Abstract
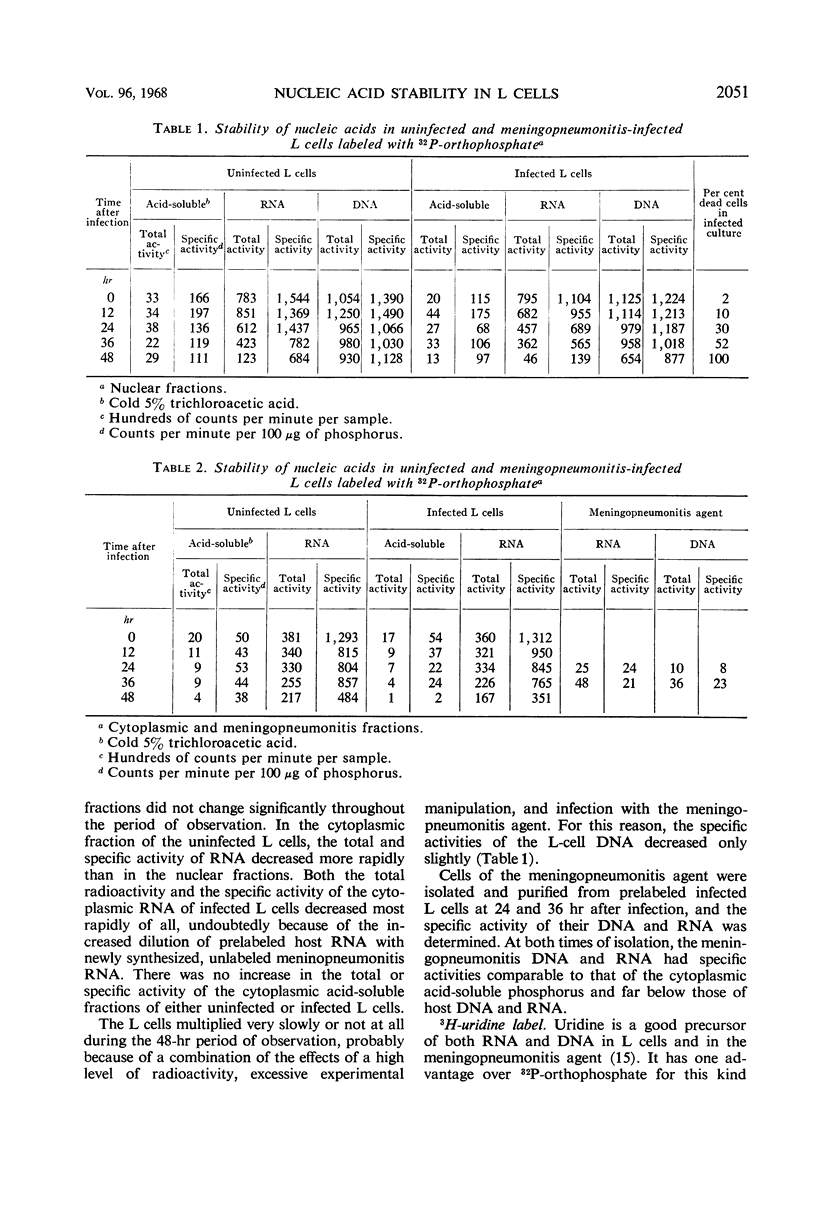
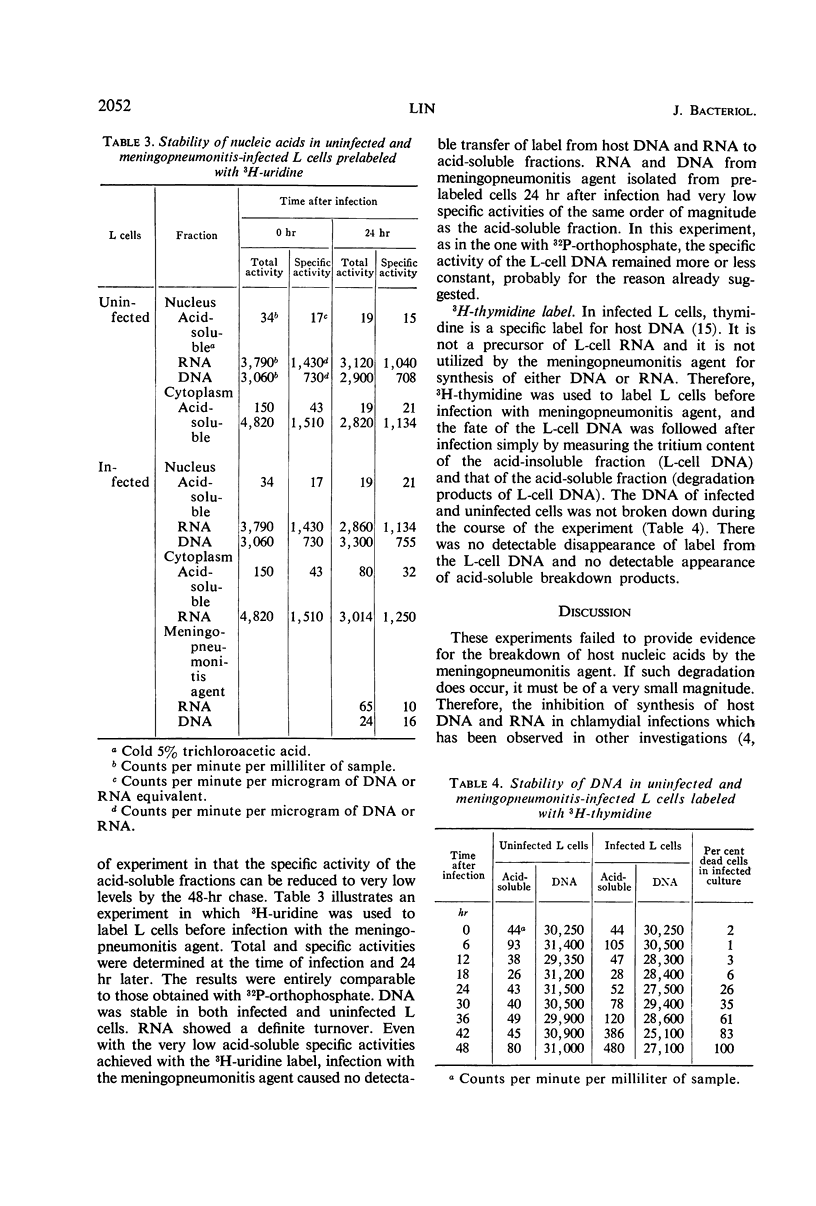
The stability of host nucleic acids in L cells infected with Chlamydia psittaci (strain meningopneumonitis) was studied. The L cells were prelabeled with either 32P-orthophosphate, 3H-uridine, or 3H-thymidine. After infection, the redistribution of each label among the different fractions of host and parasite was quantitatively determined and compared. There were no signs of accelerated degradation of host nucleic acid as the consequence of meningopneumonitis infection. Comparison of the specific activities of the meningopneumonitis nucleic acids with that of the acid-soluble fraction of host cell cytoplasm suggested that the major source of precursors for parasite nucleic acid synthesis was the common cytoplasmic pool of the infected host cell.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. J. Separation of protein synthesis in meningopneumonitisgent from that in L cells by differential susceptibility to cycloheximide. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):327–332. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.327-332.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROCKER T. T., PELC S. R., NIELSEN B. I., EASTWOOD J. M., BANKS J. POPULATION DYNAMICS AND DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS IN HELA CELLS INFECTED WITH AN ORNITHOSIS AGENT. J Infect Dis. 1965 Apr;115:105–122. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.2.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAHAM A. F., SIMINOVITCH L. Conservation of RNA and DNA phosphorus in strain L (Earle) mouse cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Nov;26(2):427–428. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN J. F., MORTON H. J., PARKER R. C. Nutrition of animal cells in tissue culture; initial studies on a synthetic medium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 Jan;73(1):1–8. doi: 10.3181/00379727-73-17557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. E., Moulder J. W. Autoradiographic study of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in L cells infected with the agent of meningopneumonitis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1128–1132. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1128-1132.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHECHTER E. M., TRIBBY I. I., MOULDER J. W. NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM IN L CELLS INFECTED WITH A MEMBER OF THE PSITTACOSIS GROUP. Science. 1964 Aug 21;145(3634):819–821. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3634.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARR T. J., POLLARD M., TANAMI Y., MOORE R. W. Cytochemical studies with psittacosis virus by fluorescence microscopy. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1960;18:501–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter E. M. Synthesis of nucleic acid and protein in L cells infected with the agent of meningopneumonitis. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2069–2080. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2069-2080.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMURA A., IWANAGA M. RNA SYNTHESIS IN CELLS INFECTED WITH THE MENINGOPNEUMONITIS AGENT. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jan;11:97–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tribby I. I., Moulder J. W. Availability of bases and nucleosides as precursors of nucleic acids in L cells and in the agent of meningopneumonitis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2362–2367. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2362-2367.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLKIN E., COHN W. E. Estimation of nucleic acids. Methods Biochem Anal. 1954;1:287–305. doi: 10.1002/9780470110171.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER J. R., KNOPF P. M., RICH A. A multiple ribosomal structure in protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jan 15;49:122–129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



