Abstract
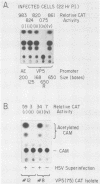
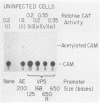
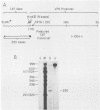
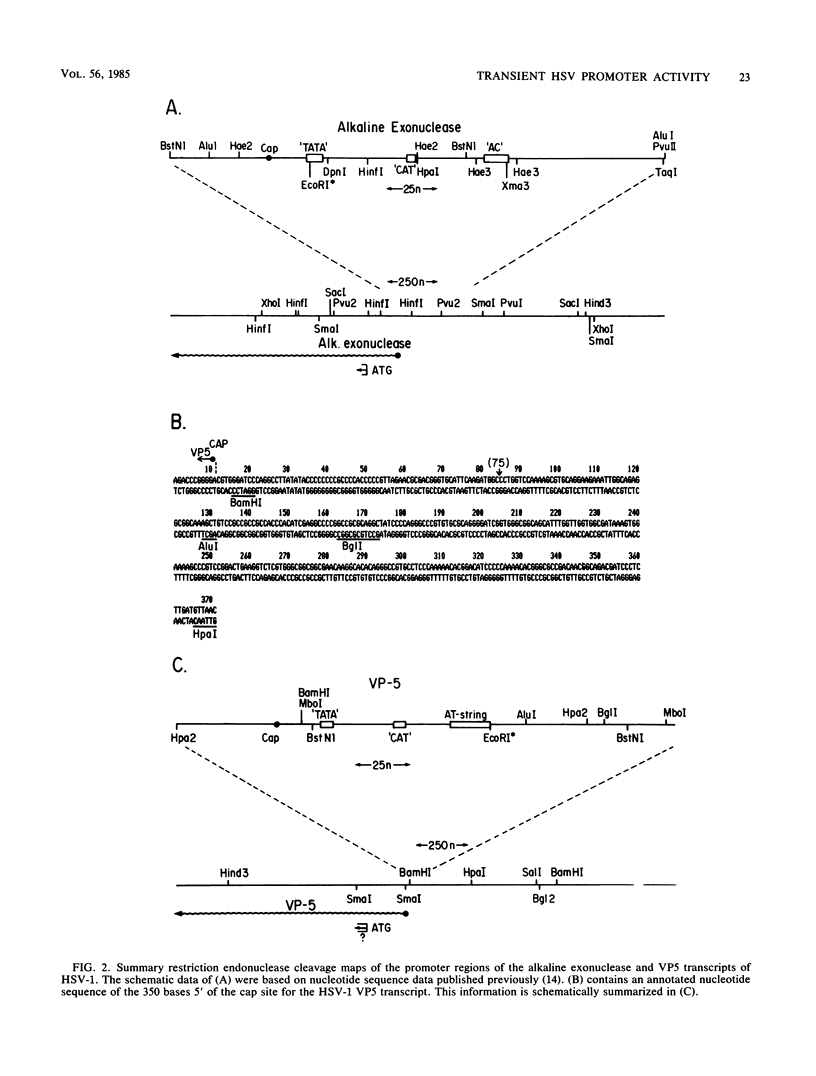
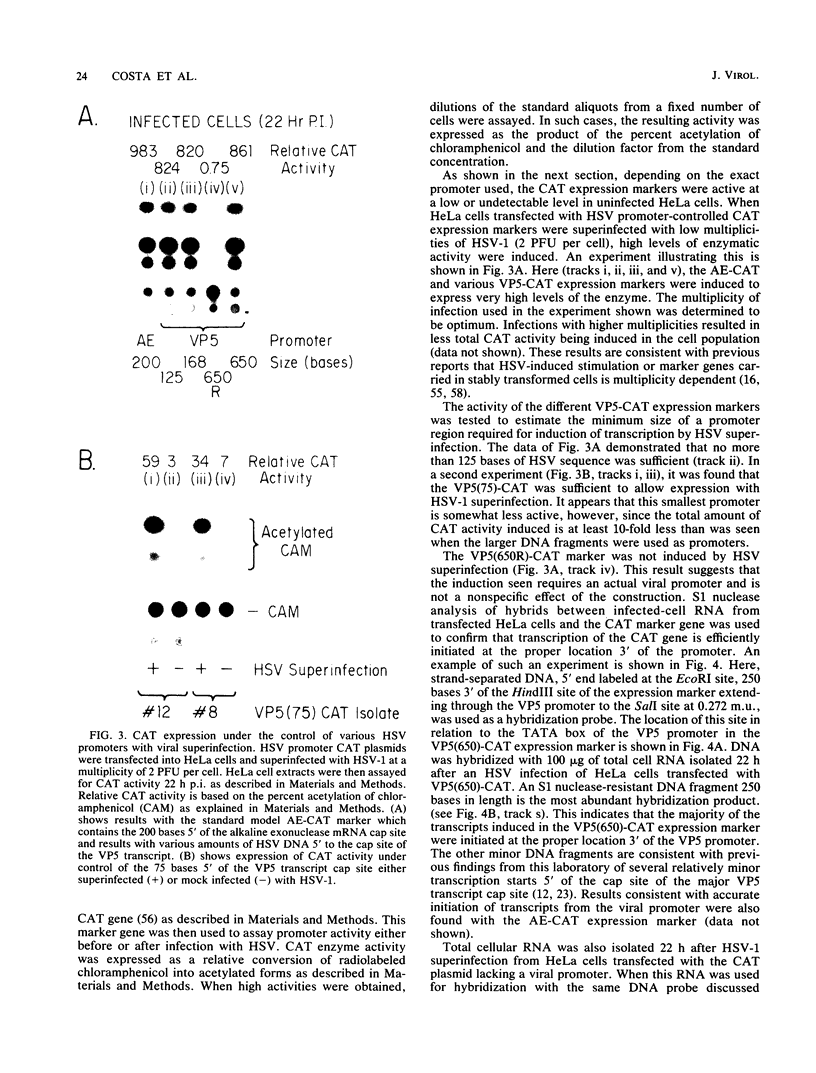
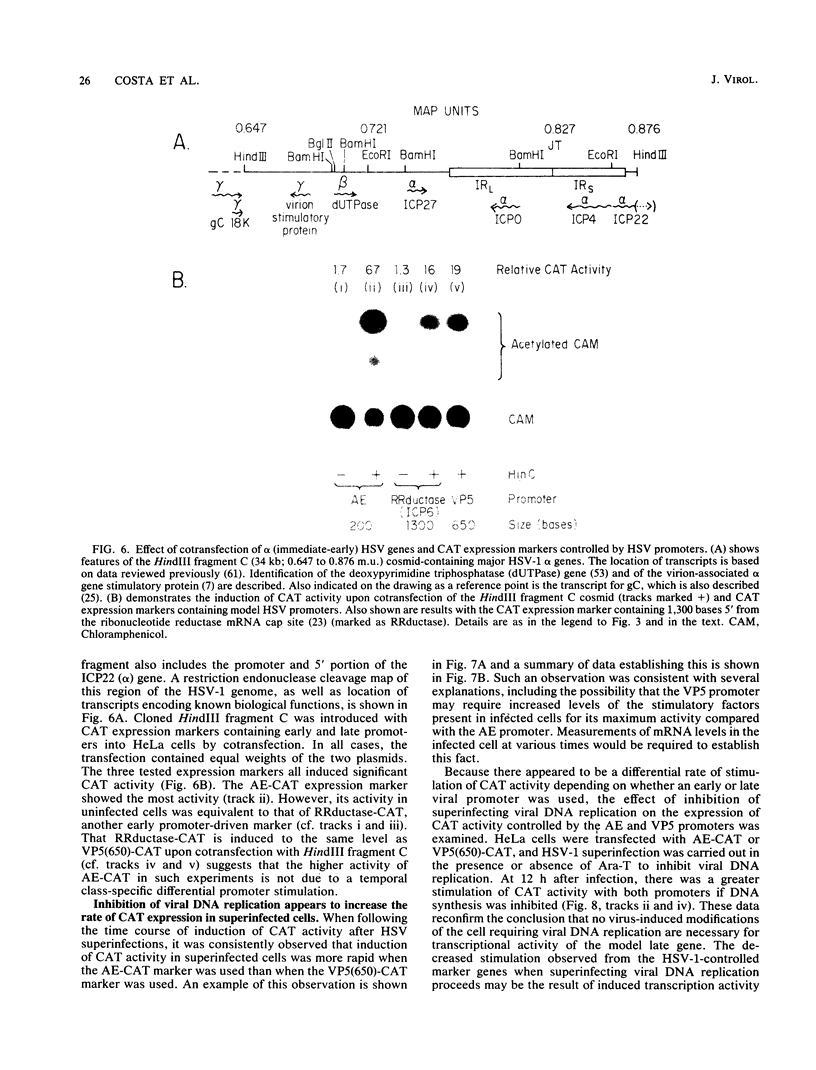
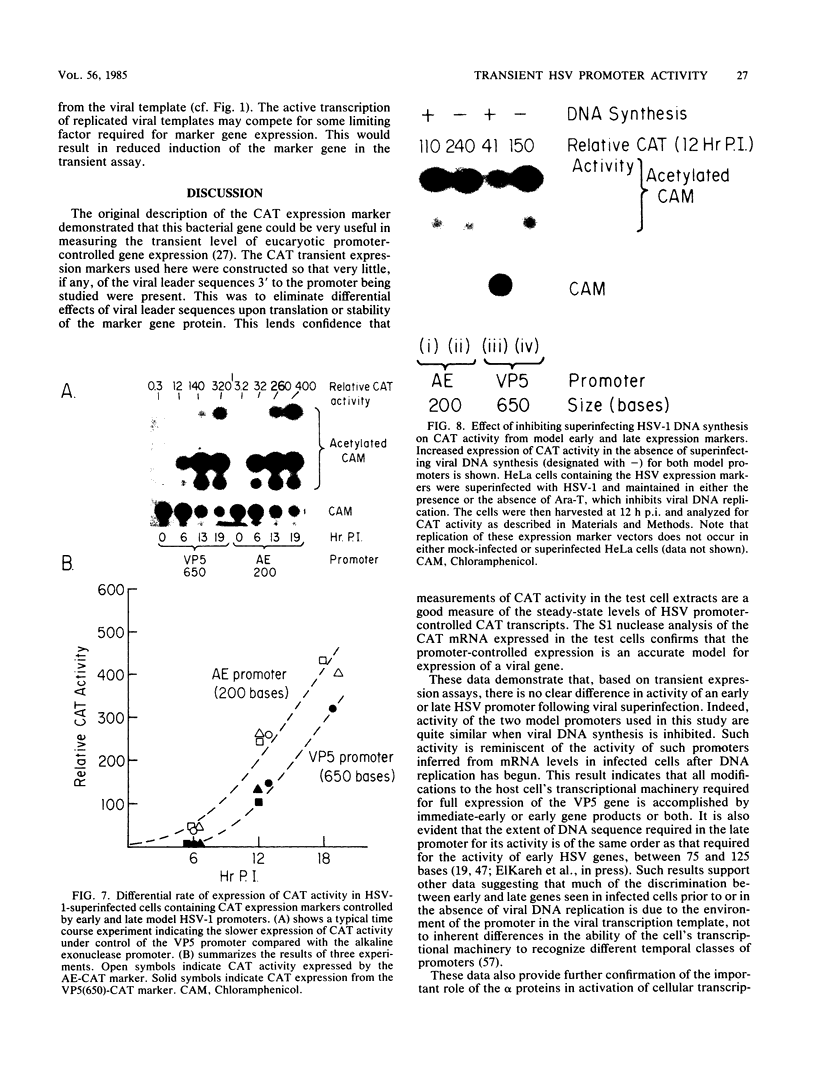
The requirements for expression of genes under the control of early (alkaline exonuclease) and late (VP5) herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) gene promoters were examined in a transient expression assay, using the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene as an expression marker. Both promoters were induced, resulting in the production of high levels of the enzyme upon low-multiplicity infection by HSV-1. S1 nuclease analysis of hybrids between RNA isolated from infected cells containing HSV-1 promoter constructs and marker gene DNA demonstrated normal transcriptional initiation of the marker gene directed by the viral promoters. Viral DNA sequences no more than 125 bases 5' of the putative transcriptional cap site were sufficient for maximum activity of the late promoter. In contrast to expression controlled by the early gene, the late promoter was not active at a measurable level in uninfected cells until DNA sequences between 75 and 125 bases 5' of the transcriptional cap site were deleted. Cotransfection of cells with the expression marker controlled by HSV promoters and a cosmid containing HSV alpha (immediate-early) genes indicated that full expression of both early and late promoters requires the same virus-induced host cell modifications. Inhibition of viral DNA synthesis results in an increased rate of transient expression of marker genes under control of either early or late promoters in contrast to the situation in normal virus infection. These data provide evidence that the normal course of expression of late HSV genes involves negative modulation of potentially active promoters in the infected cell.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. P., Costa R. H., Holland L. E., Wagner E. K. Characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 RNA present in the absence of de novo protein synthesis. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):9–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.9-27.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Frink R. J., Devi G. B., Gaylord B. H., Costa R. H., Wagner E. K. Detailed characterization of the mRNA mapping in the HindIII fragment K region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):1011–1027. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.1011-1027.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Stringer J. R., Holland L. E., Wagner E. K. Isolation and localization of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):805–820. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.805-820.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Moschonas N., Flavell R. A. Beta + thalassemia: aberrant splicing results from a single point mutation in an intron. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):289–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90412-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., McLauchlan J., McGeoch D. J. Orientation of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early mRNA's. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 11;7(1):77–91. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., Watson R. J., Wilkie N. M. Temporal regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription: location of transcripts on the viral genome. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley A. J., Knipe D. M., Jones P. C., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. VII. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant produced by in vitro mutagenesis and defective in DNA synthesis and accumulation of gamma polypeptides. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):191–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.191-206.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Campbell M. E., Preston C. M. Functional analysis of a herpes simplex virus type 1 promoter: identification of far-upstream regulatory sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2347–2365. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Cohen G., Eisenberg R., Long D., Wagner E. Direct demonstration that the abundant 6-kilobase herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA mapping between 0.23 and 0.27 map units encodes the major capsid protein VP5. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):287–292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.287-292.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Devi B. G., Anderson K. P., Gaylord B. H., Wagner E. K. Characterization of a major late herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):483–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.483-496.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Draper K. G., Banks L., Powell K. L., Cohen G., Eisenberg R., Wagner E. K. High-resolution characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcripts encoding alkaline exonuclease and a 50,000-dalton protein tentatively identified as a capsid protein. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):591–603. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.591-603.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis D., Smiley J. R. Transactivation of a late herpes simplex virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):544–551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper K. G., Costa R. H., Lee G. T., Spear P. G., Wagner E. K. Molecular basis of the glycoprotein-C-negative phenotype of herpes simplex virus type 1 macroplaque strain. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):578–585. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.578-585.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper K. G., Frink R. J., Wagner E. K. Detailed characterization of an apparently unspliced beta herpes simplex virus type 1 gene mapping in the interior of another. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1123–1128. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1123-1128.