Abstract
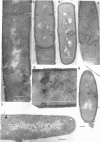
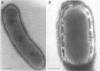
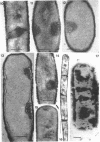
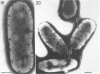
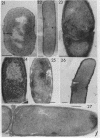
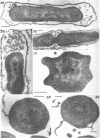
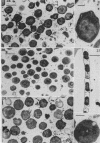
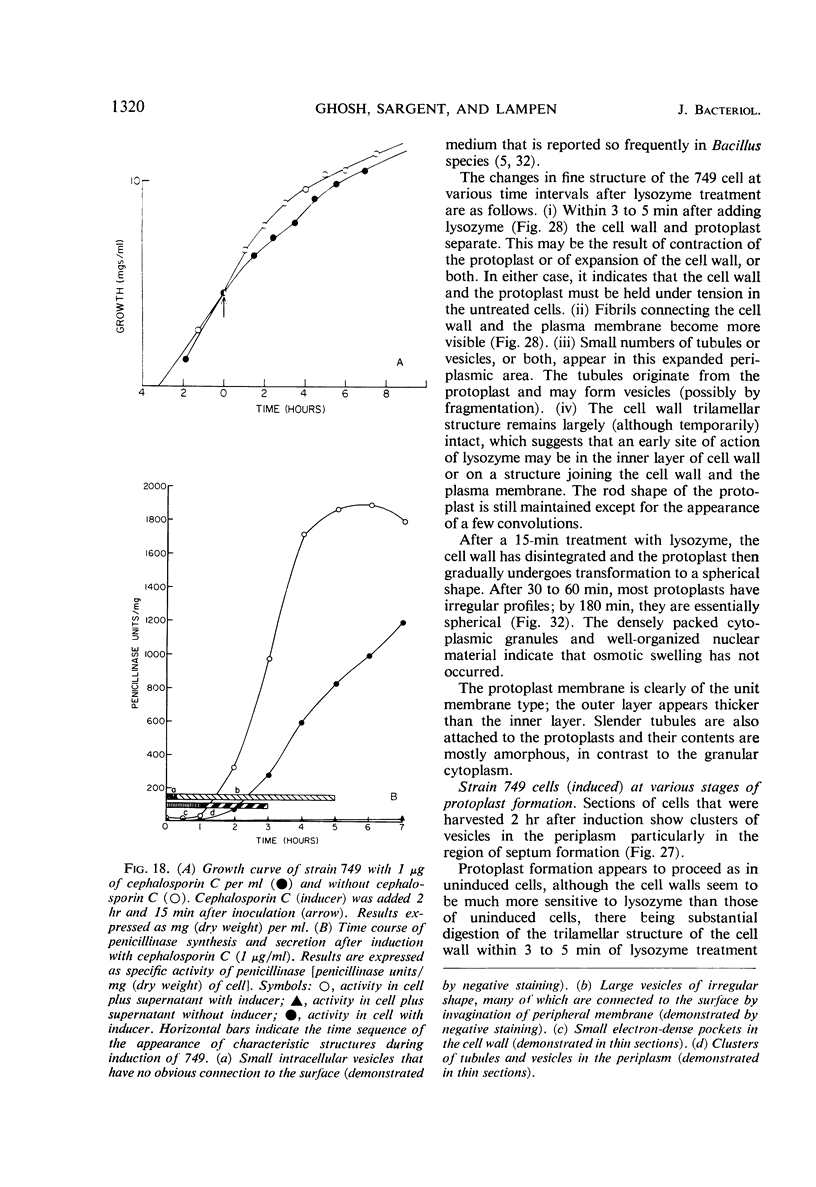
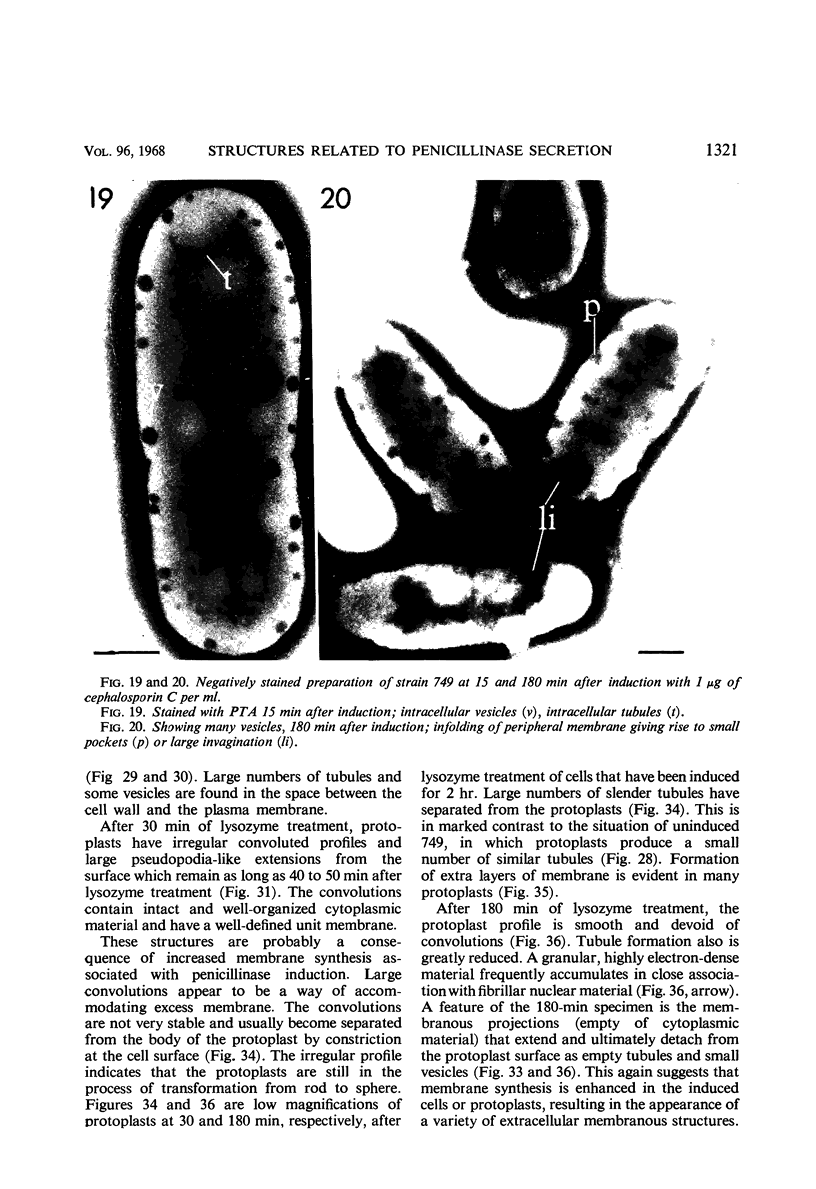
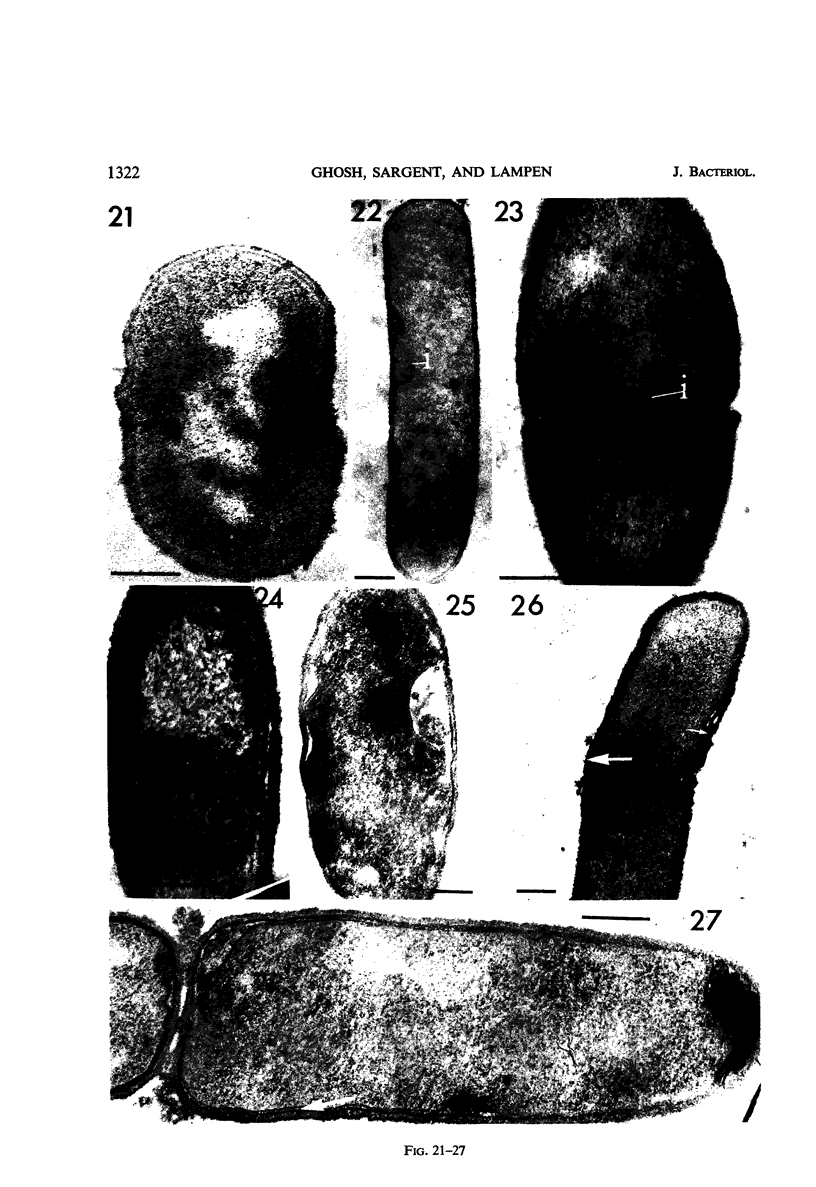
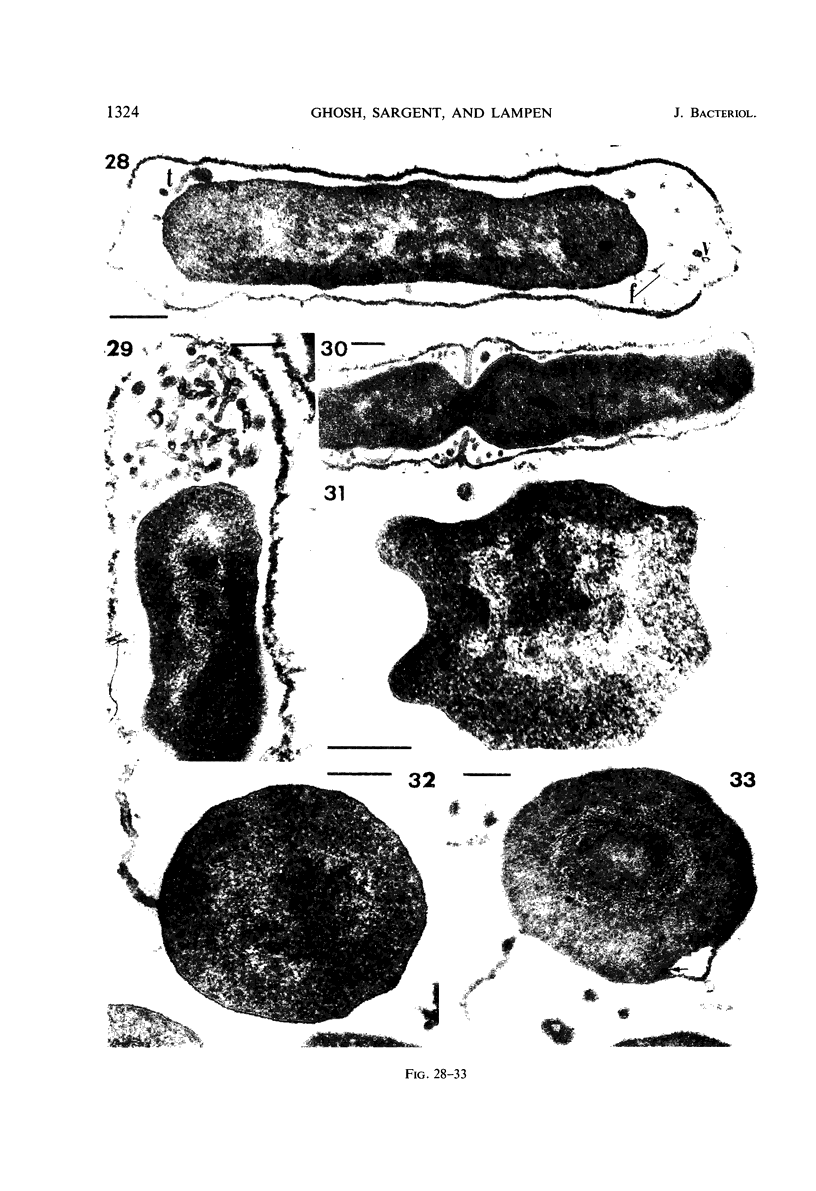
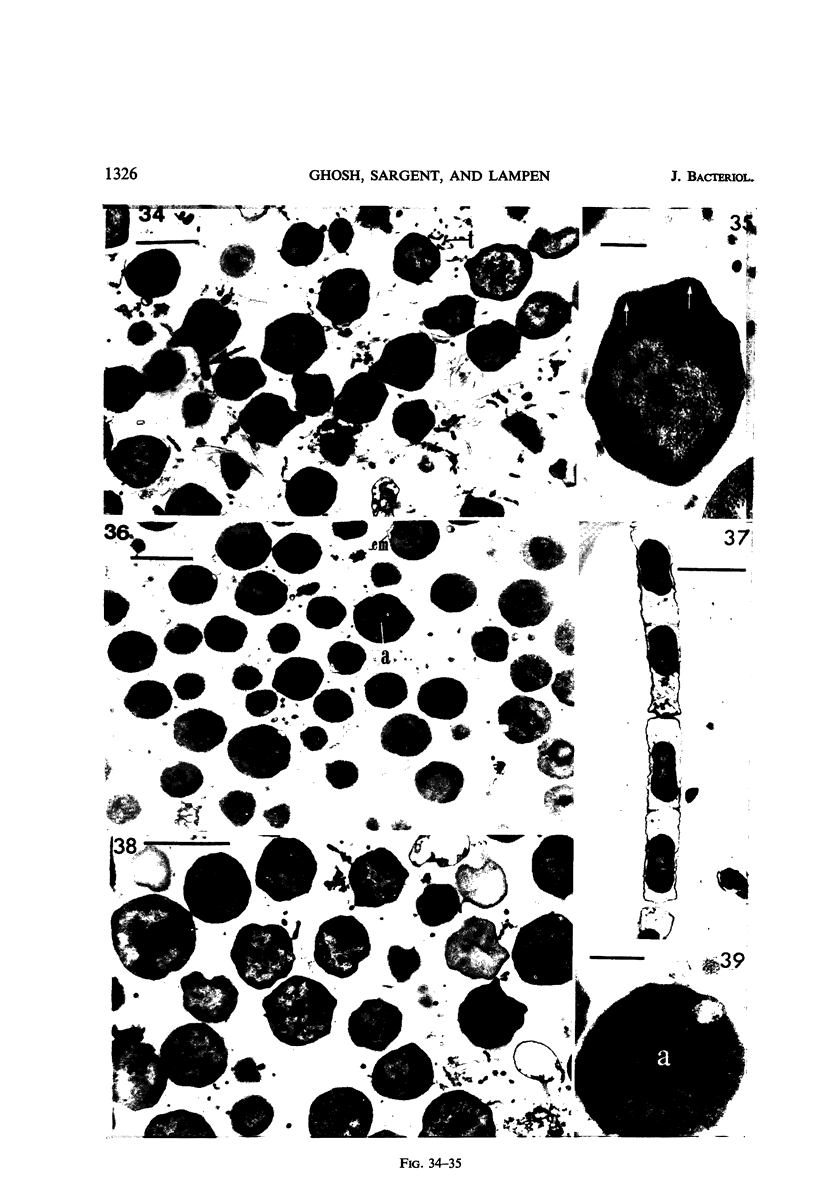
Cells of uninduced Bacillus licheniformis (strain 749) in mid-logarithmic phase have no extensive intracytoplasmic membrane. After induction with cephalosporin C, characteristic organelles that contain tubules and vesicles with single-layered membranes and no visible internal substructure can be seen in thin sections in the periplasm. A magnoconstitutive penicillinase producer (749/C) contains similar structures. It is suggested that they represent a penicillinase secretory apparatus. In the first 15 min after induction, negatively stained preparations of induced 749 show large intracellular vesicles without individual contact with the cell surface. Negatively stained 749/C and fully induced 749 contain invaginations comparable to the structures seen in thin sections. When protoplasts of induced 749 and of 749/C are prepared, vesicles and tubules similar to those seen in thin sections of whole cells are liberated from the cell. Growing protoplasts of induced 749 show massive convolutions of the peripheral membrane, multiple layers of membrane, and characteristic long, slender tubules