Abstract
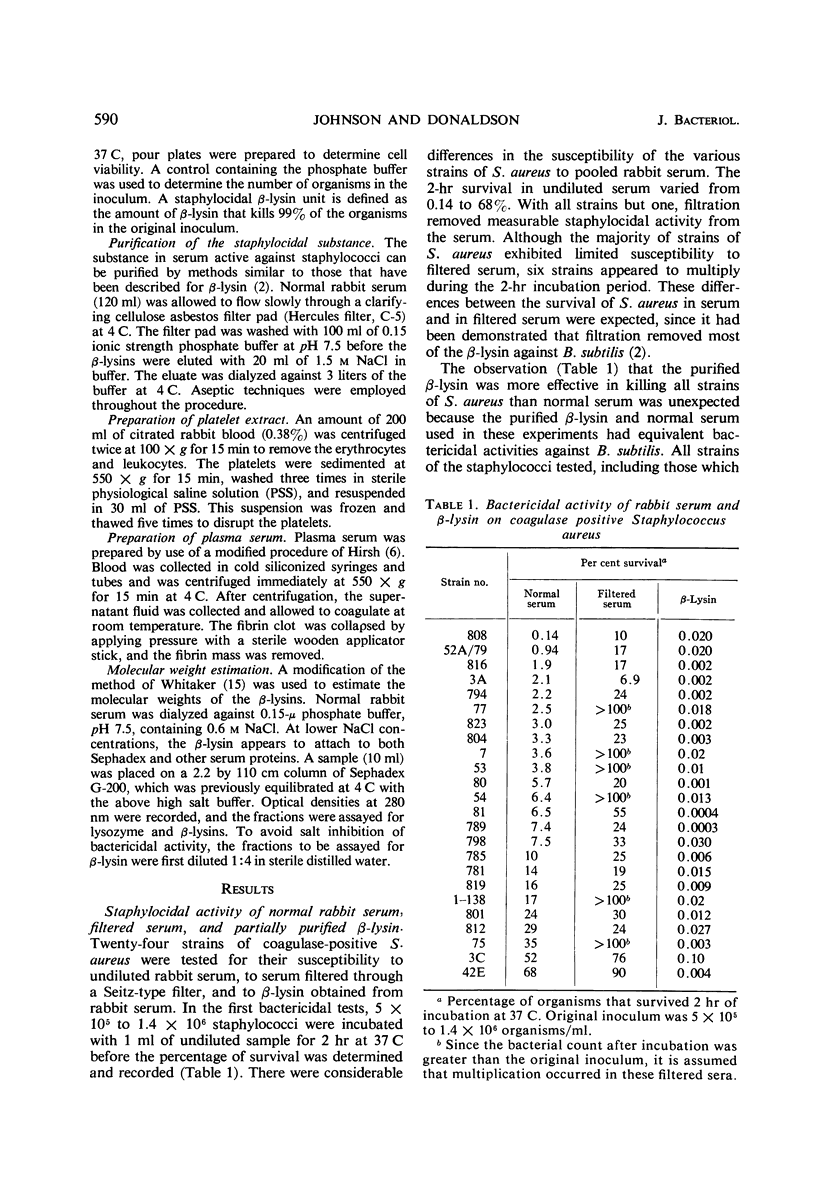
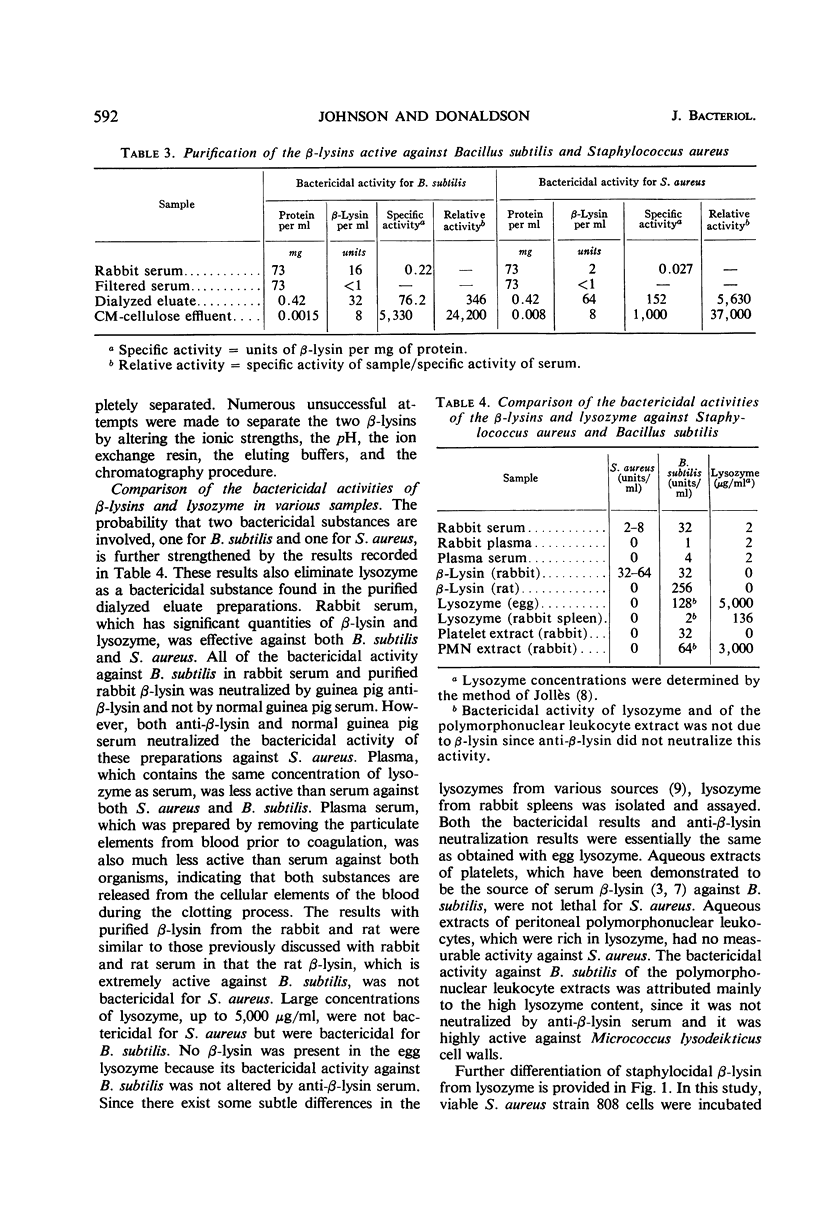
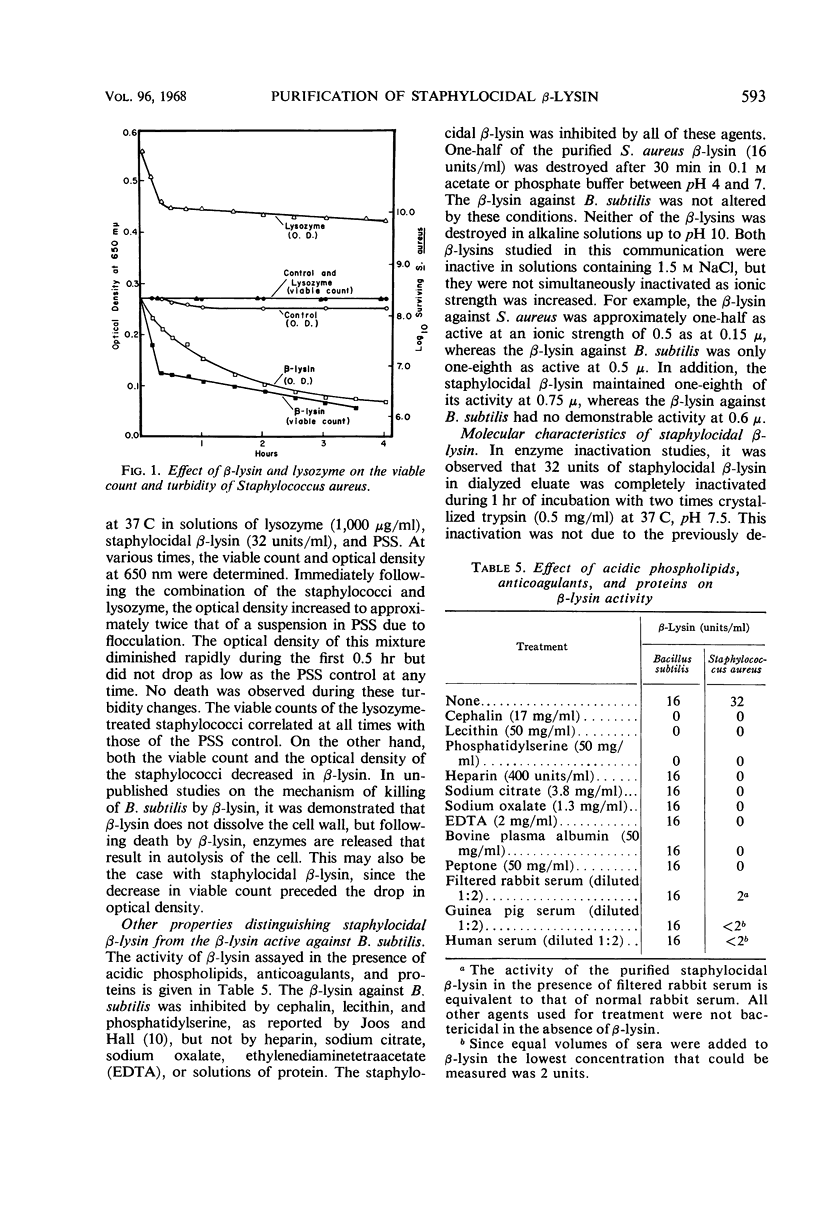
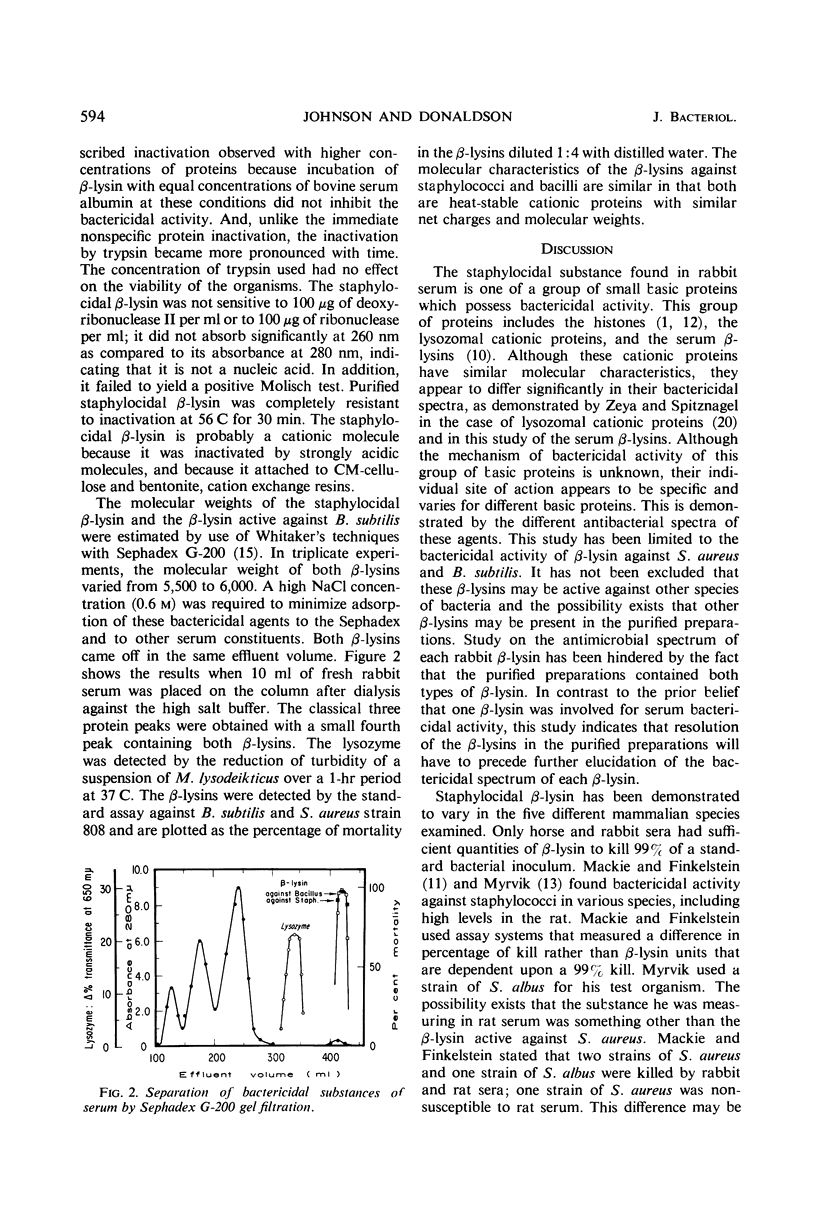
A cationic protein of rabbit serum bactericidal for Staphylococcus aureus was purified. The specific activity per unit of protein of the purified staphylocidal preparation was approximately 37,000 times greater than that of the serum from which it was isolated. Similar techniques were used to purify serum β-lysin active against Bacillus subtilis approximately 24,000 times. The staphylocidal activity cannot be attributed to the same β-lysin active against B. subtilis, lysozyme, or antibody-complement systems. The concentrations of staphylocidal β-lysin in the sera of the five mammalian species studied did not correlate with their β-lysin activities against B. subtilis. The two β-lysins are similar in that both were heat-stable, sensitive to trypsin digestion, had molecular weights near 6,000, and were found in higher concentrations in serum than in plasma. Furthermore, similar techniques can be used to absorb and elute both substances in highly purified forms using cellulose asbestos filter pads and ion exchange chromatography on carboxymethyl cellulose. In contrast to the β-lysin against B. subtilis, the staphylocidal β-lysin was not released from blood platelets, and it was inactive in the presence of heparin, sodium citrate, sodium