Abstract
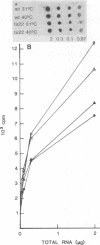
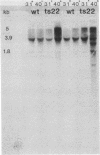
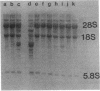
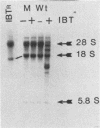
We have attempted to characterize the molecular defect in a temperature-sensitive mutant of vaccinia virus, ts22, which has an abortive late phenotype. At the nonpermissive temperature, ts22 displays normal viral protein synthesis until 8 h postinfection. Between 8 and 10 h after infection all viral protein synthesis ceases abruptly. Characterization of ts22 revealed that (i) primary transcription of late viral genes was not grossly impaired, (ii) late viral mRNA was biologically inactive since it could not stimulate in vitro protein synthesis, and (iii) extensive cleavage of rRNA and late viral mRNA occurred at the time that viral protein synthesis aborted in vivo. These data suggest that ts22 is defective in a function which prevents host rRNA and viral mRNA from being degraded. Inhibitor studies with cytosine arabinoside and cycloheximide showed that induction of and protection from rRNA breakdown occurred at approximately the same time during infection and required late viral gene expression. The viral protein synthesis pattern observed in vaccinia virus-infected cells treated with the drug isatin-beta-thiosemicarbazone was strikingly similar to that observed in ts22-infected cells at the nonpermissive temperature (J. Cooper, B. Moss, and E. Katz, Virology 96:381-392, 1979). Analysis of rRNA integrity in isatin-beta-thiosemicarbazone-treated, vaccinia virus-infected cells revealed extensive cleavage of rRNA, suggesting that the ts22 and drug inhibitor may function in the same pathway.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECKER Y., JOKLIK W. K. MESSENGER RNA IN CELLS INFECTED WITH VACCINIA VIRUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Apr;51:577–585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.4.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C. Interferon-induced enzymatic activities and their role in the antriviral state. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone R. F., Parr R. P., Moss B. Intermolecular duplexes formed from polyadenylylated vaccinia virus RNA. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):365–374. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.365-374.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernos V. I., Belanov E. F., Vasilieva N. N. Temperature-sensitive mutants of vaccinia virus. I. Isolation and preliminary characterization. Acta Virol. 1978 Mar;22(2):81–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condit R. C., Motyczka A. Isolation and preliminary characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):224–241. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90150-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condit R. C., Motyczka A., Spizz G. Isolation, characterization, and physical mapping of temperature-sensitive mutants of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1983 Jul 30;128(2):429–443. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Moss B. In vitro translation of immediate early, early, and late classes of RNA from vaccinia virus-infected cells. Virology. 1979 Jul 30;96(2):368–380. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Moss B., Katz E. Inhibition of vaccinia virus late protein synthesis by isatin-beta-thiosemicarbazone: characterization and in vitro translation of viral mRNA. Virology. 1979 Jul 30;96(2):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Moss B. Transcription of vaccinia virus mRNA coupled to translation in vitro. Virology. 1978 Jul 1;88(1):149–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Wittek R., Moss B. Extension of the transcriptional and translational map of the left end of the vaccinia virus genome to 21 kilobase pairs. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):733–745. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.733-745.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dales S., Milovanovitch V., Pogo B. G., Weintraub S. B., Huima T., Wilton S., McFadden G. Biogenesis of vaccinia: isolation of conditional lethal mutants and electron microscopic characterization of their phenotypically expressed defects. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):403–428. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90258-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dales S., Pogo B. G. Biology of poxviruses. Virol Monogr. 1981;18:1–109. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-8625-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drillien R., Spehner D., Kirn A. Complementation and genetic linkage between vaccinia virus temperature-sensitive mutants. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):372–381. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensinger M. J. Isolation and genetic characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of vaccinia virus WR. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):778–790. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.778-790.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteban M., Benavente J., Paez E. Effect of interferon on integrity of vaccinia virus and ribosomal RNA in infected cells. Virology. 1984 Apr 15;134(1):40–51. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goswami B. B., Sharma O. K. Degradation of rRNA in interferon-treated vaccinia virus-infected cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1371–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Ball L. A. Cell-free synthesis of enzymatically active vaccinia virus thymidine kinase. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):594–601. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahr A., Roberts B. E. Arrangement of late RNAs transcribed from a 7.1-kilobase EcoRI vaccinia virus DNA fragment. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):510–520. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.510-520.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Maroney P. A., Baglioni C. Synthesis of (2'-5')oligoadenylate and activation of an endoribonuclease in interferon-treated HeLa cells infected with reovirus. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):1039–1045. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.1039-1045.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington T. H. Isatin-beta-thiosemicarbazone causes premature cessation of vaccinia virus-induced late post-replicative polypeptide synthesis. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jun;35(3):567–571. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-3-567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice A. P., Kerr I. M. Interferon-mediated, double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase is inhibited in extracts from vaccinia virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):229–236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.229-236.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice A. P., Roberts W. K., Kerr I. M. 2-5A accumulates to high levels in interferon-treated, vaccinia virus-infected cells in the absence of any inhibition of virus replication. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):220–228. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.220-228.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman R. H., Cayley P. J., Knight M., Gilbert C. S., Kerr I. M. Control of the ppp(a2'p)nA system in HeLa cells. Effects of interferon and virus infection. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May;124(1):131–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacore H. R., Youngner J. S. Rescue of vesicular stomatitis virus from interferon-induced resistance by superinfection with vaccinia virus. II. Effect of UV-inactivated vaccinia and metabolic inhibitors. Virology. 1973 Dec;56(2):512–522. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traktman P., Sridhar P., Condit R. C., Roberts B. E. Transcriptional mapping of the DNA polymerase gene of vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):125–131. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.125-131.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker-Dowling P., Youngner J. S. Characterization of a specific kinase inhibitory factor produced by vaccinia virus which inhibits the interferon-induced protein kinase. Virology. 1984 Aug;137(1):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker-Dowling P., Youngner J. S. Vaccinia rescue of VSV from interferon-induced resistance: reversal of translation block and inhibition of protein kinase activity. Virology. 1983 Nov;131(1):128–136. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90539-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodson B., Joklik W. K. The inhibition of vaccinia virus multiplication by isatin-beta-thiosemicarbazone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):946–953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]