Abstract
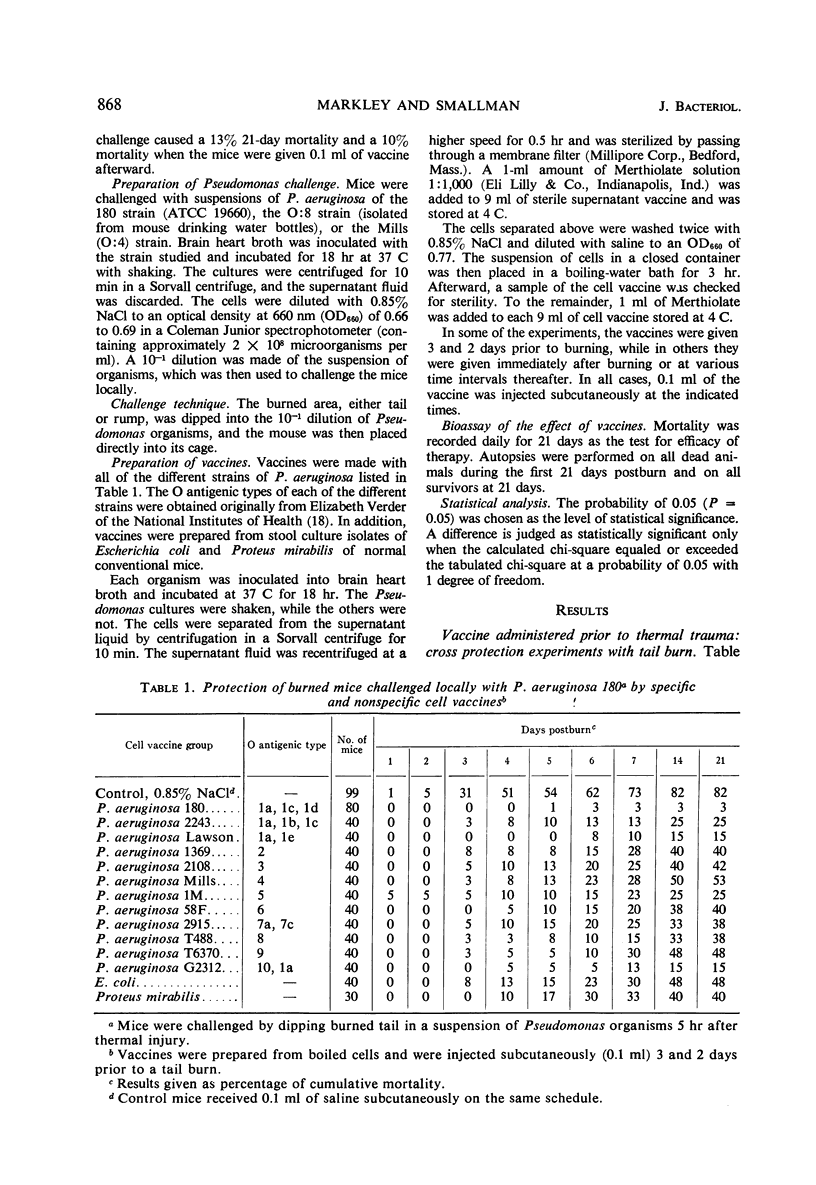
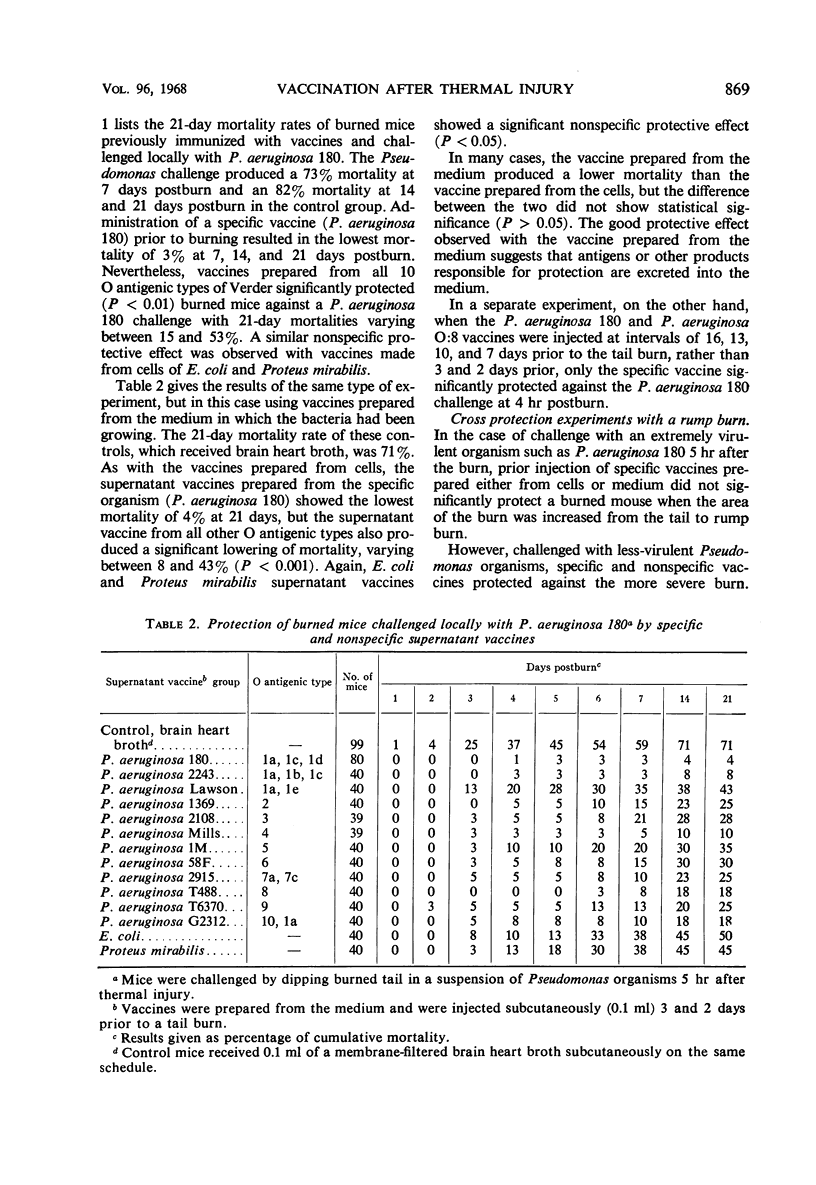
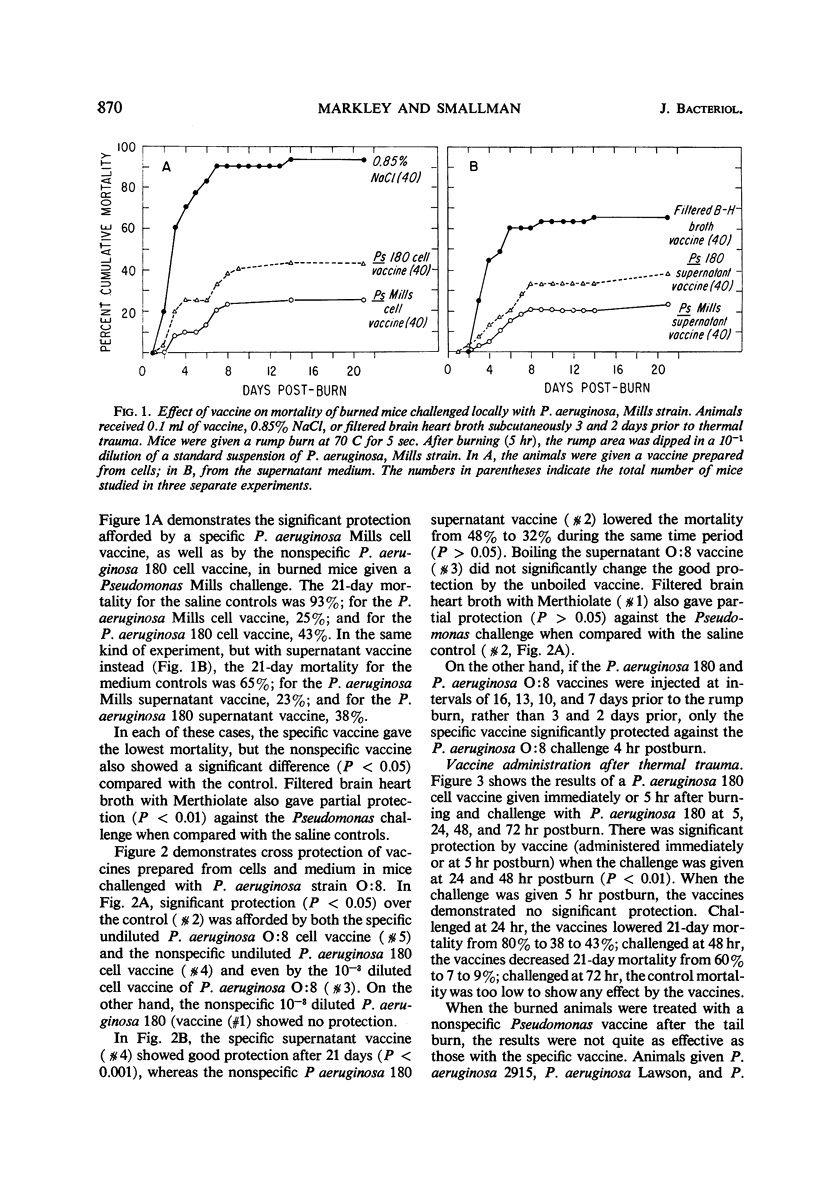
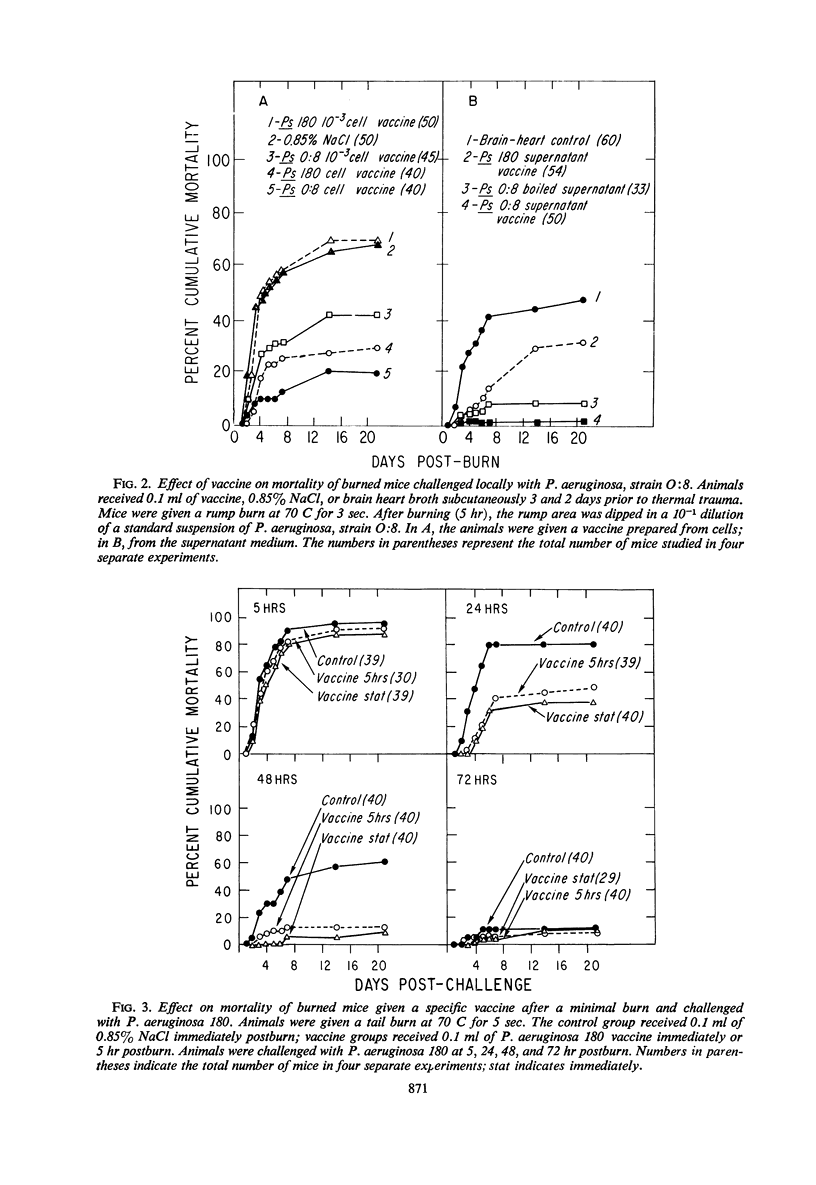
Active immunization is effective in the prophylaxis of Pseudomonas septicemia in burned mice. Vaccines were prepared from bacterial cells and growth medium of Verder's 10 different O serological types of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains, as well as from Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis. Mice given a tail burn could be significantly protected against a local Pseudomonas challenge by both specific and, to a lesser extent, by nonspecific Pseudomonas vaccines prepared either from bacterial cells or from the medium in which they were grown. The vaccine was effective when administered prior to or after thermal trauma. After a more extensive rump burn, the protective effect of a specific vaccine given after thermal injury was significant only when the challenge was postponed until 4 days postburn; the level of protection was less than in the mice with smaller burns.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. W., Moncrief J. A. Immunologic phenomena in burn injuries. JAMA. 1967 Jan 23;199(4):257–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAZAN A., CHAVEZ P. M., GURMENDI G., MARKLEY K. Fatal Pseudomonas septicemias in burned patients. Ann Surg. 1957 Feb;145(2):175–181. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195702000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELLER I., VIAL A. B., CALLAHAN W., WALDYKE J. USE OF VACCINE AND HYPERIMMUNE SERUM FOR PROTECTION AGAINST PSEUDOMONAS SEPTICEMIA. J Trauma. 1964 Jul;4:451–456. doi: 10.1097/00005373-196407000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller I. Sixth National Burn Seminar. Control of Pseudomonas infections by the immune processes. J Trauma. 1967 Jan;7(1):93–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman L. CHRONIC GENERAL INFECTION WITH THE BACILLUS PYOCYANEUS. Ann Surg. 1916 Aug;64(2):195–202. doi: 10.1097/00000658-191608000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves E. H. A Clinical Lecture ON A CASE OF BACILLUS PYOCYANEUS PYAEMIA SUCCESSFULLY TREATED BY VACCINE: Delivered at the Bristol General Hospital. Br Med J. 1909 May 15;1(2524):1169–1170. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.2524.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg R. B., Moncrief J. A., Switzer W. E., Order S. E., Mills W., Jr The successful control of burn wound sepsis. J Trauma. 1965 Sep;5(5):601–616. doi: 10.1097/00005373-196509000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGOVERN G. J., HARRISON C. S. The effect of thermal trauma on antibody formation in rabbits. Am Surg. 1957 Mar;23(3):257–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALT R. A., COPE O. Antibody production after certain forms of trauma. Surgery. 