Abstract
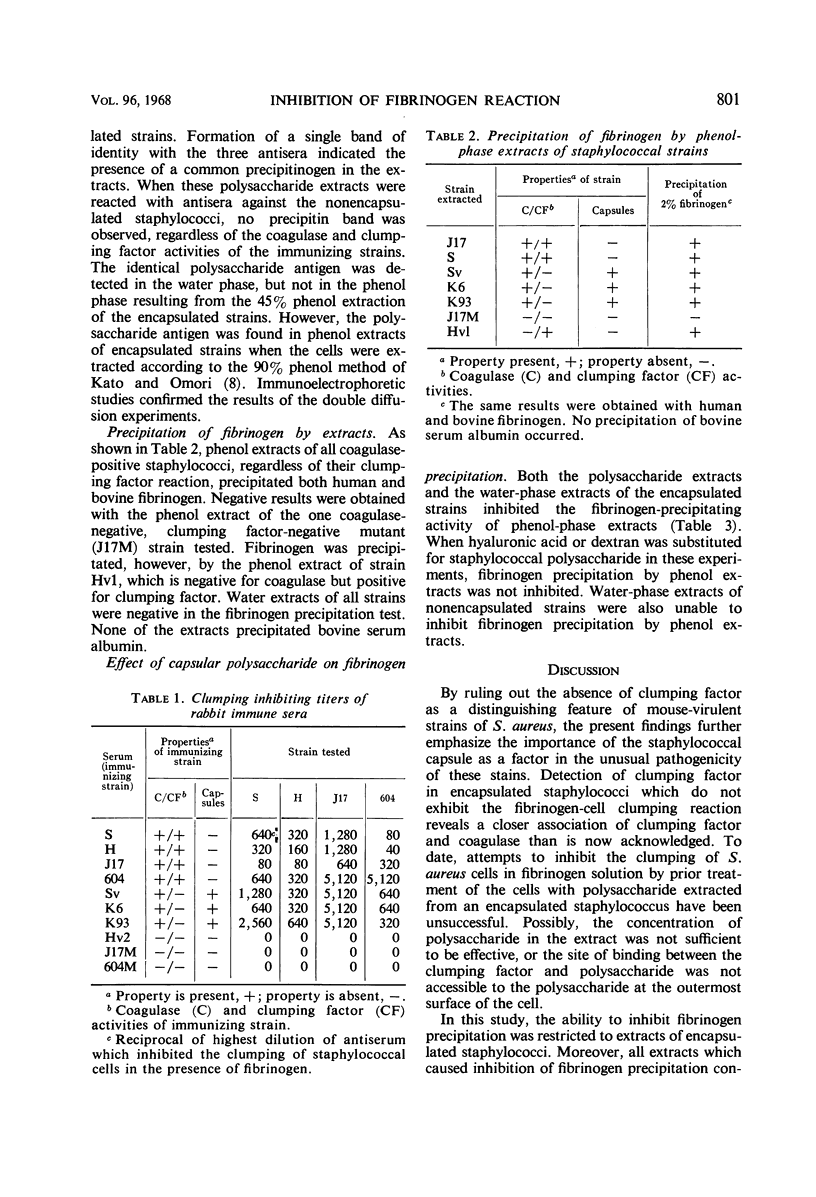
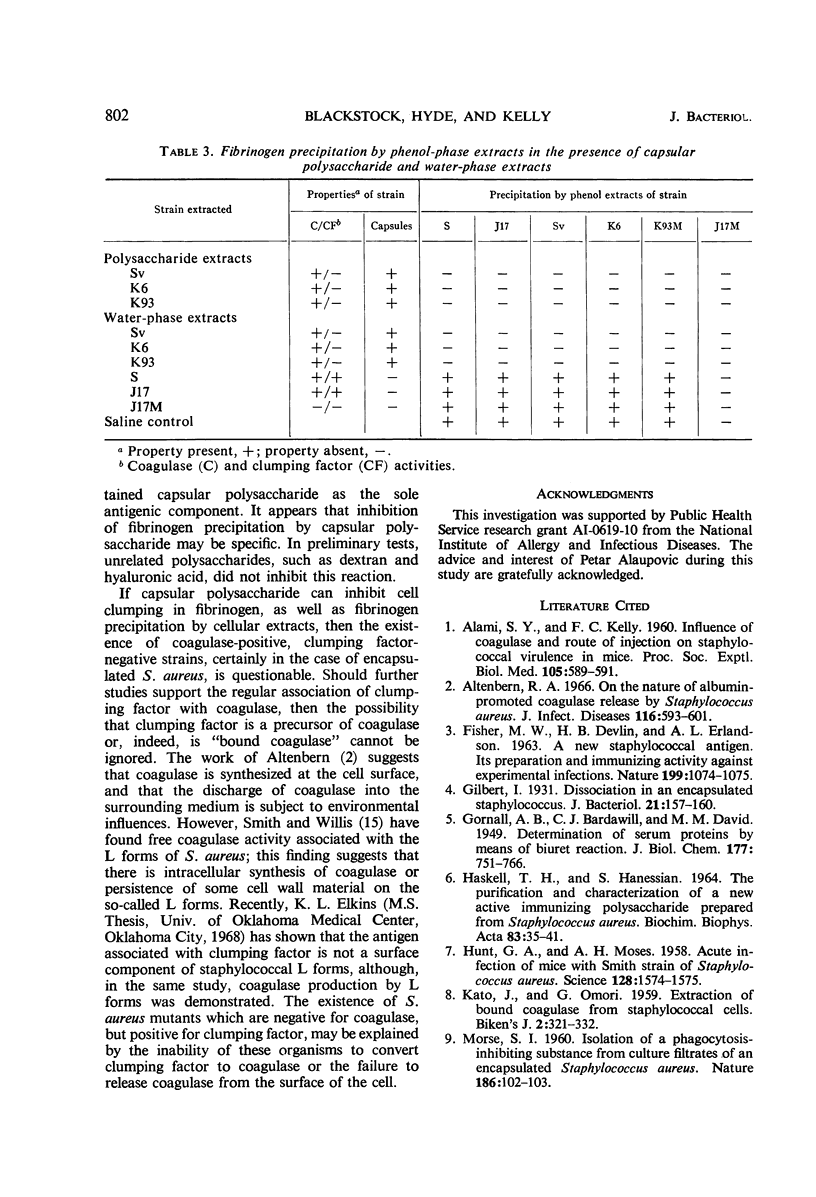
Encapsulated and nonencapsulated strains of Staphylococcus aureus which lack coagulase or clumping factor (bound coagulase), or both, were examined for the antigen associated with the fibrinogen-cell clumping reaction. Extracts of the cells were tested for the ability to react with fibrinogen or to inhibit fibrinogen precipitation. Antisera prepared against encapsulated (coagulase-positive, clumping factor-negative) variants, as well as against nonencapsulated wild-type (coagulase-positive, clumping factor-positive) S. aureus strains, contained high titers of clumping-inhibiting antibody. When coagulase-negative, clumping factor-negative mutants were the immunizing agents, antisera contained no demonstrable clumping-inhibiting antibody. Phenol extracts of all coagulase-positive strains tested precipitated fibrinogen, regardless of the ability of cells to clump in the presence of fibrinogen. Polysaccharide extracts of encapsulated, clumping factor-negative strains inhibited this fibrinogen-precipitating activity, whereas similar extracts of nonencapsulated staphylococci did not inhibit the fibrinogen reaction. From these results, it appeared that the coagulase-positive, encapsulated staphylococci which do not clump in fibrinogen solution possess clumping factor, but that their capsular polysaccharide inhibits clumping activity. These findings suggested a closer association of clumping factor and coagulase than is now recognized.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALAMI S. Y., KELLY F. C. Influence of coagulases and route of injection on staphylococcal virulence in mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Dec;105:589–591. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-26186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altenbern R. A. On the nature of albumin-promoted coagulase release by Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):593–600. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER M. W., DEVLIN H. B., ERLANDSON A. L. A NEW STAPHYLOCOCCAL ANTIGEN. ITS PREPARATION AND IMMUNIZING ACTIVITY AGAINST EXPERIMENTAL INFECTIONS. Nature. 1963 Sep 14;199:1074–1075. doi: 10.1038/1991074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert I. Dissociation in an Encapsulated Staphylococcus. J Bacteriol. 1931 Mar;21(3):157–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.21.3.157-160.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASKELL T. H., HANESSIAN S. THE PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF A NEW ACTIVE IMMUNIZING POLYSACCHARIDE PREPARED FROM STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 2;83:35–41. doi: 10.1016/0926-6526(64)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT G. A., MOSES A. J. Acute infection of mice with Smith strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1958 Dec 19;128(3338):1574–1575. doi: 10.1126/science.128.3338.1574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORSE S. I. Isolation and properties of a surface antigen of Staphylococcus aureus. J Exp Med. 1962 Feb 1;115:295–311. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORSE S. I. Isolation of a phagocytosis-inhibiting substance from culture filtrates of an encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus. Nature. 1960 Apr 2;186:102–103. doi: 10.1038/186102a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter J., Kelly F. C. Serological reactions associated with the clumping factor of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):588–594. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.588-594.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. M., DUBOS R. J. The behavior of virulent and avirulent staphylococci in the tissues of normal mice. J Exp Med. 1956 Jan 1;103(1):87–108. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. A., Willis A. T. Some physiological characters of L forms of Staphylococcus aureus. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(2):359–365. doi: 10.1002/path.1700940215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


