Abstract
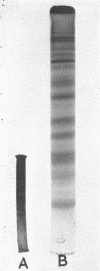
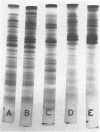
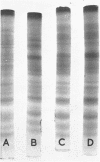
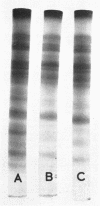
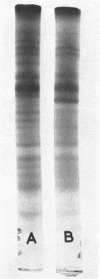
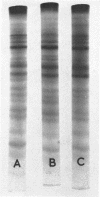
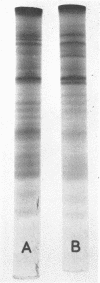
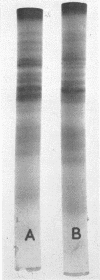
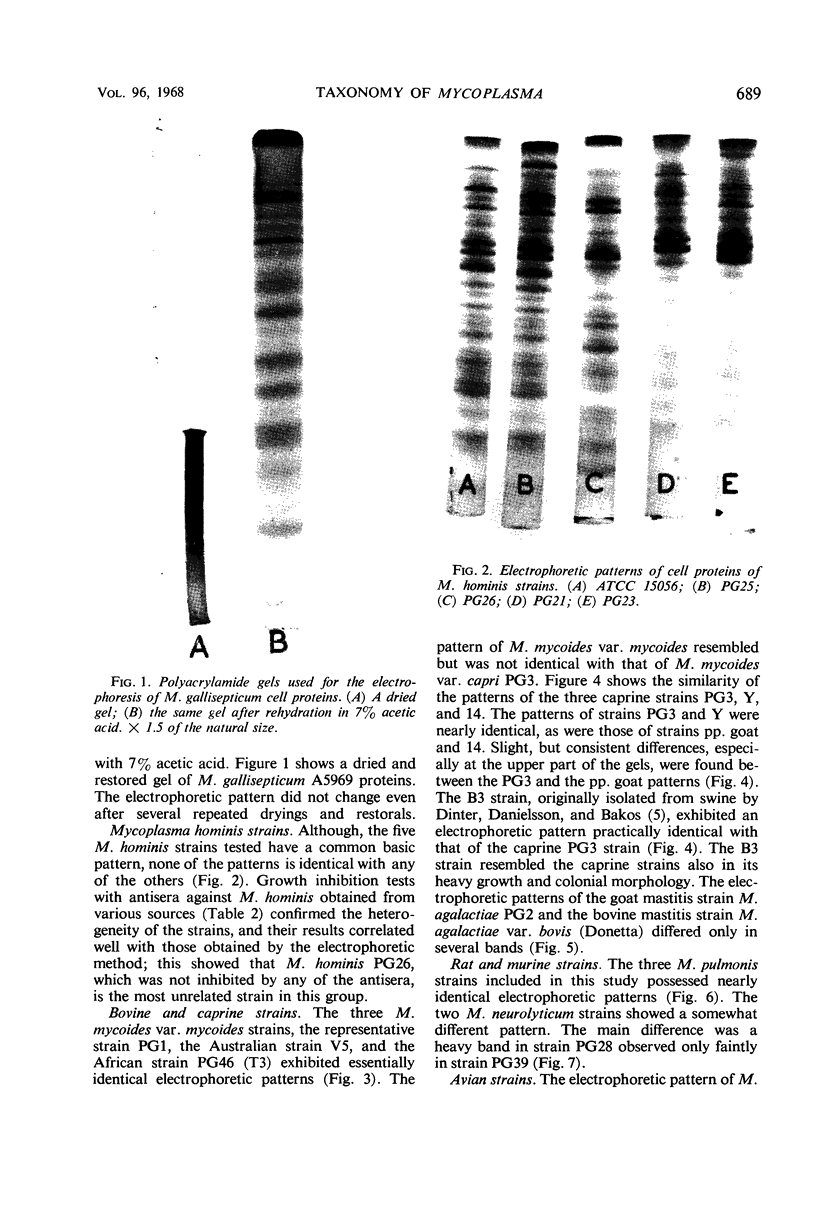
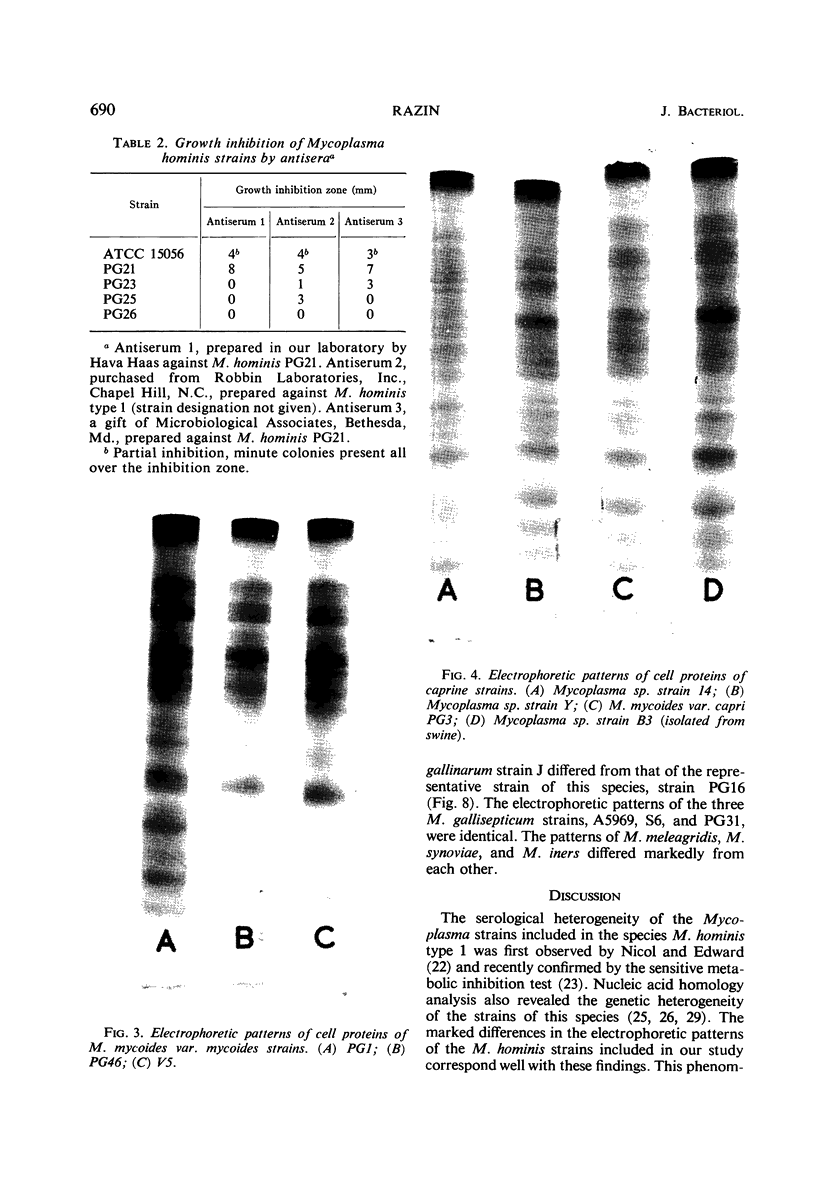
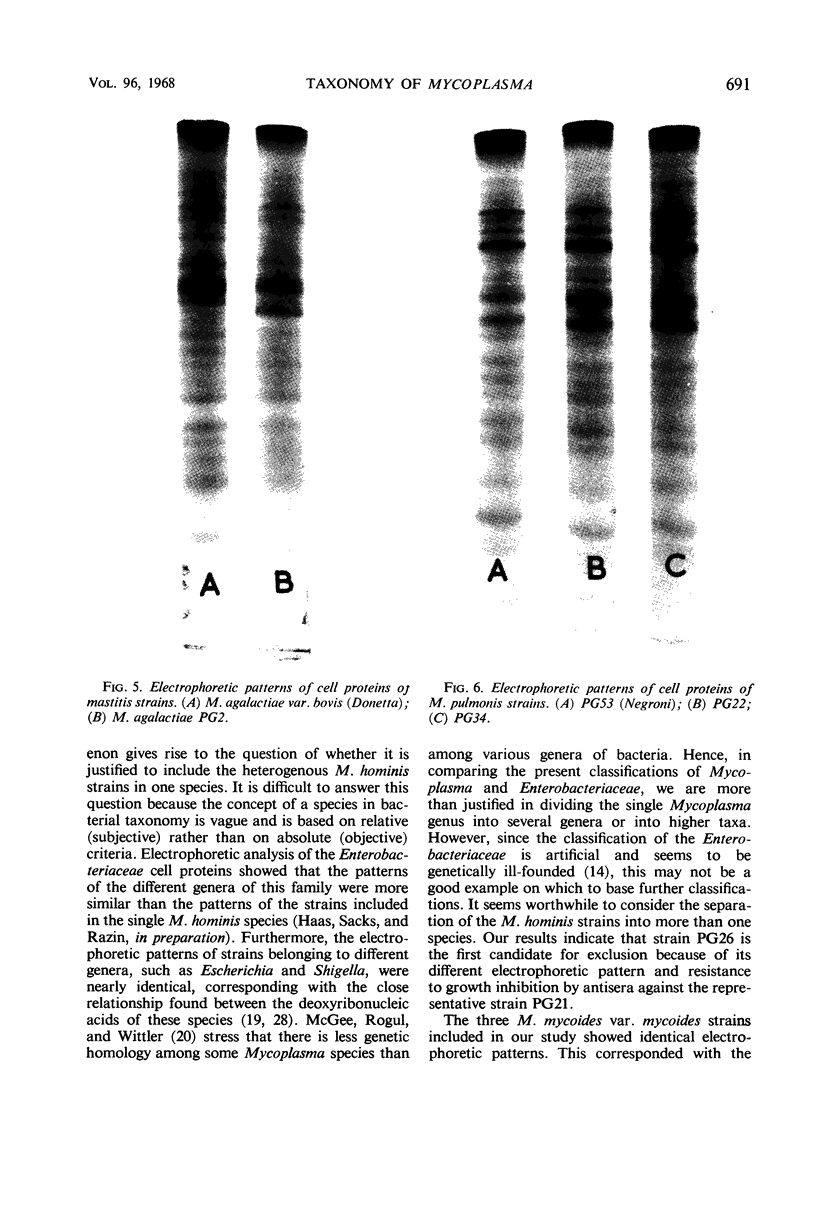
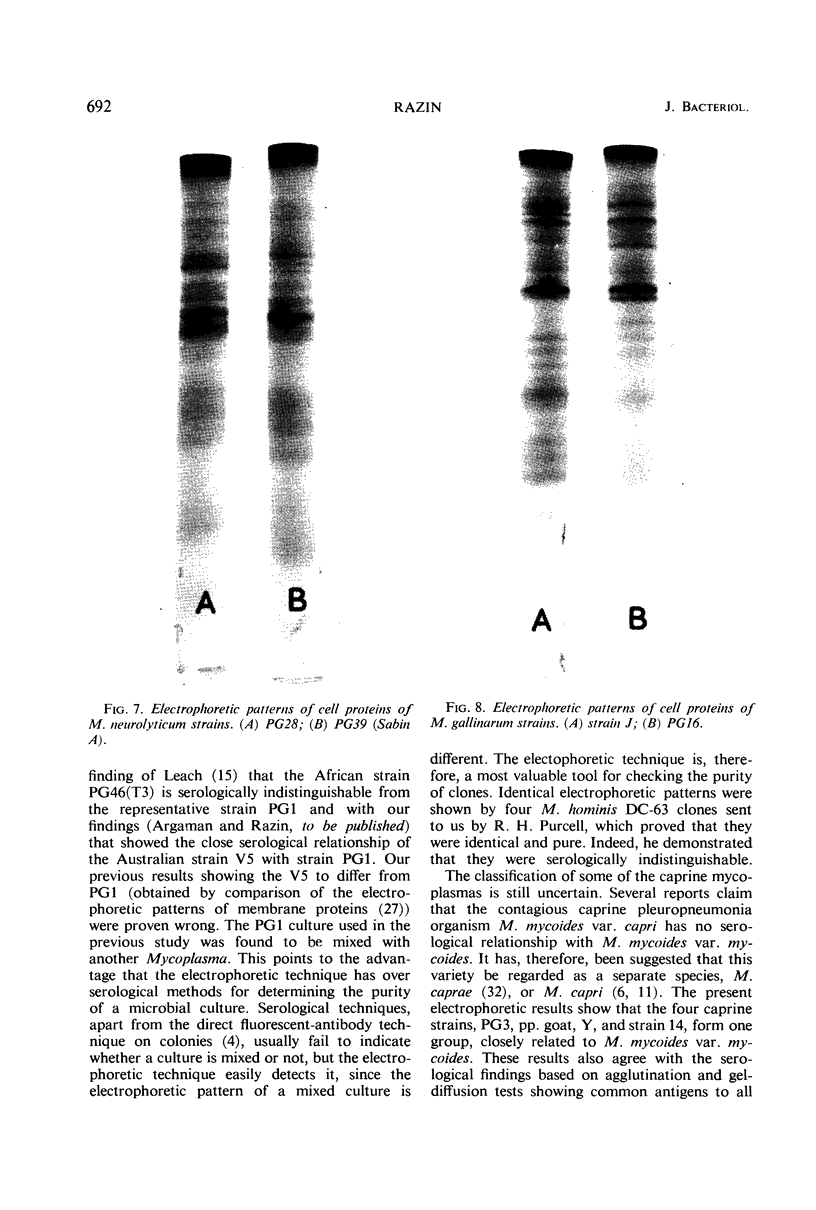
The electrophoretic patterns of cell proteins in polyacrylamide gels were used for the study of several taxonomic problems in the Mycoplasmatales. The patterns of five Mycoplasma hominis strains showed marked differences that corresponded with their known serological and nucleic acid heterogeneity. The patterns of three M. mycoides var. mycoides strains isolated in different countries were essentially identical. The electrophoretic patterns of several caprine strains resembled those of M. mycoides var. mycoides, supporting their classification as M. mycoides var. capri. Strain B3, a swine isolate, accordingly was tentatively identified as M. mycoides var. capri. The bovine mastitis strain M. agalactiae var. bovis possessed a pattern basically similar to that of the goat mastitis strain M. agalactiae, supporting the inclusion of both strains in one species. Three M. pulmonis strains isolated from rats or tissue cultures showed nearly identical patterns. The pattern of the toxigenic M. neurolyticum (Sabin A) strain resembled but was not identical with that of the nontoxigenic PG28 strain. The avian Mycoplasma species, M. gallisepticum, M. meleagridis, M. synoviae, M. gallinarum, and M. iners showed easily distinguishable and specific patterns, supporting