Abstract
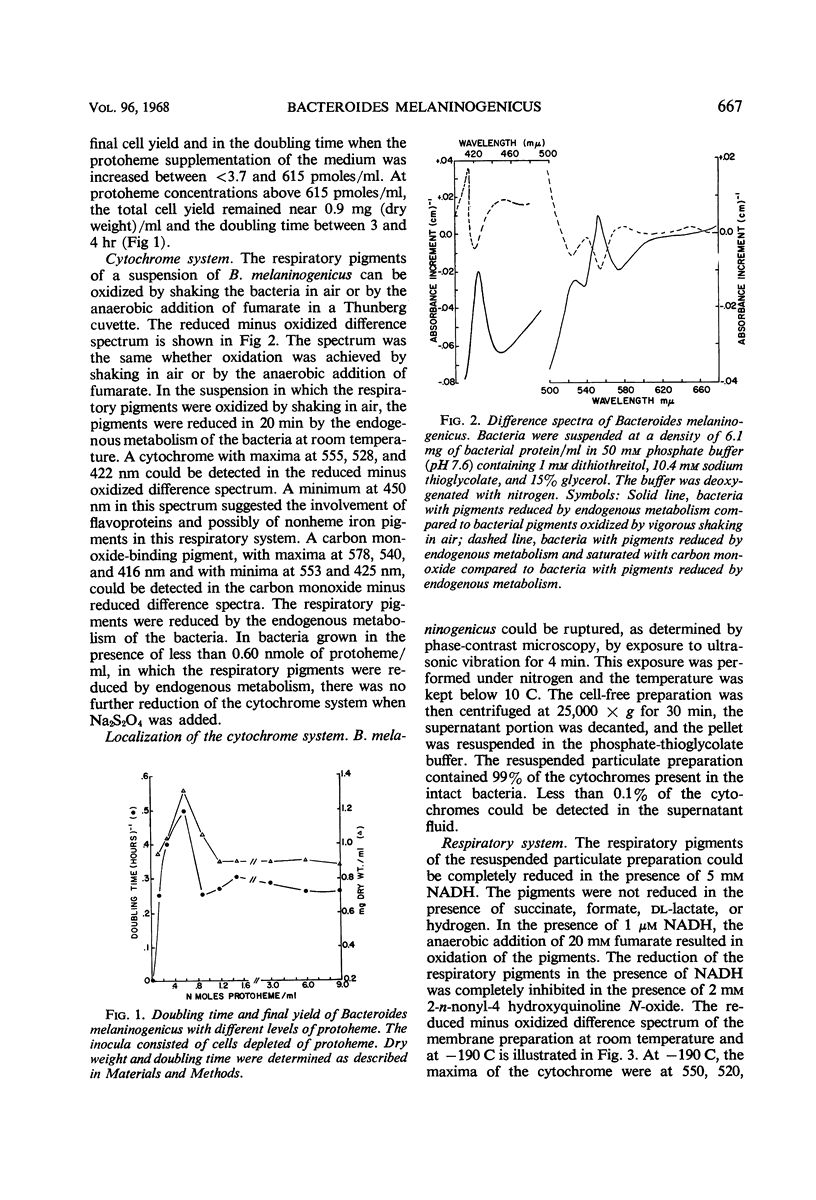
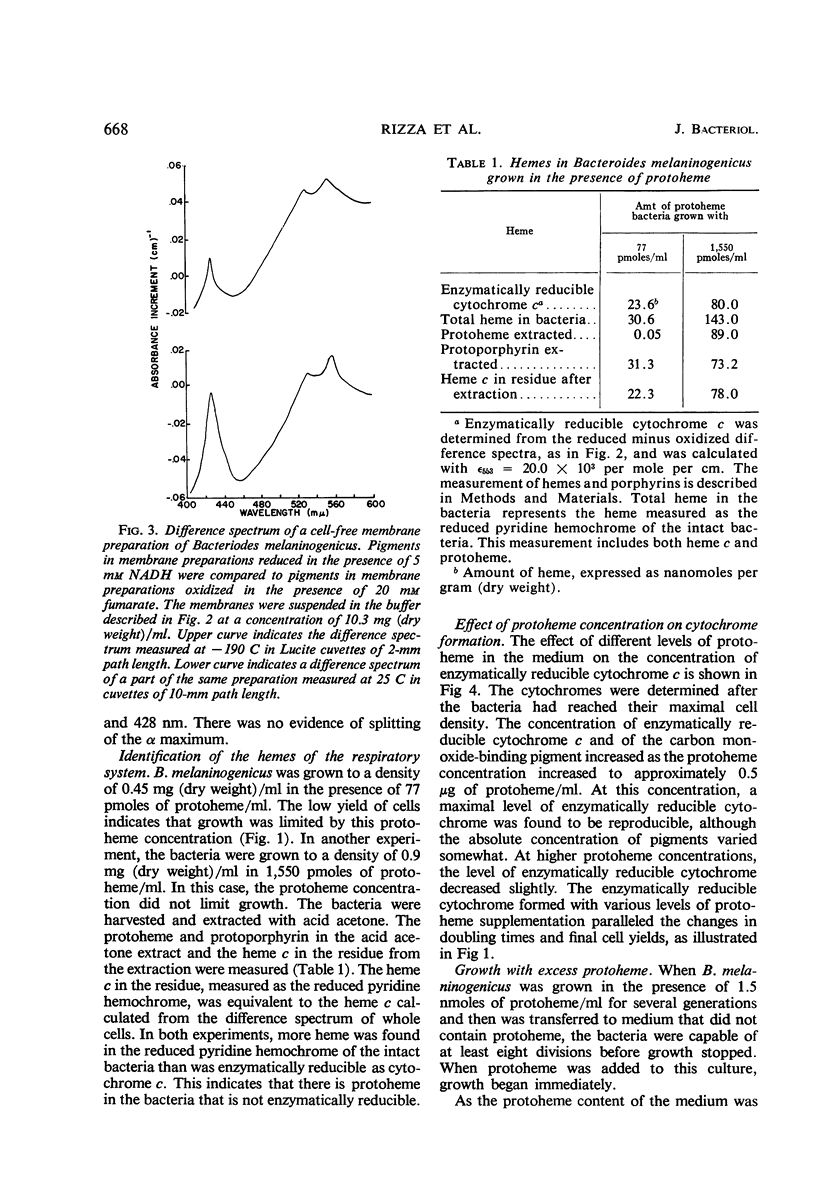
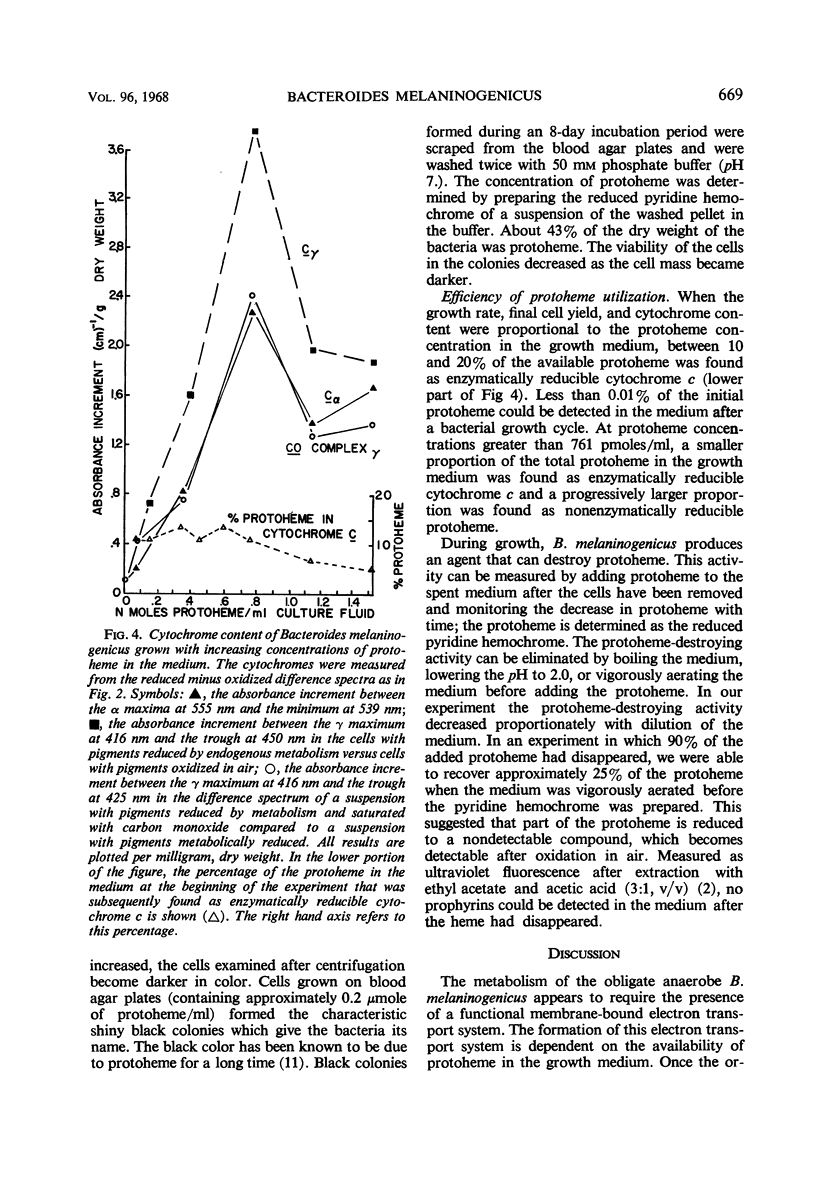
Protoheme is essential for the growth of some strains of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. At low concentrations in the growth medium, protoheme determines the doubling time, total cell yield, and amount of cytochrome per bacterium. At high protoheme concentrations, the doubling time, total cell yield, and amount of enzymatically reducible cytochrome appear to remain nearly constant, and protoheme is accumulated by the cell. The accumulated protoheme can support the growth of the bacterium for at least eight generations in a protoheme-free medium. When growth and cytochrome content are proportional during growth at low protoheme concentrations, the bacteria incorporate 10 to 20% of the total available protoheme into a membrane-bound respiratory system. This respiratory system includes cytochrome c, a carbon monoxide-binding pigment, and possibly flavoproteins. The pigments can be reversibly reduced by reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide or endogenous metabolism and can be oxidized anaerobically by fumarate or by shaking in air. Electron transport is inhibited by 2-n-nonyl-4-hydroxy-quinoline-N-oxide.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Frerman F. E., White D. C. Membrane lipid changes during formation of a functional electron transport system in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1868–1874. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1868-1874.