Abstract
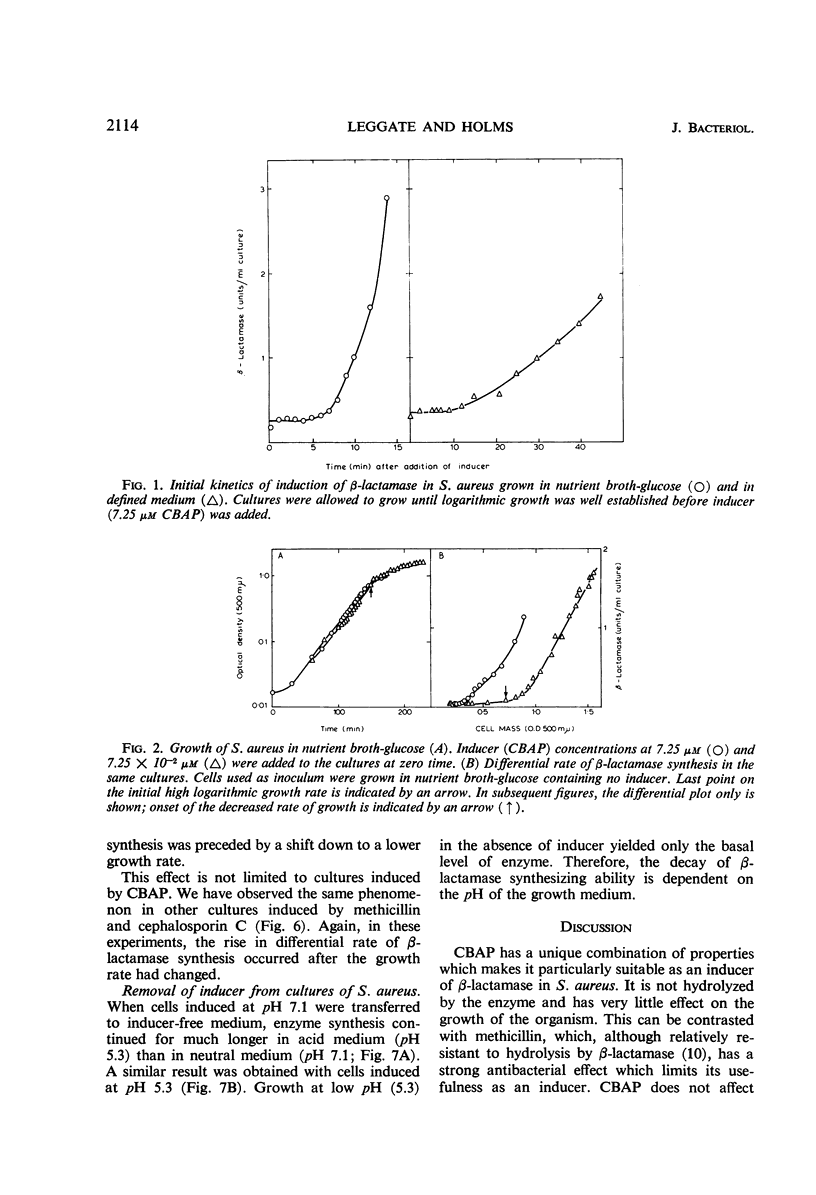
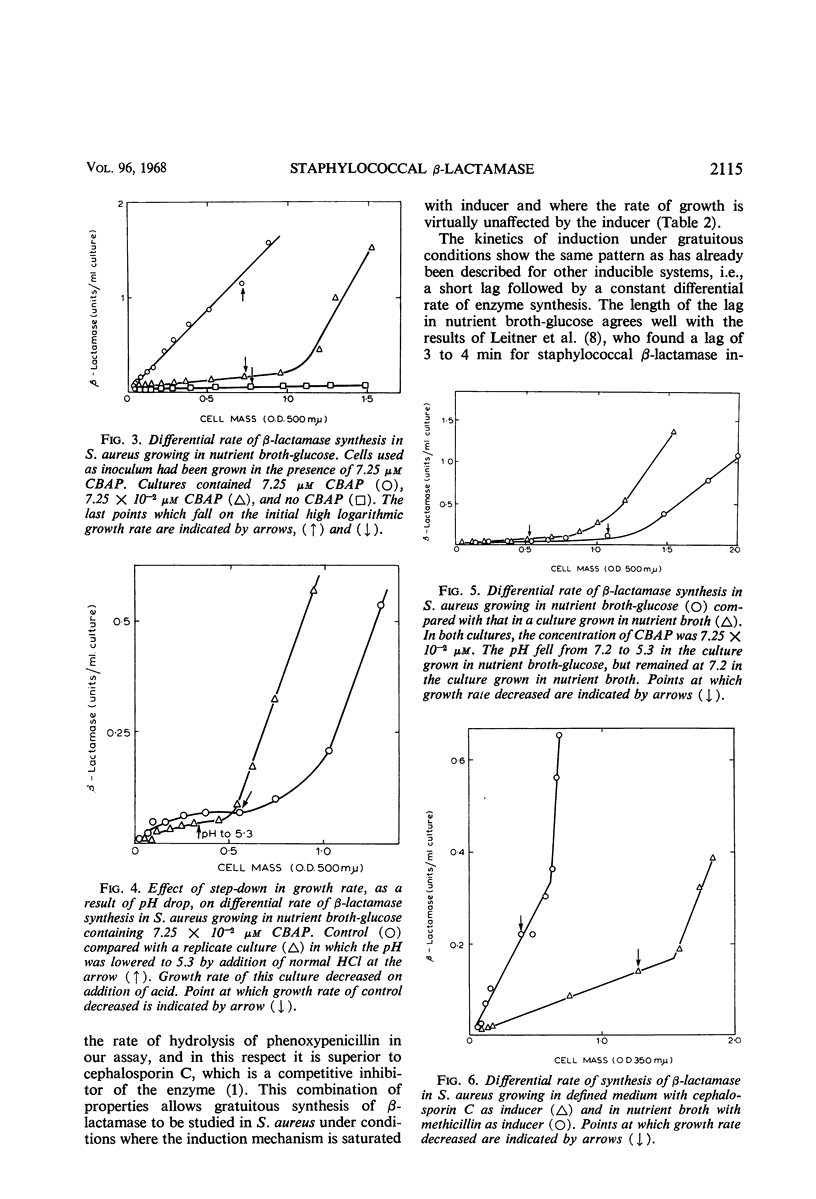
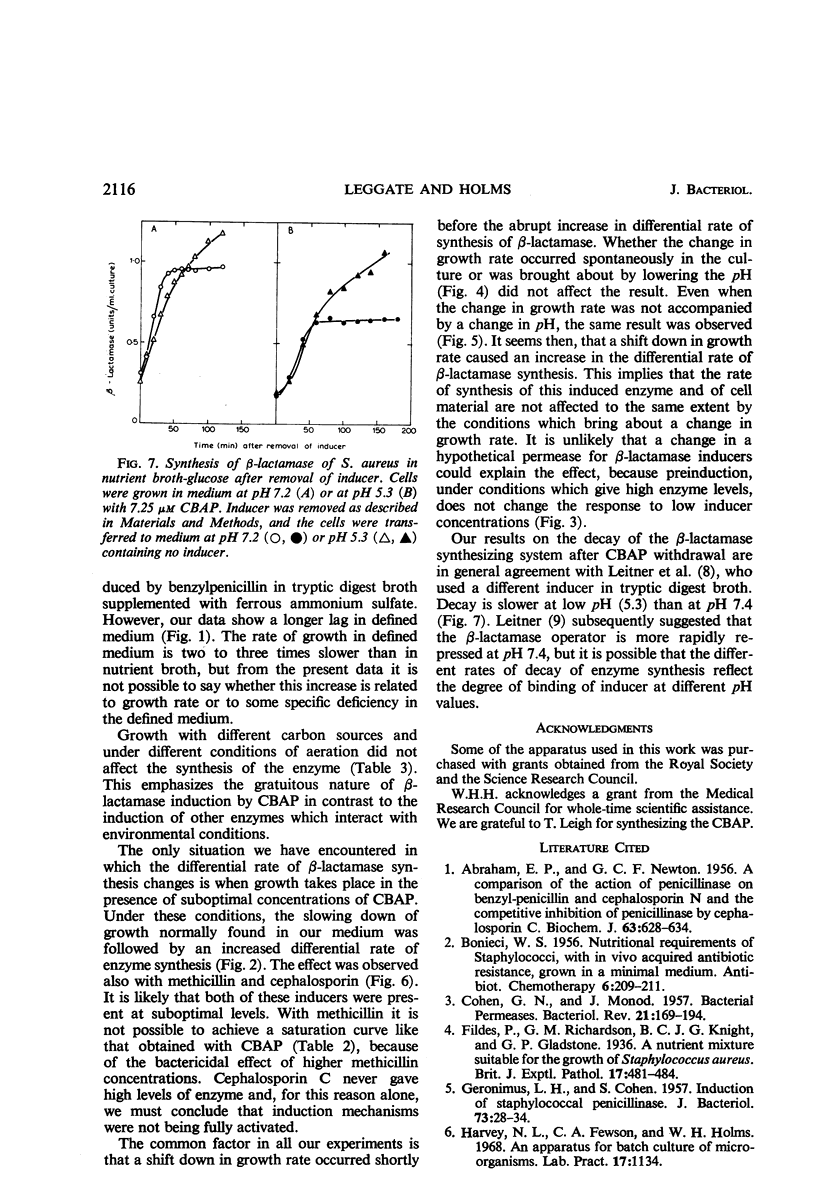
The synthesis of β-lactamase in response to 2-(2′-carboxyphenyl)-benzoyl-6-aminopenicillanic acid as inducer was studied in Staphylococcus aureus. The inducer was not detectably hydrolyzed by β-lactamase and had minimal antibacterial activity. The kinetics of induction showed a lag of 4 to 6 min in a nutrient broth medium and 8 to 12 min in a defined medium, followed by constant differential rates of synthesis of β-lactamase. The differential rate of β-lactamase synthesis in nutrient broth was unaltered by supplementing the medium with glucose, galactose, lactose, arabinose, glycerol, or sucrose. Variations in the partial pressure of oxygen did not alter the differential rate of synthesis of β-lactamase over the range 18 to 50% oxygen in nitrogen. Even when the rate of growth was considerably reduced by high-oxygen tension, the differential rate of synthesis of the enzyme remained the same. The differential rate of β-lactamase synthesis at low inducer concentration increased after a shift down in growth rate. The effect was observed with several inducers and under different nutritional conditions, but was always preceded by a change in growth rate. It is suggested that the change in growth rate itself causes the