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. A detailed analysis of an HSV-1 early promoter: sequences involved in trans-activation by viral immediate-early gene products are not early-gene specific. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3037–3056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. DNA sequence elements required for regulated expression of the HSV-1 glycoprotein D gene lie within 83 bp of the RNA capsites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6647–6666. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D., Dunlop M. Trans activation of plasmid-borne promoters by adenovirus and several herpes group viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):5969–5978. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.5969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Anderson K. P., Wagner E. K. Herpes simplex virus type 1 HindIII fragment L encodes spliced and complementary mRNA species. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):559–572. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.559-572.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Draper K. G., Wagner E. K. Uninfected cell polymerase efficiently transcribes early but not late herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6139–6143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Eisenberg R., Cohen G., Wagner E. K. Detailed analysis of the portion of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome encoding glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):634–647. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.634-647.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Knipe D. M. Mutations in the major DNA-binding protein gene of herpes simplex virus type 1 result in increased levels of viral gene expression. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):478–486. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.478-486.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Treisman R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation of cloned human beta-globin genes by viral immediate-early gene products. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Draper K. G., Frink R. J., Costa R. H., Wagner E. K. Herpes simplex virus mRNA species mapping in EcoRI fragment I. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):594–607. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.594-607.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland L. E., Anderson K. P., Shipman C., Jr, Wagner E. K. Viral DNA synthesis is required for the efficient expression of specific herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA species. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):10–24. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90479-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland L. E., Anderson K. P., Stringer J. R., Wagner E. K. Isolation and localization of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA abundant before viral DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):447–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.447-462.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huszar D., Bacchetti S. Is ribonucleotide reductase the transforming function of herpes simplex virus 2? Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):76–79. doi: 10.1038/302076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R. Activation of gene expression by adenovirus and herpesvirus regulatory genes acting in trans and by a cis-acting adenovirus enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean J. H., Ben-Porat T., Kaplan A. S. Early functions of the genome of herpesvirus. 3. Inhibition of the transcription of the viral genome in cells treated with cycloheximide early during the infective process. Virology. 1974 Jun;59(2):516–523. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90461-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Spear P. G. Evidence for translational regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 gD expression. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):389–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.389-394.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Hayward G. S., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA VII. alpha-RNA is homologous to noncontiguous sites in both the L and S components of viral DNA. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):268–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.268-276.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. VIII. The transcription program consists of three phases during which both extent of transcription and accumulation of RNA in the cytoplasm are regulated. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):299–314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.299-314.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Batterson W., Nosal C., Roizman B., Buchan A. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. VI. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant defective in the expression of all early viral gene products. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):539–547. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.539-547.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Separation of sequences defining basal expression from those conferring alpha gene recognition within the regulatory domains of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4065–4069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J. C., Spandidos D. A., Wilkie N. M. Transcriptional regulation of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene is mediated through an enhancer-type sequence. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):389–395. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01817.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E., Donerly S. DNA fragments from F9 PyEC mutants increase expression of heterologous genes in transfected F9 cells. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):693–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Structural features of the herpes simplex virus alpha gene 4, 0, and 27 promoter-regulatory sequences which confer alpha regulation on chimeric thymidine kinase genes. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):939–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.939-949.