Abstract
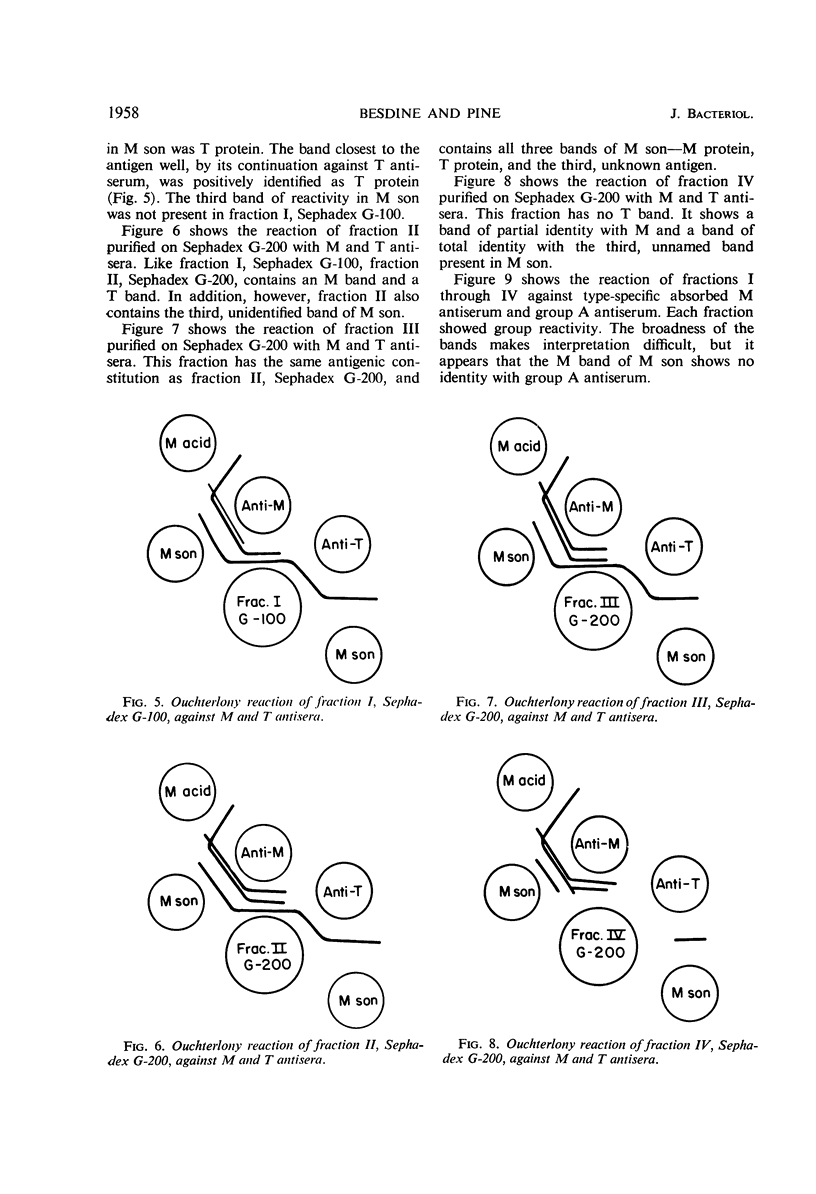
High-molecular-weight proteins having M protein reactivity were isolated without acid or alkaline digestion. Treatment of a heat-killed group A Streptococcus with sonic vibration released antigens which reacted strongly and specifically with absorbed type-specific antiserum. This antigen preparation was released without diminishing the total yield of acid-extractable M protein of the original heat-killed cells. Fractionation of the sonic preparation on a sucrose gradient yielded four peaks of M reactivity. When these fractions were placed on Sephadex G-200 columns, the M reactive material of three fractions appeared in the void volumes, suggesting that the active material in each had a molecular weight greater than 300,000. The reactivity of the fourth fraction followed closely the void volume of Sephadex G-100. Chemical analysis revealed heterogeneity of the fractions. Spectral analysis showed virtual absence of nucleic acid in three of the fractions and a moderate amount in the fourth. Bactericidal inhibition tests showed activity of three of the four fractions. Analysis of the fractions by Ouchterlony double-diffusion technique revealed that each of the four fractions had several antigenic constituents. All four contained M antigen. T antigen and a third unnamed antigen were present in some of the fractions. Group reactivity was present in all fractions, but did not reside on the M molecule. The enhanced potential of sonically released antigens to induce high-titer specific precipitating antibodies to M protein is discussed.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLEIWEIS A. S., KARAKAWA W. W., KRAUSE R. M. IMPROVED TECHNIQUE FOR THE PREPARATION OF STREPTOCOCCAL CELL WALLS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1198–1200. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1198-1200.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brentani R., Brentani M., Raw I. Zone sedimentation analysis of RNA in angle-head rotors. Anal Biochem. 1967 Aug;20(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHARLWOOD P. A. Applications of radioactively labeled marker proteins in density gradient ultracentrifugation. Anal Biochem. 1963 Mar;5:226–245. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(63)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. O., Pine L. Quantitative aspects of the M protein capillary precipitin test. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Jan;16(1):122–127. doi: 10.1128/am.16.1.122-127.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z. Spectrophotometric method for the determination of free pentose and pentose in nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):379–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EKSTEDT R. D., STOLLERMAN G. H. Factors affecting the chain length of group A streptococci. II. Quantative M-anti-M relationships in the long chain test. J Exp Med. 1960 Oct 1;112:687–698. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.4.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Wittner M. K. The multiple molecular structure of the M proteins of group A streptococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1118–1125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAHN J. J., COLE R. M. STREPTOCOCCAL M ANTIGEN LOCATION AND SYNTHESIS, STUDIED BY IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE. J Exp Med. 1963 Nov 1;118:659–666. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.5.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLADE H. D., VETTER J. K. Studies on Streptococcus pyogenes. I. Observations on the microscopical and biological aspects of the disintegration and solubilization of a type 6 strain by sonic oscillation. J Bacteriol. 1956 Feb;71(2):236–243. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.2.236-243.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. E. Laboratory diagnosis of streptococcal infections. Bull World Health Organ. 1958;19(1):153–176. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