oxalate, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, acidic phospholipids, and acid pH values. A variety of proteins, including those of normal serum, preferentially inhibited the bactericidal activity of staphylocidal β-lysin but not the β-lysin against B. subtilis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOOM W. L., WINTERS M. G., WATSON D. W. The inhibition of two antibacterial basic proteins by nucleic acids. J Bacteriol. 1951 Jul;62(1):7–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.1.7-13.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON D. M., ELLSWORTH B., MATHESON A. SEPARATION AND PURIFICATION OF BETA-LYSIN FROM NORMAL SERUM. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:896–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON D. M., JENSEN R. S., JENSEN B. M., MATHESON A. SEROLOGICAL RELATIONSHIPS AMONG BETA-LYSIN, PLAKIN, AND LEUKIN. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1049–1055. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1049-1055.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EKSTEDT R. D., NUNGESTER W. J. Coagulase in reversing antibacterial activity of normal human serum on Micrococcus pyogenes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 May;89(1):90–94. doi: 10.3181/00379727-89-21724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J. G. Comparative bactericidal activities of blood serum and plasma serum. J Exp Med. 1960 Jul 1;112:15–22. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J. G. Phagocytin: a bactericidal substance from polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1956 May 1;103(5):589–611. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.5.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAGO R., JACOX R. F. Cellular source and charcter of a heatstable bactericidal property associated with rabbit and rat platelets. J Exp Med. 1961 Apr 1;113:701–711. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.4.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOLLES P. RECENT DEVELOPMENTS IN THE STUDY OF LYSOZYMES. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1964 Jan;3:28–36. doi: 10.1002/anie.196400281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joos R. W., Hall W. H. Neutralization of beta-lysin and cationic bactericidal agents by acidic phospholipid. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):9–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.9-13.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. F., Abrams R., Dorfman A., Klein M. ANTIBACTERIAL PROPERTIES OF PROTAMINE AND HISTONE. Science. 1942 Nov 6;96(2497):428–430. doi: 10.1126/science.96.2497.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADDELL W. J. A simple ultraviolet spectrophotometric method for the determination of protein. J Lab Clin Med. 1956 Aug;48(2):311–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITNEY D. M., ANIGSTEIN L., MICKS D. W. Antibacterial activity of hydrolyzed red blood cells in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 Jun;74(2):346–350. doi: 10.3181/00379727-74-17902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOTIS W. W., EKSTEDT R. D. Studies on staphylococci. I. Effect of serum and coagulase on the metabolism of coagulase positive and coagulase negative strains. J Bacteriol. 1959 Oct;78:567–574. doi: 10.1002/path.1700780225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZEYA H. I., SPITZNAGEL J. K. ANTIBACTERIAL AND ENZYMIC BASIC PROTEINS FROM LEUKOCYTE LYSOSOMES: SEPARATION AND IDENTIFICATION. Science. 1963 Nov 22;142(3595):1085–1087. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3595.1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeya H. I., Spitznagel J. K. Cationic proteins of polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysosomes. I. Resolution of antibacterial and enzymatic activities. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):750–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.750-754.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeya H. I., Spitznagel J. K. Cationic proteins of polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysosomes. II. Composition, properties, and mechanism of antibacterial action. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):755–762. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.755-762.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


