Abstract
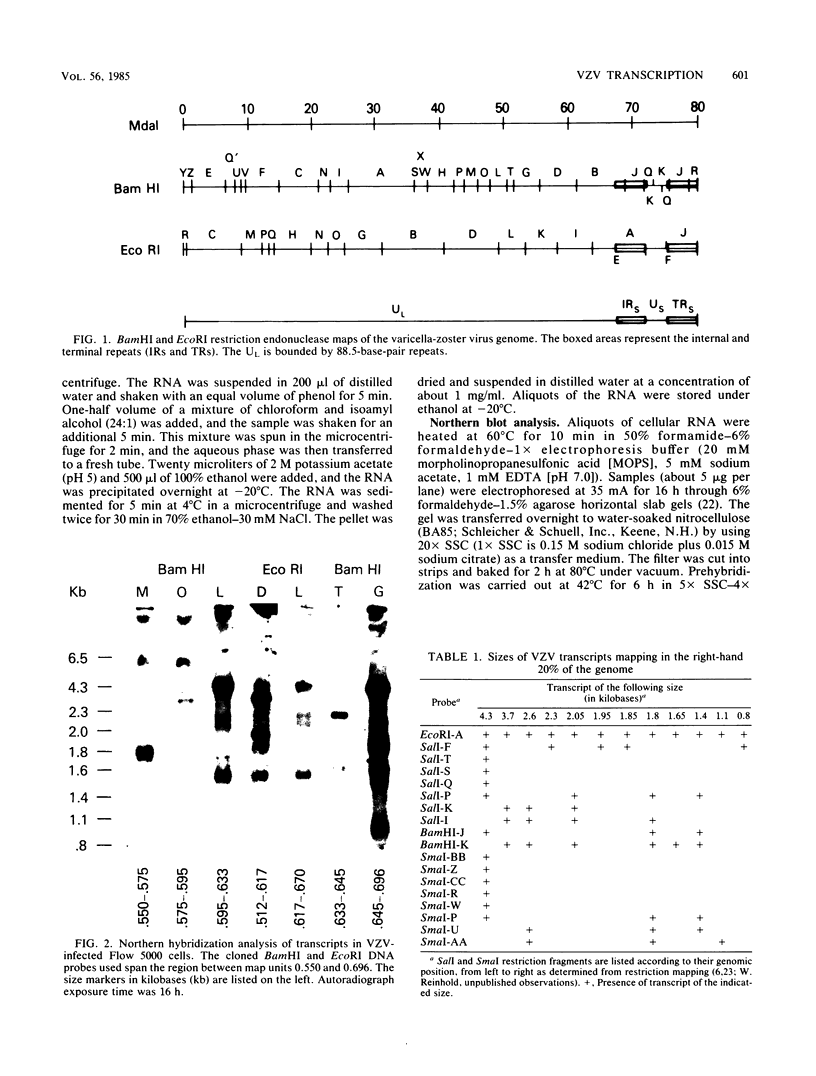
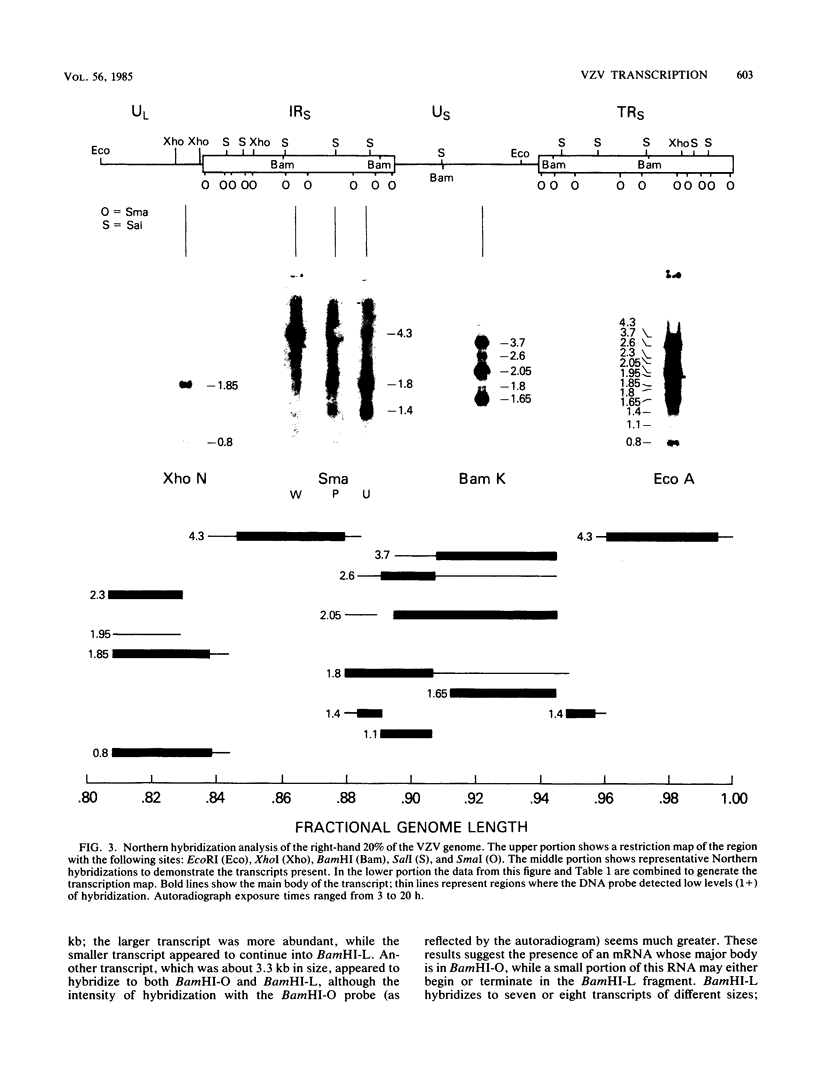
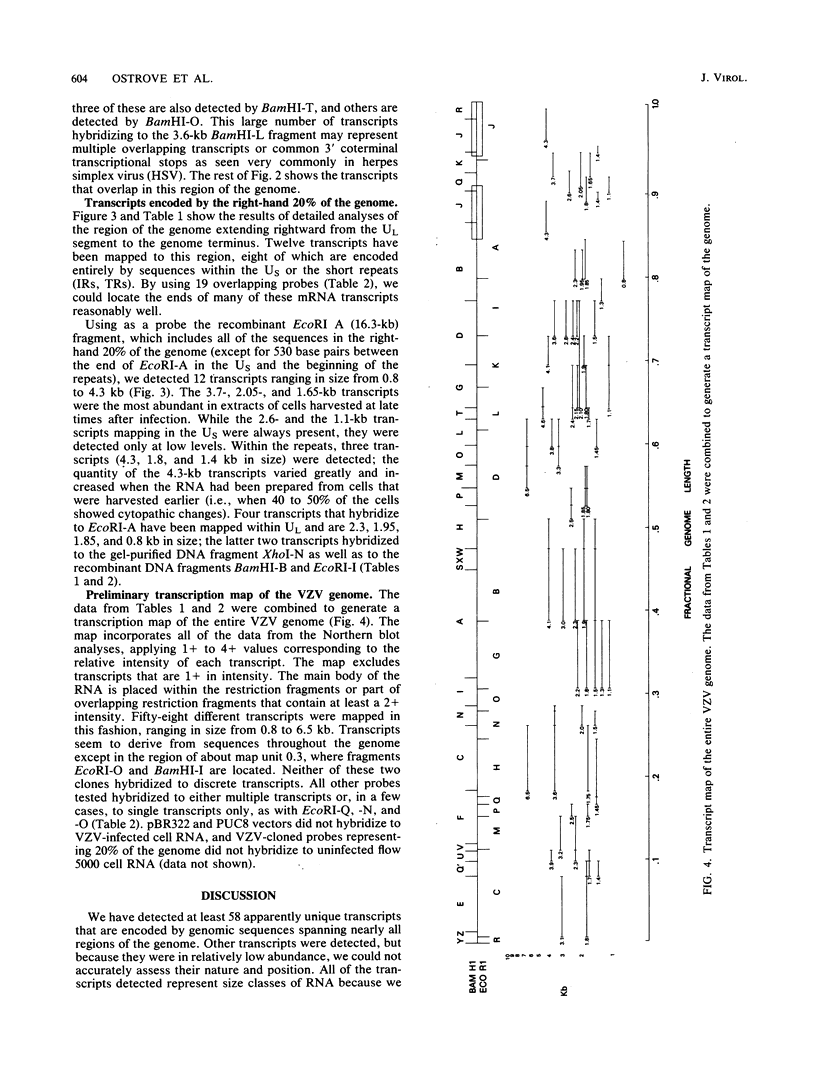
RNA was isolated from varicella-zoster virus-infected Flow 5000 cells (diploid fibroblasts) at late times after infection. With the use of overlapping DNA probes representing all regions of the varicella-zoster genome, an extensive Northern blot analysis of the RNA was carried out. The analysis revealed at least 58 discrete transcripts ranging in size from approximately 0.8 to 6.5 kilobases. RNAs were found to be homologous to all probes used except for those mapping at approximately map unit 0.3, where no RNA transcripts could be detected. Comparison of the sizes and locations of RNA transcripts mapping in the right-hand ends of the varicella-zoster virus and the herpes simplex virus DNAs shows a number of striking analogies, suggesting their similar genomic organization.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. P., Costa R. H., Holland L. E., Wagner E. K. Characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 RNA present in the absence of de novo protein synthesis. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):9–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.9-27.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J. DNA sequence of the US component of the varicella-zoster virus genome. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2203–2209. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01724.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. DNA sequence of the major inverted repeat in the varicella-zoster virus genome. J Gen Virol. 1985 Feb;66(Pt 2):207–220. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-2-207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. Molecular cloning of the varicella-zoster virus genome and derivation of six restriction endonuclease maps. J Gen Virol. 1983 Aug;64(Pt 8):1811–1814. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-8-1811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J. Structure of the genome termini of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1984 Nov;65(Pt 11):1969–1977. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-11-1969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Wilkie N. M. Location and orientation of homologous sequences in the genomes of five herpesviruses. J Gen Virol. 1983 Sep;64(Pt 9):1927–1942. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-9-1927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumas A. M., Geelen J. L., Weststrate M. W., Wertheim P., van der Noordaa J. XbaI, PstI, and BglII restriction enzyme maps of the two orientations of the varicella-zoster virus genome. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):390–400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.390-400.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecker J. R., Hyman R. W. Varicella zoster virus DNA exists as two isomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):156–160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., Keller P. M., Lowe R. S., Zivin R. A. Use of a bacterial expression vector to map the varicella-zoster virus major glycoprotein gene, gC. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):81–88. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.81-88.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Dupuis K. W., Schmidt N. J. Varicella-zoster viral glycoproteins analyzed with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):55–62. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.55-62.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C., Edwards D. P., Friedrichs W. E., Weigle K. A., McGuire W. L. Monoclonal antibodies against three major glycoproteins of varicella-zoster virus. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):381–388. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.381-388.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C. The synthesis of glycoproteins in human melanoma cells infected with varicella-zoster virus. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90478-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Ihara T., Grose C., Starr S. Human leukocytes kill varicella-zoster virus-infected fibroblasts in the presence of murine monoclonal antibodies to virus-specific glycoproteins. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):98–103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.98-103.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller P. M., Neff B. J., Ellis R. W. Three major glycoprotein genes of varicella-zoster virus whose products have neutralization epitopes. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):293–297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.293-297.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar E. C., Huang Y. S., Huang E. S. Purification and characterization of varicella-zoster virus-induced DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):249–256. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.249-256.