Abstract
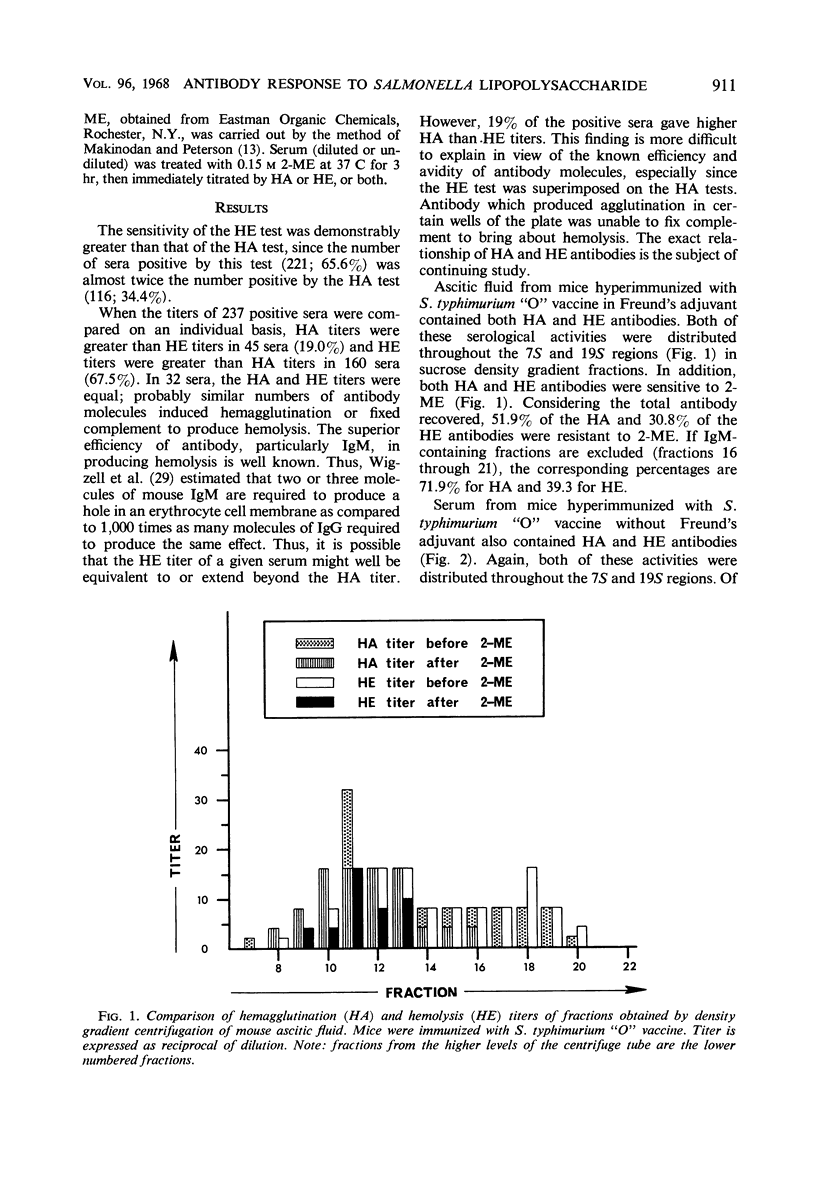
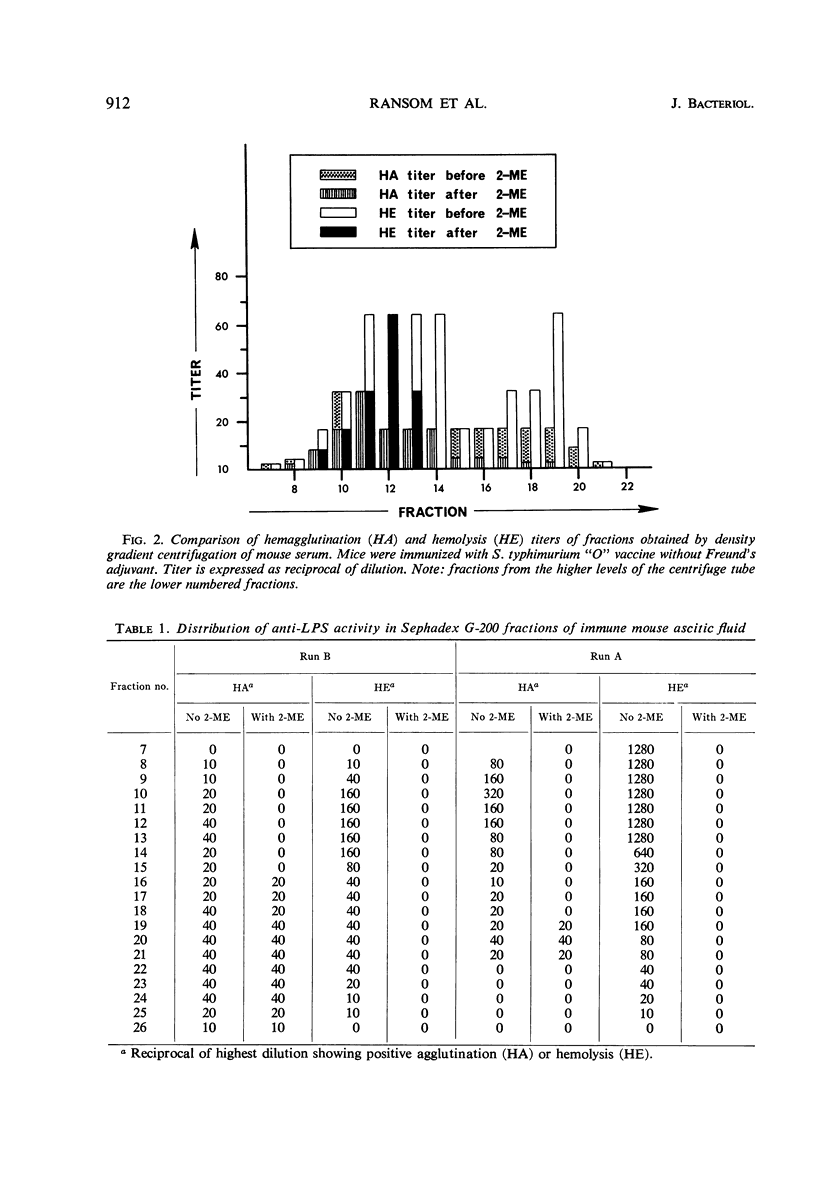
The complement-requiring passive hemolysis test with Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharide-coated sheep erythrocytes is more sensitive for antibodies directed against the lipopolysaccharide than is the passive hemagglutination test. The hemagglutinating and hemolyzing antibodies produced in Swiss mice by hyperimmunization, either with or without Freund's adjuvant, were distributed in both the light and heavy fractions isolated by sucrose density gradient fractionation and gel filtration. IgM fractions, whether tested by hemagglutination or hemolysis, were sensitive to 2-mercaptoethanol (0.15 m). On the other hand, IgG hemolytic antibodies were more sensitive to 2-mercaptoethanol than were IgG hemagglutinating antibodies. The resistance of IgG hemagglutinating activity amounted to about 72 to 95% of the total IgG recovered, whereas the resistant portion of the IgG hemolytic activity was approximately 40 to 53%. It is suggested that, although mercaptoethanol sensitivity is not a definitive test for IgM antibody, its use in connection with the hemagglutination test gives at least an approximation of the IgG antibody, whereas the hemolysis test gives a better approximation of maximal measurable antibody against Salmonella lipopolysaccharides.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADLER F. L. STUDIES ON MOUSE ANTIBODIES. I. THE RESPONSE TO SHEEP RED CELLS. J Immunol. 1965 Jul;95:26–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAUER D. C., MATHIES M. J., STAVITSKY A. B. Sequences of synthesis of gamma-1 macroglobulin and gamma-2 globulin antibodies during primary and secondary responses to proteins, salmonella antigens, and phage. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:889–907. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRECHER G., JAKOBEK E. F., SCHNEIDERMAN M. A., WILLIAMS G. Z., SCHMIDT P. J. Size distribution of erythrocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1962 Jun 29;99:242–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb45310.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth W. F., McLaughlin C. L., Fahey J. L. The immunoglobulins of mice. VI. Response to immunization. J Immunol. 1965 Nov;95(5):781–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich F. M. The immune response to heterologous red cells in mice. Immunology. 1966 Apr;10(4):365–376. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN H. S., MASAITIS L. The complement-fixing properties of gamma1 and gamma2 rabbit anti-sheep hemolytic antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1960 Nov-Dec;107:351–355. doi: 10.1093/infdis/107.3.