extending from the protoplast surface. These phenomena are not observed in uninduced 749 except for the production of a relatively small number of tubules. In 749/C, there were fewer convolutions than in induced 749, although tubule production was similar. Multiple layers of membrane were not observed in 749/C. The relation of the penicillinase secretory structures to mesosomes and to secretory structures of other organisms is discussed.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaton C. D. An electron microscope study of the mesosomes of a penicillinase-producing staphylococcus. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Jan;50(1):37–42. doi: 10.1099/00221287-50-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. M., Carroll G. C. Fine-structural correlates of growth in hyphae of Ascodesmis sphaerospora. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):658–671. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.658-671.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLINS J. F. THE DISTRIBUTION AND FORMATION OF PENICILLINASE IN A BACTERIAL POPULATION OF BACILLUS LICHENIFORMIS. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Mar;34:363–377. doi: 10.1099/00221287-34-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZ-JAMES P. FATE OF THE MESOSOMES OF BACILLUS MEGATERIUM DURING PROTOPLASTING. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1483–1491. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1483-1491.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrandes B., Chaix P., Ryter A. Localisation des cytochromes de Bacillus subtilis dans les structures mésosomiques. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1966 Nov 21;263(21):1632–1635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh B. K., Murray R. G. Fine structure of Listeria monocytogenes in relation to protoplast formation. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):411–426. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.411-426.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob F., Ryter A., Cuzin F. On the association between DNA and membrane in bacteria. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Mar 22;164(995):267–278. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson J. D., Palade G. E. Role of the Golgi complex in the intracellular transport of secretory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Feb;55(2):424–431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.2.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUSHNER D. J., POLLOCK M. R. The location of cell-bound penicillinase in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Oct;26:255–265. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-2-255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampen J. O. Cell-bound penicillinase of Bacillus licheniformis; properties and purification. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Aug;48(2):249–259. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-2-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATILE P. INTRAZELLULAERE LOKALISATION PROTEOLYTISCHER ENZYME VON NEUROSPORA CRASSA. I. FUNKTION UND SUBZELLULAERE VERTEILUNG PROTEOLYTISCHER ENZYME. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1965 Mar 16;65:884–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moor H. Endoplasmic reticulum as the initiator of bud formation in yeast (S. cerevisiae). Arch Mikrobiol. 1967 Jun 6;57(2):135–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00408697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKS H. F. Morphological study of the extrusion of secretory materials by the parotid glands of mouse and rat. J Ultrastruct Res. 1962 Jun;6:449–465. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(62)80002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF PENICILLINASES FROM TWO STRAINS OF BACILLUS LICHENIFORMIS: A CHEMICAL, PHYSICOCHEMICAL AND PHYSIOLOGICAL COMPARISON. Biochem J. 1965 Mar;94:666–675. doi: 10.1042/bj0940666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R. The measurement of the liberation of penicillinase from Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Oct;26:239–253. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-2-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., LANDMAN O. E. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MESOSOME LOSS AND THE STABLE L STATE (OR PROTOPLAST STATE) IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:457–467. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.457-467.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remsen C. C. Fine structure of the mesosome and nucleoid in frozen-etched Bacillus subtilis. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;61(1):40–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00704290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A. Association of the nucleus and the membrane of bacteria: a morphological study. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Mar;32(1):39–54. doi: 10.1128/br.32.1.39-54.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent M. G., Ghosh B. K., Lampen J. O. Localization of cell-bound penicillinase in Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1329–1338. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1329-1338.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent M. G. Rapid fixed-time assay for penicillinase. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1493–1494. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1493-1494.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBULL C. PLASMOLYSIS IN BACILLUS MEGATERIUM. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:1151–1154. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.1151-1154.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolstenholme D. R., Vermeulen C. A., Venema G. Evidence for the involvement of membranous bodies in the processes leading to genetic transformation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1111–1121. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1111-1121.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Kamp JA O. P., van Iterson W., van Deenen L. L. Studies of the phospholipids and morphology of protoplasts of Bacillus megaterium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;135(5):862–884. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]