Abstract
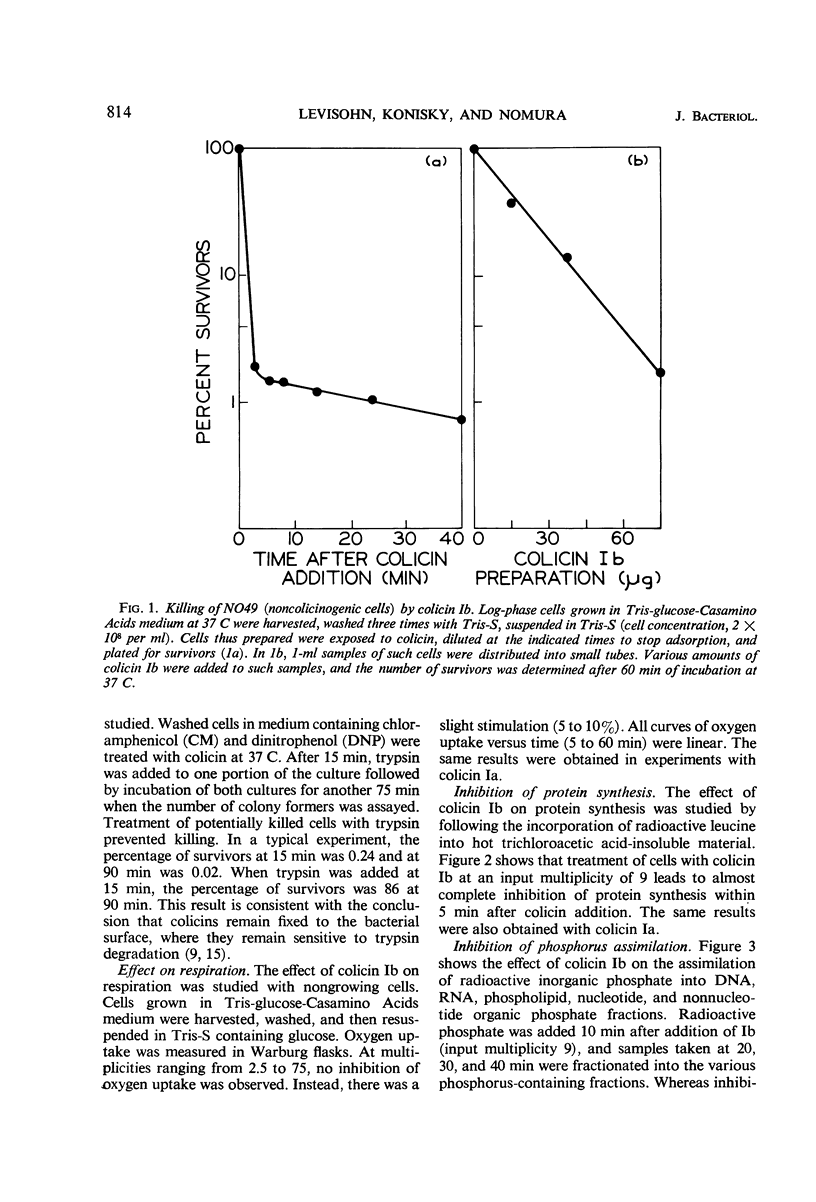
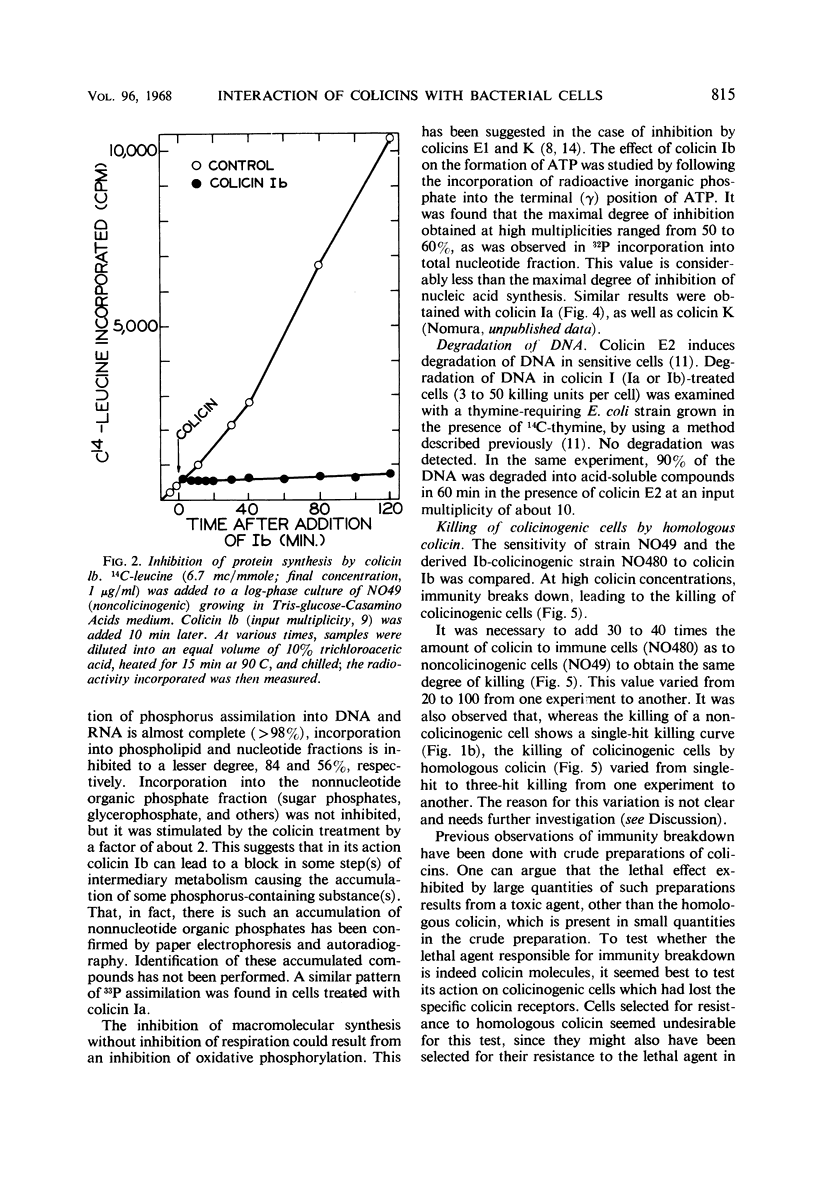
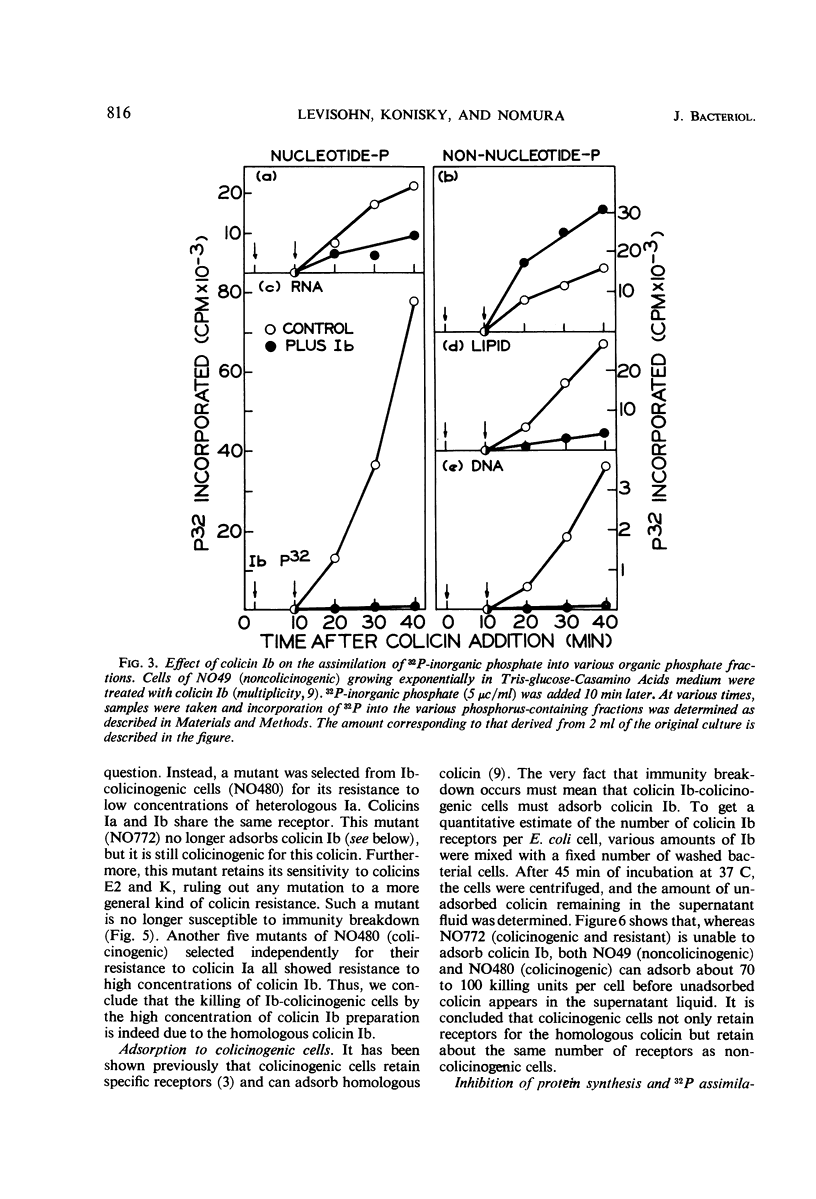
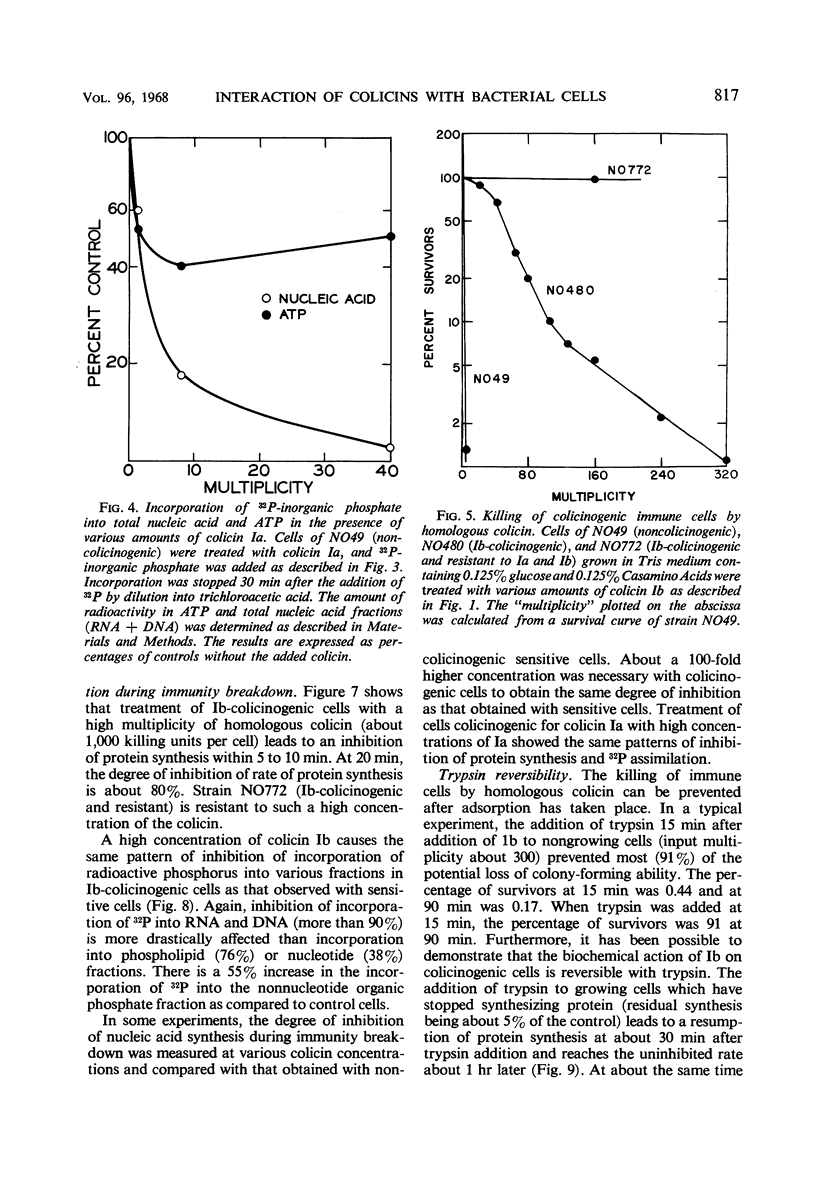
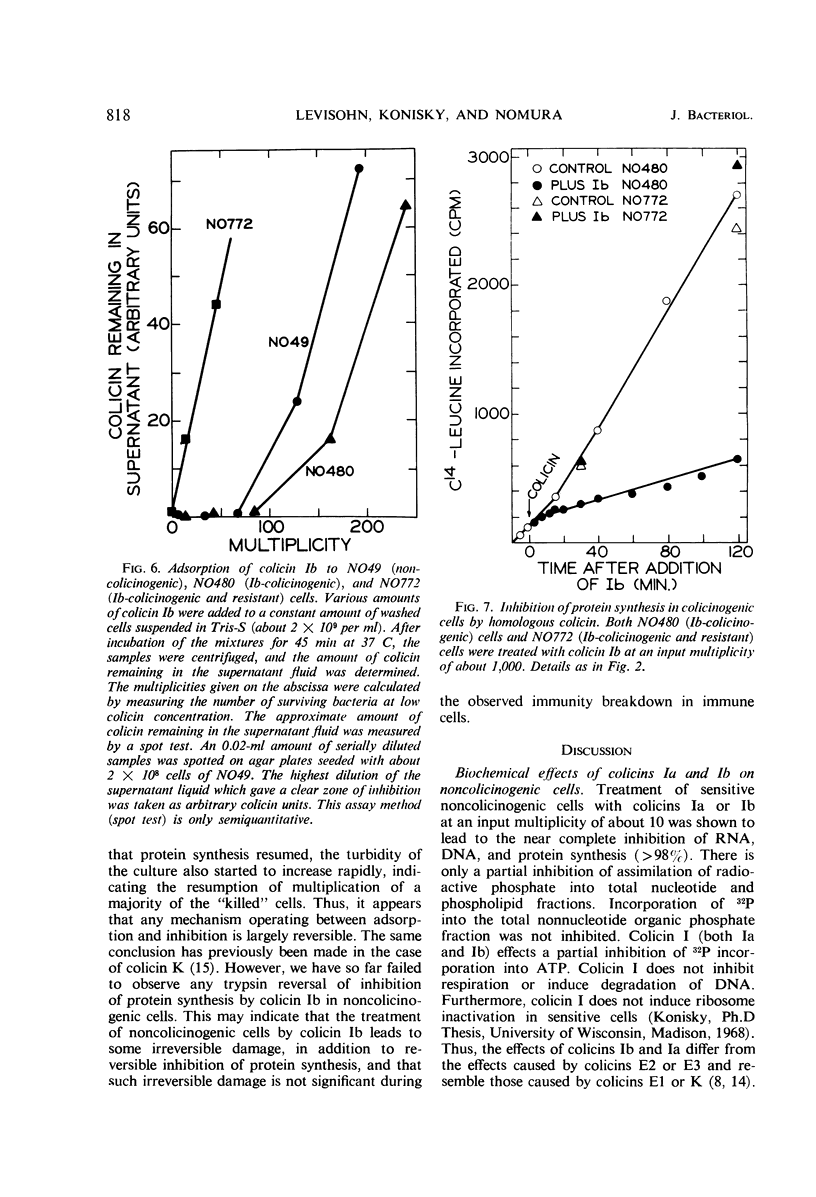
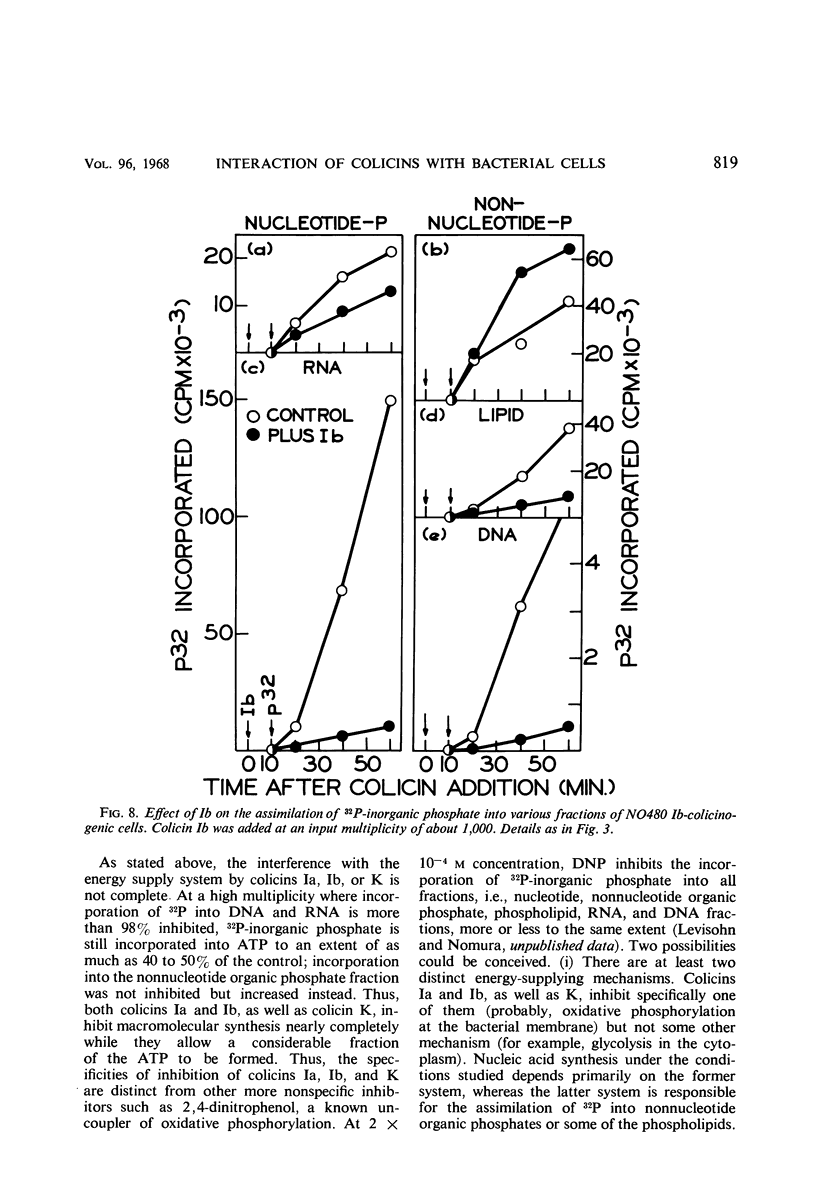
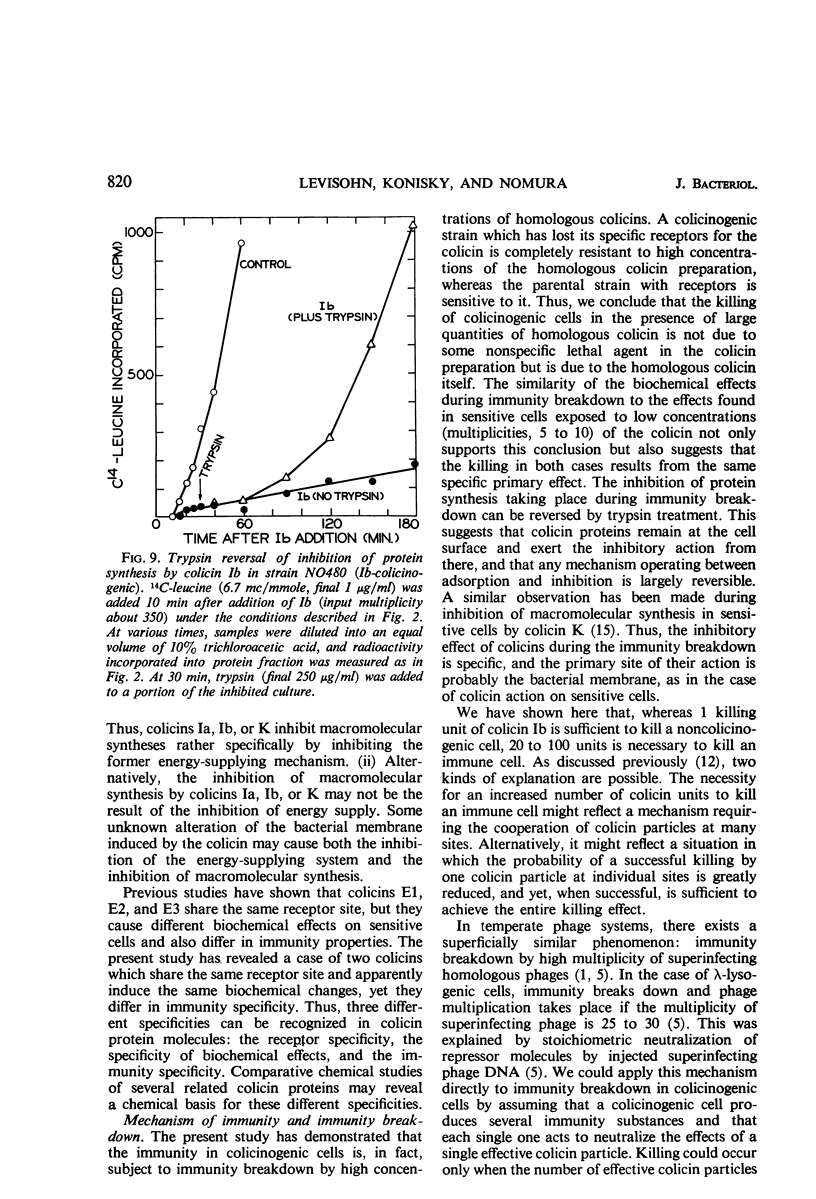
Colicinogenic cells are immune to the lethal effect of the colicin which they produce. In the presence of very high concentrations of colicin, however, colicinogenic cells are no longer immune to the homologous colicin. This phenomenon, immunity breakdown, was studied with colicins Ia and Ib. The biochemical effects of colicin Ib on Escherichia coli were studied with a standard noncolicinogenic