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN H. S. The relationship of antibody size of hemolytic and complement-fixing activities. J Infect Dis. 1959 Jul-Aug;105(1):69–72. doi: 10.1093/infdis/105.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORZYNSKI E. A., LUDERITZ O., NETER E., WESTPHAL O. The bacterial hemagglutination test for the demonstration of antibodies to Enterobacteriaceae. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1956 Aug 10;66(1):141–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1956.tb40113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENBURY C. L., MOORE D. H., NUNN L. A. REACTION OF 7S AND 19S COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE RABBIT ANTISERA WITH HUMAN GROUP A AND AB RED CELLS. Immunology. 1963 Sep;6:421–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEREMANS J. F., VAERMAN J. P., VAERMAN C. STUDIES ON THE IMMUNE GLOBULINS OF HUMAN SERUM. II. A STUDY OF THE DISTRIBUTION OF ANTI-BRUCELLA AND ANTI-DIPHTHERIA ANTIBODY ACTIVITIES AMONG GAMMA-SS, GAMMA-IM AND GAMMA-1A-GLOBULIN FRACTIONS. J Immunol. 1963 Jul;91:11–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T., Lee E. H., Fudenberg H. Immunochemical properties of human gamma-A isohemagglutinin. I. Comparisons with gamma-G and gamma-M-globulin antibodies. J Immunol. 1965 Aug;95(2):197–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOSPALLUTO J., MILLER W., Jr, DORWARD B., FINK C. W. The formation of macroglobulin antibodies. I. Studies on adult humans. J Clin Invest. 1962 Jul;41:1415–1421. doi: 10.1172/JCI104596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist K., Bauer D. C. Precipitin activity of rabbit macroglobulin antibody. Immunochemistry. 1966 Sep;3(5):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(66)90175-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNOZ J. Production in mice of large volumes of ascites fluid containing antibodies. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Aug-Sep;95(4):757–759. doi: 10.3181/00379727-95-23355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makinodan T., Peterson W. J. Further studies on the secondary antibody-forming potential of juvenile, young adult, adult, and aged mice. Dev Biol. 1966 Aug;14(1):112–129. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(66)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March R. W., Cooney D. Technique for volume production of mouse ascites fluid containing Bordetella pertussis antibody. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Jul;14(4):693–694. doi: 10.1128/am.14.4.693-694.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller G. 19S antibody production against soluble lipopolysaccharide antigens by individual lymphoid cells in vitro. Nature. 1965 Sep 11;207(5002):1166–1168. doi: 10.1038/2071166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIKE R. M., SCHULZE M. L. PRODUCTION OF 7S AND 19S ANTIBODIES TO THE SOMATIC ANTIGENS OF SALMONELLA TYPHOSA IN RABBITS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Mar;115:829–833. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-29050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike R. M. Antibody heterogeneity and serological reactions. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Jun;31(2):157–174. doi: 10.1128/br.31.2.157-174.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike R. M., Schulze M. L., Chandler C. H. Agglutinating and precipitating capacity of rabbit anti-Salmonella typhosa gamma G and gamma M-antibodies during prolonged immunization. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):880–886. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.880-886.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J. B., KENNY K., SUTER E. THE ISOLATION AND BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITIES OF RABBIT GAMMA M- AND GAMMA G-ANTI-SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM ANTIBODIES. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:385–402. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom J. P. Passive hemolytic antibody response of primed, partially resistant mice to heat-killed Salmonella typhimurium vaccine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jun;128(2):419–423. doi: 10.3181/00379727-128-33027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAVITSKY A. B. Micromethods for the study of proteins and antibodies. I. Procedure and general applications of hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition reactions with tannic acid and protein-treated red blood cells. J Immunol. 1954 May;72(5):360–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STELOS P., TALMAGE D. W. The separation by starch electrophoresis of two antibodies in sheep red cells differing in hemolytic efficiency. J Infect Dis. 1957 Mar-Apr;100(2):126–135. doi: 10.1093/infdis/100.2.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAERMAN J. P., HEREMANS J. F., VAERMAN C. STUDIES OF THE IMMUNE GLOBULINS OF HUMAN SERUM. I. A METHOD FOR THE SIMULTANEOUS ISOLATION OF THE TREE IMMUNE GLOBULINS (GAMMA-SS, GAMMA-IM AND GAMMA-1A) FROM INDIVIDUAL SMALL SERUM SAMPLES. J Immunol. 1963 Jul;91:7–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDANZ W. P., JACKSON A. L., LANDY M. SOME ASPECTS OF THE ANTIBODY RESPONSE OF RABBITS TO IMMUNIZATION WITH ENTEROBACTERIAL SOMATIC ANTIGENS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Jul;116:832–837. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigzell H., Möller G., Andersson B. Studies at the cellular level of the 19S immune response. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;66(4):530–540. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.66.4.530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