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS R. J., ENGLE L. P. VITAMIN K COMPOUNDS IN BACTERIA THAT ARE OBLIGATE ANAEROBES. Science. 1964 Dec 4;146(3649):1307–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3649.1307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS R. J., MACDONALD J. B. Degradation of collagenous substrates by Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:614–621. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.614-621.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS R. J., MACDONALD J. B. Hemin and vitamin K compounds as required factors for the cultivation of certain strains of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Bacteriol. 1960 Aug;80:164–170. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.2.164-170.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. W., Nankiville D. D. Electrophoretic and other studies on haem pigments from Rhodopseudomonas palustris: cytochrome 552 and cytochromoid c. Biochem J. 1966 Feb;98(2):587–593. doi: 10.1042/bj0980587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEV M. Apparent requirement for vitamin K of rumen strains of Fusiformis nigrescens. Nature. 1958 Jan 18;181(4603):203–204. doi: 10.1038/181203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWYER S. J., MACDONALD J. B., GIBBONS R. J. Biochemical characteristics of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. A study of thirty-one strains. Arch Oral Biol. 1962 Nov-Dec;7:685–691. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(62)90117-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH L. Bacterial cytochromes. Bacteriol Rev. 1954 Jun;18(2):106–130. doi: 10.1128/br.18.2.106-130.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C., BRYANT M. P., CALDWELL D. R. Cytochromelinked fermentation in Bacteroides ruminicola. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:822–828. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.822-828.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C. Respiratory systems in the hemin-requiring Haemophilus species. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85:84–96. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.1.84-96.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C. SYNTHESIS OF 2-DEMETHYL VITAMIN K2 AND THE CYTOCHROME SYSTEM IN HAEMOPHILUS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Feb;89:299–305. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.2.299-305.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C. Effect of glucose on the formation of the membrane-bound electron transport system in Haemophilus parainfluenzae. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):567–573. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.567-573.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C. The obligatory involvement of the electron transport system in the catabolic metabolism of Haemophilus parainfluenzae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1966;32(2):139–158. doi: 10.1007/BF02097454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka T., De Klerk H., Kamen M. D. Highly purified cytochromes C derived from the diatom, Navicula pelliculosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 6;143(2):416–424. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(67)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


