Abstract
A new serotype of simian acquired immune deficiency syndrome (SAIDS) retrovirus (type 2) belonging to the D genus of retroviruses is associated with a SAIDS occurring spontaneously in a colony of Celebes macaques (Macaca nigra) and rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta) at the Oregon Regional Primate Research Center. This syndrome resembles SAIDS in M. mulatta at the California Primate Research Center, which is associated with a similar type D retrovirus (type 1). However, at the Oregon Center, SAIDS is distinguished by the occurrence of retroperitoneal fibromatosis in some of the affected monkeys. Type 2 virus was isolated from seven of seven macaques with SAIDS, retroperitoneal fibromatosis, or both and from one of six healthy macaques. The new strain is closely related to SAIDS retrovirus type 1 and Mason-Pfizer monkey virus but can be distinguished by competitive radioimmunoassay for minor core (p10) antigen and by genomic restriction endonuclease cleavage patterns. Neutralization tests indicate that type 1 and type 2 SAIDS retroviruses are distinct serotypes. Therefore, separate vaccines may be necessary to control these infections in colonies of captive macaques.
Full text
PDF


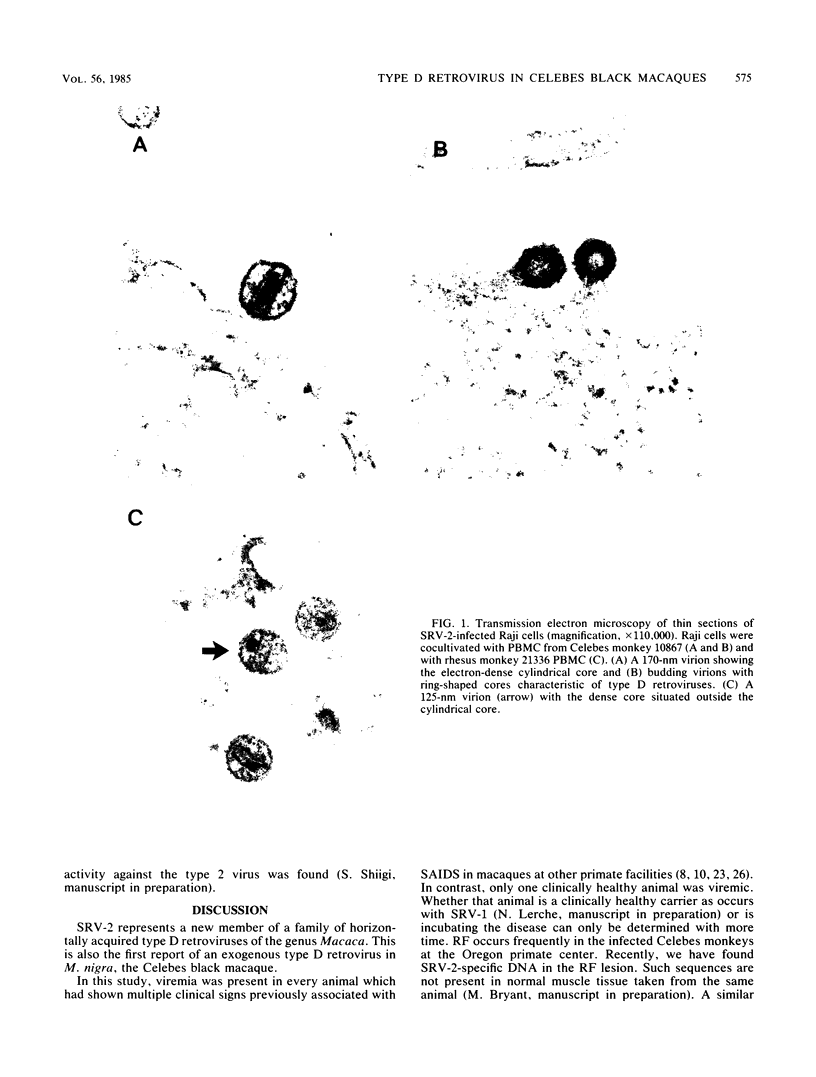
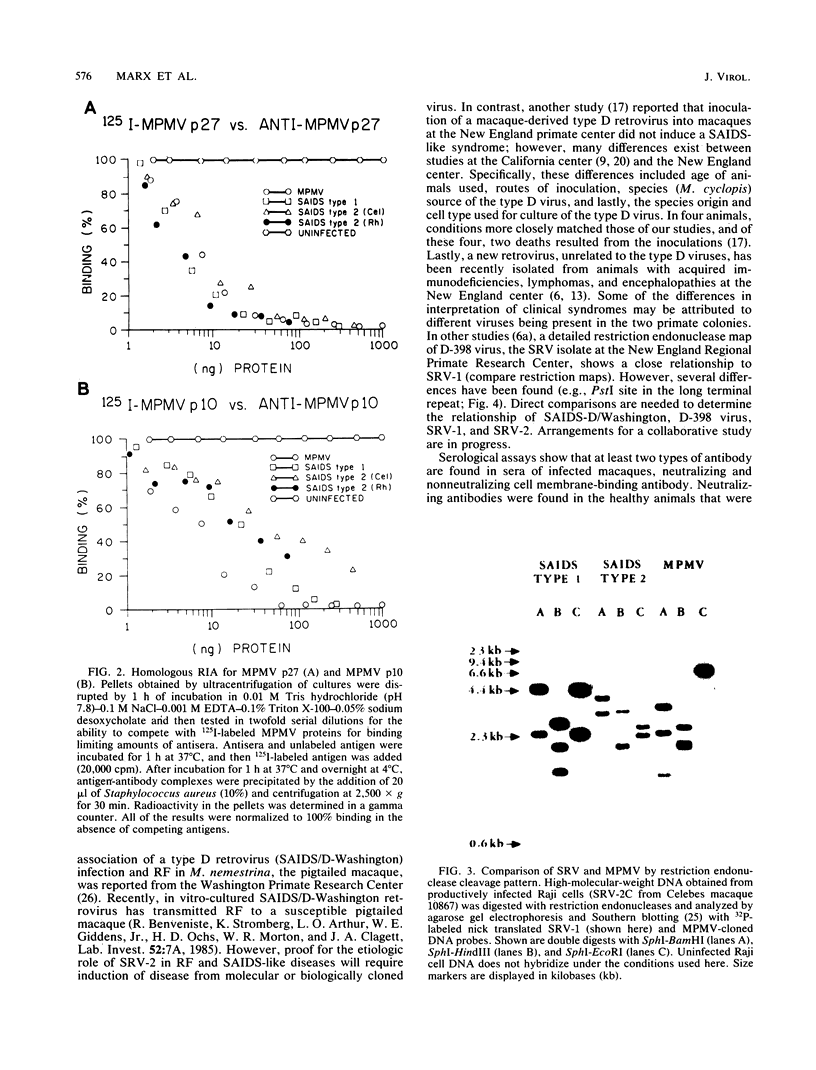
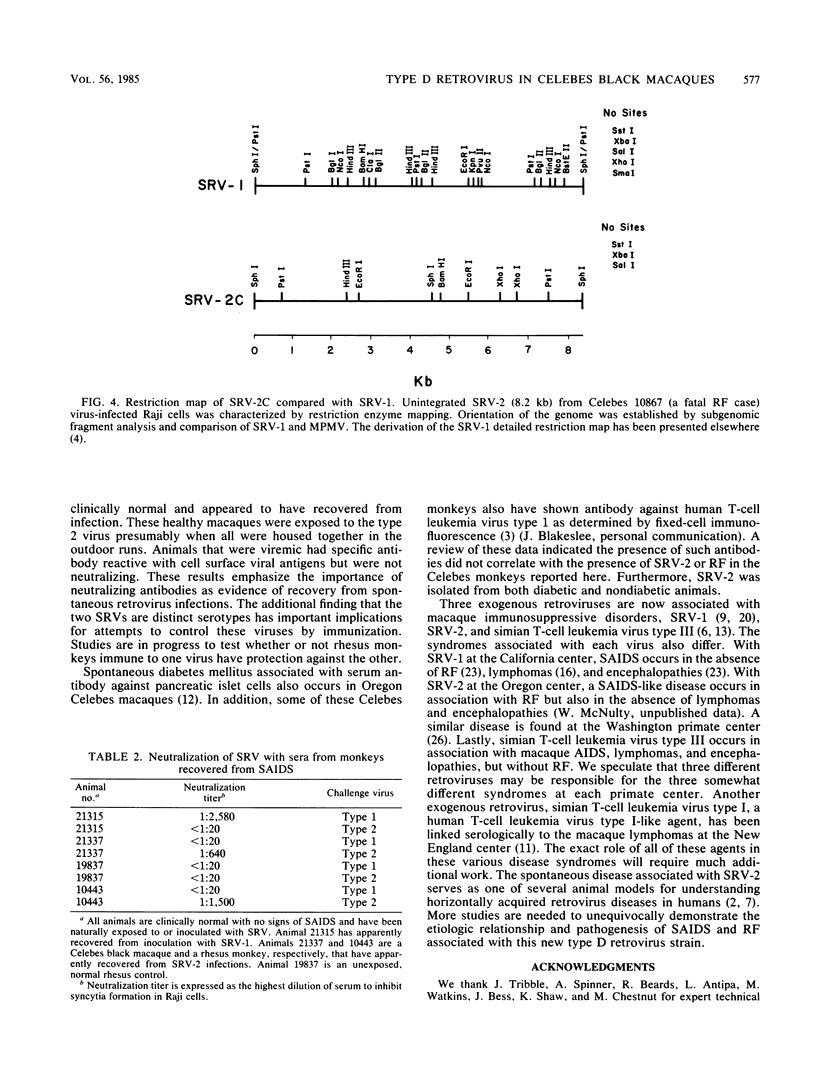

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker C. S., Wills J. W., Bradac J. A., Hunter E. Molecular cloning of the Mason-Pfizer monkey virus genome: characterization and cloning of subgenomic fragments. Virology. 1985 Apr 30;142(2):223–240. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90331-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakeslee J. R., Jr, Sowder W. G., Baulu J. Wild African green monkeys of Barbados are HTLV negative. Lancet. 1985 Mar 2;1(8427):525–525. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92129-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. L., Yamamoto J., Luciw P., Munn R., Marx P., Higgins J., Pedersen N., Levine A., Gardner M. B. Molecular comparison of retroviruses associated with human and simian AIDS. Hematol Oncol. 