Abstract
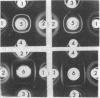
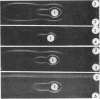
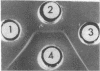
Surface antigens of smooth brucellae were extracted by ether-water, phenol-water, trichloroacetic acid, and saline and examined by immunoelectrophoresis and gel diffusion with antisera from infected and immunized rabbits. Ether-water extracts of Brucella melitensis contained a lipopolysaccharide protein component, which was specific for the surface of smooth brucellae and was correlated with the M agglutinogen of Wilson and Miles, a polysaccharide protein component devoid of lipid which was not restricted to the surface of smooth brucellae and was not correlated with the smooth agglutinogen (component 1), and several protein components which were associated with internal antigens of rough and smooth brucellae. Immunoelectrophoretic analysis of ether-water extracts of B. abortus revealed only two components, a lipopolysaccharide protein component, which was correlated with the A agglutinogen, and component 1. Component 1 from B. melitensis and B. abortus showed identity in gel diffusion tests, whereas component M from B. melitensis and component A from B. abortus showed partial identity with unabsorbed antisera and no cross-reactions with monospecific sera. Attempts to prepare monospecific sera directly by immunization of rabbits with cell walls or ether-water extracts were unsuccessful. Absorption of antisera with heavy fraction of ether-water extracts did not always result in monospecific sera. It was concluded (as has been described before) that the A and M antigens are present on a single antigenic complex, in different proportions depending upon the species and biotype, and that this component is a lipopolysaccharide protein complex of high molecular weight that diffuses poorly through agar gel. Components 1, A, and M were also demonstrated in trichloroacetic acid and phenol-water extracts. With all extracts, B. melitensis antigen showed greater diffusibility in agar than B. abortus antigens. After mild acid hydrolysis, B. abortus ether-water extract was able to diffuse more readily.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEER H., STAEHELIN T., DOUGLAS H., BRAUDE A. I. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PARTICLE SIZE AND BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF E. COLI BOIVIN ENDOTOXIN. J Clin Invest. 1965 Apr;44:592–602. doi: 10.1172/JCI105172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUCE W., JONES L. M. The use of gel diffusion precipitin plates in the study of Brucella. Bull World Health Organ. 1958;19(1):187–196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Wilson J. B. Chemical composition and biological properties of the endotoxin of Brucella abortus. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):895–902. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.895-902.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Wilson J. B. Hypoferremia in mice and its application to the bioassay of endotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):903–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.903-910.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beer H., Braude A. I., Brinton C. C., Jr A study of particle sizes, shapes and toxicities present in a boivin-type endotoxic preparation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):450–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Chordi A. Immunoelectrophoretic analysis of Brucella suis. Experientia. 1966 Dec 15;22(12):825–826. doi: 10.1007/BF01897440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Jones L. M., Leong D., Wilson J. B. Differences between Brucella antigens involved in indirect hemagglutination tests with normal and tanned red blood cells. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):499–505. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.499-505.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Jones L. M., Wilson J. B. Antigenic relationship of Brucella ovis and Brucella melitensis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1262–1268. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1262-1268.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Jones L. M., Wilson J. B. Antigenic relationship of the gram-negative organism causing canine abortion to smooth and rough brucellae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):618–624. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.618-624.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES L. M. A recommended method for the preparation of monospecific Brucella sera. Bull World Health Organ. 1958;19(1):177–186. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGAN I. G., NORMAN L. Antigenic analysis of Echinococcus antigens by agar diffusion techniques. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1961 Sep;10:727–734. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1961.10.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong D., Diaz R., Wilson J. B. Identification of the toxic component of Brucella abortus endotoxin and its labeling with radioactive chromate. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):612–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.612-617.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy L. K. Studies on the precipitin content of bovine sera prepared against various biotypes of Brucella abortus. Immunology. 1967 Apr;12(4):463–474. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REDFEARN M. S., BERMAN D. T. Application of the gel-diffusion technique for typing brucellae. Bull World Health Organ. 1960;23:133–134. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIBI E., MILNER K. C., PERRINE T. D. Endotoxic and antigenic fractions from the cell wall of Salmonella enteritidis; methods for separation and some biologic activities. J Immunol. 1959 Jan;82(1):75–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SULITZEANU D. Relationship of agar diffusion patterns to agglutinating and protective properties of Brucella suis antisera. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Aug;39(4):367–375. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- URIEL J., GRABAR P. Emploi de colorants dans l'analyse électrophorétique et immuno électrophorétique en milieu gélifié. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Apr;90(4):427–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]