increase in differential rate of β-lactamase synthesis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAHAM E. P., NEWTON G. G. A comparison of the action of penicillinase on benzylpenicillin and cephalosporin N and the competitive inhibition of penicillinase by cephalosporin C. Biochem J. 1956 Aug;63(4):628–634. doi: 10.1042/bj0630628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., MONOD J. Bacterial permeases. Bacteriol Rev. 1957 Sep;21(3):169–194. doi: 10.1128/br.21.3.169-194.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERONIMUS L. H., COHEN S. Induction of staphylococcal penicillinase. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jan;73(1):28–34. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.1.28-34.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey N. L., Fewson C. A., Holms W. H. Apparatus for batch culture of micro-organisms. Lab Pract. 1968 Oct;17(10):1134–1136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEITNER F., SWEENEY H. M., MARTIN T. F., COHEN S. INDUCTION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL PENICILLINASE BY BENZYLPENICILLIN: EFFECT OF PH, CONCENTRATION OF FERROUS ION AND INDUCER, AND DURATION OF EXPOSURE OF CELLS TO INDUCER. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:717–727. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.717-727.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leggate J., Holms W. H. Gratuitous synthesis of beta-lactamase in Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):28P–29P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitner F. Kinetics of penicillinase induction and variation of penicillinase translation in Staphylococcus aureus. Biophys J. 2008 Dec 31;7(6):913–923. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86629-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P. Staphylococcal penicillinase and the new penicillins. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:229–235. doi: 10.1042/bj0830229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R. Penicillinase adaptation in B. cereus; adaptive enzyme formation in the absence of free substrate. Br J Exp Pathol. 1950 Dec;31(6):739–753. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLEGEL H. G., KALTWASSER H., GOTTSCHALK G. [A submersion method for culture of hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria: growth physiological studies]. Arch Mikrobiol. 1961;38:209–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman H. G. FACTORS MODIFYING INDUCED FORMATION OF PENICILLINASE IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jun;81(6):895–902. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.6.895-902.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