1985 Jul-Sep;3(3):187–197. doi: 10.1002/hon.2900030307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel M. D., King N. W., Letvin N. L., Hunt R. D., Sehgal P. K., Desrosiers R. C. A new type D retrovirus isolated from macaques with an immunodeficiency syndrome. Science. 1984 Feb 10;223(4636):602–605. doi: 10.1126/science.6695172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel M. D., Letvin N. L., King N. W., Kannagi M., Sehgal P. K., Hunt R. D., Kanki P. J., Essex M., Desrosiers R. C. Isolation of T-cell tropic HTLV-III-like retrovirus from macaques. Science. 1985 Jun 7;228(4704):1201–1204. doi: 10.1126/science.3159089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C., Daniel M. D., Butler C. V., Schmidt D. K., Letvin N. L., Hunt R. D., King N. W., Barker C. S., Hunter E. Retrovirus D/New England and its relation to Mason-Pfizer monkey virus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):552–560. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.552-560.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Shearer G. M., Kaplan M., Haynes B. F., Palker T. J., Redfield R., Oleske J., Safai B. Frequent detection and isolation of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and at risk for AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.6200936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddens W. E., Jr, Tsai C. C., Morton W. R., Ochs H. D., Knitter G. H., Blakley G. A. Retroperitoneal fibromatosis and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in macaques. Pathologic observations and transmission studies. Am J Pathol. 1985 May;119(2):253–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravell M., London W. T., Hamilton R. S., Sever J. L., Kapikian A. Z., Murti G., Arthur L. O., Gilden R. V., Osborn K. G., Marx P. A. Transmission of simian AIDS with type D retrovirus isolate. Lancet. 1984 Feb 11;1(8372):334–335. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrickson R. V., Maul D. H., Osborn K. G., Sever J. L., Madden D. L., Ellingsworth L. R., Anderson J. H., Lowenstine L. J., Gardner M. B. Epidemic of acquired immunodeficiency in rhesus monkeys. Lancet. 