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. C., Spence A., Smith M. The distal transcription signals of the herpesvirus tk gene share a common hexanucleotide control sequence. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Expression of recombinant genes containing herpes simplex virus delayed-early and immediate-early regulatory regions and trans activation by herpesvirus infection. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):522–531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.522-531.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Control of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA synthesis in cells infected with wild-type virus or the temperature-sensitive mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):275–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.275-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Cordingley M. G., Stow N. D. Analysis of DNA sequences which regulate the transcription of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):708–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.708-716.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G., Fisher F. B. Identification of the herpes simplex virus type 1 gene encoding the dUTPase. Virology. 1984 Oct 15;138(1):58–68. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90147-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read G. S., Summers W. C. In vitro transcription of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5215–5219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandri-Goldin R. M., Goldin A. L., Holland L. E., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Expression of herpes simplex virus beta and gamma genes integrated in mammalian cells and their induction by an alpha gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2028–2044. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:737–755. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley J. R., Swan H., Pater M. M., Pater A., Halpern M. E. Positive control of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene requires upstream DNA sequences. J Virol. 1983 Aug;47(2):301–310. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.2.301-310.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. L., Devi-Rao G. V., Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K. Rescue of a herpes simplex virus type 1 neurovirulence function with a cloned DNA fragment. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):504–508. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.504-508.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 function continuously required for early and late virus RNA synthesis. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):329–330. doi: 10.1038/285329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Preston C. M., Clements J. B. Separation and characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early mRNA's. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):42–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.42-52.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]