strain. At multiplicities of about 10 or higher, colicin Ib inhibited incorporation of leucine into protein and incorporation of 32P-inorganic phosphate into deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid by more than 95%. Under the same conditions, 32P incorporation into phospholipid and nucleotide fractions was inhibited only partially (about 80 and 60%, respectively). Inhibition of 32P incorporation into the terminal phosphorus of adenosine triphosphate was also considerably less than that of macromolecular synthesis (50 to 60%). 32P incorporation into the nonnucleotide organic phosphate fraction was not inhibited. Respiration was not affected. Colicin Ia showed the same biochemical effects as colicin Ib. A mutant of an Ib-colicinogenic E. coli strain selected for resistance to low concentrations of colicin Ia was shown to be resistant to high concentrations of homologous colicin Ib, whereas the parent Ib-colicinogenic strain is sensitive to high concentrations of colicin Ib. This mutant lost its specific receptors for colicin Ib. Moreover, the biochemical effects of high concentrations of colicin Ib on Ib-colicinogenic cells during immunity breakdown were similar to the effects found in sensitive cells exposed to low concentrations of the same colicin. It is concluded that the killing of colicinogenic cells in the presence of high concentrations of homologous colicin is indeed caused by the homologous colicin molecules.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FREDERICQ P. Colicins and colicinogenic factors. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1958;12:104–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., SIMINOVITCH L., WOLLMAN E. Sur la biosynthèse d'une colicine et sur son mode d'action. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1952 Sep;83(3):295–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konisky J., Nomura M. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. II. Specific alteration of Escherichia coli ribosomes induced by colicin E3 in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):181–195. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90290-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E. ON THE MECHANISMS OF ACTION OF COLICINS. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Nov;107:SUPPL–SUPPL:73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda A., Nomura M. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. I. Studies with radioactive colicins. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):685–694. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.685-694.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOMURA M. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF COLICINES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOMURA M., NAKAMURA M. Reversibility of inhibition of nucleic acids and protein synthesis by colicin K. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 4;7:306–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90196-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M. Colicins and related bacteriocins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:257–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS B. L., REEVES P. R. Some observations on the mode of action of colicin F. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Apr 23;11:140–145. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