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. H., Dohner D. E., Wellinghoff W. J., Gelb L. D. Restriction endonuclease analysis of varicella-zoster vaccine virus and wild-type DNAs. J Med Virol. 1982;9(1):69–76. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890090110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rave N., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H. Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3559–3567. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C. R., Weir A. C., Hay J., Straus S. E., Ruyechan W. T. DNA-binding proteins present in varicella-zoster virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):45–53. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.45-53.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruyechan W. T., Casey T. A., Reinhold W., Weir A. C., Wellman M., Straus S. E., Hay J. Distribution of G + C-rich regions in varicella-zoster virus DNA. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jan;66(Pt 1):43–54. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-1-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shemer Y., Leventon-Kriss S., Sarov I. Isolation and polypeptide characterization of varicella-zoster virus. Virology. 1980 Oct 15;106(1):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90228-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraki K., Takahashi M. Virus particles and glycoprotein excreted from cultured cells infected with varicella-zoster virus (VZV). J Gen Virol. 1982 Aug;61(Pt 2):271–275. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-61-2-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus S. E., Aulakh H. S., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J., Casey T. A., Vande Woude G. F., Owens J., Smith H. A. Structure of varicella-zoster virus DNA. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):516–525. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.516-525.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff M. H. The proteins of varicella-zoster-virus. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1978 Nov 17;166(1-4):21–28. doi: 10.1007/BF02121130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanishi K., Matsunaga Y., Ogino T., Lopetegui P. Biochemical transformation of mouse cells by varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1981 Oct;56(Pt 2):421–430. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-56-2-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]