1956 Jun;39(6):959–969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKLEY K., SMALLMAN E. FACTORS AFFECTING SHOCK MORTALITY IN MICE BURNED BY SCALDING. Ann Surg. 1964 Jul;160:146–159. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196407000-00021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOYER C. A., BRENTANO L., GRAVENS D. L., MARGRAF H. W., MONAFO W. W., Jr TREATMENT OF LARGE HUMAN BURNS WITH 0.5 PER CENT SILVER NITRATE SOLUTION. Arch Surg. 1965 Jun;90:812–867. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1965.01320120014002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markley K., Smallman E., Evans G. Antibody production in mice after thermal and tourniquet trauma. Surgery. 1967 Jun;61(6):896–903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millican R. C., Evans G., Markley K. Susceptibility of burned mice to Pseudomonas aeruginosa and protection by vaccination. Ann Surg. 1966 Apr;163(4):603–610. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196604000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABIN E. R., GRABER C. D., VOGEL E. H., Jr, FINKELSTEIN R. A., TUMBUSCH W. A. Fatal pseudomonas infection in burned patients. A clinical, bacteriologic and anatomic study. N Engl J Med. 1961 Dec 21;265:1225–1231. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196112212652501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal S. M. A procedure for measurement of wound healing, with special reference to burns. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Nov;123(2):347–349. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STONE H. H., MARTIN J. D., Jr, HUGER W. E., KOLB L. GENTAMICIN SULFATE IN THE TREATMENT OF PSEUDOMONAS SEPSIS IN BURNS. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1965 Feb;120:351–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERDER E., EVANS J. A proposed antigenic schema for the identification of strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1961 Sep-Oct;109:183–193. doi: 10.1093/infdis/109.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERDER E., ROSENTHAL S. M. Role of infection in the delayed deaths of mice following extensive burn injury. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Nov;108:501–505. doi: 10.3181/00379727-108-26978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER H. L., MASON A. D., Jr, RAULSTON G. L. SURFACE INFECTION WITH PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. Ann Surg. 1964 Aug;160:297–305. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196408000-00019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



