aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jan;236:31–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIN E. C., LERNER S. A., JORGENSEN S. E. A method for isolating constitutive mutants for carbohydrate-catabolizing enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 2;60:422–424. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90423-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIN E. C., LEVIN A. P., MAGASANIK B. The effect of aerobic metabolism on the inducible glycerol dehydrogenase of Aerobacter aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1824–1829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L., Davis B. D. The transport of diaminopimelate and cystine in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4362–4369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGASANIK B., BROOKE M. S., KARIBIAN D. Metabolic pathways of glycerol dissimilation; a comparative study of two strains of Aerobacter aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1953 Nov;66(5):611–619. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.5.611-619.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTLOCK R. P., FOSSITT D. D., PETERING D. H., WOOD W. A. METABOLISM OF PENTOSES AND PENTITOLS BY AEROBACTER AEROGENES. 3. PHYSICAL AND IMMUNOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF PENITOL DEHYDROGENASES AND PENTULOKINASES. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:129–135. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.129-135.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTLOCK R. P., WOOD W. A. METABOLISM OF PENTOSES AND PENTITOLS BY AEROBACTER AEROGENES. I. DEMONSTRATION OF PENTOSE ISOMERASE, PENTULOKINASE, AND PENTITOL DEHYDROGENASE ENZYME FAMILIES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:838–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.838-844.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTLOCK R. P., WOOD W. A. METABOLISM OF PENTOSES AND PENTITOLS BY AEROBACTER AEROGENES. II. MECHANISM OF ACQUISITION OF KINASE, ISOMERASE, AND DEHYDROGENASE ACTIVITY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:845–849. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.845-849.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhedran P., Sommer B., Lin E. C. CONTROL OF ETHANOL DEHYDROGENASE LEVELS IN AEROBACTER AEROGENES. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jun;81(6):852–857. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.6.852-857.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortlock R. P., Fossitt D. D., Wood W. A. A basis for utlization of unnatural pentoses and pentitols by Aerobacter aerogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):572–579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORDLIE R. C., FROMM H. J. Ribitol dehydrogenase. II. Studies on the reaction mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1959 Oct;234:2523–2531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick A., Weiner M. ENZYME INDUCTION AS AN ALL-OR-NONE PHENOMENON. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1957 Jul 15;43(7):553–566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.43.7.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESTIDGE L. S., PARDEE A. B. A SECOND PERMEASE FOR METHYL-THIO-BETA-D-GALACTOSIDE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 May 4;100:591–593. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSH D., KARIBIAN D., KARNOVSKY M. L., MAGASANIK B. Pathways of glycerol dissimilation in two strains of Aerobacter aerogenes; enzymatic and tracer studies. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jun;226(2):891–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S., Schenkein I. Beta-glucoside permeases and phospho beta-glucosidases in Aerobacter aerogenes: relationship with cryptic phospho beta-glucosidases in Enterobacteriaceae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):285–292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Levinthal M., Kundig F. D., Kundig W., Anderson B., Hartman P. E., Roseman S. Genetic evidence for the role of a bacterial phosphotransferase system in sugar transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):1963–1970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Fraenkel D. G., Lin E. C. The enzymatic lesion of strain MM-6, a pleiotropic carbohydrate-negative mutant of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Apr 7;27(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Lerner S. A., Lin E. C. Replacement of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase by a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-linked dehydrogenase for the utilization of mannitol. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):642–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.642-648.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Lin E. C. Two classes of pleiotropic mutants of Aerobacter aerogenes lacking components of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):913–919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD W. A., McDONOUGH M. J., JACOBS L. B. Rihitol and D-arabitol utilization by Aerobacter aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1961 Aug;236:2190–2195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. A hexose-phosphate transport system in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 28;117(1):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Wilson T. H. The role of energy coupling in the transport of beta-galactosides by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2200–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]