their present classification in different species. Several improvements in the electrophoretic technique are described, and its advantages and limitations as a taxonomic tool are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLYDE W. A., Jr MYCOPLASMA SPECIES IDENTIFICATION BASED UPON GROWTH INHIBITION BY SPECIFIC ANTISERA. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:958–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORDY D. R., ADLER H. E. Patterns of reaction in infection with a virulent form of PPLO from goats. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 15;79:686–695. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeb B. J., Kenny G. E. Characterizion of Mycoplasma pulmonis variants isolated from rabbits. II. Basis for differentiation of antigenic subtypes. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1425–1429. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1425-1429.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Giudice R. A., Robillard N. F., Carski T. R. Immunofluorescence identification of Mycoplasma on agar by use of incident illumination. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1205–1209. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1205-1209.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinter Z., Danielsson D., Bakos K. Differentiation of porcine Mycoplasma strains. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Oct;41(1):77–84. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer R., Turano P., Turner W. J. Destaining apparatus for disc electrophoresis gels by current at right angles to gel axis. J Chromatogr. 1966 Sep;24(1):204–205. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)98129-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALE H. H., HELMBOLDT C. F., PLASTRIDGE W. N., STULA E. F. Bovine mastitis caused by a Mycoplasma species. Cornell Vet. 1962 Oct;52:582–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. Tissue cultures and mycoplasmas. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Jun;23(Suppl):285+–285+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J. R., Cottew G. S., Adler H. E. Diseases of goats caused by mycoplasma: a review of the subject with some new findings. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):287–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27668.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg R. E., Lockhart W. R. Classification of enterobacteria based on overall similarity. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1275–1280. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1275-1280.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEMCKE R. M. A SEROLOGICAL COMPARISON OF VARIOUS SPECIES OF MYCOPLASMA BY AN AGAR GEL DOUBLE-DIFFUSION TECHNIQUE. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Jan;38:91–100. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach R. H., Butler M. Compraison of mycoplasmas associated with human tumors, leukemia, and tissue cultures. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):934–941. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.934-941.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach R. H. Comparative studies of mycoplasma of bovine origin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):305–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTHY B. J., BOLTON E. T. An approach to the measurement of genetic relatedness among organisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jul;50:156–164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee Z. A., Rogul M., Wittler R. G. Molecular genetic studies of relationships among mycoplasma, L-forms and bacteria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):21–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICOL C. S., EDWARD D. G. Role of organisms of the pleuropneumonia group in human genital infections. Br J Vener Dis. 1953 Sep;29(3):141–150. doi: 10.1136/sti.29.3.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasri M E. l. Mycoplasma from contagious caprine pleuropneumonia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):298–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neimark H. Heterogeneity among the mycoplasma and relationships to bacteria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):31–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Wong D., Chanock R. M., Taylor-Robinson D., Canchola J., Valdesuso J. Significance of antibody to mycoplasma as measured by metabolic-inhibition techniques. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):664–675. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27712.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Rottem S. Identification of Mycoplasma and other microorganisms by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis of cell proteins. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1807–1810. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1807-1810.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich P. R., Somerson N. L., Hybner C. J., Chanock R. M., Weissman S. M. Genetic differentiation by nucleic Acid homology I. Relationships among Mycoplasma species of man. J Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;92(2):302–310. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.2.302-310.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich P. R., Somerson N. L., Rose J. A., Weissman S. M. Genetic relatedness among mycoplasmas as determined by nucleic acid homology. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):153–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.153-160.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Razin S. Electrophoretic patterns of membrane proteins of Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):359–364. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.359-364.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILDKRAUT C. L., MARMUR J., DOTY P. The formation of hybrid DNA molecules and their use in studies of DNA homologies. J Mol Biol. 1961 Oct;3:595–617. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerson N. L., Reich P. R., Walls B. E., Chanock R. M., Weissman S. M. Genetic Differentiation by Nucleic Acid Homology II. Genotypic Variations Within Two Mycoplasma Species. J Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;92(2):311–317. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.2.311-317.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TULLY J. G., RUCHMAN I. RECOVERY, IDENTIFICATION, AND NEUROTOXICITY OF SABIN'S TYPE A AND C MOUSE MYCOPLASMA (PPLO) FROM LYOPHILIZED CULTURES. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Feb;115:554–558. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-28966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L., Aleu F., Bitensky M. W., Davidson M., Gesner B. Studies of PPLO infection. II. The neurotoxin of Mycoplasma neurolyticum. J Exp Med. 1966 Dec 1;124(6):1067–1082. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.6.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]