1983 Feb 19;1(8321):388–390. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91503-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma T., Kanki P. J., King N. W., Jr, Hunt R. D., O'Connell M. J., Letvin N. L., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., Yang C. S., Essex M. Lymphoma in macaques: association with virus of human T lymphotrophic family. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):716–718. doi: 10.1126/science.6087453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. F., Jr, Fang T. Y. Islet cell cytoplasmic antibodies in Macaca nigra. Diabetes. 1984 Mar;33(3):219–223. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanki P. J., McLane M. F., King N. W., Jr, Letvin N. L., Hunt R. D., Sehgal P., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., Essex M. Serologic identification and characterization of a macaque T-lymphotropic retrovirus closely related to HTLV-III. Science. 1985 Jun 7;228(4704):1199–1201. doi: 10.1126/science.3873705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerche N. W., Henrickson R. V., Maul D. H., Gardner M. B. Epidemiologic aspects of an outbreak of acquired immunodeficiency in rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). Lab Anim Sci. 1984 Apr;34(2):146–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., Daniel M. D., Sehgal P. K., Chalifoux L. V., King N. W., Hunt R. D., Aldrich W. R., Holley K., Schmidt D. K., Desrosiers R. C. Experimental infection of rhesus monkeys with type D retrovirus. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):683–686. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.683-686.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., Eaton K. A., Aldrich W. R., Sehgal P. K., Blake B. J., Schlossman S. F., King N. W., Hunt R. D. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in a colony of macaque monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2718–2722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx P. A., Maul D. H., Osborn K. G., Lerche N. W., Moody P., Lowenstine L. J., Henrickson R. V., Arthur L. O., Gilden R. V., Gravell M. Simian AIDS: isolation of a type D retrovirus and transmission of the disease. Science. 1984 Mar 9;223(4640):1083–1086. doi: 10.1126/science.6695196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer P. R., Ormerod L. D., Osborn K. G., Lowenstine L. J., Hendrickson R. V., Modlin R. L., Smith R. E., Gardner M. B., Taylor C. R. An immunopathologic evaluation of lymph nodes from monkey and man with acquired immune deficiency syndrome and related conditions. Hematol Oncol. 1985 Jul-Sep;3(3):199–210. doi: 10.1002/hon.2900030308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munn R. J., Marx P. A., Yamamoto J. K., Gardner M. B. Ultrastructural comparison of the retroviruses associated with human and simian acquired immunodeficiency syndromes. Lab Invest. 1985 Aug;53(2):194–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn K. G., Prahalada S., Lowenstine L. J., Gardner M. B., Maul D. H., Henrickson R. V. The pathology of an epizootic of acquired immunodeficiency in rhesus macaques. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jan;114(1):94–103. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiigi S. M., Wilson B. J., Malley A., Howard C. F., Jr, McNulty W. P., Olson L., Olson S., Regan D., Burger D., Marx P. A. Virus-associated deficiencies in the mitogen reactivity in celebes black macaques (Macaca nigra). Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 May;35(2):200–210. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(85)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
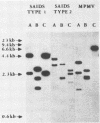
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stromberg K., Benveniste R. E., Arthur L. O., Rabin H., Giddens W. E., Jr, Ochs H. D., Morton W. R., Tsai C. C. Characterization of exogenous type D retrovirus from a fibroma of a macaque with simian AIDS and fibromatosis. Science. 1984 Apr 20;224(4646):289–282. doi: 10.1126/science.6200929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]